EOMs
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
What does EOM stand for?
Extraocular muscles/motilities
What are eye movements caused by?
The extraocular muscles
What are versions?
Conjugate eye movements, both eyes move in the same direction
What are ductions?
Monocular eye movements
What are vergences?
Disjunctive eye movement, eyes move in opposite direction
Version
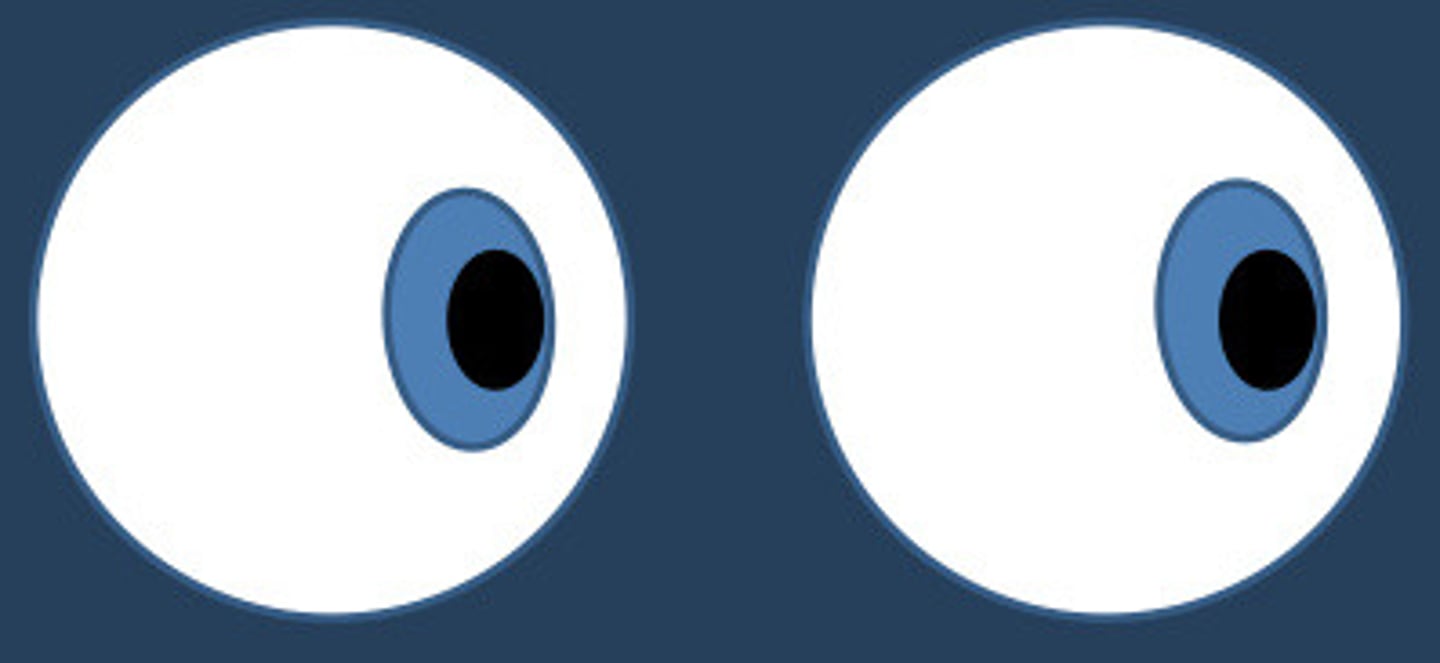
Vergence
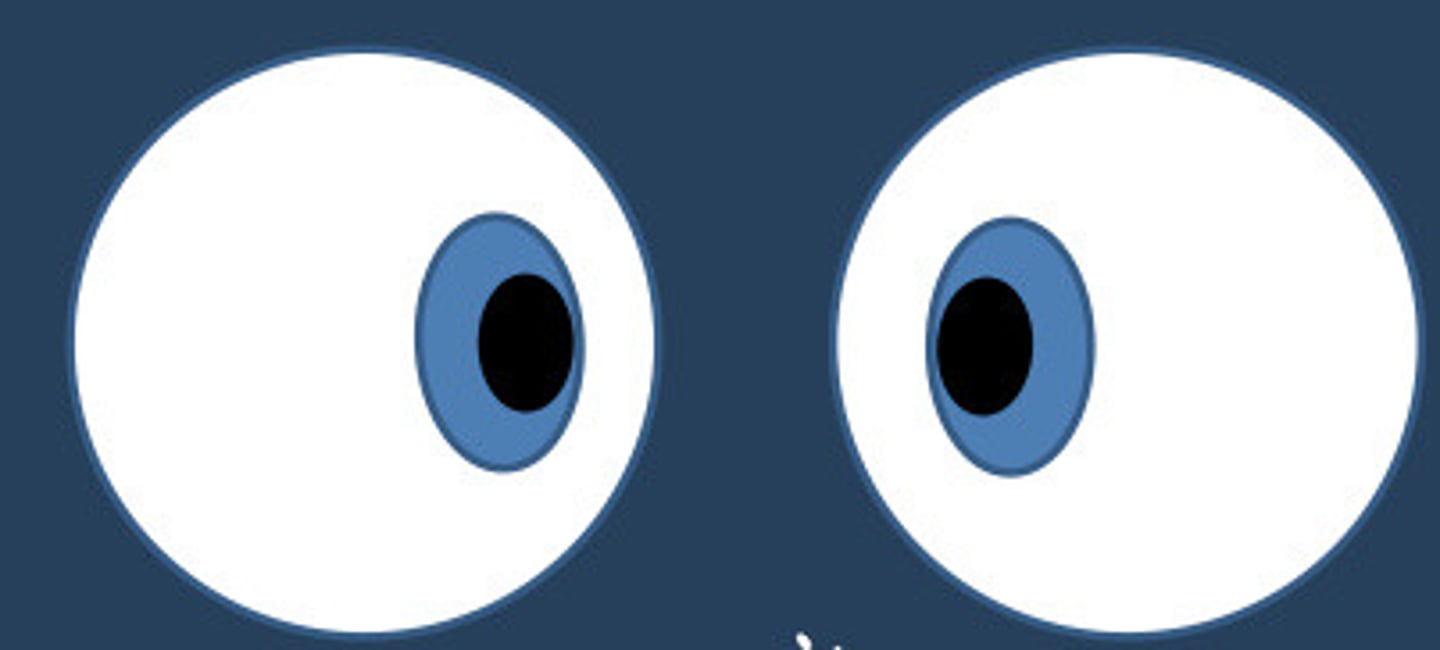

What are the names of the ductions?
Adduction
Abduction
Supraduction
Infraduction
Movements are defined in respect to the ______ of the cornea or pupil
Center
What is adduction?
Nasal "toward the midline"
What is abduction?
Temporal "away from the midline"
What is supraduction?
Movement up
What is infraduction?
Movement down
What are the names of the versions?
Dextroversion
Levoversion
Supraversion
Infraversion
What is dextroversion?
Right
What is levoversion?
Left
What is supraversion?
Up
What is infraversion?
Down
What is intorsion?
Rotates toward the nose
What is extortion?
Rotates away from the nose
How many extraocular muscles are there?
6
Each EOM is innervated by a ________ cranial nerve
Single
The extraocular muscles are innervated by what cranial nerves?
CN III, CN IV, CN VI
What is strabismus?
Misalignment of the eyes, problem with the muscle/nerve
What is an agonist?
Muscle that causes a movement
What is an antagonist?
Muscle that inhibits a movement
What are the horizontal recti muscles?
Isolate primary action in the same direction as their names
Medial recutus moves the eye _______ the midline
Toward
What are the vertical recti muscles?
Primary action in the same direction as their names
What is the primary action of the lateral rectus muscle?
Abduction
What is the primary action of the medial rectus muscle?
Adduction
What is the primary, secondary, and tertiary action of the superior rectus muscle?
Elevation
Intorsion
Adduct
What is the primary, secondary, and tertiary action of the inferior rectus?
Depression
Extortion
Adduct
What is the primary, secondary, and tertiary action of the inferior oblique?
Extortion
Elevation
Abduct
What is the primary, secondary, and tertiary action of the superior oblique?
Intorsion
Depression
Abduction
What are yoked muscles?
During versions, the agonist muscle in each eye that cause both eyes to move in the same direction
What are antagonists?
The muscles in the same eye that move the eye in the opposite direction of an agonist muscle
What is Sherrington's Law of Reciprocal Innervation?
Stimulation of an agonist muscle must have simultaneous relaxation of an antagonist muscle
What is physiological H?
Directing the eye into a position in which the eye is aligned with the axis of insertion of the muscle you wish to test
You have to position the eye to _______ specific actions of one muscle at a time
Isolate
What is O's to the nose?
When the eye is adducted
Superior oblique
Primary depressor
Inferior oblique
Primary elevator
Physiological H
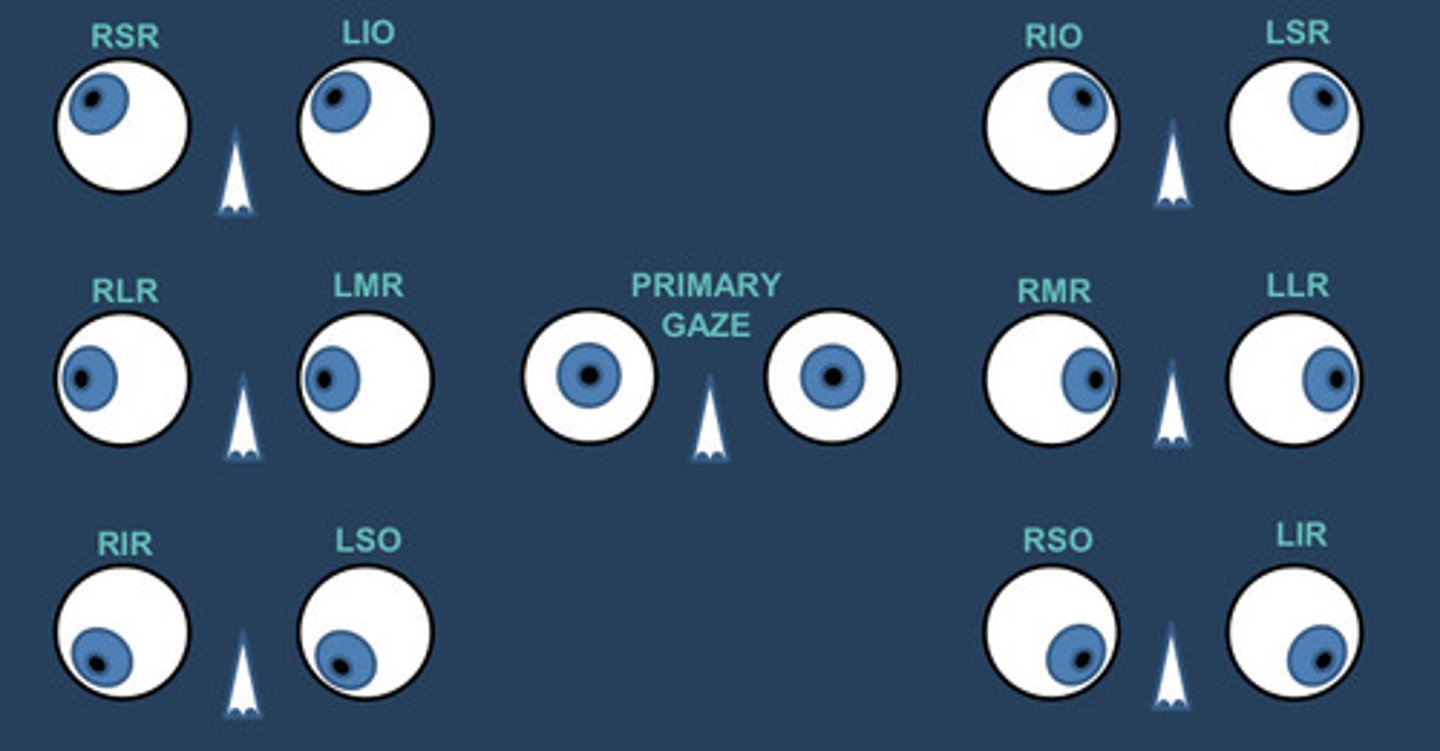
Physiological H is done in ________ gazes for best comparability between future and past examinations
Extreme
You use a light source as a target to allow comparison of corneal ________ reflexes off both eyes
Light
What can abnormal eyelid positioning be a sign of?
Neurological issues
You should physically lift the eyelids to view eye movements if ________, especially with down-gaze positing
Obstructed
Do patients wear there glasses for EOMs?
No
What is Hirschberg Reflex?
Shine pen light at eyes, should be in center
What is an external examination of EOMs?
Are the eyes symmetrical
Head tilt, turn, tip
If head is misaligned move to ______ position
Proper
What is a normal result of EOMs?
Full range of motion - FROM
Smooth accurate full extensive - SAFE
What issue can arise from patients that see diplopia?
CN palsy, thyroid eye disease, myasthenia Travis, orbital inflammatory syndrome, cavernous sinus fistula, or orbital fracture
What does it mean if a patient feels pain during EOMs?
Optic neuritis, orbital inflammatory syndrome
What EOMs are in the oculomotor nerve (CN III)?
Medial Rectus
Inferior Rectus
Superior Rectus
Inferior Oblique
What EOMs are in the trochlear nerve (CN IV)?
Superior Oblique
What EOMs are in the abducens nerve (CN VI)?
Lateral Rectus
What is a palsy?
A paralysis of a muscle, unable to perform the action(s) it is responsible for
What is a complete palsy?
No ability of the muscle to perform its action(s)
What is a partial palsy?
Limited ability to perform its action(s)
What is a right cranial nerve palsy CN III?
Down and out eye in primary gaze with little to no ability to elevate, and reduced depression and adduction on EOM testing
What muscles are affected in cranial nerve palsy III?
Medial Rectus
Inferior Rectus
Superior Rectus
Inferior Oblique
What is right cranial nerve palsy CN IV?
Up and sometimes in slightly in primary gaze when reduced depression - worse when abducting
What muscles are affected in cranial nerve palsy IV?
Superior Oblique
What is left cranial nerve palsy CN VI?
Affected eye in on primary gaze with no/reduced ability to abduct, patient would move their head to the left to reduce diplopia
What muscles are affected in cranial nerve palsy CN VI?
Lateral Rectus
What are vergences?
Disjunctive eye movements - moving in opposite direction
What is convergence?
Eyes move nasally
What is divergence?
Eyes move temporally
What is supra/infravergence?
Movement vertically (up/down)
Is divergence or convergence ability the greatest?
Convergence
How do you determine the point of maximum convergence while both eyes are still fixated on a target (fused)?
NPC
NPC is a quick method to quantify _______ ability by pushing a target towards a patient until they report diplopia
Convergence
How can you determine if possible convergences problems are present?
Eye strain while reading, diplopia at near
Borderline or high exophoria
What do vergences allow us to do?
To view targets a different distances without seeing double
Alignment allows placing of the image of the object of regard on _________ retinal points (fovea)
Corresponding
What is the break?
The closest point in which one just loses the ability to maintain fusion (one image)
What is the recovery?
The point in which one is able to regain fusion (comes back to one)
Where do you measure NPC from?
The rotational axis of the eyes to the target being used in centimeters
The eye is about 24 mm long, we can assume the rotational axis is ______ behind the cornea
12 mm
Where do you align the ruler in NPC?
The lateral canthus (temporal corner of the eye)
What accommodative targets do we use to test NPC with?
Small targets that must be kept clear, so accommodation occurs
What are normal results for NPC?
Break <5 cm
Recovery <7 cm
What happens if you get an abnormal result in NPC?
Test with transilluminator and red/green glasses
When would you use red/green glasses?
Receded NPC
Large difference between recovery and break
Eyestrain, HAs, diplopia
What classifies a convergence insufficiency?
Break findings >5cm more receded
Recover findings >8cm more receded
What is the target for NPC?
Isolated letters 2 lines above BCVA of poorer seeing eye
How far away does the target need to be for NPC to start?
40 cm and in primary gaze
How slow should you bring the target into the patients eyes during NPC?
~5 cm/sec
How do you notate diplopia?
Subjective break or (+) diplopia
How do you notate an eye turn out?
Objective break
How do you test for an objective break?
Observe the distance at which the eye that turned out regains fusion
How do you notate if the patient maintains fusion with the target?
To the nose (TTN)