IB Biology Organelles and compartmentalisation
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
What is compartmentalisation?
formation of compartments within the cell by membrane bound organelles
Why are centrifuges important in biology?
They isolate individual organelles which allows us to learn more about cell structure and functions within cells
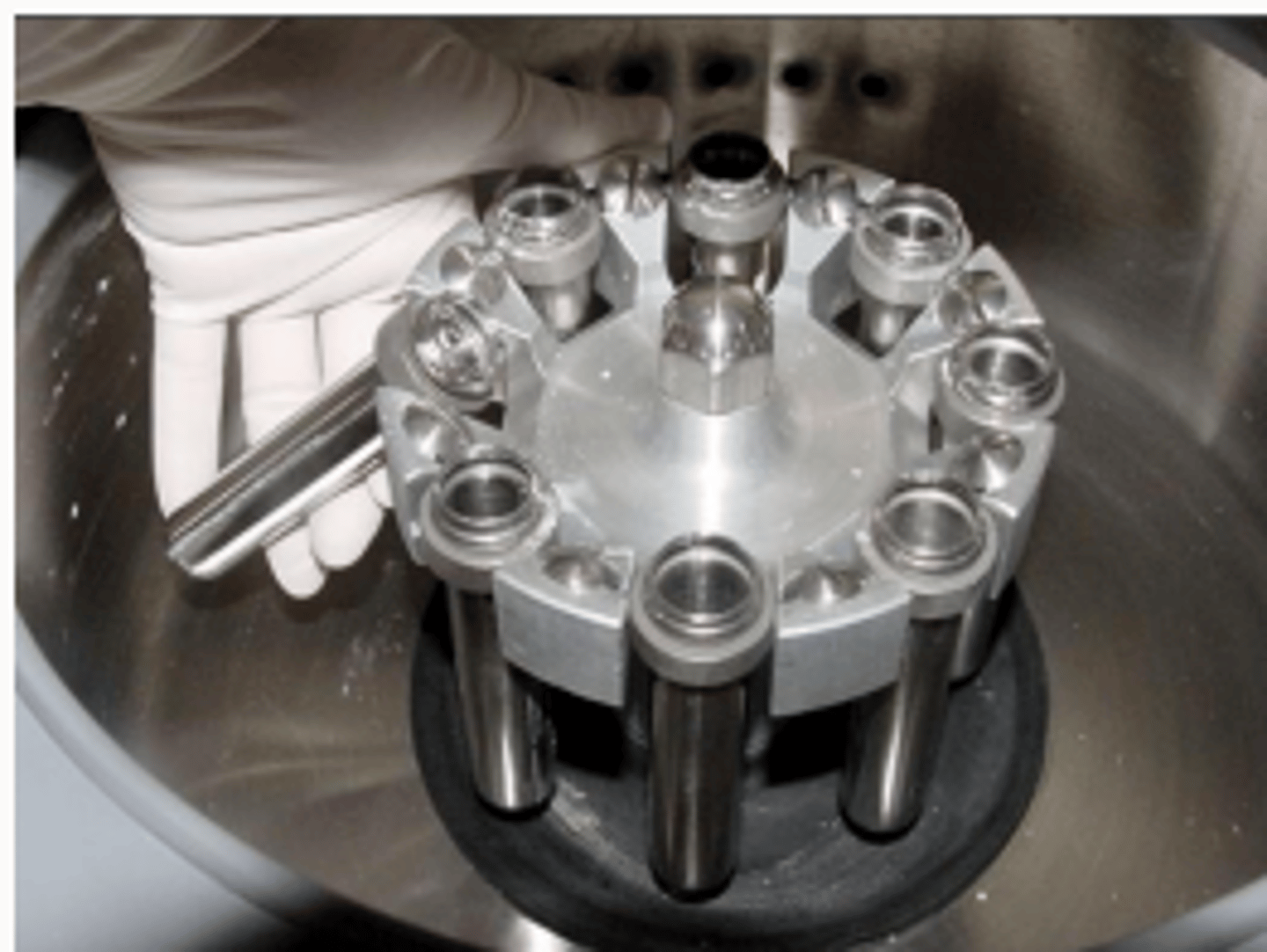
What are the advantages of cell compartmentalisation?
Toxic and damaging substances can be isolated. Within membrane bound organelles, conditions can become optimal. The number and location of organelles can be changes.
Why is it an advantage for eukaryotes to have a nucleus?
DNA can be protected from damage and it allows for the post transcriptional modification of proteins
Why is the nucleus' double membrane an advantage?
It has pores that enable mRNA and proteins synthesised by the nucleus to be exported to the cytoplasm. Secondly, it can break into vesicles that trap chromosomes to make new cells during mitosis and meiosis
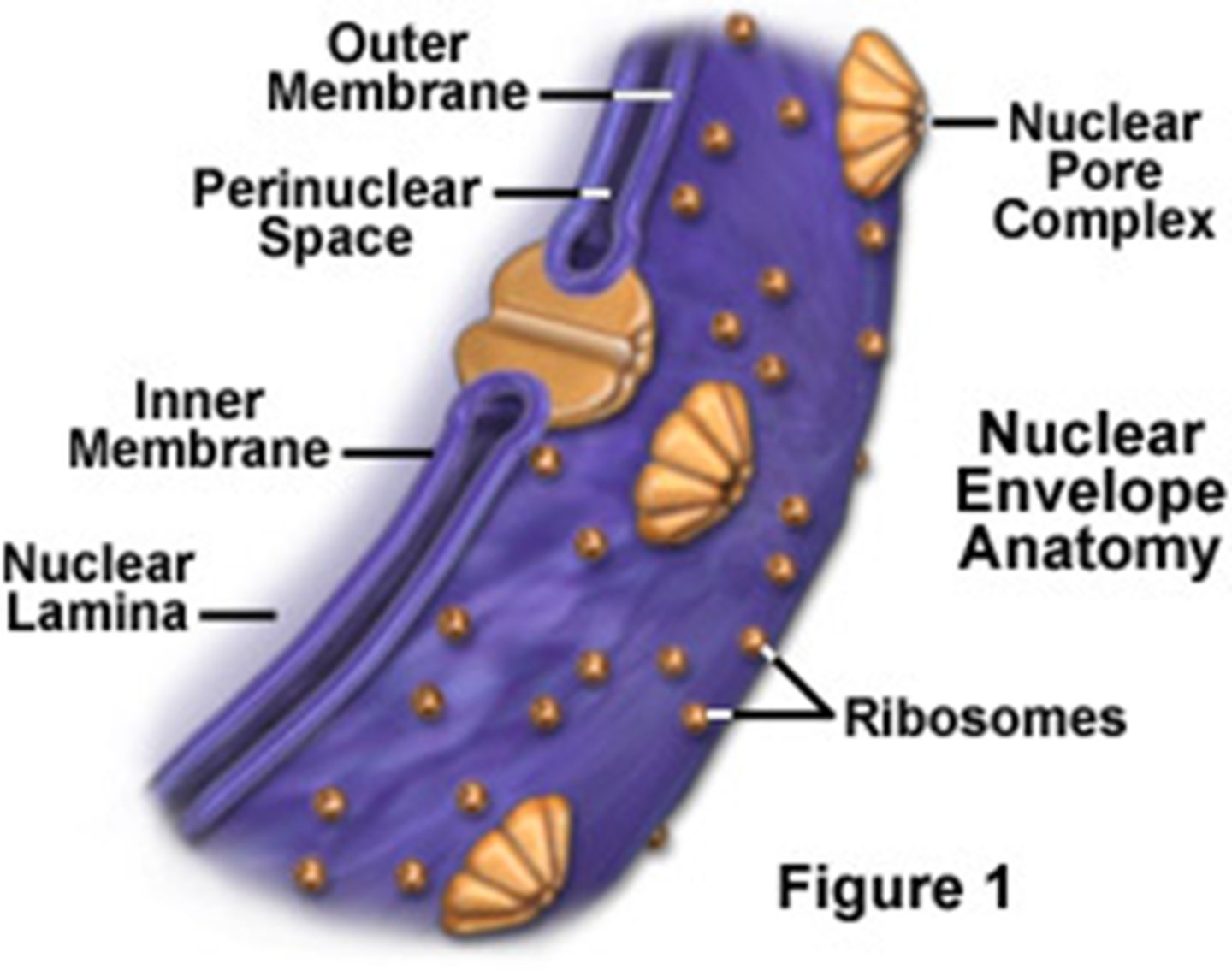
Why is it an advantage for prokaryotes to have a nucleoid region?
As there's no membrane, transcription and translation can happen faster. Secondly, functions can be more integrated
How does the RER send proteins out of the cell?
its membrane forms vesicles that trap the proteins and send them to the Golgi
Describe the processing sequential of polypeptides that occurs at the Golgi?
Start at the cis side of the Golgi (close to the RER) then it moves to the trans side, closest to the plasma membrane
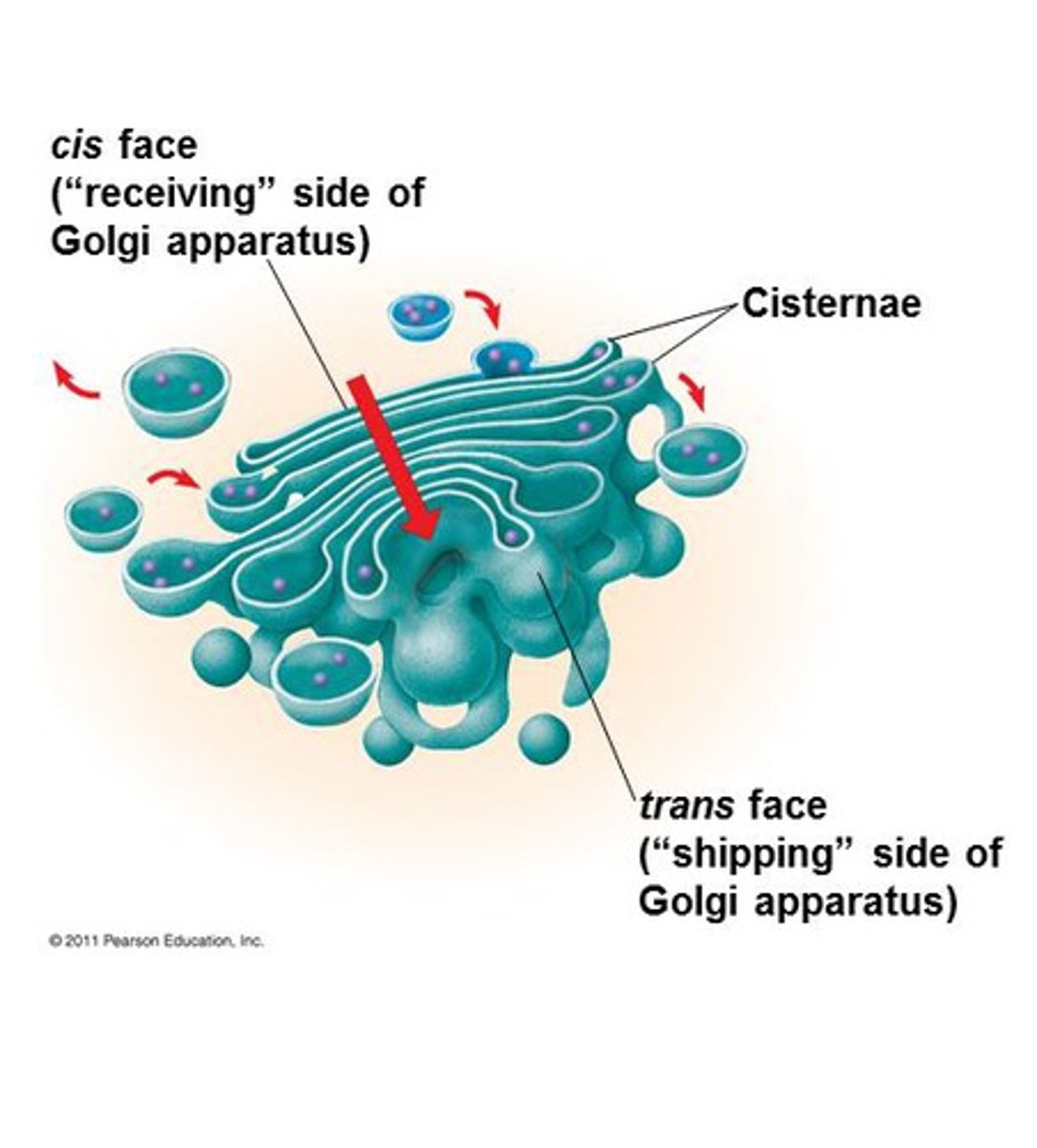
In what ways does the golgi modify proteins within its medial compartment?
- Adding prosthetic group, adding a carbohydrate, adding a phosphate or sulphate group, forming their quaternary structure
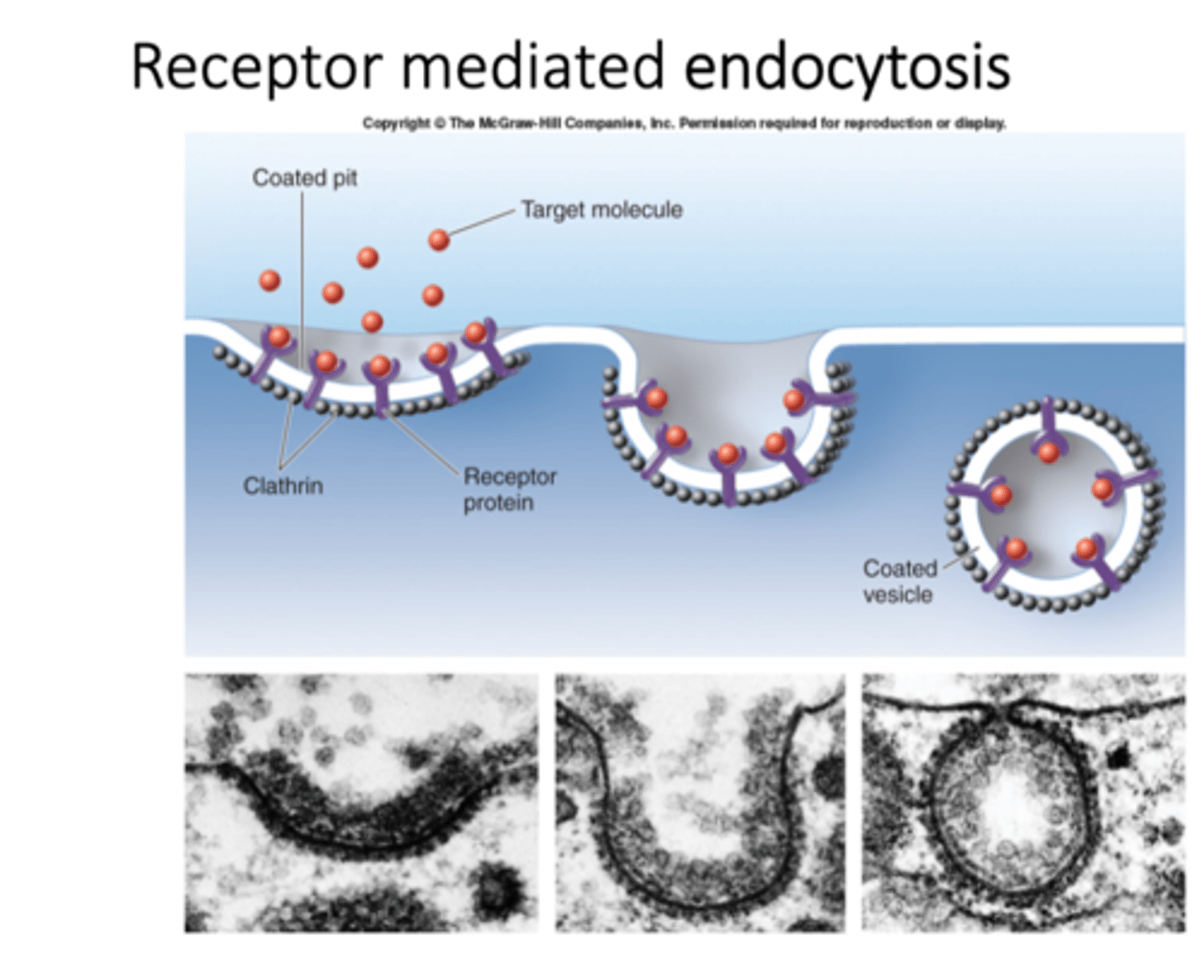
How do vesicles form for endocytosis?
An invagination of the membrane is formed. It fills with the necessary molecules. Then, this small region of membrane is pinched off into the cell and surrounded by clathrin proteins. This coating breaks down once the vesicle has reached its destination.
What is the role of the mitochondria's outer membrane?
separates its contents from the rest of the mitochondria so that ideal conditions for aerobic respiration can be achieved
Why is the matrix needed in the mitochondria?
it contains all the enzymes and substrates needed for the Krebs cycle
What is the benefit of cristae in the mitochondria?
increases the surface area and has proteins needed for the ETC embedded in it
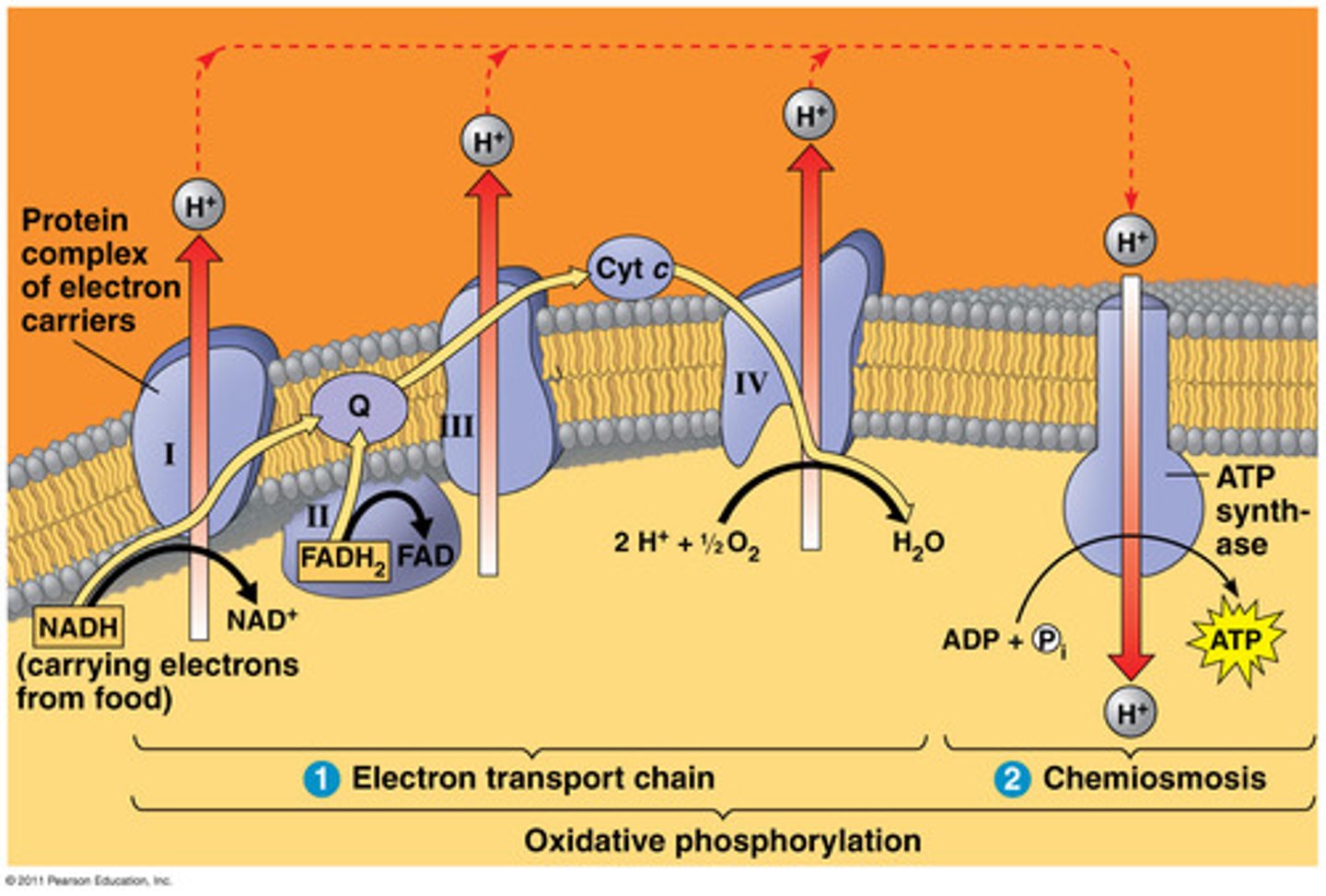
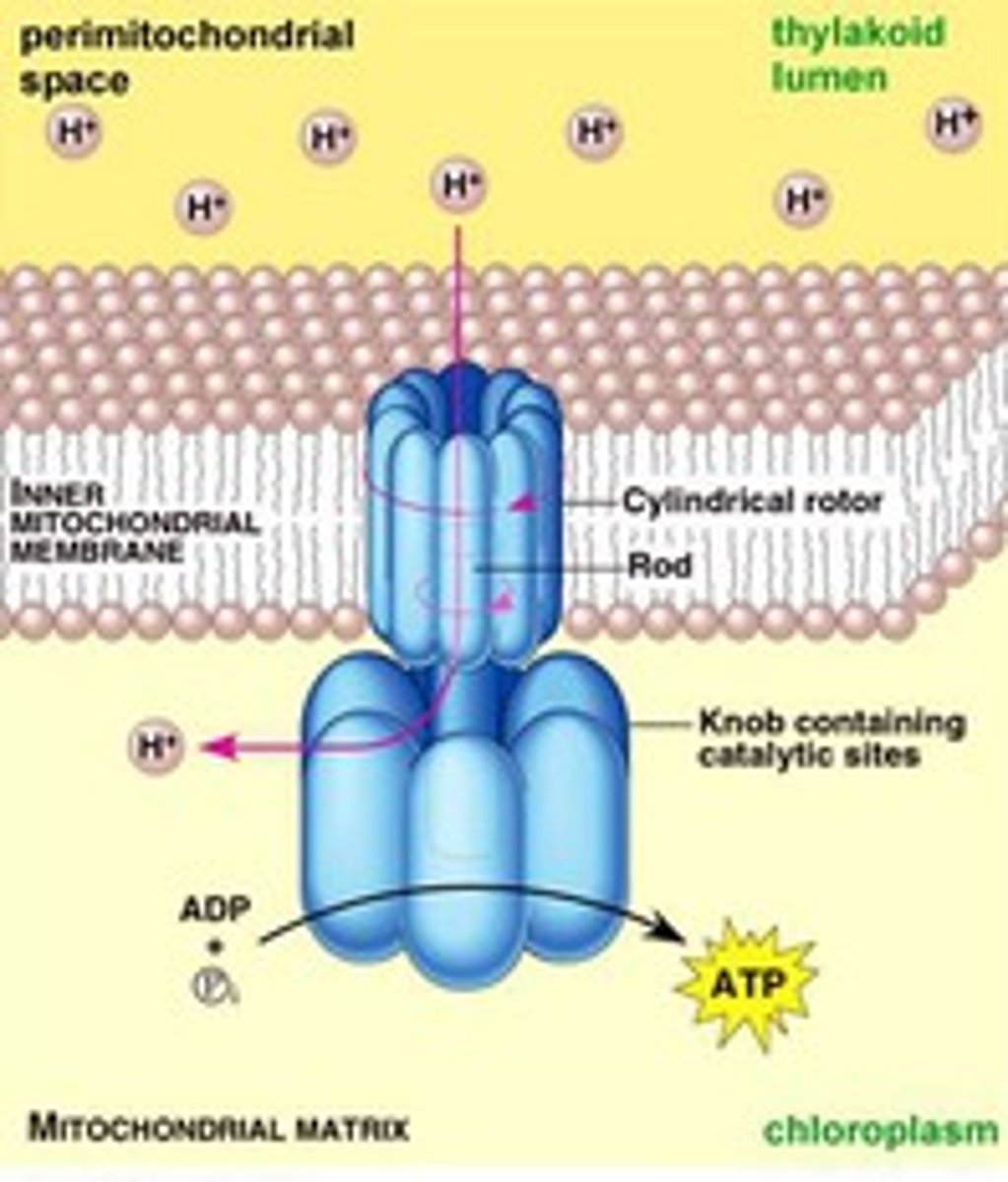
What is the benefit of the intermembrane space in the mitochondria and chloroplasts?
it's a small area so the concentration of H+ ions builds up rapidly and creates a concentration gradient needed to generate ATP
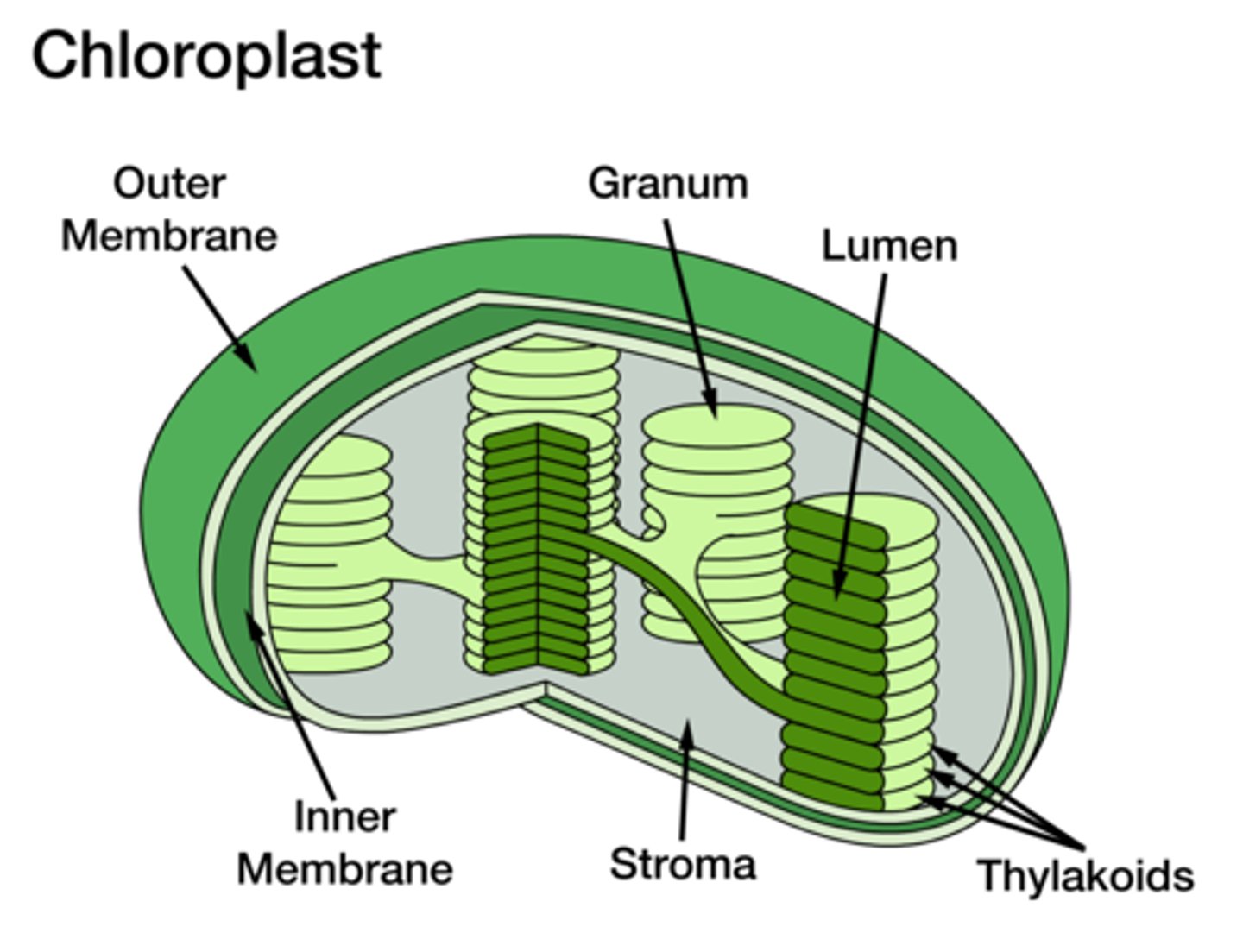
What is the stroma in chloroplasts?
it's a colourless fluid that contains the enzymes, ribosomes and DNA needed for the Calvin cycle
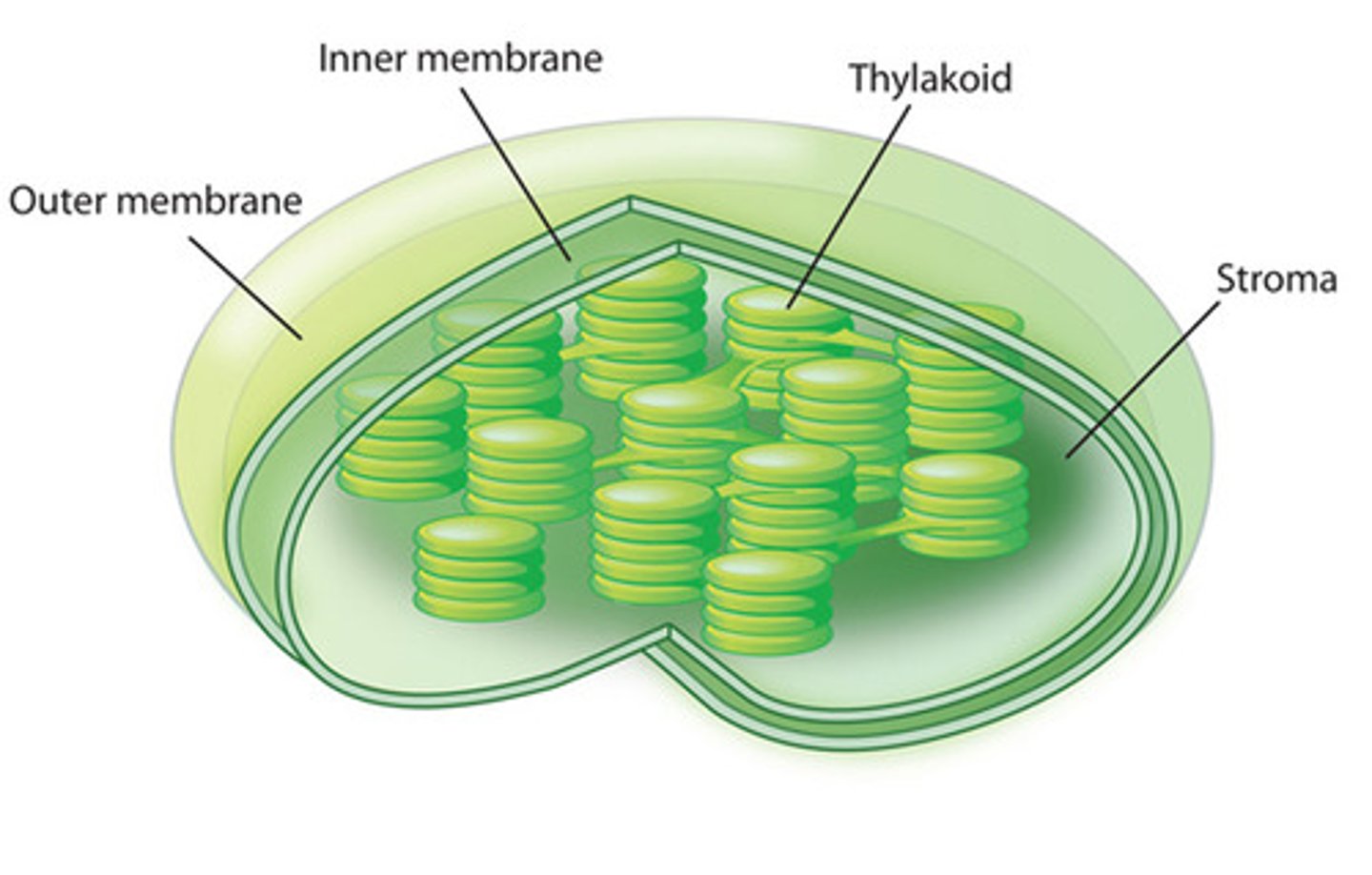
What are the advantages of the granum (stacks of thylakoids)?
They have a large surface area which allows more light energy to be absorbed for photosynthesis
Why are starch grains and lipid droplets sometimes seen in chloroplasts?
Because they've been synthesising rapidly and those are stores of glucose
What is the chloroplast envelope?
A double plasma membrane that surrounds the organelle