Financial Accounting (Midterm 1 FS)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
1
New cards
Securities Exchange Commission
An organization created by the Securities Exchange Act in 1934, that is responsible for enforcing the securities industry and protecting investors. It determines the measurement rules for financial statements companies must provide to stakeholders and oversees financial reporting for U.S companies.
2
New cards
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles
The common set of accounting principles, standards, and procedures that companies use to compile their financial statements. These are the principles that the SEC requires publicly traded companies to comply with. Ensures there's an apples to apples comparison between competitors when an investor/ finance person looks into businesses.
3
New cards
True or False: GAAP are only used in the United States
True
4
New cards
External Auditors
Independent people who aren't employees of a company, but are paid by them to ensure that companies are accurately recording and detailing their financial information. Auditors are used because people inside a company might inflate their and financial statements.
5
New cards
PCAOB
Public Company Accounting Oversight Board: a board established after the fall failures of Enron that requires auditors to be independently & externally reviewed and overseen to monitor the quality of their audits. Enron was a company that had a lot of debt and went bankrupt after a scandal caused their stock to plummet along with their reputation.
6
New cards
What organization serves as a check for external auditors?
PCAOB
7
New cards
Balance Sheet
Consists of assets, liabilities, and shareholders' equity: reports a company's financial position at a point in time. It consists of the heading, name of entity, title of the statement, the date, and the unit of measurement. The date is written as "At/As Specific Date," because it's referring to a specific point in time. When looking at liabilities, most helpful to look at short-term significant debt, instead of long term
Equation is A-L=Shareholders' Equity
Equation is A-L=Shareholders' Equity
8
New cards
Income Statement
Consists of revenue, expenses, and profit: measures the accountant's primary measure of economic performance during the accounting period (profitability). The date is written "For The Date"
9
New cards
Gross Profit Margin
Gross Profit/Sales Revenue x 100
10
New cards
Gross Profit Equation
Revenues-Cost of goods sold
11
New cards
Equation for Income Statement
Revenue-Expenses=Net Income
12
New cards
Revenue
Measures the inflow of assets incurred in generating incomes. Formally defined as increases in assets or settlements of liabilities from the major ongoing operations of the business
Examples: Fee/Interest/Rent Revenue
Examples: Fee/Interest/Rent Revenue
13
New cards
Earned Revenue
Revenue that is generated as the result of selling something. Money that actively puts money into a company's pocket
14
New cards
Unearned Revenue
Revenue that has the potential to officially put money in a company's pocket, but either hasn't been delivered yet (to the customer) or hasn't been paid by the customer
15
New cards
Expense
measures the outflow of assets incurred in generating revenues: Cost of goods sold
16
New cards
Expenditure
Any money outflow, used for any purpose
17
New cards
Statement of Stockholders' Equity
Reports additional contributions from or payments to investors and the amount of income the company reinvested for future growth during the accounting period
18
New cards
Equation for Stockholders' Equity
Beginning Retained Earnings+Net Income-Dividends=Ending Retained Earnings
19
New cards
Components of stockholder's equity
(1) contributed capital/ common stock: the value of shareholder's cash contributed to the business in exchange for shares.
(2) earned capital/retained earnings: The amount of profits retained by the business (less any dividends distributed to shareholders)
(2) earned capital/retained earnings: The amount of profits retained by the business (less any dividends distributed to shareholders)
20
New cards
Statement of Cash Flows
Consists of operating, investing, and financing materials: shows a business's ability to generate cash and how it was used during the accounting period
21
New cards
Equation for Cash Flow
+/- Cash Flows from Operating Activities +/- Cash Flows from Investing Activities +/- Financing Cash Flows
22
New cards
Operating Cash Flow
(!)Cash received from customers
(2) Cash expenditures in normal operations (like wages, inventory purchases, taxes, utilities, etc.
*cash expenditures used to provide services to customers & and run properly*
(2) Cash expenditures in normal operations (like wages, inventory purchases, taxes, utilities, etc.
*cash expenditures used to provide services to customers & and run properly*
23
New cards
Investing Cash Flows
(1)Cash received from the sale of PPE, intangibles, and investments
(2) Cash paid for the purchase of PPE, intangibles investments, equipment, etc.
*activities used to acquire long term assets*
(2) Cash paid for the purchase of PPE, intangibles investments, equipment, etc.
*activities used to acquire long term assets*
24
New cards
Financing Cash Flows
(1)Cash received from the issuance of debt and stock (2)Cash expenditures for the repayment of debt, repurchase of stock, and payment of dividends
*activities performed to financially sustain the company and retain its investors*
*activities performed to financially sustain the company and retain its investors*
25
New cards
Assets
An object that has all of the following qualities:
(1) Confers expected future benefits
(2) Must be objectively measured
(3) Must be owned by the company
-On financial statements, they are measured by liquidity
(1) Confers expected future benefits
(2) Must be objectively measured
(3) Must be owned by the company
-On financial statements, they are measured by liquidity
26
New cards
Cash, accounts receivable, investments, and equipment are all examples of what?
Assets
27
New cards
True or False: On financial statements, assets are measured by their amount
False
28
New cards
Current Asset
An asset that is expected be converted to cash, sold, or consumed within a year
29
New cards
What are three examples of current assets?
-Cash
-Accounts receivable
-Prepaid expenses
-Accounts receivable
-Prepaid expenses
30
New cards
Future Assets
An asset that isn't expected to be converted to cash, sold, or consumed within a year
31
New cards
What are three examples of future assets?
-Equipment
-Supplies (when they haven't been used)
-Land
-Supplies (when they haven't been used)
-Land
32
New cards
Liabilities
A term that represents a company's future obligations.
33
New cards
What are some common examples of liabilities? List 3
-Accounts payable
-Wages
-Utilities
-Wages
-Utilities
34
New cards
Current Liabilities
Liabilities that are due within a year
-On financial statements, they are arranged by what you have to pay first
-On financial statements, they are arranged by what you have to pay first
35
New cards
Pervasive Cost Benefit Constraint
The idea that the benefits of providing information should outweigh its cost
36
New cards
Fundamental Qualitative Characteristics Of Useful Information
A set of qualities that specify how financial information should be gathered and presented. These qualities include
*relevance,* meaning that the information given is capable of influencing decisions and allowing investors to assess past activities or predict future activities
*faithful representation:* giving a truthfully accurate depiction of a company's financial standing
-in addition, information should be complete, neutral, and free of error
*relevance,* meaning that the information given is capable of influencing decisions and allowing investors to assess past activities or predict future activities
*faithful representation:* giving a truthfully accurate depiction of a company's financial standing
-in addition, information should be complete, neutral, and free of error
37
New cards
Separate Entity Assumption
Business activités must be accounted for by themselves, and not with the activities of its owners, investors, etc.
38
New cards
Going Concern Assumption
The assumption that the company will continue in operation for the foreseeable future
-If financial statements show that it most likely won't be, however, then its assets and values should be reported as if they were liquidated
-If financial statements show that it most likely won't be, however, then its assets and values should be reported as if they were liquidated
39
New cards
Monetary Time Unit Assumption
The assumption that financial statement values should be reported in the currency/ measurement of its base of operations
40
New cards
External Events
exchanges of assets, goods, or services by one party for assets, services, or promises to pay (liabilities) from one or more other parties
41
New cards
Internal Events
events that directly affect the financial position of the company but don't involve an exchange transaction with another entity
42
New cards
Accounts
A separate detailed record associated with a specific liability, equity, or expense item
43
New cards
Fundamental Accounting model
The equation that states that assets=liabilities+shareholders' equity
44
New cards
Transaction Analysis
The process of studying a transaction to determine its economic effect on the business in terms of the accounting equation A=L+SE
(1) Every transaction affects at least two accounts: correctly identifying them is important
(2) The accounting equation must remain in balance
(1) Every transaction affects at least two accounts: correctly identifying them is important
(2) The accounting equation must remain in balance
45
New cards
Guide To Systematically Analyzing Transactions
1) Identify what was received and what was given
-Goods? Services? Giftards?
2) Identify account affected by each title
3) Classify each account by Asset, Liability, or SE
4) Determine the direction of the effect
5) Ensure accounting equation is in balance
-Goods? Services? Giftards?
2) Identify account affected by each title
3) Classify each account by Asset, Liability, or SE
4) Determine the direction of the effect
5) Ensure accounting equation is in balance
46
New cards
General Journal
-Typically include a date, a short description, a debit account (located on the left) and a credit account (located on the right)
-This is the first place where data is recorded
-This is the first place where data is recorded
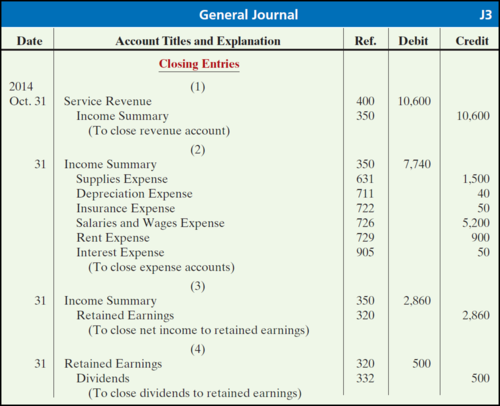
47
New cards
General Ledger
A record of a transactions effects and the balances of each account
-a T account is a simplified version of this
-contains a date
-typically track expenses, liabilities, assets, revenues, and capital
-a T account is a simplified version of this
-contains a date
-typically track expenses, liabilities, assets, revenues, and capital
48
New cards
Compound Entry
Any journal entry that affects more than two accounts
49
New cards
Current Ratio
An equation that equals a company's current assets divided by its current liabilities. It's a way to measure a company's ability to pay short term obligations with short term assets.
50
New cards
External Users
People who are not directly involved with the company's interworking
51
New cards
What does the stock market act react the most to?
a. Increased earnings
b. Decreased earnings
c. Unexpected earnings
a. Increased earnings
b. Decreased earnings
c. Unexpected earnings
c
52
New cards
Cash Basis Accounting
A style of accounting typically conducted by small retailers who don't have to report to external users
-A style of accounting that records revenue and expenses when cash is paid, regardless of when revenue/expenses were actually incurred
-A style of accounting that records revenue and expenses when cash is paid, regardless of when revenue/expenses were actually incurred
53
New cards
Accrual Accounting
A style of accounting more useful to external decision makers that records revenues when they are earned (the goods promised to the consumer have been given) and expenses when they are used to generate revenues
54
New cards
Revenue Recognition Principal
A principal of accrual accounting that states that revenue is measured when a company transfers promised goods or services to its customers in the amount it expects to be entitled to receive.
55
New cards
Expense Recognition
Record expenses in the period the related revenue is recognized
-if Chipotle recognizes revenue at the moment food is delivered, then the supplies, the gas, the utilities used to deliver the good are recorded at the same time?
-if Chipotle recognizes revenue at the moment food is delivered, then the supplies, the gas, the utilities used to deliver the good are recorded at the same time?
56
New cards
Accrued Adjustments
Financial adjustments that are unpaid and unrecorded, and will be paid (for) or received in the future
57
New cards
Accrued Expenses
expenses that have been incurred but not yet recorded because cash will be paid after the goods or services are used
58
New cards
Accrued Revenues
Revenues that have been earned but not yet recorded because cash will be received after the services are performed
59
New cards
Deferred Adjustments
Financial adjustments have been paid, received, or recorded, (1) before their services have actually been fulfilled or delivered or (2) before expenses have been incurred
60
New cards
Deferred Expenses
previously recorded assets (Prepaid Rent, Supplies, and Equipment) that must be adjusted for the amount of expense incurred during the period.
61
New cards
Deferred Revenue
A liability created when a business collects cash from customers in advance of completing a service or delivering a product, that must be reduced by the amount of revenue earned during the period
62
New cards
Amounts collected in advance of being recorded are recorded as what three things?
1) Unearned revenue
2) Deferred revenue
3) A liability
2) Deferred revenue
3) A liability
63
New cards
TRUE OR FALSE QUESTIONS RESERVED FOR END
64
New cards
True or False: Unearned revenue is considered a "liability" account?
True
65
New cards
Which of the following are found on the balance sheet?
a)Accrued expenses payable (wages, utilities, etc)
b) Dividends declared
c) Supplies expense
d)Supplies
e) Unearned revenue
a)Accrued expenses payable (wages, utilities, etc)
b) Dividends declared
c) Supplies expense
d)Supplies
e) Unearned revenue
a, d, e,
66
New cards
Under which of the following circumstances would cash basis accounting report higher expenses than accrual basis accounting in the current accounting period?
A) Cash is paid in advance of when services are provided
B) Cash is paid in the following accounting period of when the services were performed
C) Cash is paid in the same period as the services were performed?
A) Cash is paid in advance of when services are provided
B) Cash is paid in the following accounting period of when the services were performed
C) Cash is paid in the same period as the services were performed?
A
67
New cards
trial balance
68
New cards
On the balance sheet, where are the three places where the $ symbol is located?
All subtotals
On the top and bottom of the asset section
On the top and bottom of the liability and SE section
On the top and bottom of the asset section
On the top and bottom of the liability and SE section
69
New cards
Why are adjustments important to the preparation of financial statements?
-They ensure that the balance sheet reports all of the economic resources the company owns and the obligations a company owes
-Unadjusted financial statements could provide a misleading and incomplete picture of a company's financial results
-Adjustments ensure that the revenues earned and expenses incurred during the period are reflected in the income statement
-Unadjusted financial statements could provide a misleading and incomplete picture of a company's financial results
-Adjustments ensure that the revenues earned and expenses incurred during the period are reflected in the income statement
70
New cards
What type of adjustment is this?
Deferred Expense
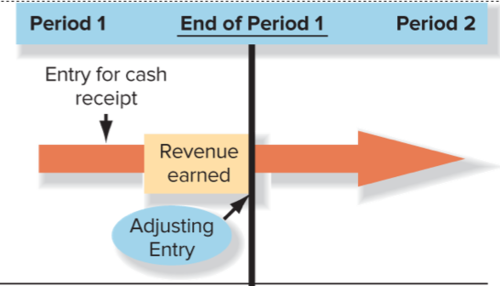
71
New cards
Contra account
An account that is an offset to, or reduction of the primary account
72
New cards
Net profit margin
net income/Net Sales (Or Operating Revenues)
73
New cards
Total Asset Turnover
(Net Sales or Operating Revenue)/ Average total assets
74
New cards
Closing process
the last step in the accounting cycle that marks the end of the current period and the beginning of the next
75
New cards
Closing Process (for permanent or real accounts)
-Ending balance in period 1 is the beginning balance in period two
-The ending balance of these accounts (assets, liabilities, SE) only equal zero when an account is no longer owed or owned
-The ending balance of these accounts (assets, liabilities, SE) only equal zero when an account is no longer owed or owned
76
New cards
Closing Process (for temporary or nominal accounts)
-The ending balance actually must be equal to zero at the end of the period
-Consists of revenues, expenses, gains, and loss
-Closing entries must be ordered with debits (revenue, because on top and credits on bottom
-Consists of revenues, expenses, gains, and loss
-Closing entries must be ordered with debits (revenue, because on top and credits on bottom
77
New cards
If cash was received and previously recorded, and you're trying to update the entires, what should you do?
Decrease Unearned Revenue (-L) and increase Revenue, which in turn increases SE
78
New cards
Who is the most responsible for making sure that a company is following the SEC's standards?
the CEO and CFO
79
New cards
Board of Directors
People elected by shareholder's that are responsible for maintaining the integrity of a company's financial reports
80
New cards
Institutional Investors
Managers of pension, mutual, endowment, and other funds that invest on the behalf of others.
81
New cards
Private investors
individuals who purchase shares in companies
82
New cards
Lenders/Creditors
People and financial institutions who lend money to companies
83
New cards
Form 10K
An annually audited financial report that consists of (1) Business descriptions of operations and strategy
(6) Select financial data
(7) Management discussion and analysis of financial position
(8) FInancial statements and supplemental data (including auditors report) x
(6) Select financial data
(7) Management discussion and analysis of financial position
(8) FInancial statements and supplemental data (including auditors report) x
84
New cards
Form 10Q
85
New cards
Form 8K
A current event report that reports material important to investors but wasn't previously reported or disclosed
86
New cards
Private Company Annual Report
A report that cons tis of.....
-financial statements
-
Report of independent accountants
-financial statements
-
Report of independent accountants
87
New cards
Historical Cost Principle
The idea that assets should be recorded at the value they were purchased for, regardless of how much they are worth now
88
New cards
True or False: Comparative financial statements include separate columns for more than one's periods results?
True