Unit 3: Urinalysis (Microscopic Exam Crystals) (Cram)
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Fill in the blank: The presence of crystals in urine depends on the ____, which affects the solubility of the crystals
pH
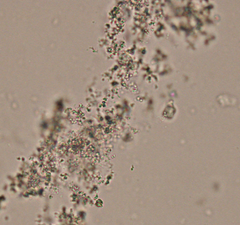
What type of acid urine crystal is this?
Amorphous urates

What type of acid urine crystal is this?
Calcium oxalate
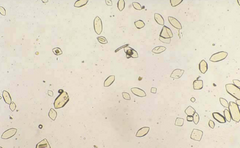
What type of acid urine crystal is this?
Uric acid

What type of acid urine crystal is this?
Bilirubin

What type of acid urine crystal is this?
Tyrosine

What type of acid urine crystal is this?
Cystine

What type of acid urine crystal is this?
Leucine

What type of acid urine crystal is this?
Cholesterol
Which acid urine crystal indicates ethylene glycol (antifreeze) poisoning when found in large numbers?
Calcium oxalate

Which acid urine crystal indicates abnormal bilirubin metabolism?
Bilirubin

Bilirubin is found in horse or cat urine, this indicates a problem with which organ?
Liver
Fill in the blank: Urine must be tested quickly because bilirubin breaks down in the presence of _______.
light
Which acid urine crystal indicates renal tubular dysfunction?
Cystine

Which two acid urine crystals indicate liver disease?
- Uric acid
- Leucine (pictured)


What type of alkaline urine crystal is this?
Ammonium phosphate (struvite)
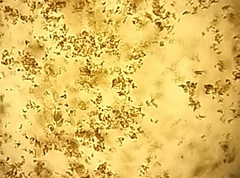
What type of alkaline urine crystal is this?
Amorphous phosphates
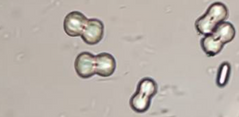
What type of alkaline urine crystal is this?
Calcium carbonate
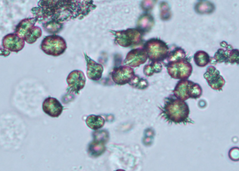
What type of alkaline urine crystal is this?
Ammonium biurate
Which alkaline urine crystal indicates liver disease?
Ammonium biurate
Which alkaline urine crystal can be normal or indicates a UTI or urolithiasis?
Ammonium phosphate (struvite)
Which alkaline urine crystal are normal and seen in large numbers in horses and rabbits?
Calcium carbonate
What are the four factors that affect urolithiasis?
Remember: Alkaline Urine Makes it Worse
Anatomic considerations (male vs. female)
Urinary pH
Metabolic factors (diet, dehydration, etc.)
Water intake
Fill in the blank: Uroliths most commonly form in ______ urine, but they may form in ______ or ______ urine depending on the mineral composition of the stones.
alkaline, acidic, neutral
Do UTI's often increase or decrease urine pH?
Increase, this encourages the formation of uroliths
Are uroliths more likely to form in concentrated or dilute urine?
Concentrated, hence why water intake is a factor
Which is more prone to urolithisasis, males or females?
Males
What does FLUTD stand for?
Feline Lower Urinary Tract Disease
Is FLUTD more common in male or female cats?
Males
What are the five signs of FLUTD?
Remember: Help! PAIN
Hematuria
Painful urination
Anorexia/vomiting/depression
Inappropriate urination/straining
No urination (can cause coma, death)
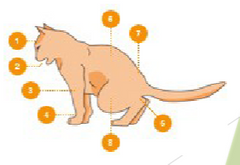
What are the eight things that are different about this urinating FLUTD cat vs. a normal cat urinating?
Head slightly inclined downwards
May cry out
Hunched–up posture
Front legs vertical
Hind legs more vertical
Arched back
Tense muscles
Stifle joint forward
Is urolithiasis more common in dogs or cats?
Dogs
What is urolithiasis called in steers?
Water belly
Inflammation of the bladder (associated with UTI)
Cystitis
Inflammation of the kidneys (associated with UTI)
Pyelonephritis
Inflammation of the glomeruli (associated with UTI)
Glomerulonephritis
What are the two structures whose function is tested in renal function testing?
- Glomerular function
- Renal tubule function
What are the two substances tested for in glomerular function tests? These tests are usually performed at the same time
- Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
- Creatinine
Two terms for the increase in non–protein nitrogen (NPN) in the blood
- Uremia
- Azotemia
What are the three causes of increased BUN?
- Prerenal azotemia
- Renal azotemia
- Post–renal azotemia
Which cause of increased BUN is this: It is caused by the leakage of obstruction of urine, so urine is absorbed into the bloodstream
Post–renal azotemia
Which cause of increased BUN is this: 75% of the nephrons in the kidneys are non–functional, causing decreased filtration of urea from the blood
Renal azotemia
Which cause of increased BUN is this: It involves either reduced glomerular circulation (shock, heart disease, dehydration), high protein diet, or increased protein catabolism (starvation)
Prerenal azotemia
Fill in the blank: High BUN indicates ______ disease. Low BUN indicates ______ disease.
kidney, liver
What are the two causes of decreased BUN?
- Protein malnutrition
- Chronic liver disease
What are the two methods of testing for BUN?
- Measure ammonia
- Chemical analysis
True or false: Like BUN, high creatinine levels can be caused by diet
False. Creatinine levels are NOT affected by diet. They are increased only when the glomeruli are not functioning
What are the two tubular function tests?
Phenol sulphophthalein (PSP) clearance test
Water deprivation (or concentration test)