Final Leadership Review
1/165
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
Assets of Teams
- Perform better than individuals on complex tasks
- Synergy
- Divergent Ideas
- Creativity
- Use more information
- Share responsibility
Liabilities of Teams
- Perform worse than individuals working alone on simpler tasks
- Social loafing, free riders
- Diffused responsibility
- Time
- Groupthink
Teams are most beneficial if the work is ______ & ______
Complex & Creative
Tuckman's Stages of Development
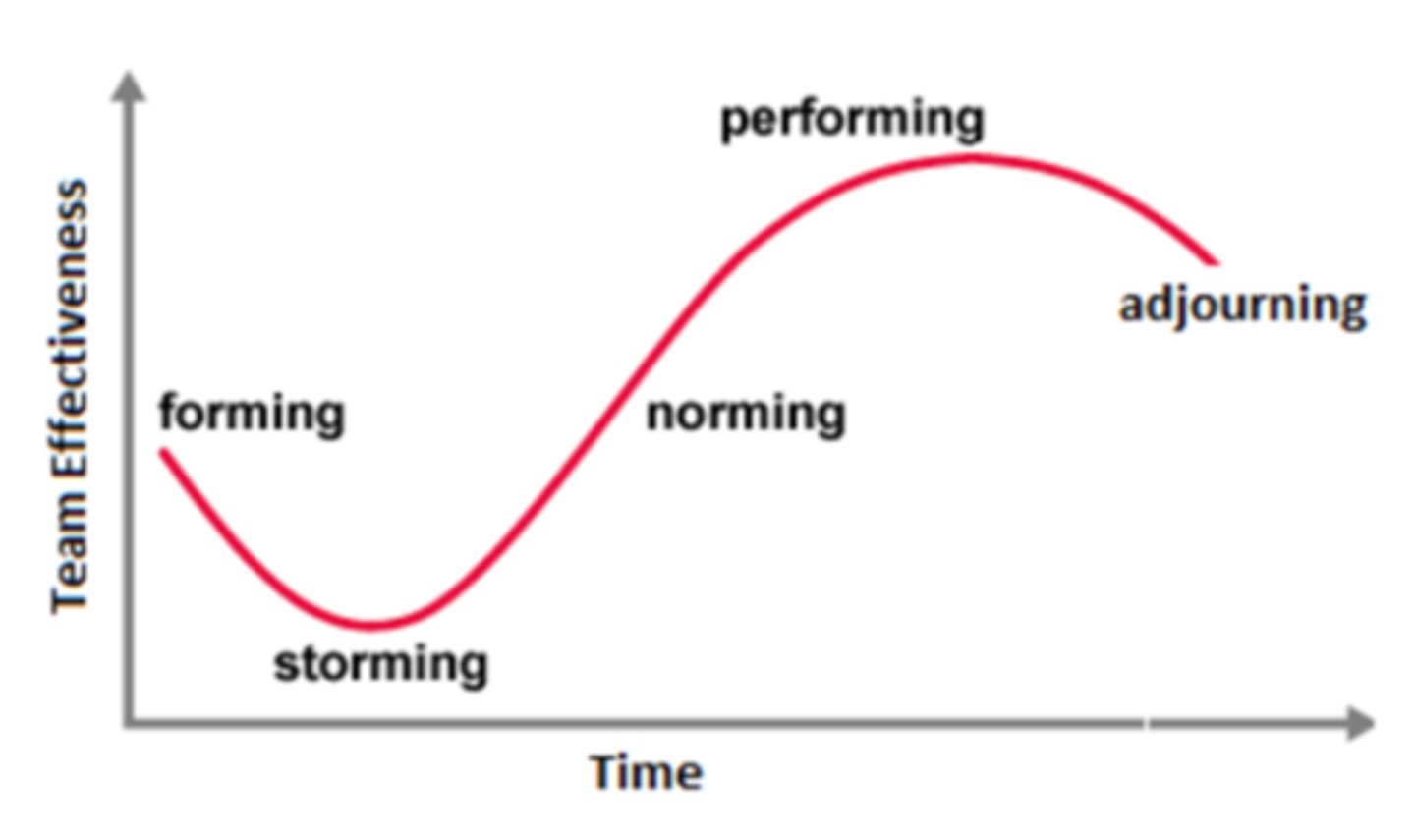
Characteristics of Forming
- Displaying eagerness
- Socializing
- Generally Polit Tone
- Sticking to Safe Topics
- Unclear about how one fits in
Characteristics of Storming
- Some resistance
- Lack of participation
- Conflict based on differences of feelings/opinions
- Competition
- High emotions
- Starting to move towards group norms
Characteristics of Norming
- Purpose & Goals are well-understood
- More confident
- Improved commitment
- Members are engaged and supportive
- Relief, lowered anxiety
- Developing cohesion
Characteristics of Performing
- High motivation, trust & empathy
- Individuals defer to teams needs
- Effectively producing deliverables
- Consistent performance
- Demonstrations of interdependence & self-management
Characteristics of Adjourning
- Shift to process orientation
- Sadness
- Recognition of team & individual efforts
- Disbanding
Strategies of Forming
- Taking the 'lead'
- Being highly visible
- Facilitating introductions
- Providing the 'big picture'
- Est. clear expectations
- Communicating success criteria
- Ensuring response times are quick
Strategies of Storming
- Requesting & encouraging feedback
- Identifying issues & facilitating their resolution
- Normalizing matters
- Building trust by honoring commitments
Strategies of Performing
- Minimal intervention
- Celebrating successes
- Encouraging collective decision-making & problem-solving
Strategies of Adjourning
- Recognizing change
- Providing an opportunity for summative team evaluations ('lessons learned')
- Providing opportunity for individual acknowledgements
- Celebrating the team's accomplishments (an 'after-party')
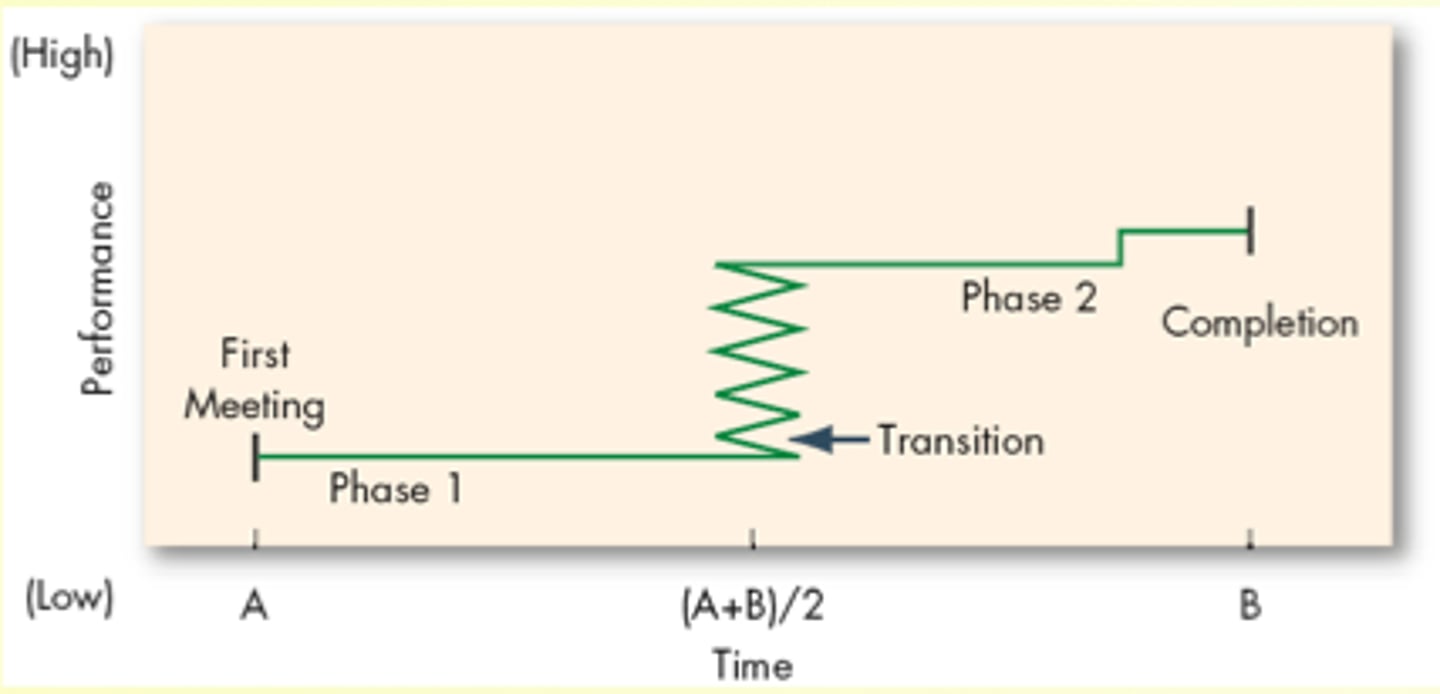
Punctuated Equilibrium Model
Belbin's Team Roles
- Action-Oriented Roles
- People-Oriented Roles
- Thinking-Oriented Roles
Role Perception
An individual's view of how he/she is supposed to act in a given situation
Role Expectations
How others believe a person should act in a given situation
Role Conflict
Conflict among the roles connected to two or more statuses
Shaper
Pushes the team to focus and improve, a leader
(ACTION-oriented roles)
Implementer
Plans practical, workable strategies to achieve goals (ACTION-oriented roles)
Completer/Finisher
Finishes and quality controls team's work
(ACTION-oriented roles)
Coordinator
Focuses the team around objectives
(PEOPLE-oriented roles)
Team Worker
Helps the team coordinate with one another/connect
(PEOPLE-oriented roles)
Resource Investigator
Considers external applications and connections needed for the team's work
(PEOPLE-oriented roles)
Plant
Creative solutions/problem solving
(THINKING-oriented roles)
Monitor/Evaluator
Evaluates team's opinions
(THINKING-oriented roles)
Specialist
Unique knowledge input/expertise
(THINKING-oriented roles)
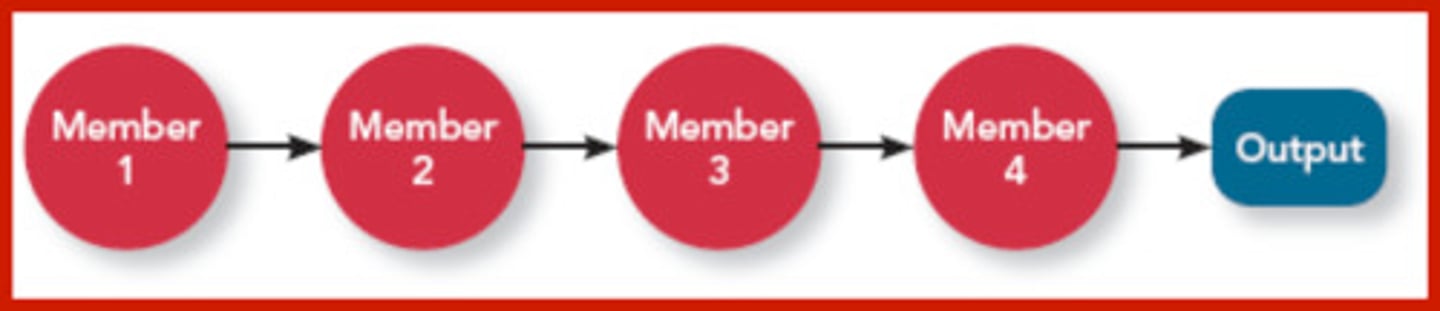
Sequential Interdependence
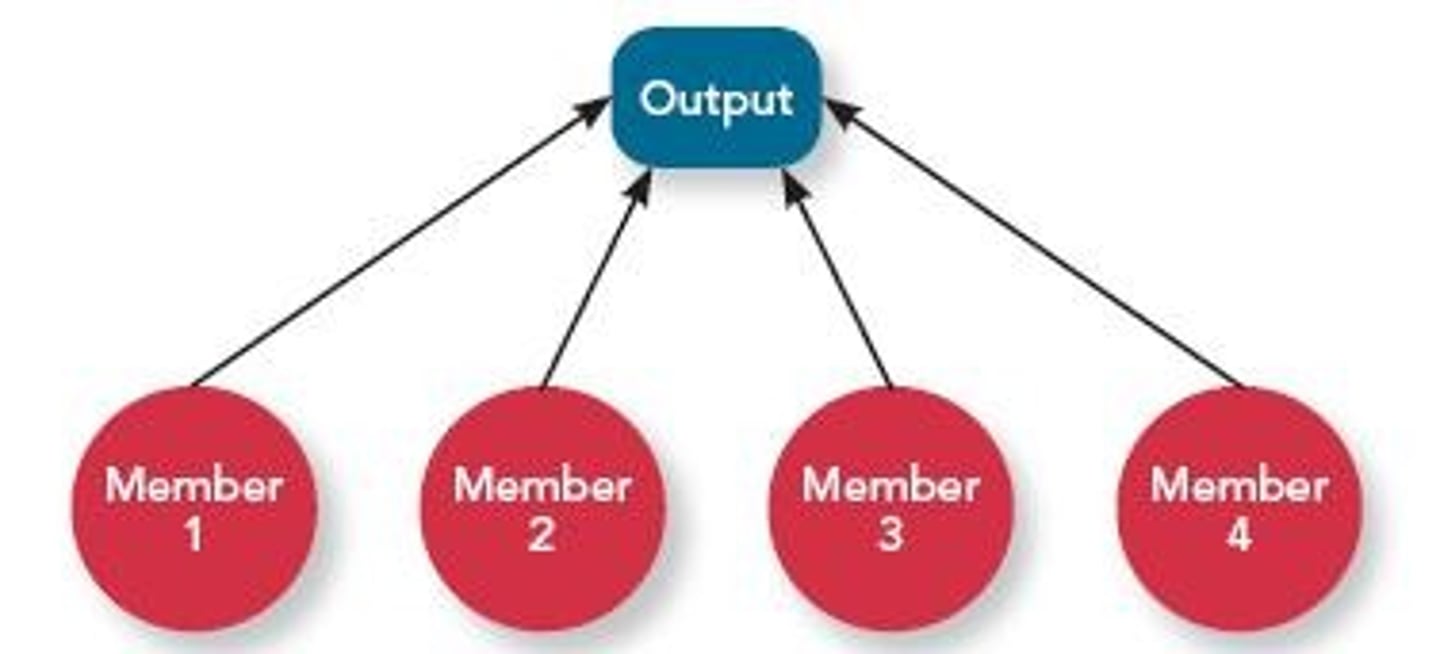
Pooled Interdependence
Reciprocal Interdependence
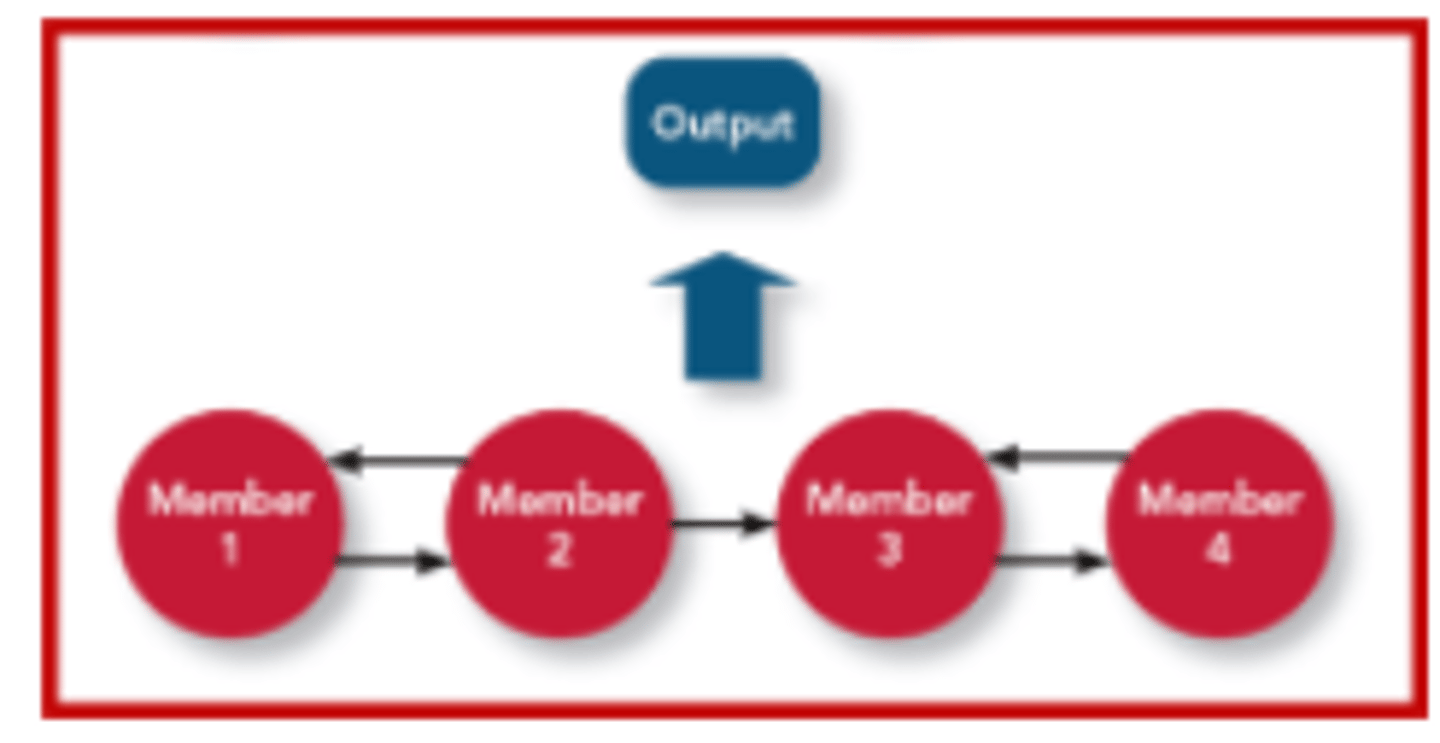
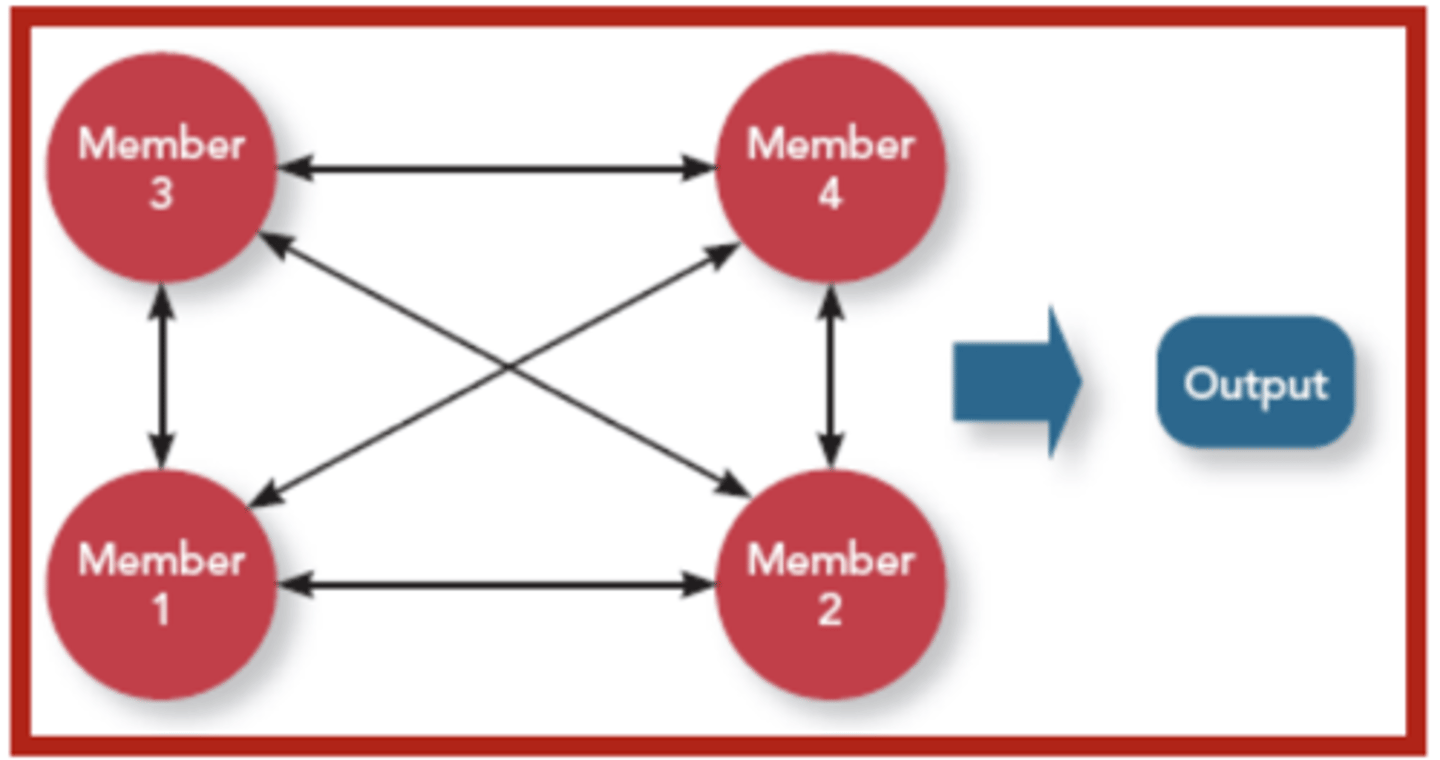
Intensive Interdependence
Illusion of Invulnerability
Excessive optimism
Collective Rationalization
Members discount warnings and don't reconsider their assumptions
Belief in Inherent Morality
Members ignore the ethical/moral consequences of their decisions
Stereotyped Views of Out-Groups
Others are the "enemy"
Direct Pressure on Dissenters
Members are under pressure not to express arguments against any of the groups views
Self-Censorship
Doubts are not expressed
Self-Appointed 'mindguards'
Members protect the group & leader from information that is problematic or contradictory
Social Loafing
Individuals exerting less effort when they work in a team than when they work alone
Passive Listening
Listening to the conversation/sound but doesn't verbally talk
Involved Listening
You're "present" and attentive, but you may not be driving the conversation; inconsistent participation in the conversation
Detached Listening
You're listening in a very boring or neutral way, without processing or reacting much
Non-Defensive Communication
Asking questions and making statements in an open and neutral manner
Non-Defensive Question
"Are you upset about something"
Defensive Question
"Why are you upset?"
Crucial Conversations occur when:
- Stakes are high
- Opinions vary
- Emotions run strong
Level of Conflict: Low
Work Unit Characteristics: Apathetic, stagnant, lack of new ideas, groupthink
Work Unit Performance: Low
Level of Conflict: Moderate
Work Unit Characteristics: Viable, Self-critical, Innovative
Work Unit Performance: High
(we want this)
Level of Conflict: High
Work Unit Characteristics: Disruptive, Chaotic, Uncooperative
Work Unit Performance: Low
Task Conflict
Conflict over content and goals of the work
(Functional)
Process Conflict
Conflict over how the work gets done
(Functional)
Relationship Conflict
Conflict based on interpersonal relationship
(Dysfunctional)
Conflict Handling Style
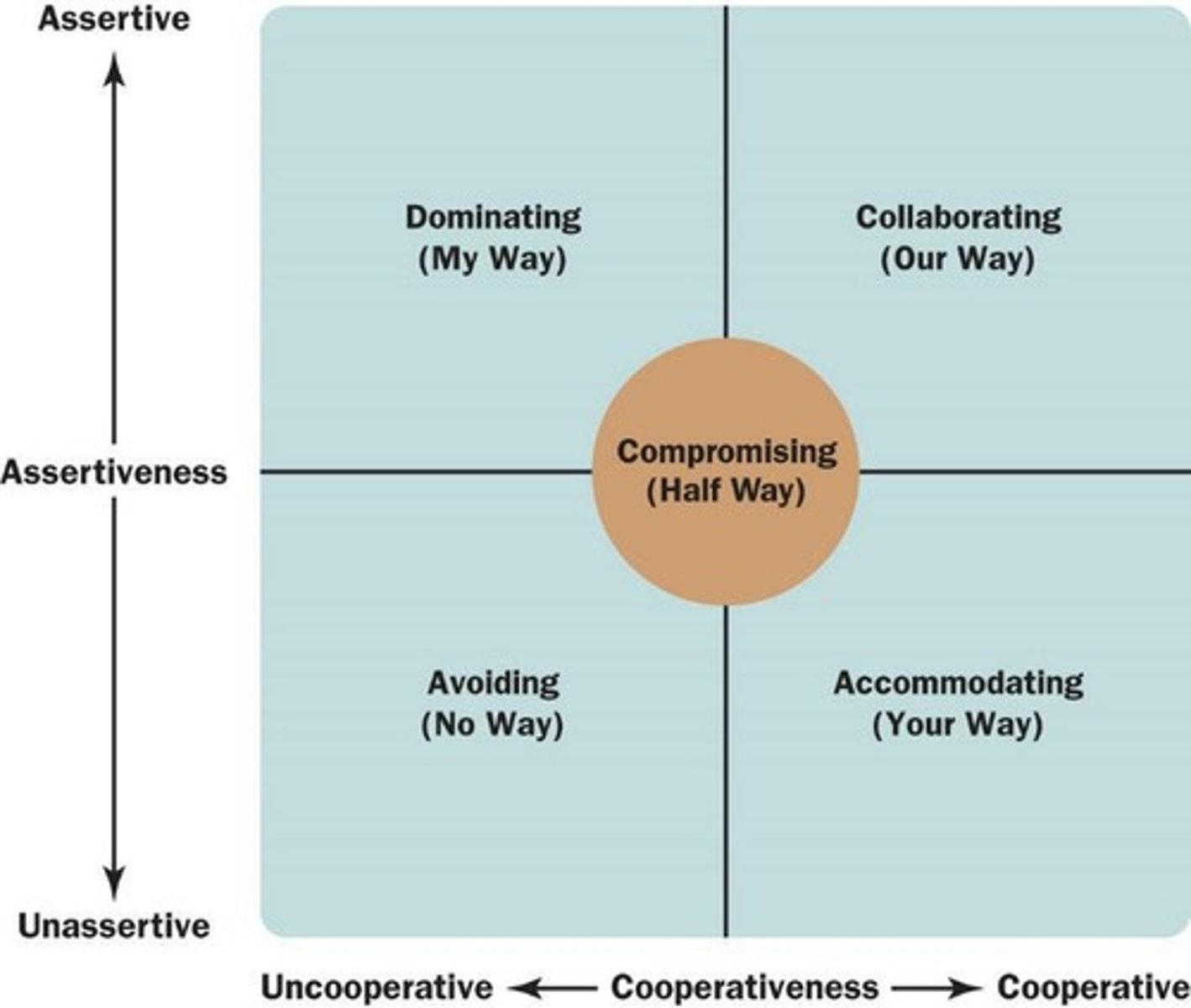
Tangible Negotiation
The things in the contract: salary, start date, position, location, other terms
Intangible Negotiation
The unspoken things: "winning", reputation, being fair, the relationships
Distributive Bargaining
- Win-Lose
- Get as much of the pie as possible
- Focuses on Positions
- Short-Term
- Low Information Sharing
Integrative Bargaining
- Win-Win
- Expand the pie so that both parties are satisfied
- Focuses on Interests
- Long-Term
- High information sharing
Negotiation Positions
"I want Thanksgiving off work"
(Surface statement of where a person/organization stands)
Negotiation Interests
"I want to spend time with my family"
(WHY you want what you are asking for)
Best Alternative to a Negotiated Agreement (BATNA)
- A fallback option if a negotiated agreement can't be reached
- GOAL: Beat your BATNA
- Better BATNA, greater power
Resistance Point
- Worst deal you are willing to accept
- Base it on your BATNA
System 1 Thinking
Automatic, fast, little or no effort, no sense of voluntary control
System 2 Thinking
Slower, paying more attention, putting more effort
Rational Decision-Making Model
(1) Identify the problem
(2) Generate alternative solution
(3) Evaluate alternatives and select a solution
(4) Implement and evaluate the solution chosen
Non-Rational Decision Making Model
- Satisficing when arriving at a solution (good enough)
Intuitive Based Decision Making
- Gut Feeling
- Automated Experience (helps us make quick decisions)
Confirmation Bias
Tendency to search for, interpret, favor and recall information in a way that confirms or supports one's prior beliefs or values
Overconfidence Bias (Dunning-Kruger Effect)
Overestimating our skills relative to those of others and overestimating the accuracy of our predictions
Availability Bias
Represents a decision maker's tendency to base decisions on information that is readily available in memory
Anchoring Bias
Decision makers are influenced by the first information received about a decision, even if it is irrelevant (usually numbers)
Priming Effect
Similar to anchoring but instead you use other stimulus influences
Hindsight Bias
When knowledge of an outcome influences our belief about the probability that we could have predicted the outcome earlier. Danger of this bias is that, in retrospect, we get overconfident about our foresight, which leads to bad decisions
Framing Bias
Decisions are influenced by the manner in which a problem/question is framed
Escalation of Commitment Bias (Sunk Cost Fallacy)
The tendency to continue investing in a failing course of action due to an unwillingness to admit a past mistake
Trait Theory
Some people are born with special qualities that make them natural leaders
Behavioral Theory
People can learn to be good leaders by the way they act, not just by the traits they are born with
Behavioral Theory: Initiation of Structure
Task Oriented
EX: Assign group members to specific tasks, schedule & coordinates the work
Behavioral Theory: Consideration
Relationship Oriented
EX: Treat group members as equals
Situational Leadership Theory
- Focuses on leader's need to adapt to different follower situations
- Acknowledges the importance of followers and builds on the logic that leaders can compensate for their limited ability and motivation
Fiedler's Situational Theory
Leaders are thought to have a dominant style: motived by either relationship or task.
Leader effectiveness depends on the extent to which leader style matches the situation.
As situations change, different styles become more appropriate.
Transformational Leadership
Inspires followers to commit to a shared vision that provides meaning to their work
Sources of Personal Power
"What leaders with power bring to the party"
Sources of Position Power
"Power that you get from a position"
Legitimate Power
Control of resources, flexibility to make decision, hierarchical authority
Reward Power
Control of positive outcomes/benefits
(Big motivator)
Coercive Power
Fighting Control = Negative Consequences - comply or it will be negative for you
Expert
Comes from the leader's knowledge, competence, and expertise
People follow because they respect what the leader knows.
Referent
Comes from the leader's charisma, likability, and the respect others have for them
People follow because they want to be associated with the leader.
Information
Comes from having access to valuable or timely information.
People follow because the leader can provide insight or knowledge others need.
Rational Persuasion
Use reason, logical, facts
Consultation
Seek participation & input
Ingratiation
Give flattery, praise, humility
Exchange
Give rewards & reciprocity
Personal Appeals
Invoke loyalty & friendship
Coalitions
Make an alliance with others
Inspirational Appeals
Appeal to values, ideals, emotions
Legitimacy
Show request is within your authority, rules, procedures or their responsibility
Hard Tactics
Exert more overt pressure
- Coalition
- Pressure
- Legitimizing tactics
Soft Tactics
Friendlier & Less coercive
- Rational persuasion
- Inspirational Appeals
- Consultations
- Ingratiation
- Personal Appeals
Retribution
"If you don't do X, you will regret it"