Mankiw Principles of Macroeconomics
1/198
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
199 Terms
Scarcity
Resources are limited
Economics
Study of how society manages scarce resources
Efficiency
Society obtaining the maximum benefits from scarce resources
Equality
The distribution of the benefits obtained from society's scarce resources
Opportunity Cost
The cost of what is given up to obtain something
Rational People
People who systematically and purposefully do the best they can to achieve their objectives
Marginal Change
Small incremental adjustments
Incentive
Something that induces a person to act
Property Rights
Ability of an individual to own and exercise control over scarce resources
Market Failure
A situation in which a market left on its own fails to allocate resources efficiently
Externality
The impact of one person's actions on the well-being of a bystander
Market Power
The ability of a single economic actor (or small group of actors) to have unduly influence on market prices
Productivity
Quantity of goods and services produced from each unit of labor input; Correlated with high standards of living
Inflation
An increase in the overall price level in the economy; Inversely related with unemployment in the short run
Cause of inflation
Growth in the quantity of money
Business cycle
Fluctuations in economic activity, such as employment and production
Circular Flow Diagram
Visual model of the economy that shows how dollars flow through markets among households and firms
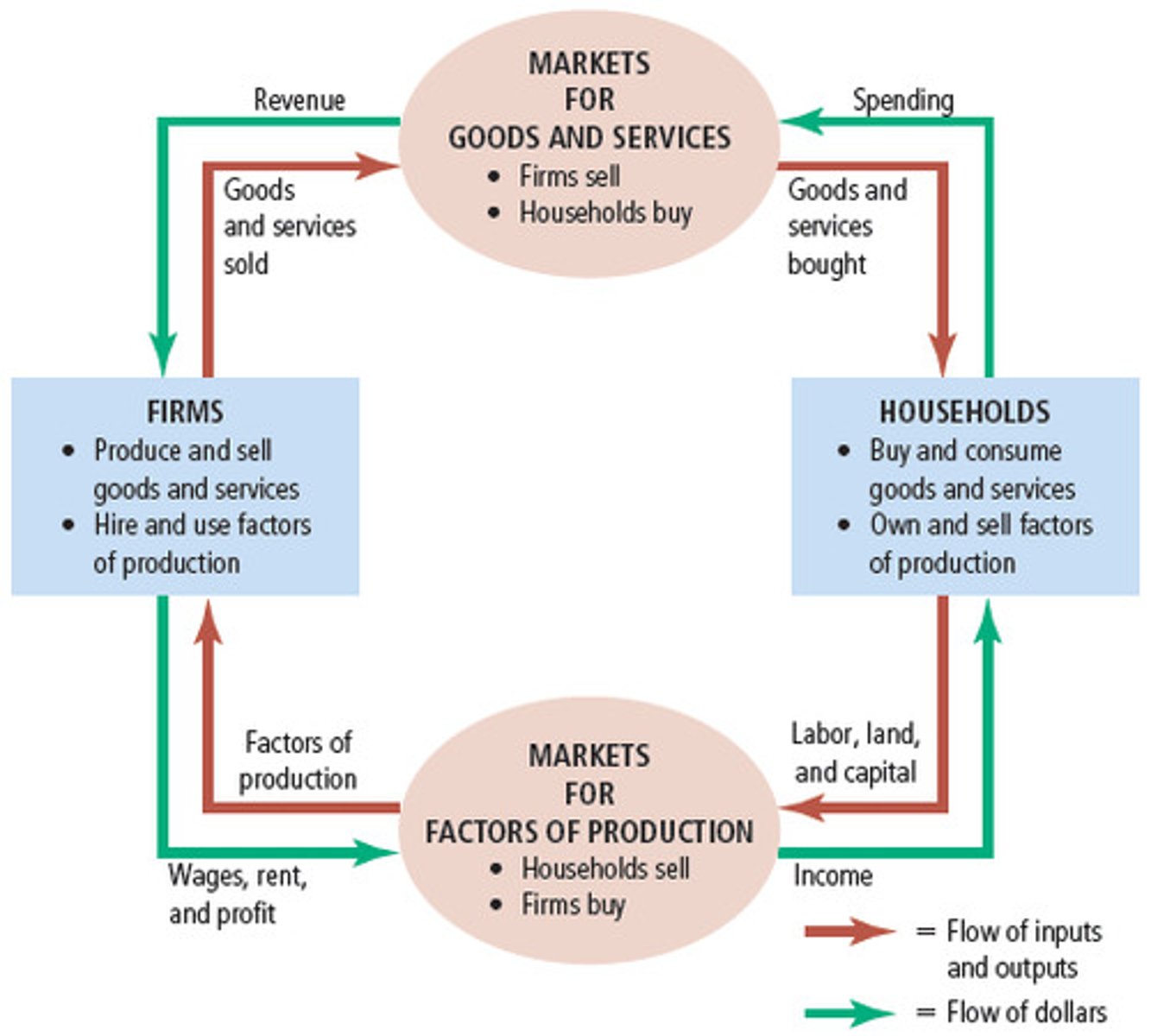
Factors of Production
Labor land, capital, natural resources, and other inputs used to make goods and services
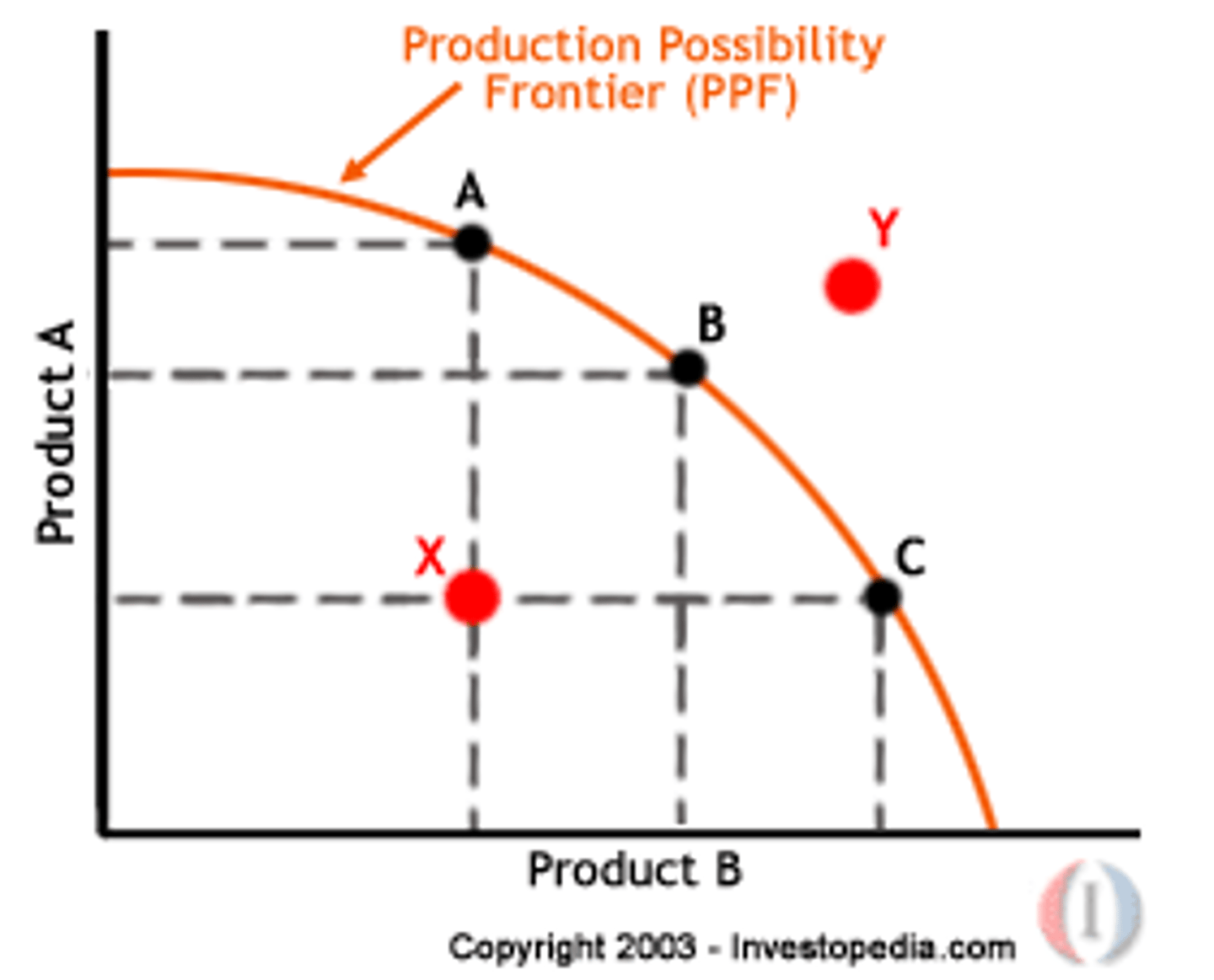
Production Possibilities Frontier
A graph that shows the combinations of output that the economy can possibly produce. The slope of the PPF measures opportunity cost. Any point on the PPF curve (rather than inside) is efficient.
Microeconomics
The study of how households and firms make decisions and how they interact in specific markets
Macroeconomics
The study of economy-wide phenomena, including inflation, unemployment, and economic growth
Positive Statement
A descriptive statement
Normative Statement
A prescriptive statement
Absolute Advantage
The ability to produce a good using fewer inputs than another producer
Comparative Advantage
The ability to produce a good at a lower opportunity cost than another producer
Imports
Goods produced abroad and sold domestically
Exports
Goods produced domestically and sold abroad
Market
A group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service
Competitive Market
A market in which there are many buyers and sellers so that each has a negligible impact on the market price
Perfect Competition
A market in which all goods are exactly the same and no single buyer or seller has any influence over price
Monopoly
A market with only one seller
Quantity Demanded
Amount of a good that buyers are willing and able to purchase
Law of Demand
Claim that, all else being equal, the quantity demanded of a good falls when the price of the good rises and vice versa
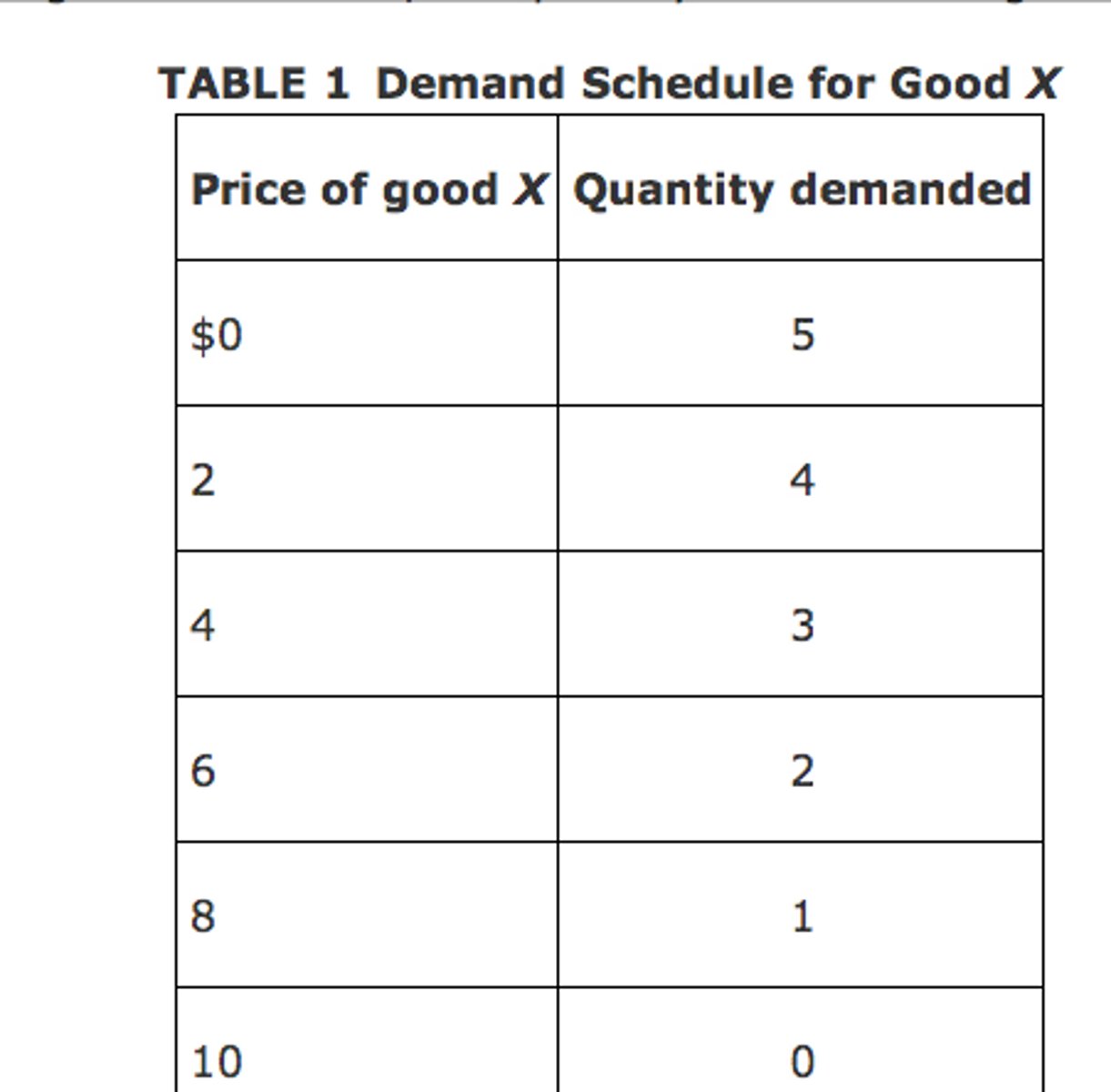
Demand Schedule
A table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded
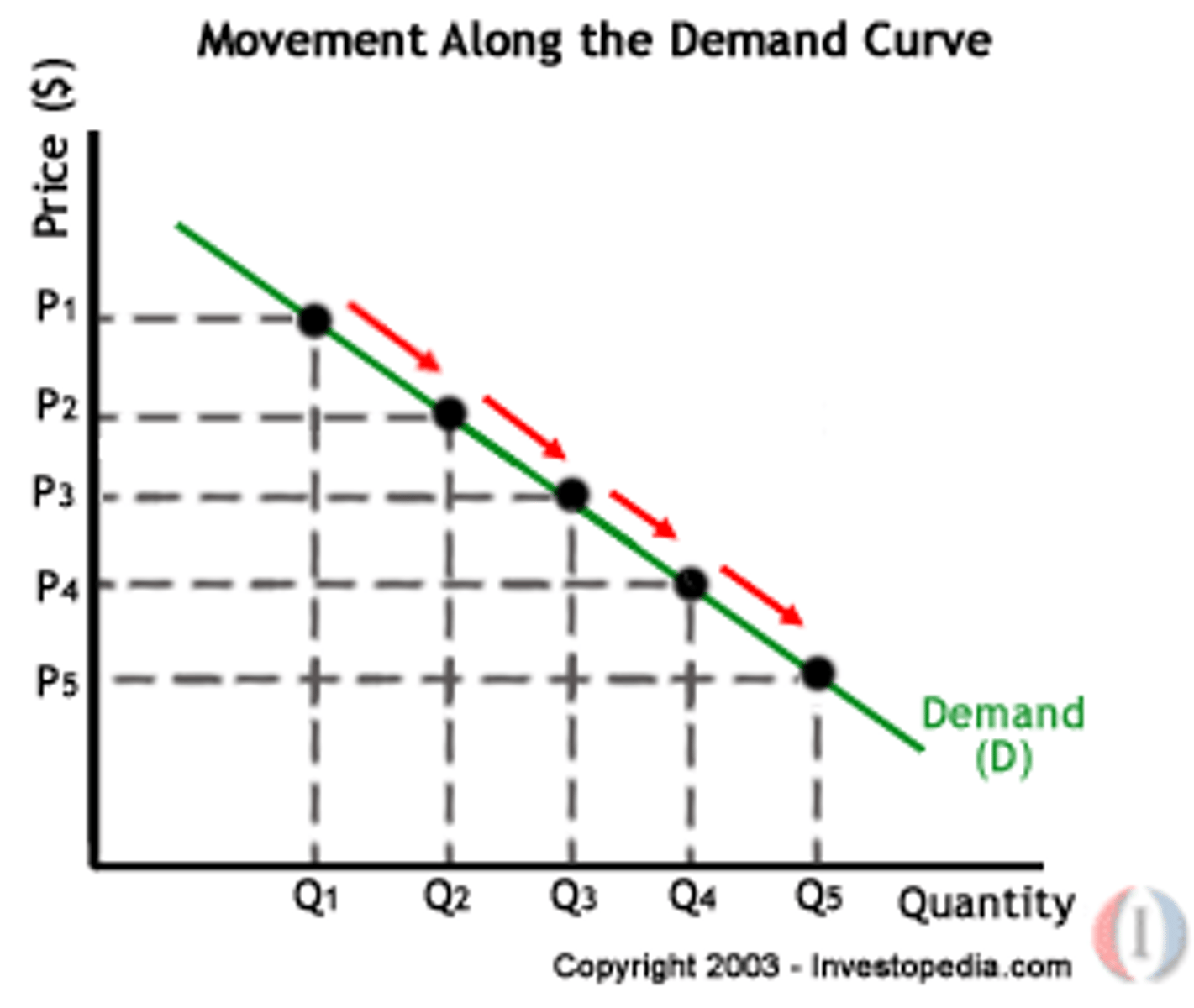
Demand Curve
A graph of the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded. Downward sloping
Shift in Demand Curve
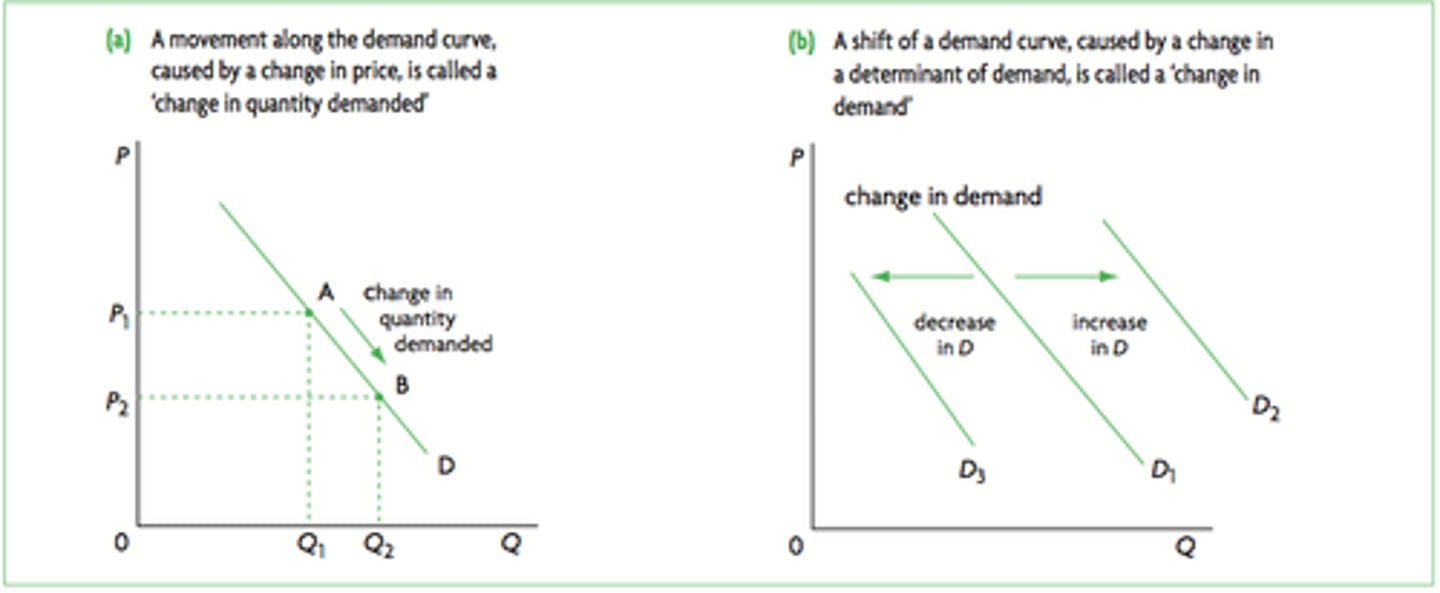
Normal Good
A good for which an increase in income leads to an increase in demand
Inferior Good
A good for which an increase in income leads to a decrease in demand
Substitutes
Two goods for which an increase in the price of one leads to an increase in the demand for the other
Complements
Two goods for which an increase in the price of one leads to a decrease in demand for the other
Determinants of Demand
Income, Tastes, Expectations, Number of Buyers; Determine shifts of the demand curve
Quantity Supplied
Amount of a good that sellers are willing and able to sell
Law of Supply
Claim that the quantity supplied of a good rises when the price of a good rises, and vice versa
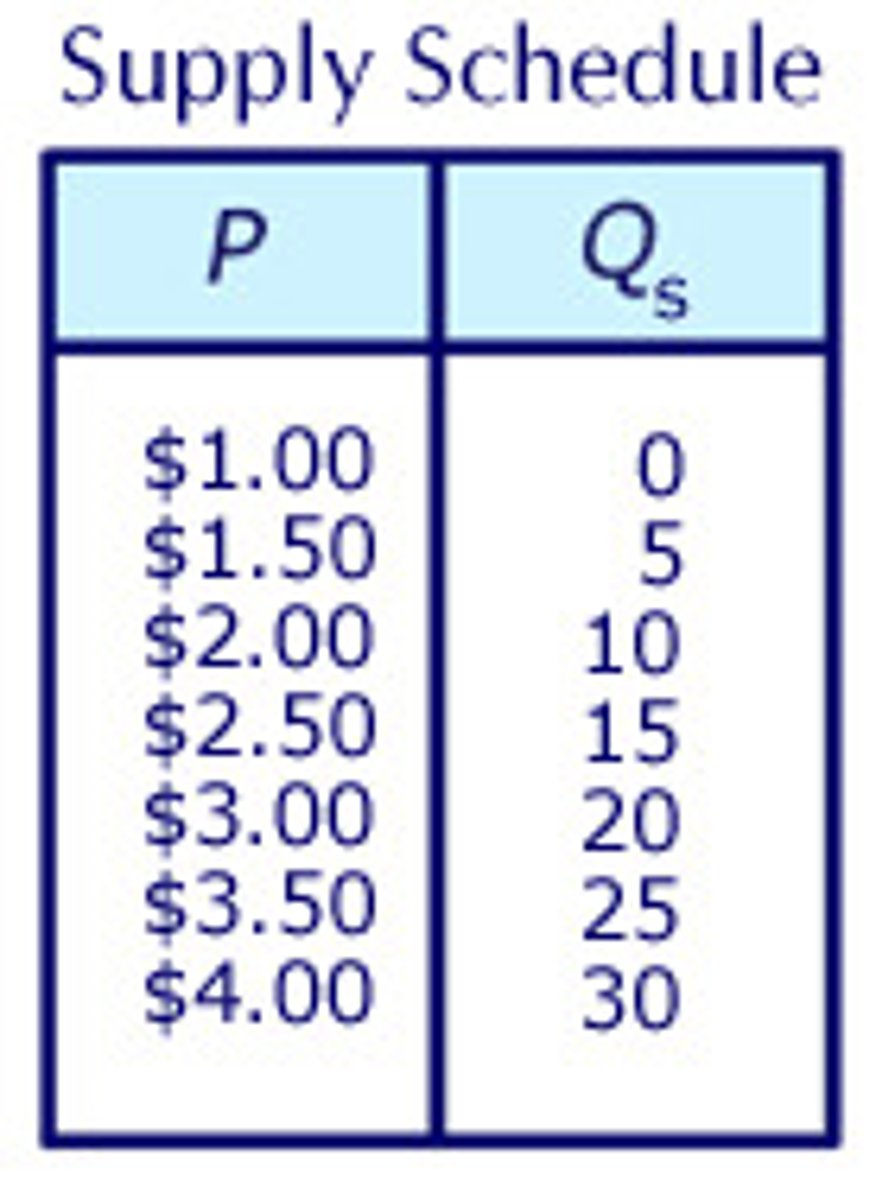
Supply Schedule
A table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied
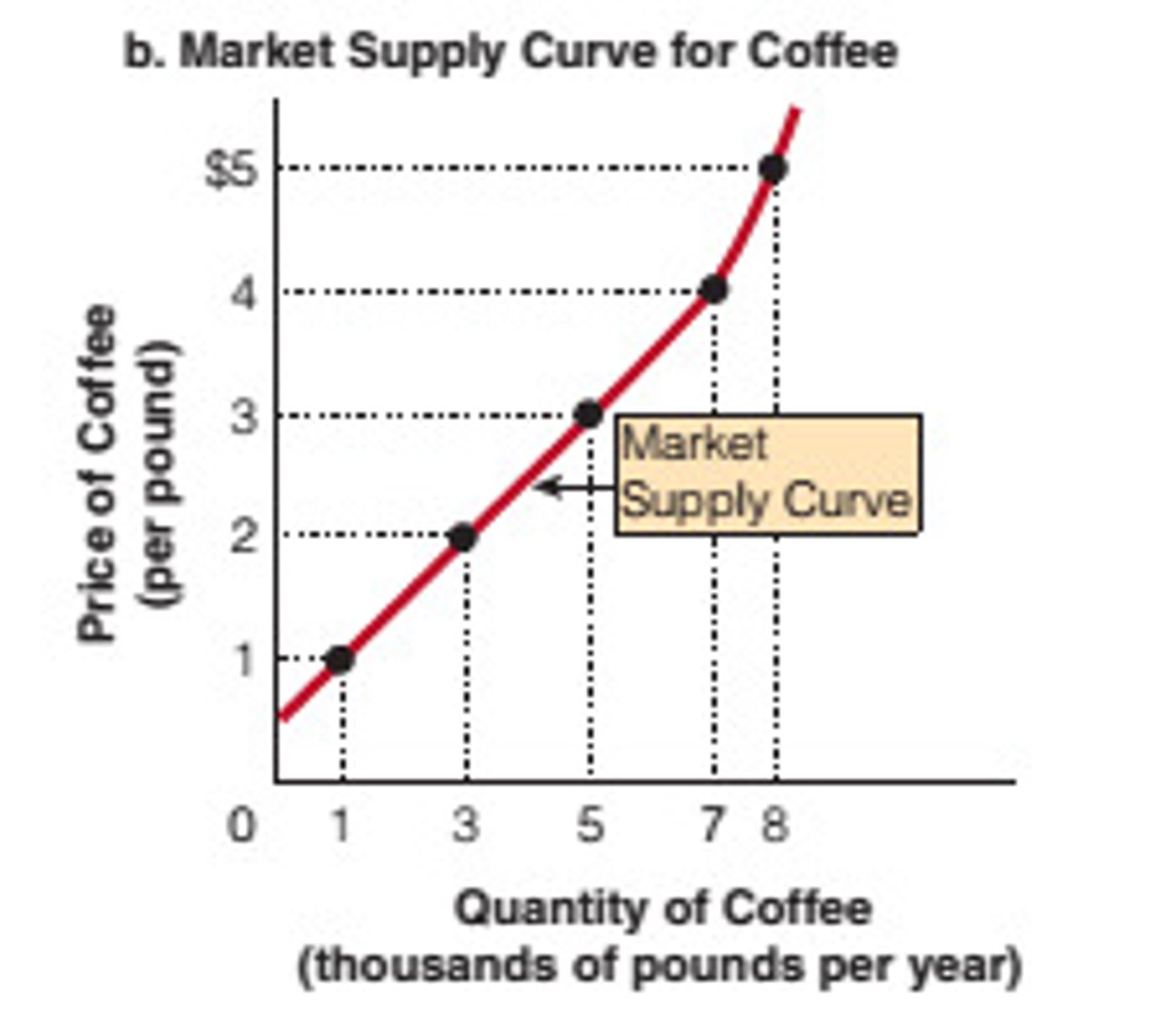
Supply Curve
A graph of the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied
Shift in Supply Curve
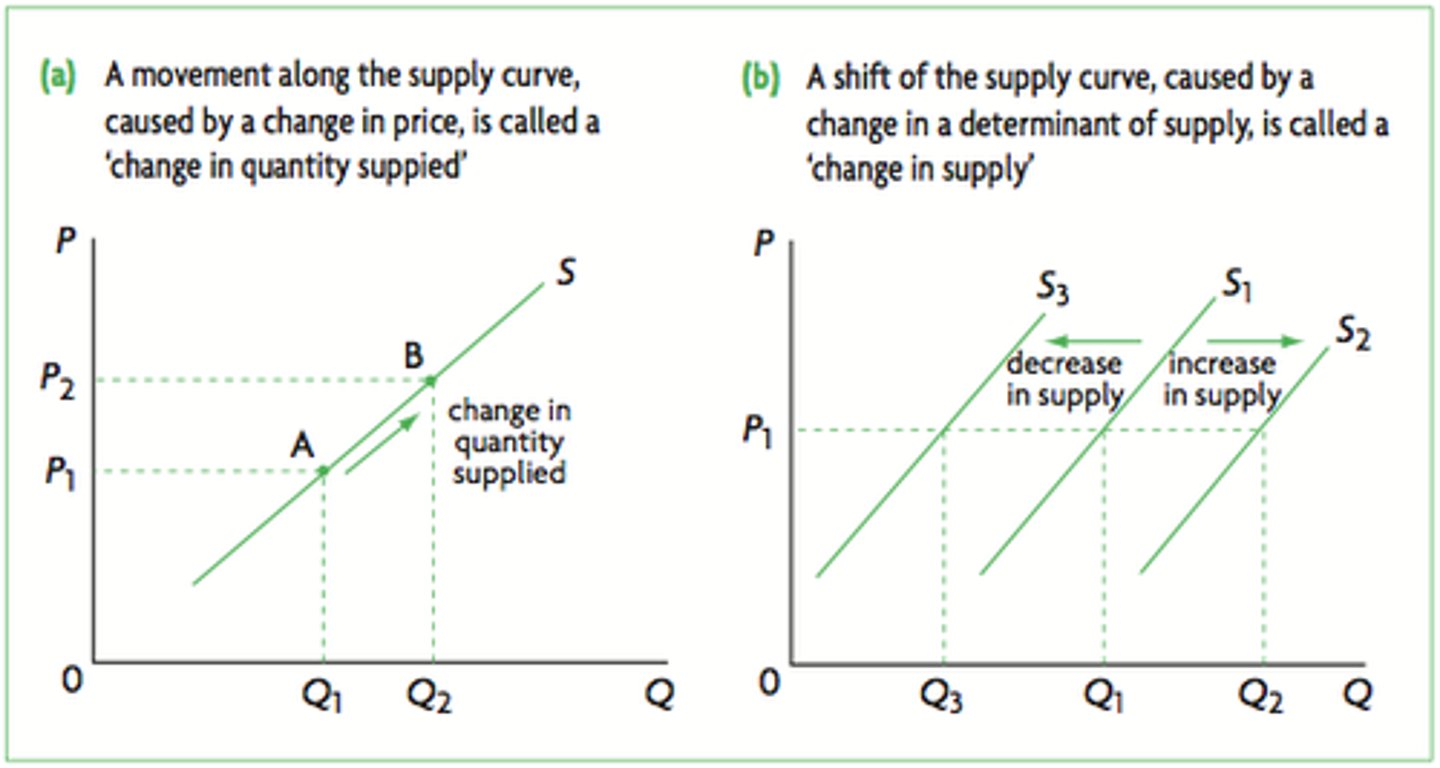
Determinants of Supply
Input Prices, Technology, Expectations, Number of Sellers; Determine shifts of the supply curve
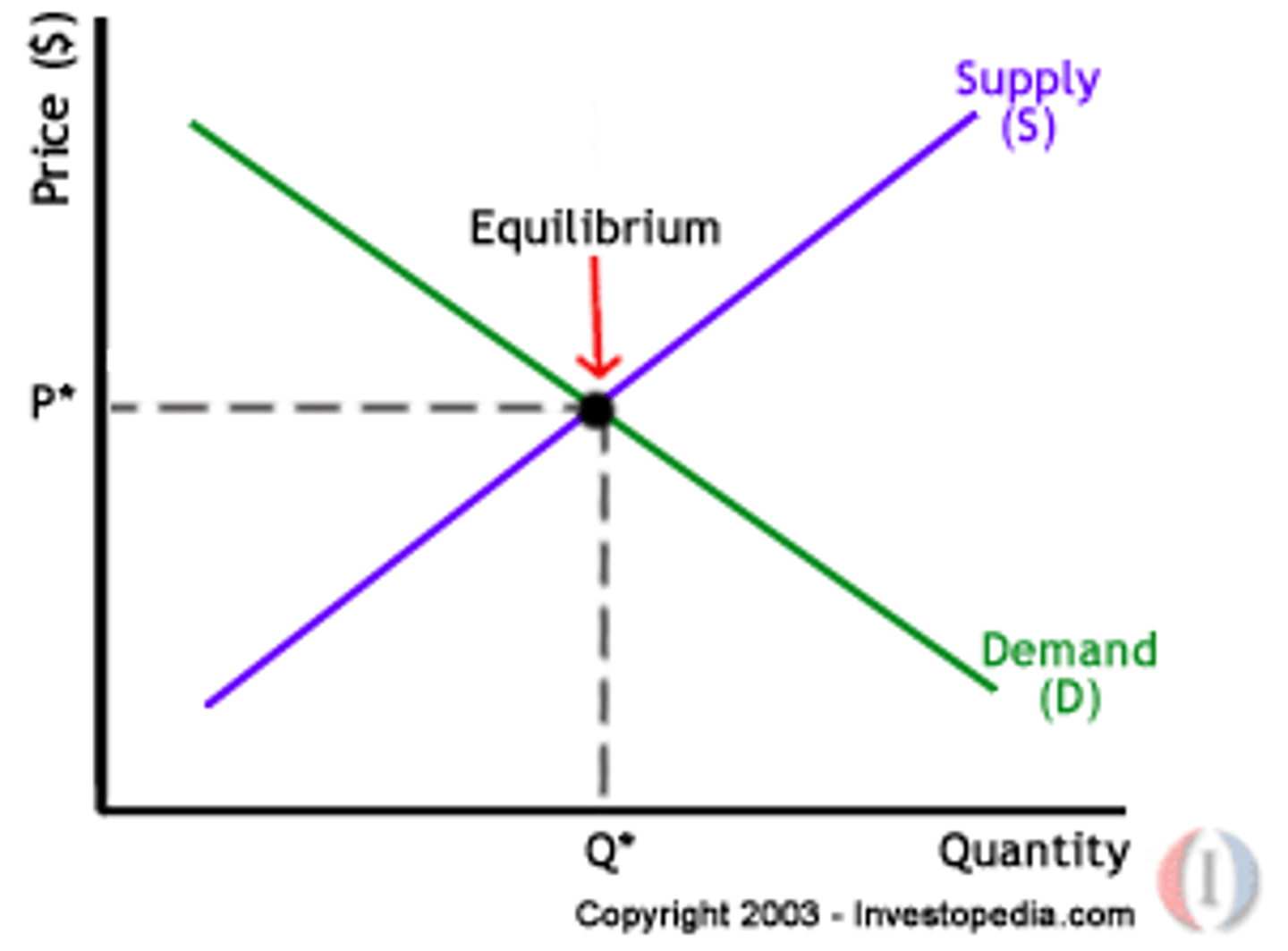
Equilibrium
A situation in which the market price has reached the level at which quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded
Equilibrium Price
The price that balances quantity supplied and quantity demanded
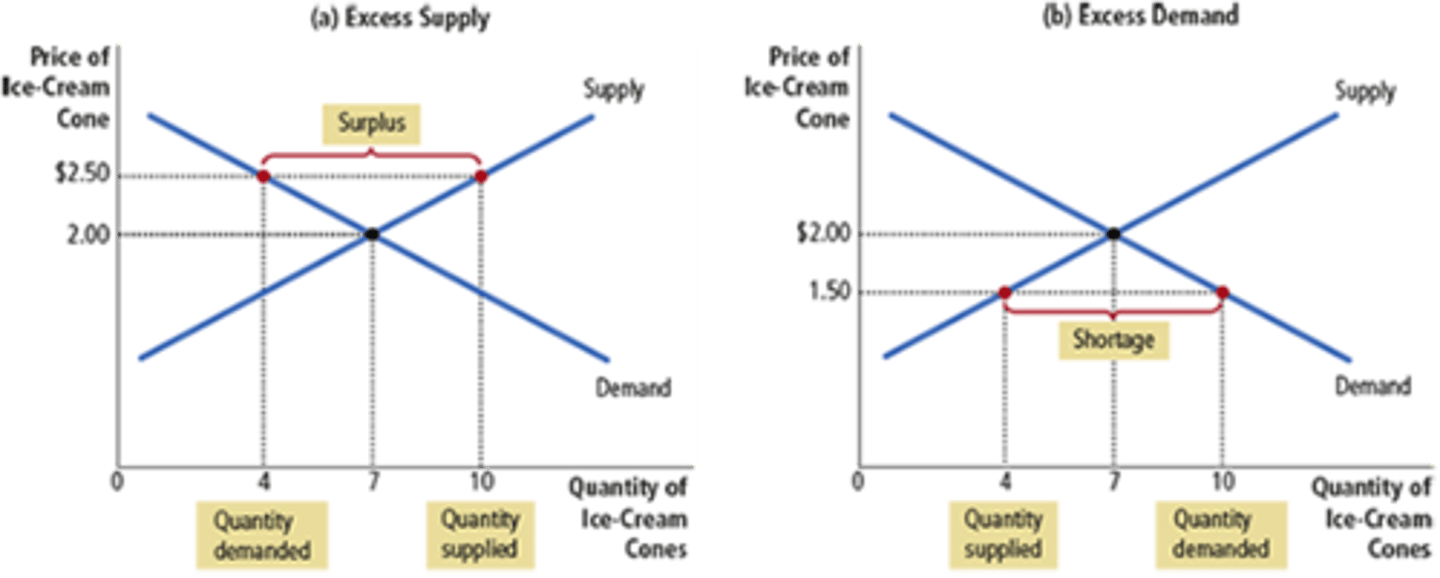
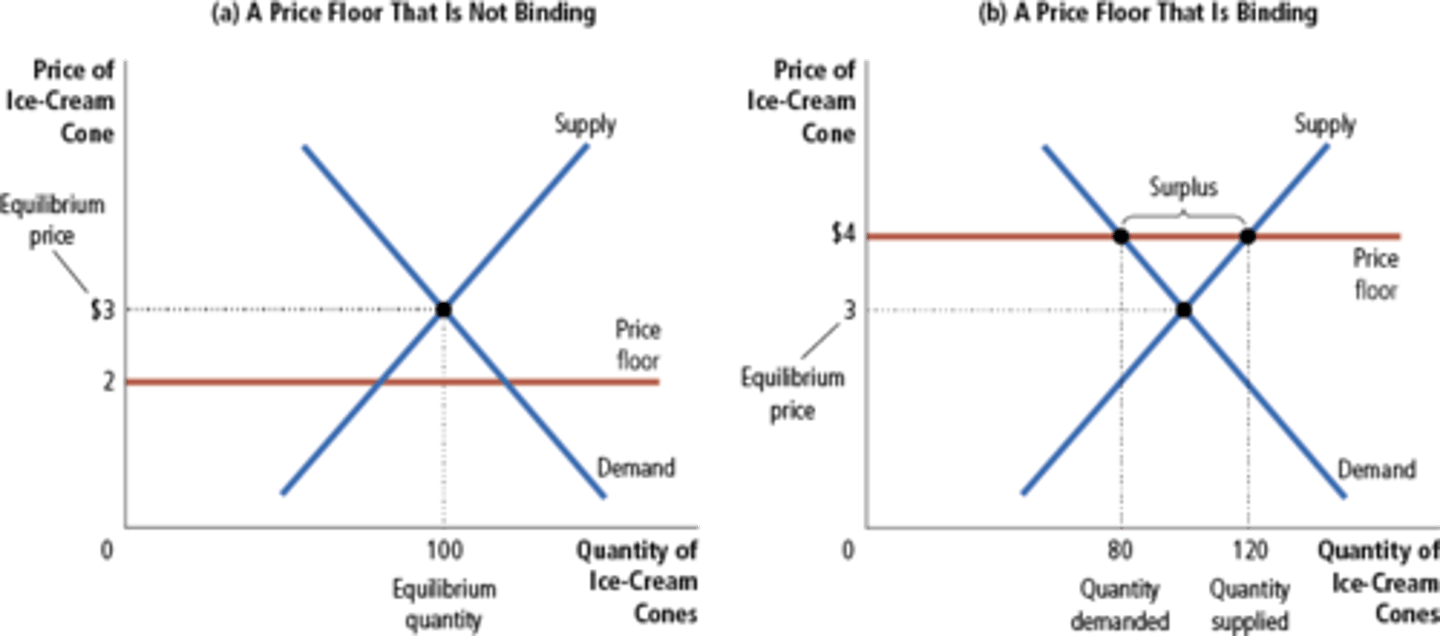
Surplus
A situation in which quantity supplied is greater than quantity demanded. Caused by price floors
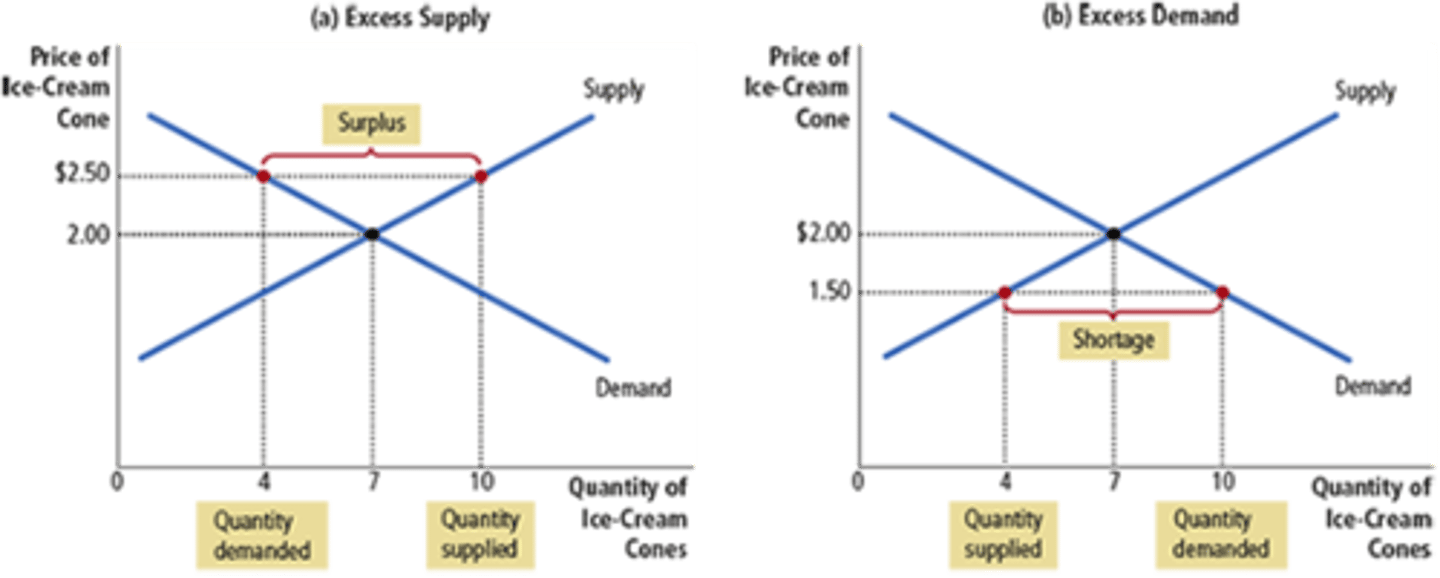
Shortage
A situation in which quantity demanded is greater than quantity supplied. Caused by price ceilings
Law of Supply and Demand
The claim that the price of any good adjusts to bring the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded for that good into balance
Increase in Demand
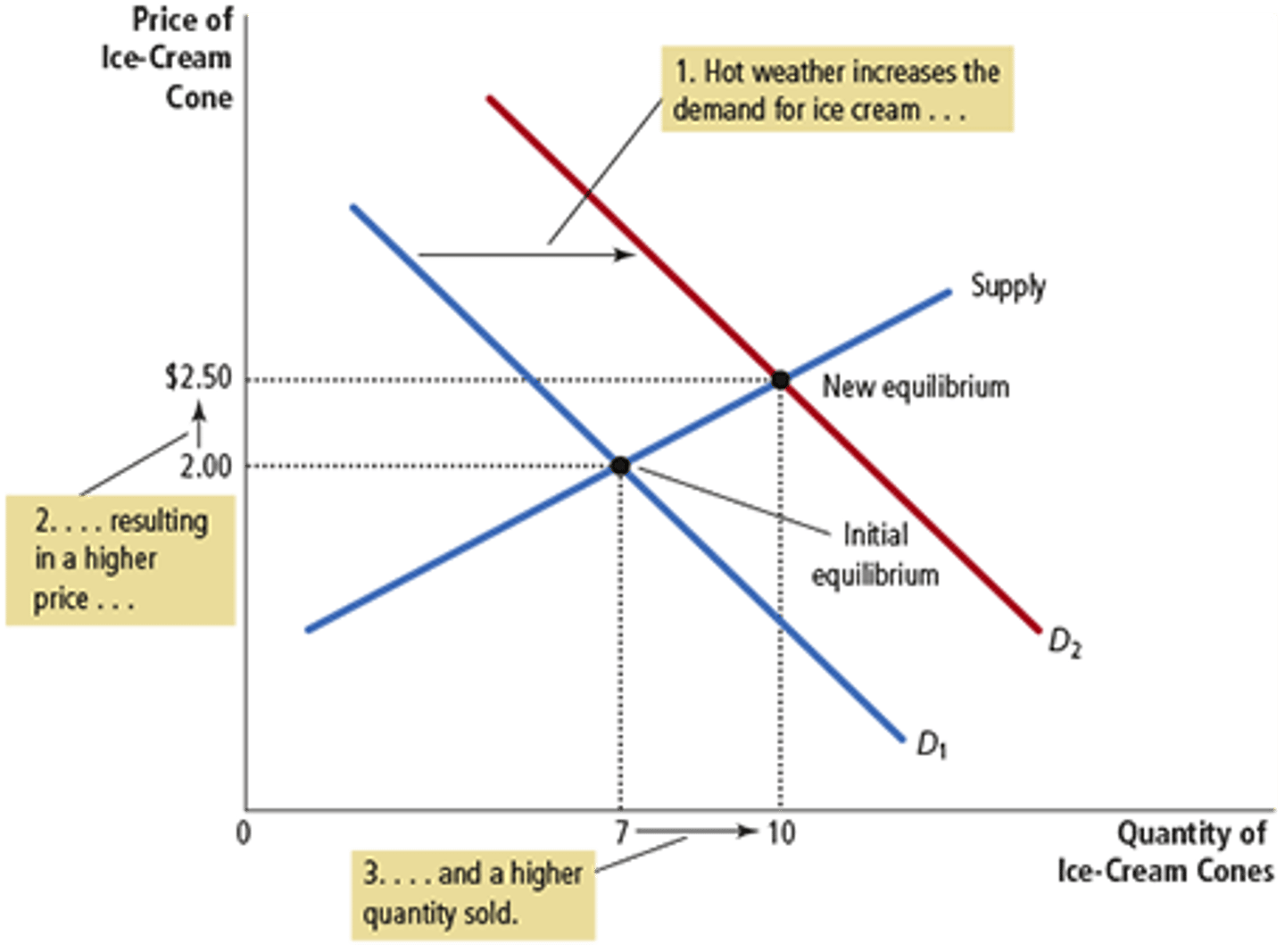
Decrease in Supply
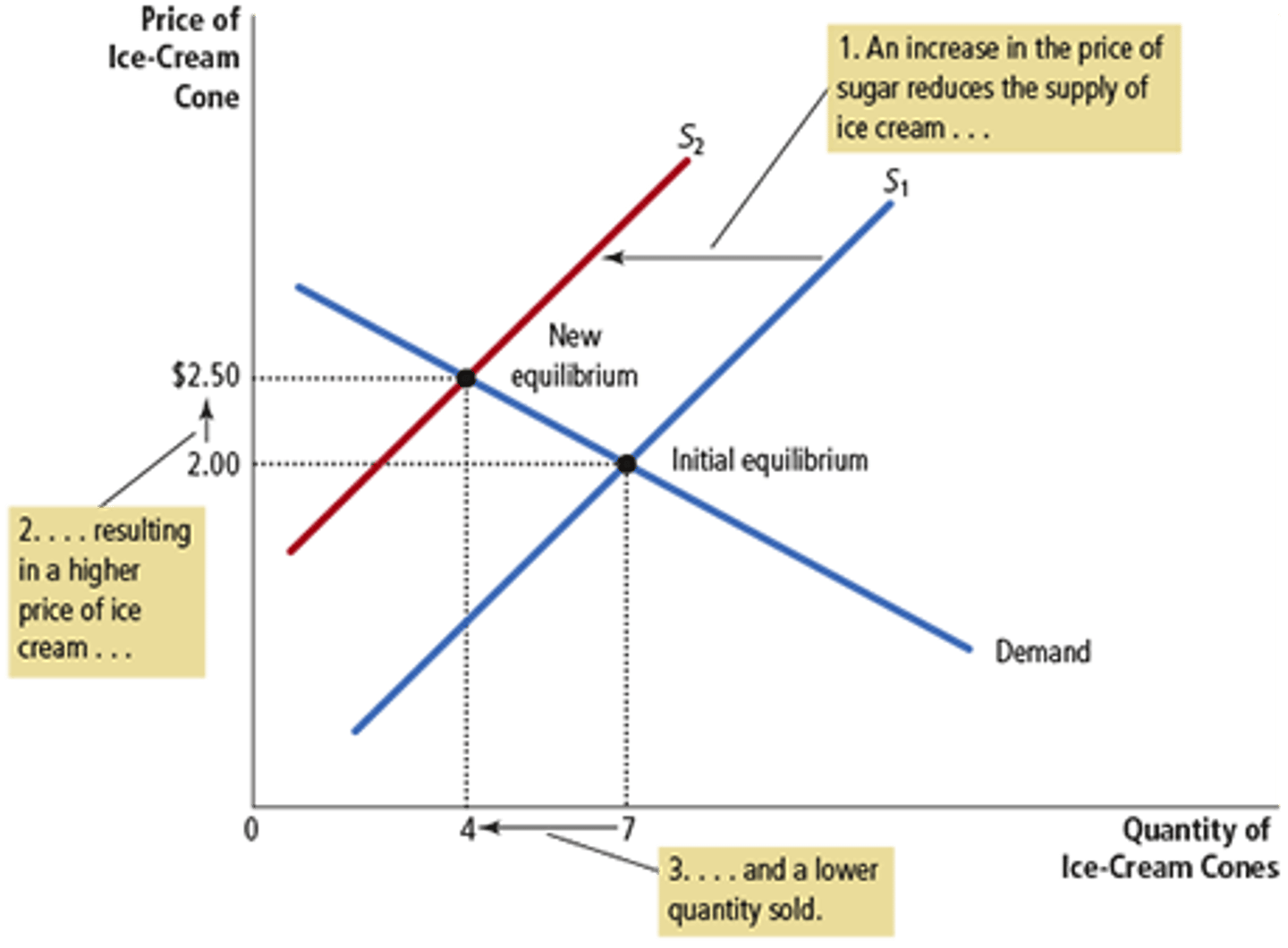
Elasticity
A measure of the responsiveness of quantity demanded or quantity supplied to a change in one of its determinants
Price Elasticity of Demand
A measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in the price of that good.
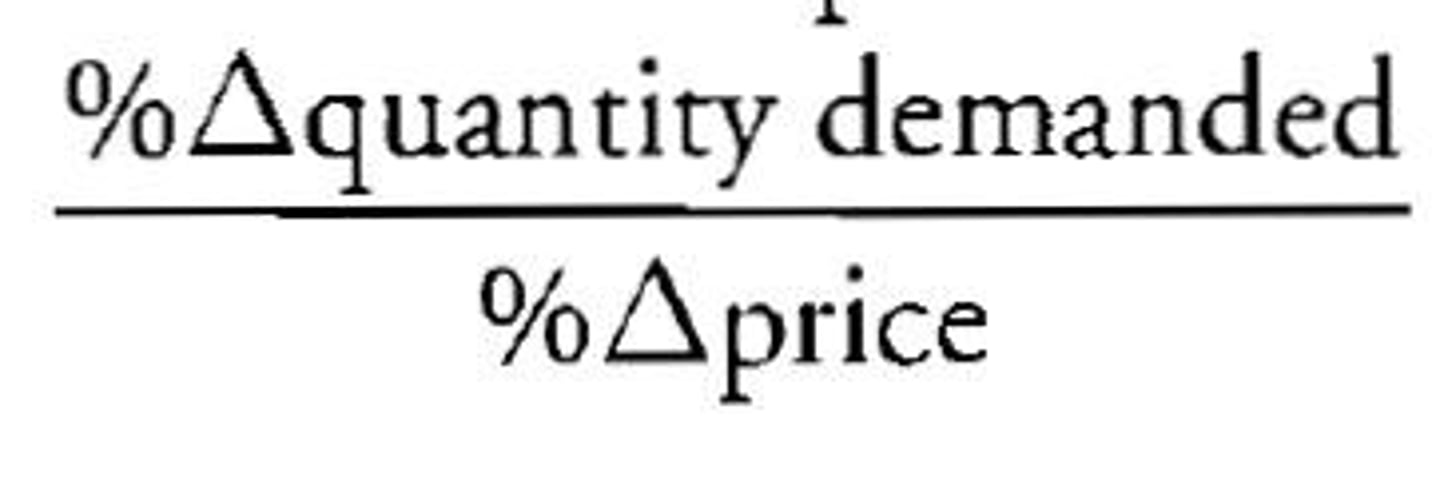
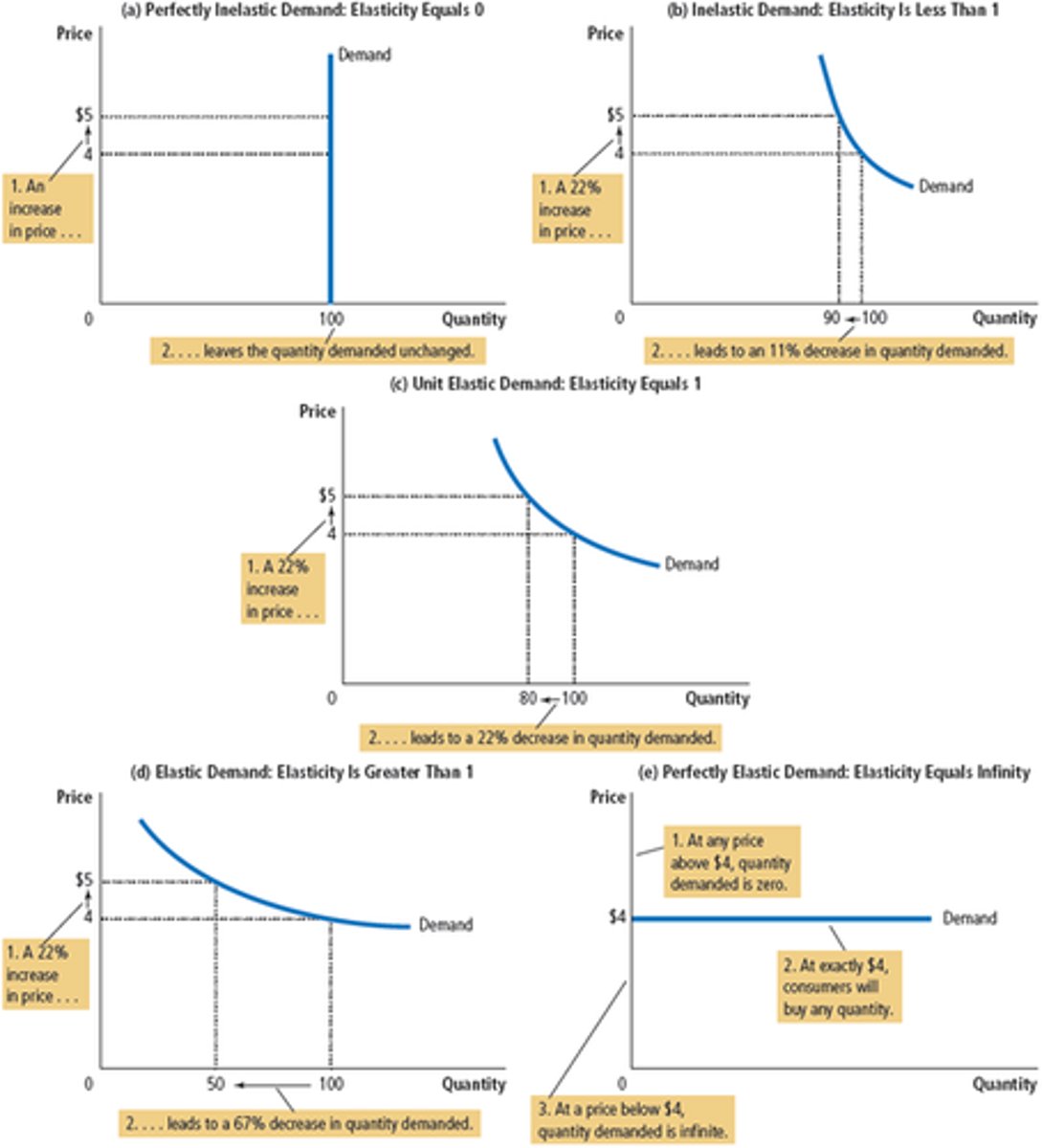
Elasticity of Demand Examples
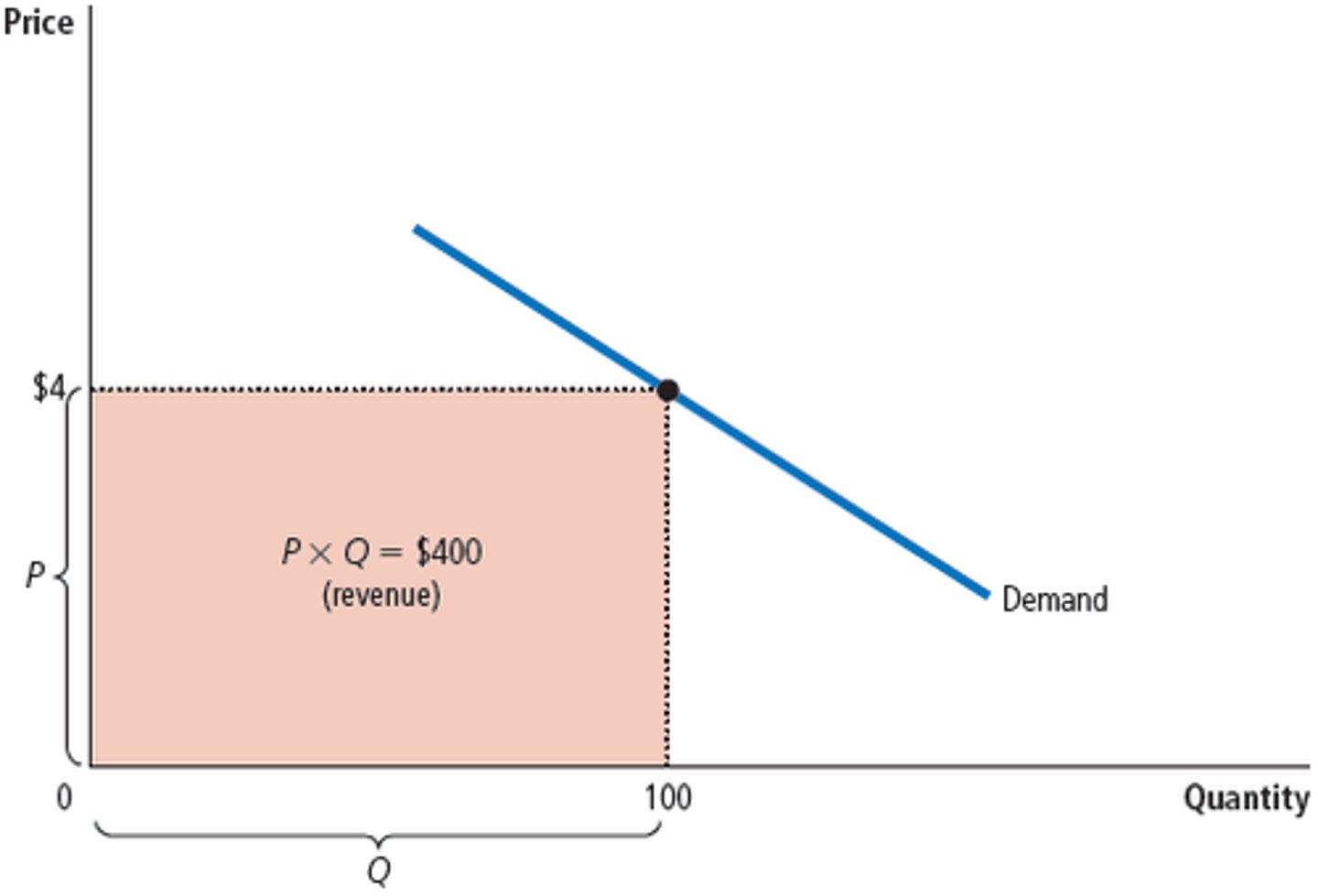
Total Revenue
The amount paid by buyers and received by sellers of a good
Income Elasticity of Demand
A measure of how much the quantity demanded of a good responds to a change in consumers' income; Positive for normal goods, Negative for inferior goods
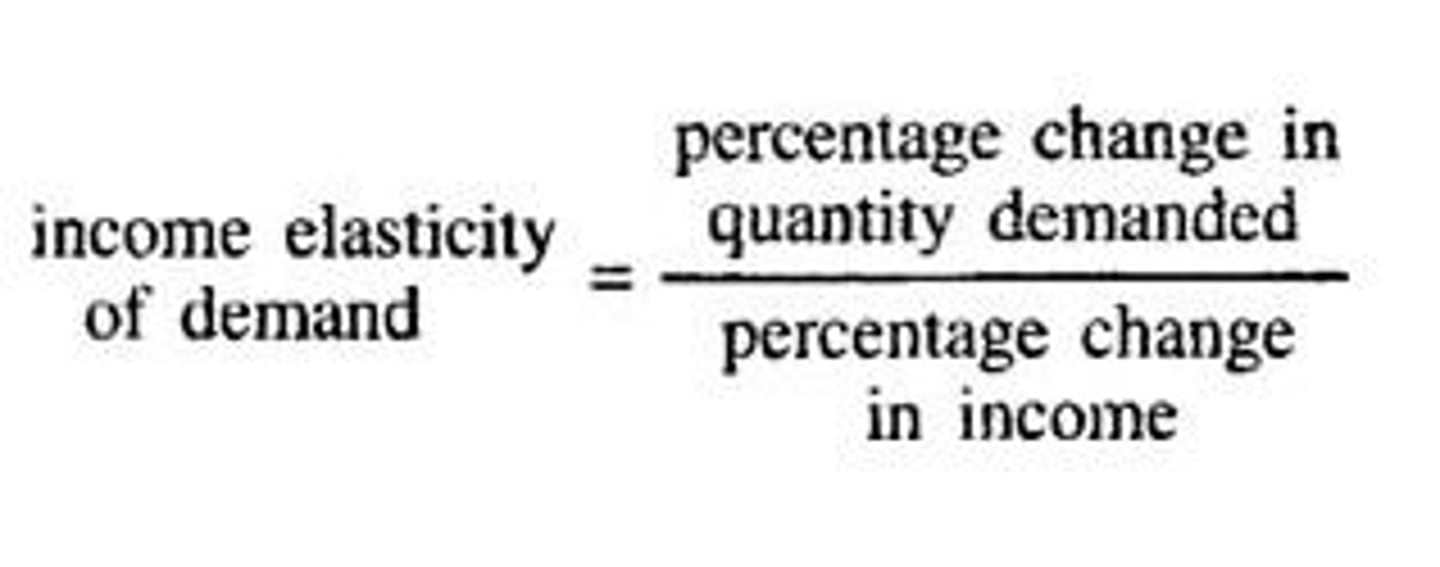
Cross Price Elasticity of Demand
A measure of how much the quantity demanded of one good responds to a change in the price of another good; Positive for substitutes, Negative for complements
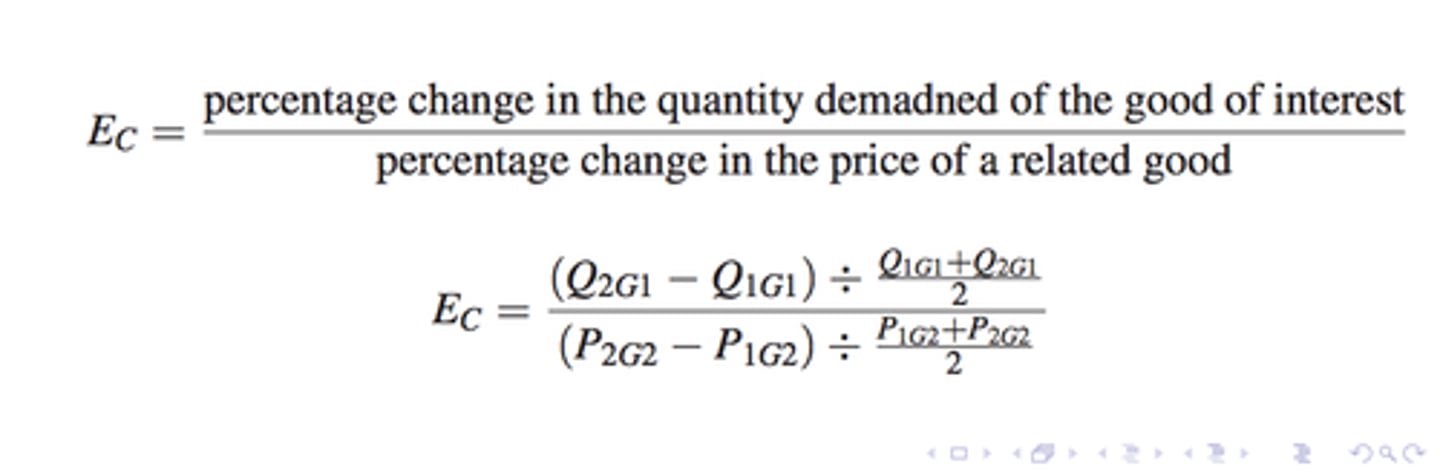
Price Elasticity of Supply
A measure of how much the quantity supplied of a good responds to a change in the price of that good
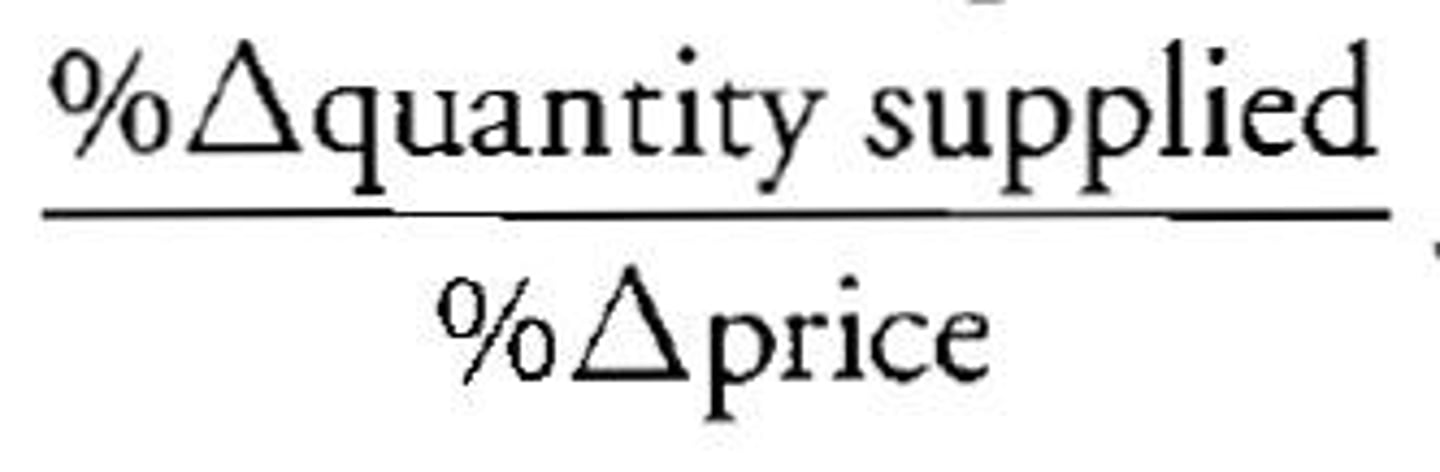
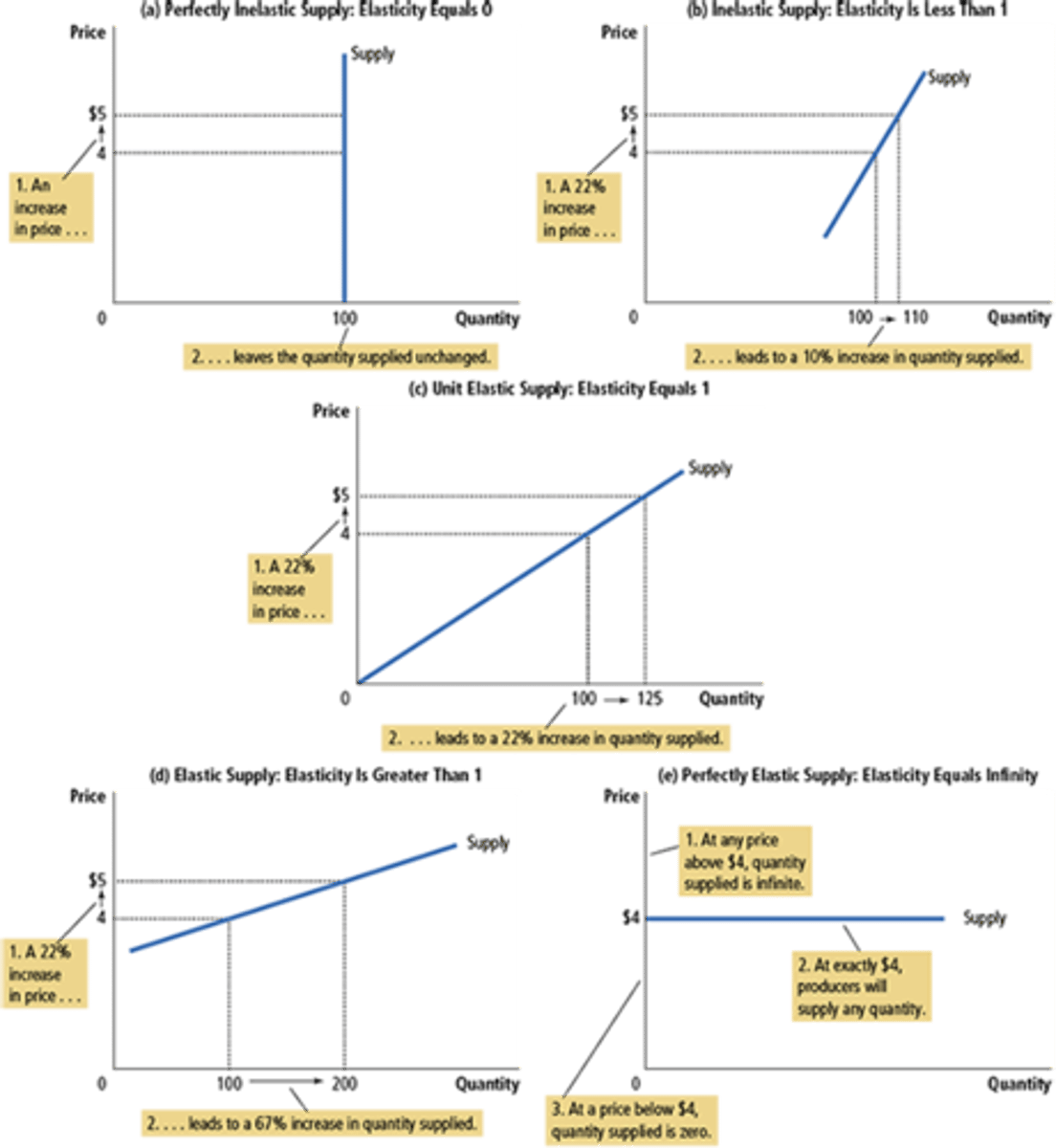
Elasticity of Supply Examples
Price Ceiling
A legal maximum on the price at which a good can be sold
Price Floor
A legal minimum on the price at which a good can be sold
Binding Price Ceiling
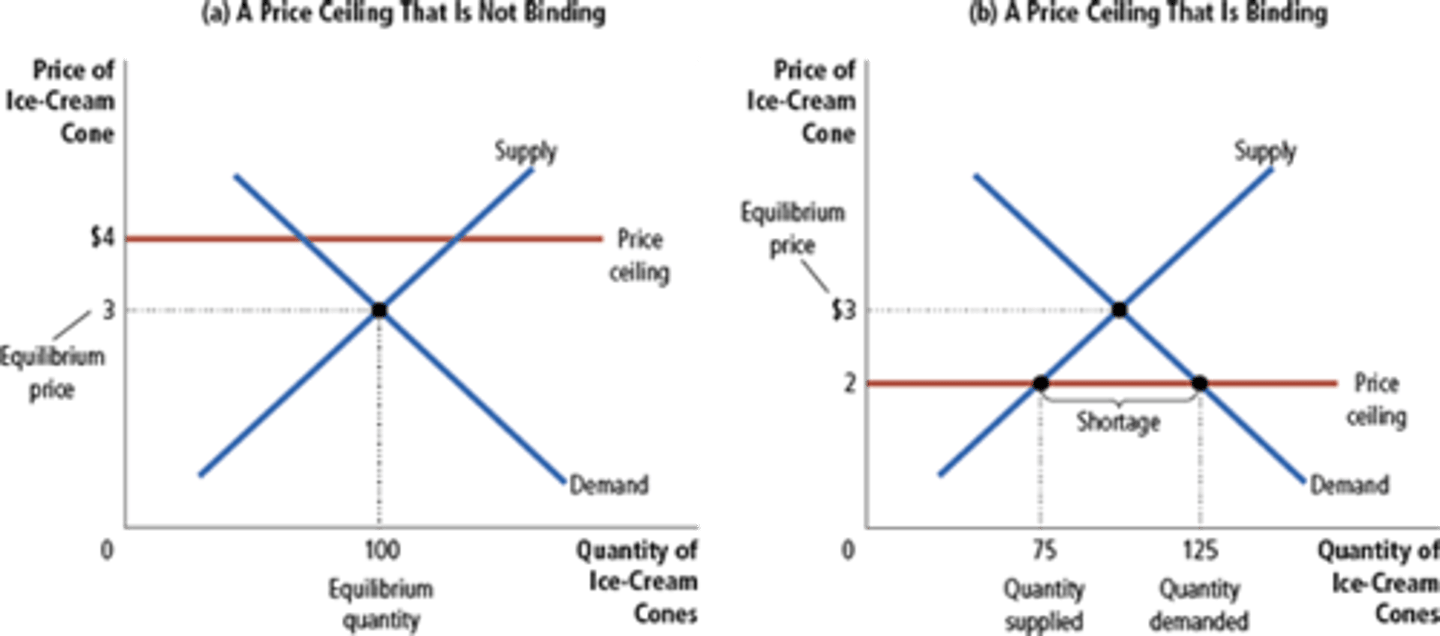
Binding Price Floor
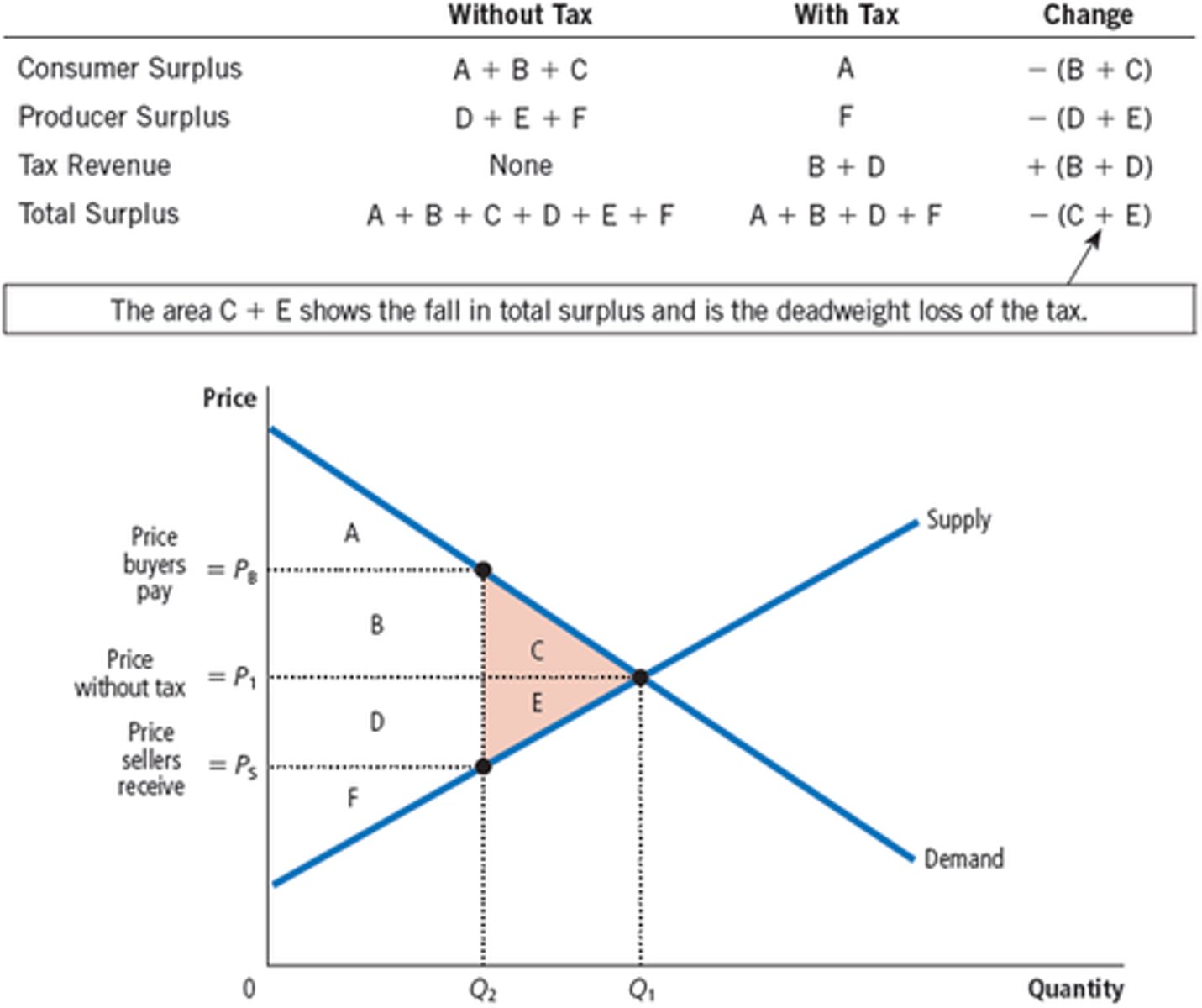
Tax Incidence
The manner in which the burden of a tax is shared among participants of a market
Tax on Sellers
Shifts the supply curve up by the amount of the tax
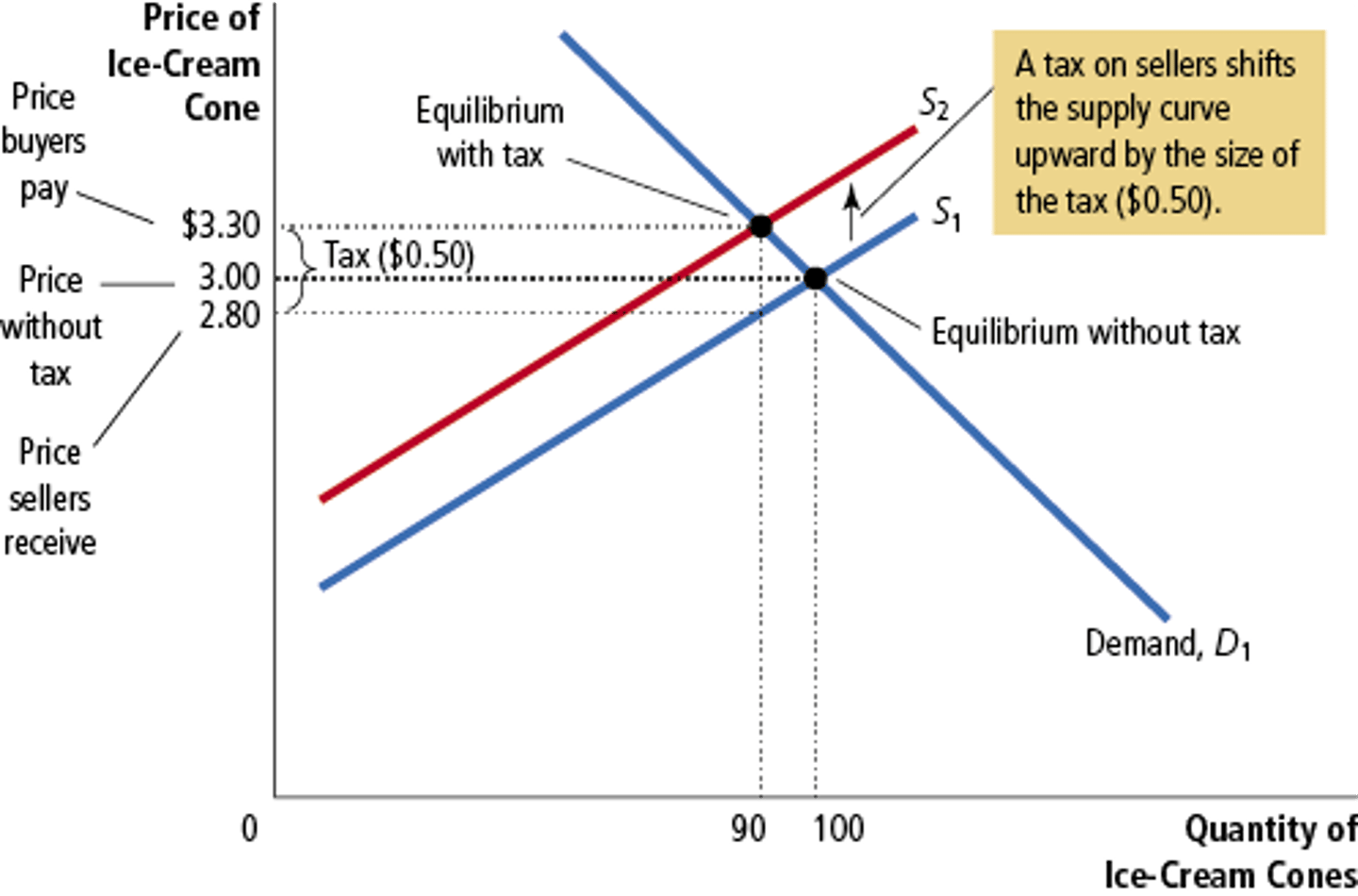
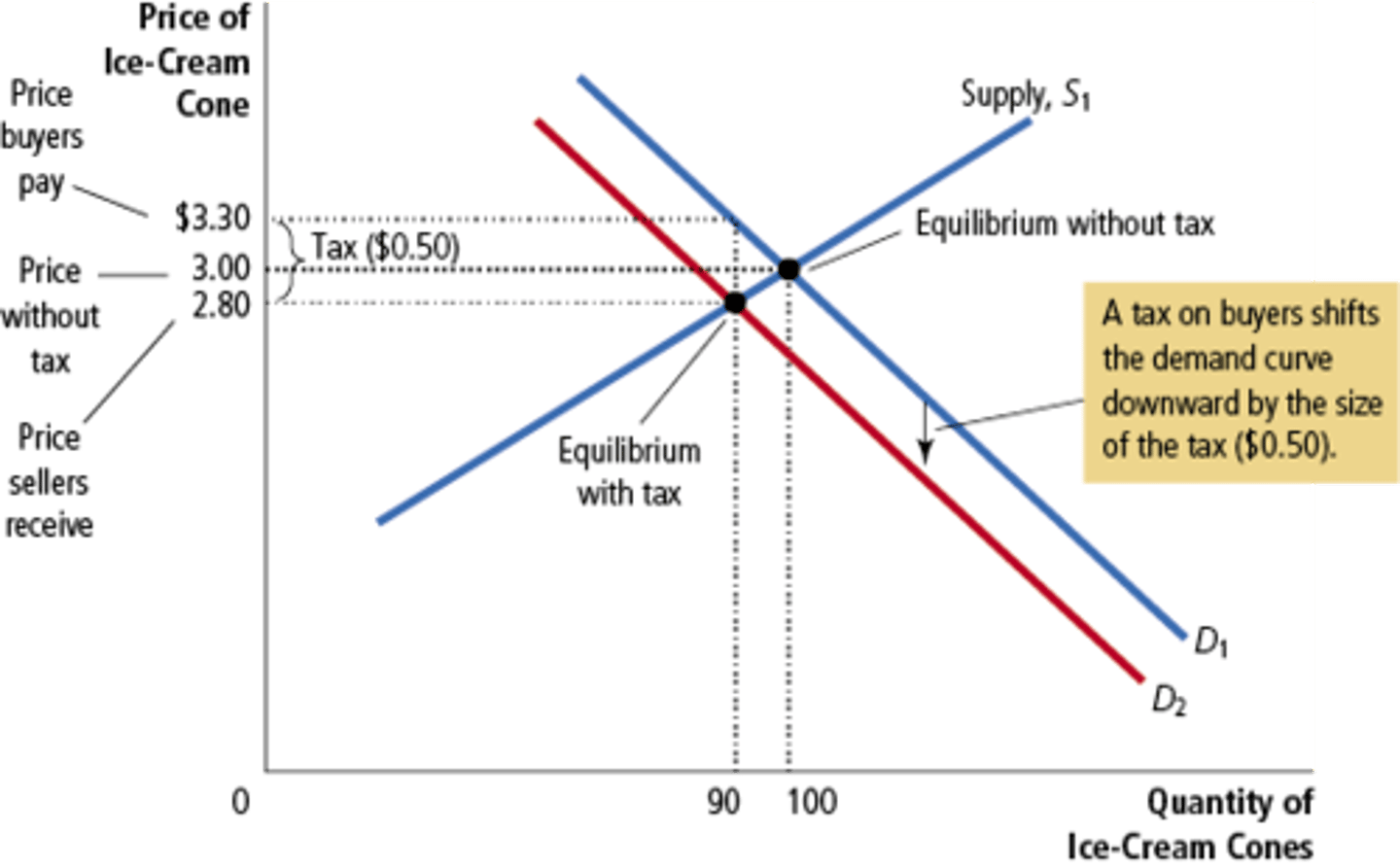
Tax on Buyers
Shifts the demand curve down by the amount of the tax
Willingness to Pay
The maximum amount that a buyer will pay for a good; measurement of how much the buyer values the good
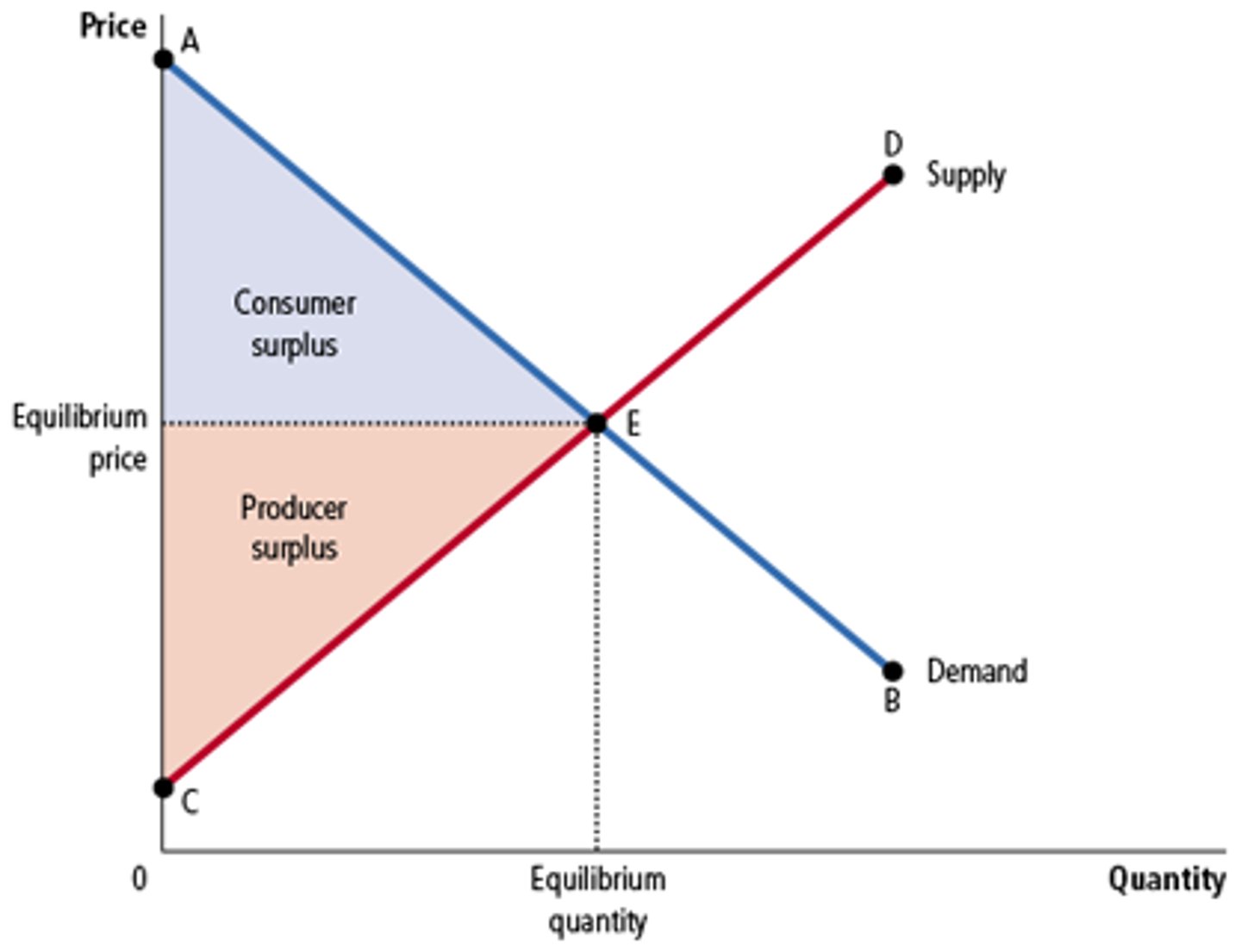
Consumer Surplus
The amount a buyer is willing to pay for a good minus the amount actually paid for it
Cost
The value of everything a seller must give up to produce a good
Producer Surplus
The amount a seller is paid for a good minus the seller's cost of providing it
Efficiency of Allocation
The property of a resource allocation of maximizing the total surplus received by all members of society
Equality
The property of distributing economic prosperity uniformly among the members of society
Consumer and Producer Surplus in the Market Equilibrium
Deadweight Loss
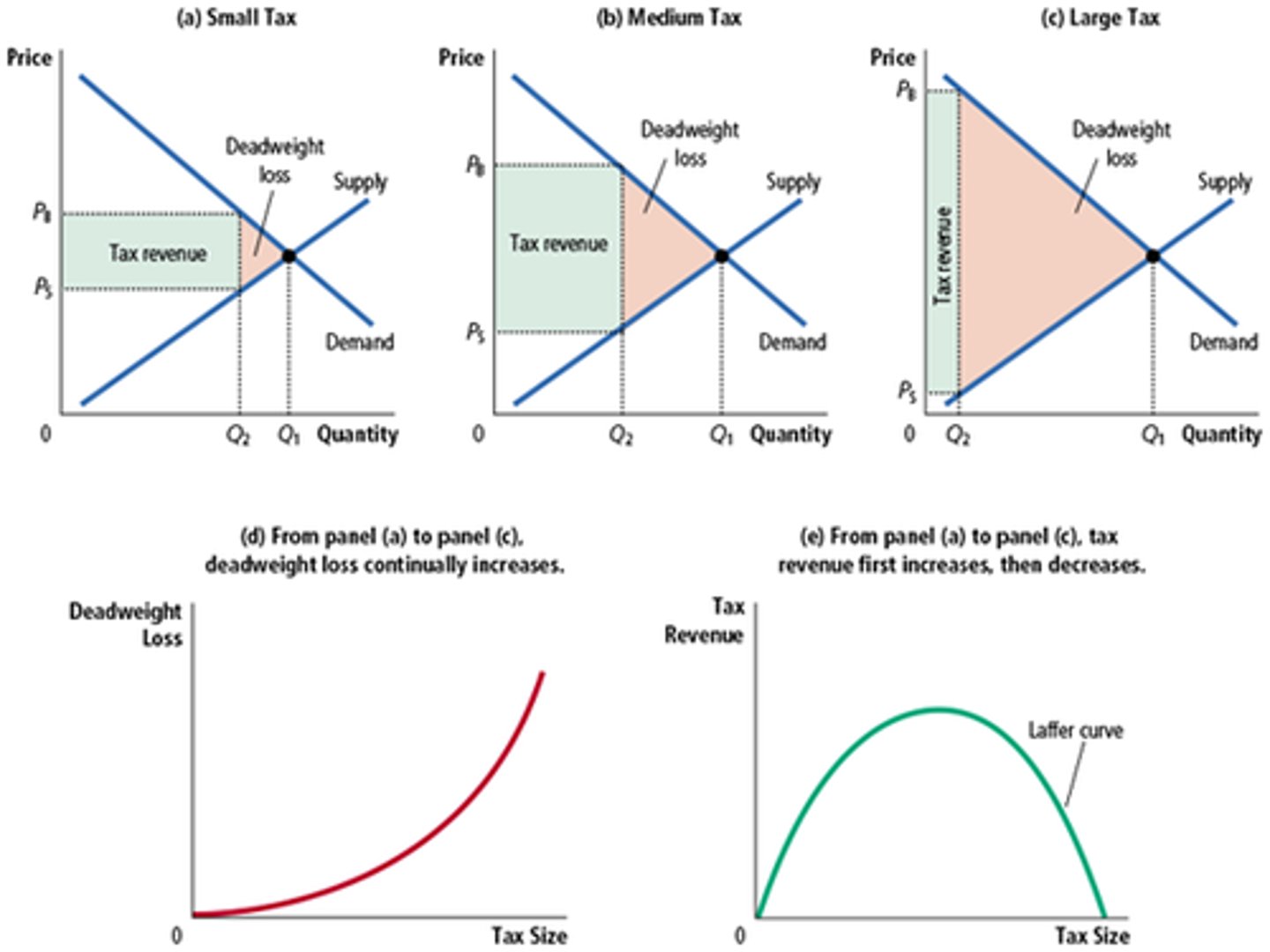
The fall in total surplus that results from a market surplus, such as a tax
Laffer Curve
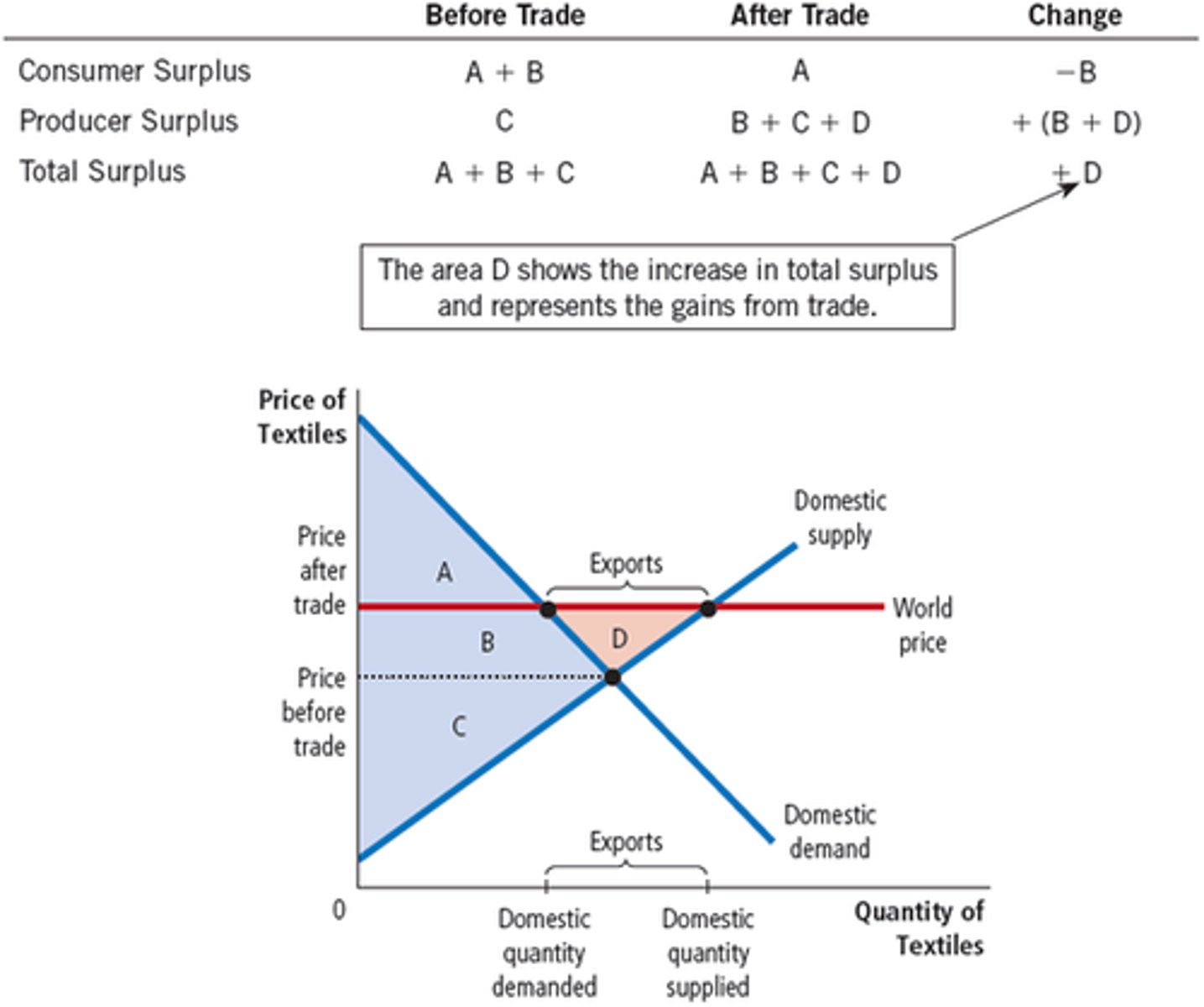
World Price
The price of a good that prevails in the world market for that good
International Trade in an Exporting Country
tariff
a tax on goods produced abroad and sold domestically
Effects of a Tariff
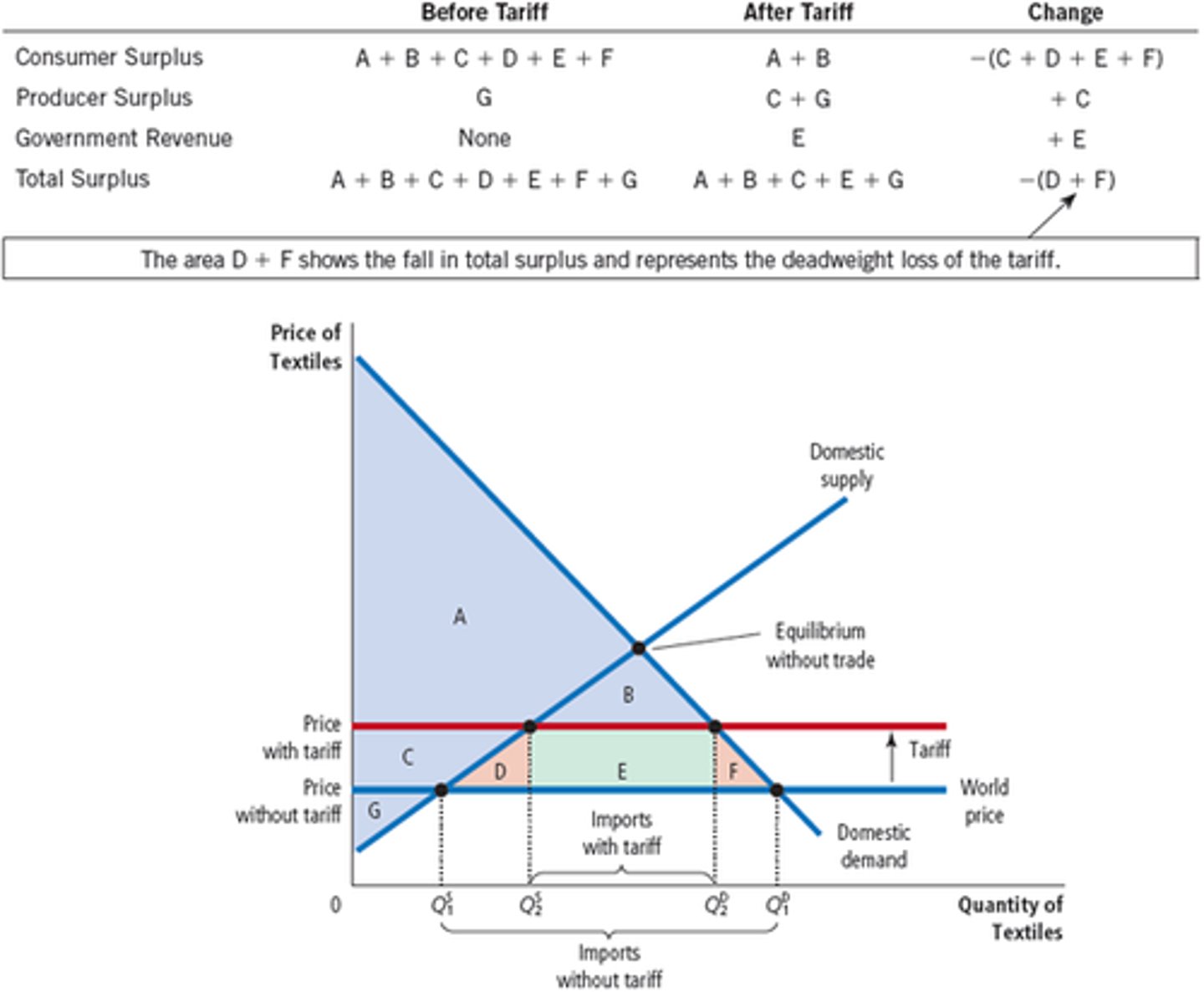
Gross Domestic Product
The market value of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given period of time. Y = C + I + G + NX
Consumption
Spending by households on goods and services, with the exception of purchases of new housing
Investment
Spending on business capital, residential capital, and inventories
Government Purchases
Spending on goods and services by local, state, and federal governments
Net Exports
Spending on domestically produced goods by foreigners (exports) minus spending on foreign goods by domestic residents (imports)
Nominal GDP
The production of goods and services valued at current prices
Real GDP
The production of goods and services valued at constant prices
Real vs. Nominal GDP
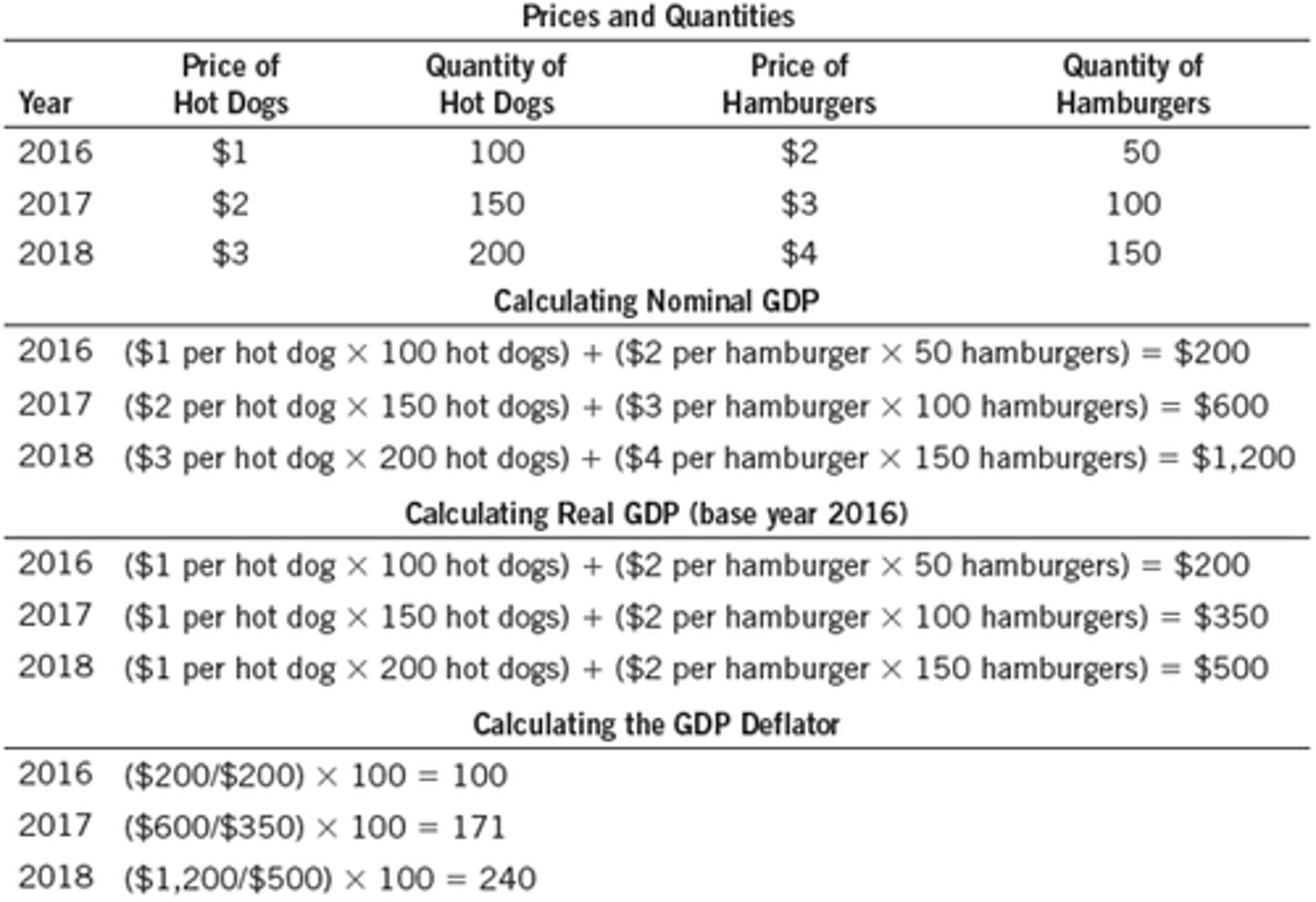
GDP Deflator
A measure of the price level calculated as the ratio of nominal GDP to real GDP times 100
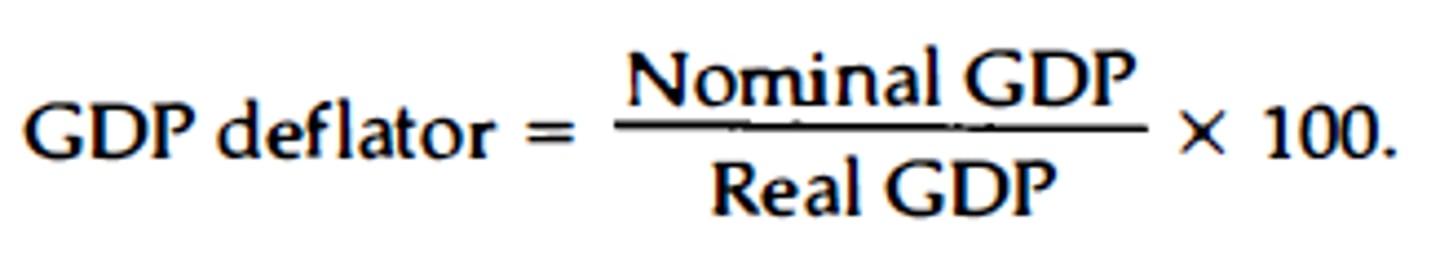
Inflation Rate
The percentage change in the price index from the preceding period
Consumer Price Index
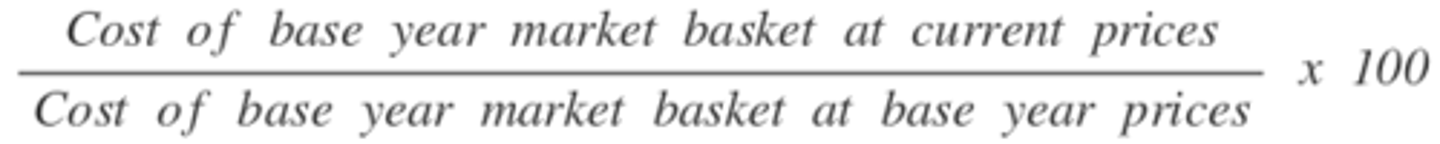
Indexing for Inflation
The automatic correction by law or contract of a dollar amount for the effects of inflation
Nominal Interest Rate
The interest rate as usually reported without a correction for the effects of inflation
Real Interest Rate
The interest rate corrected for the rates of inflation

Physical Capital
The stock of equipment and structures that are used to produce goods and services
Human Capital
the knowledge and skills that workers acquire through education, training, and experience
Natural Resources
The inputs into the production of goods and services that are provided by nature such as land, rivers, and mineral deposits
Technological Knowledge
Society's understanding of the best ways to produce goods and services