Secondary storage
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What are the three types of secondary storage?
Optical
What is magnetic storage?
Mechanical parts move over the disks surface to read and write data magnetically
What are the basic features of a hard disk (magnetic storage)?
- Disks contains concentric circles called tracks
- Each track is divided into sectors
- Disks heads mounted on mechanical arms read and write the data
Parts of a hard disk drive (magnetic)
components including platters, read/write heads, actuator arms, and spindle motor.
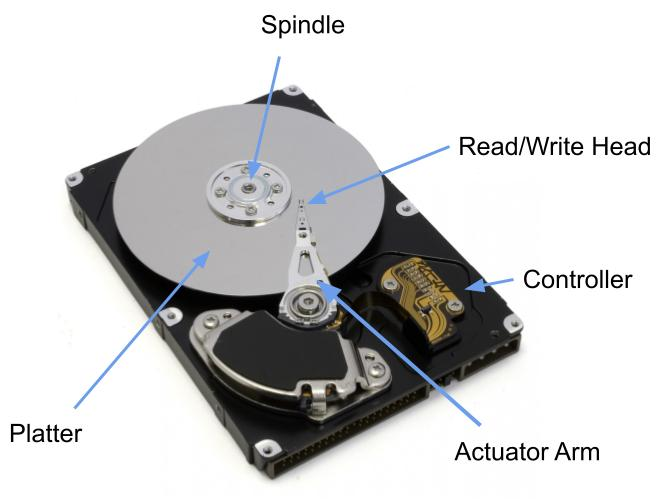
What storage capacity do hard disks have (magnetic)?
Very large storage capacity
How expensive is a hard disk drive (magnetic)?
They are a very cheap form of storage compared to solid state drives
How are portable hard disks (magnetic) connected to a computer?
Via a USB port
What was the primary magnetic secondary storage used at the beginning of the computer's creation?
Magnetic tape
Examples of magnetic storage
Floppy disk
What do cassettes require to be read?
A special tape-drive for reading and writing to the tape
How are magnetic tapes read? What order?
Magnetic tape is read/written sequentially
What is the speed of magnetic storage?
Slow when finding specific data stored on it but
has a Fast read/write speed when in the correct place to begin
How durable is magnetic storage?
When stored properly they are quite durable
What is optical storage?
Lasers read and write data using light
Examples of optical storage
CD
What formats can optical storage appear in?
ROM (read only memory)
How is data stored in optical storage?
Data is stored in pits
How do CD's work?
A laser beam passes over the pits and lands where the level of reflection is measured
What is the difference between CD's and Blu-rays?
A CD has bigger pits and lands as red light has a larger wavelength
The smaller Blu-ray pits and lands allow it to store more data and use a more precise wavelength
How expensive is optical storage?
Cheapest secondary storage
How durable is optical storage?
More durable than magnetic and less durable than solid state
How portable is optical?
Very portable
What kind of capacity does optical storage have?
50GB
What is solid state storage?
Data is recorded onto solid memory chips without any moving parts
How do solid state drives work?
A flow of electricity forcing electrons into floating gates between 2 oxide layers
This causes a change in the charge in the floating gate which can be measured as a 0 or 1
Oxide layers deteriorate over time
They have a limited number of read/write cycles
Examples of solid state
Memory sticks
What are the advantages of solid state storage?
- Very quick access to data
- No moving parts (durable and reliable)
- No noise (great for videoing)
- Low power (doesn't drain your phone battery)
- No need to defragment
What are the disadvantages of solid state storage?
- Limited number of read/write cycles
- More expensive per byte of storage than other types of storage
How expensive is solid state storage?
Very expensive
Is secondary storage volatile?
No