chem
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What is a chemical bond?
An interaction that holds ions or atoms together.
What is the difference between an atom and a molecule?
An atom is the smallest unit that holds the chemical properties of an element; a molecule is a group of atoms that are held together by chemical bonds.
What is the law of conservation of mass?
Mass can neither be created nor destroyed, only transformed into different substances.
What happens to the atom during chemical changes?
Atoms are rearranged by forming or breaking chemical bonds to make new substances with different properties.
How can atoms make chemical bonds?
They rearranging themselves by losing, gaining, or sharing their valence electrons.
What does an electron cloud model show about an atom?
It shows how electrons are found in a region around the nucleus and helps showing the general location of the different parts of the atom, but it does not show the number of electrons.
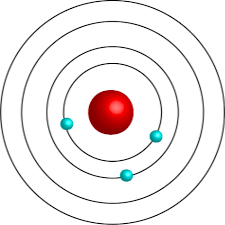
What does Bohr’s model show about an atom?
It shows the number of electrons in an atom by representing the energy levels in an atom that rings surround the nucleus, each ring has the number of electrons the atom contains.
What does the space-filling model show about an atom?
It shows the atoms represented as solid spheres that are connected to each other, this model shows the inner parts that make up an atom, it only shows how many atoms there are in a substance.
What are valence electrons?
Electrons that are found in the outermost energy level of an atom.
How many atoms can get filled in the 1st energy level?
2 electrons
How many atoms can get filled in the 2nd energy level?
8 electrons
What happens if there are more than 8 electrons in the 2nd energy level?
A 3rd energy level can be started, and get filled with the remaining electrons.
How many valence electrons are in Group 1 of the periodic table?
1 valence electron
How many valence electrons are in Group 2 of the periodic table?
2 valence electrons
How many valence electrons are in Group 13 of the periodic table?
3 valence electrons
How many valence electrons are in Group 14 of the periodic table?
4 valence electrons
How many valence electrons are in Group 15 of the periodic table?
5 valence electrons
How many valence electrons are in Group 16 of the periodic table?
6 valence electrons
How many valence electrons are in Group 17 of the periodic table?
7 valence electrons
How many valence electrons are in Group 18 of the periodic table?
8 valence electrons
Why do atoms form bonds?
So they can fill their outermost energy level when it’s not full
What is an ion?
A charged particle that forms when an atom loses or gains an electron.
What is a positive ion (cation)?
An ion that forms when it gains an electron
What is a negative ion (anion)?
An ion that forms when it loses an electron
What type of ions are formed by metals?
Lose their electrons easily, so they form positive ions
What type of ions are formed by nonmetals?
Gain their electrons easily, so they form negative ions
Bohr’s model
Electron cloud model
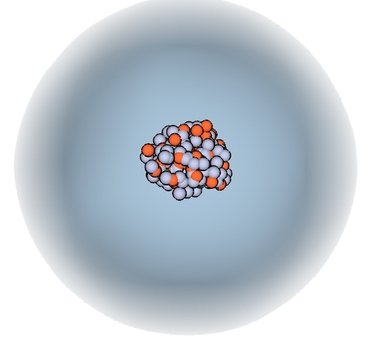
Space-filling model
How did Dmitri Mendeleev arrange the periodic table?
According to increasing atomic mass
How did Henry Moseley arrange the periodic table?
According to increasing atomic number
What is atomic number?
The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus
What is atomic mass?
The number of protons + neutrons combined
What does the zigzag line in the periodic table separate?
It separates the metals from nonmetals
Why do elements of the same group have similar properties?
Because they have the same number of valence electrons
Why are valence electrons able to form chemical bonds?
Because they are far from the attractive force of the nucleus
Chemical symbol
The two or three-letter symbols on the periodic table
Chemical name
The element’s name
Why are the elements from group 1 considered to be very reactive?
Because they only have 1 valence electron
Why are the elements from Group 18 considered to be unreactive?
Because they have 8 valence electrons
Which side of the periodic table is denser: left or right?
The left side is less dense, the right side is more dense