US History: WWI Key Concepts and Causes Review
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Militarism
This was the development of armed forces, and their use in diplomacy. During World War 1 the cost of building, defending empires led to more military spending.
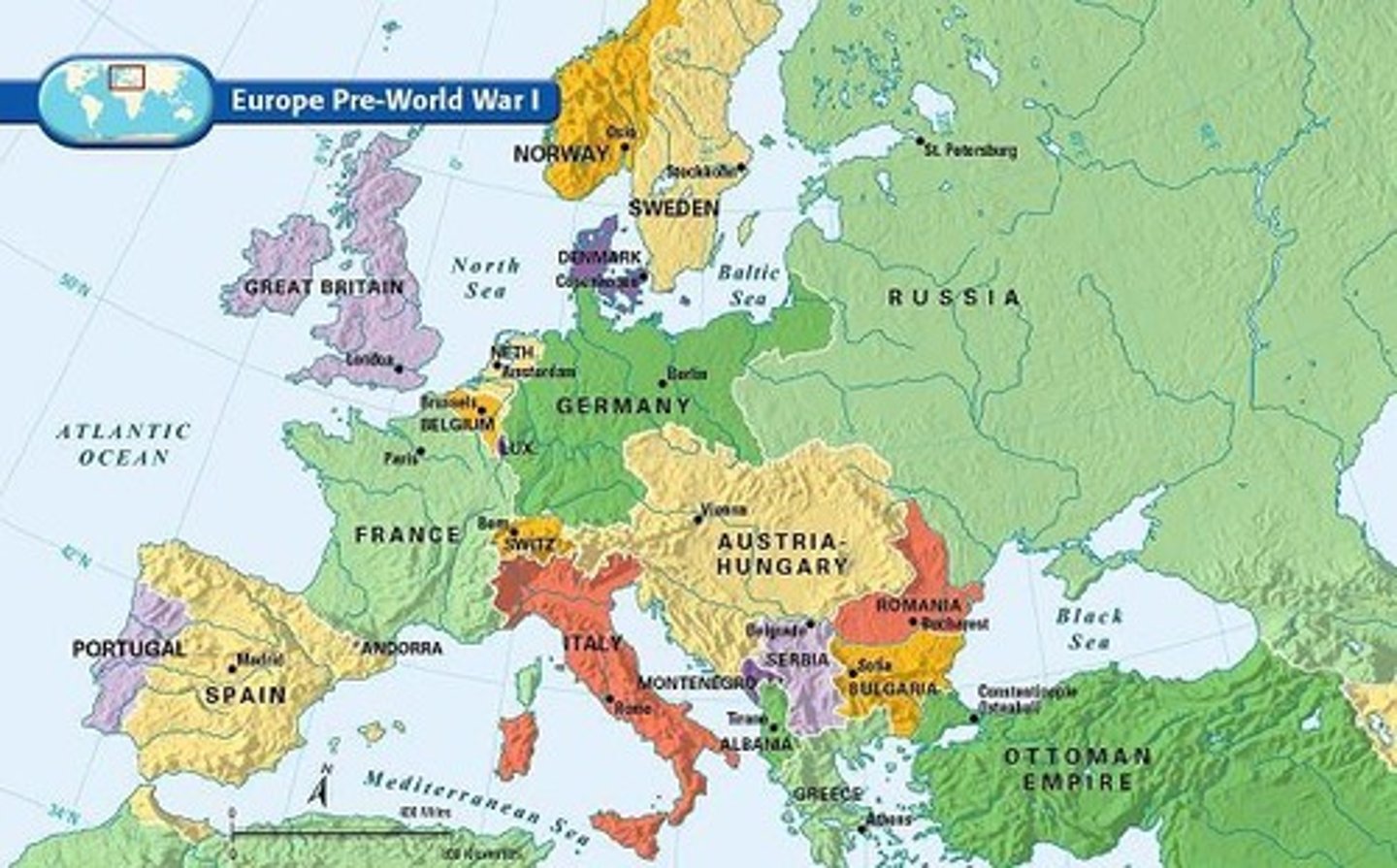
Alliances
During the war there were many alliances. One alliance was called the Triple Entente, and this was made up for France, Britain, and Russia. While Germany, Austria Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire alliance were called central powers.
Imperialism
When different countries fight for land, this can increase tensions between them and can make them enemies. This can lead to conflicts and even wars.
Nationalism
This is when you love your country a lot, and you brag about it to other countries causing you to compete or become enemies with other countries.
Archduke Franz Ferdinand
The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand by a Serbian nationalist was the breaking point, and the start for World War 1.
Triple Entente
The Triple Entente was an allied group that consisted of France, Britain and Russia.
Central Powers
This was another allied group during World War 1, and this consisted of Germany, Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire, Bulgaria.
Woodrow Wilson
He was the president at the time, and before the U.S joined the war he wanted us to stay neutral and to try and not to join the war.
Propaganda
False lies that were told by the government.
Lusitania
This was a British passenger ship that was sunk by a German U-boat in 1915. Over 1,000 people died, including Americans.
Zimmerman telegram
This was a note from Germany to Mexico basically saying that they should create an alliance and attack the U.S.
War Industries Board
Bernard Baruch led the War Industries Board. He helped factories make goods faster using mass production.
Liberty bonds and victory bonds
Liberty bonds were sold during World War I so people could lend money to help pay for the war. While victory bonds were sold after the war to help the government pay back what the war cost.
Women in the War Effort
In the war women worked in jobs traditionally held by men. For example railroads, cooking, dock workers, shipbuilding, and mining. They also were nurses during the war, red cross volunteers and active in the peace movement. Women also gained a lot of support for women's suffrage and the 19th amendment
Great Migration
Many southern and African Americans migrated to Northern cities. They migrated from the south to the north because they faced many racial discrimination in the south. There were also more job opportunities in the north. A lot of the immigrants worked in factors..
Ways to Avoid War
Diplomatic negotiations, forming alliances for peace, and promoting economic interdependence among nations.
Committee on Public Information
This recruited artists, writers and advertising to encourage Americans to support World War 1, be patriotic, save resources and buy war bonds.
Espionage and Sedition Acts
The Espionage and Sedition Acts punished people who interfered with the war or spoke badly about the government, the war, or the flag. Penalties included fines and up to 20 years in jail.