Module 2: Stress, Adrenergics, Cholinergics, and Urology
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
What is the General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS)?
A model describing the body's response to stress, which includes three stages: alarm, resistance, and exhaustion.
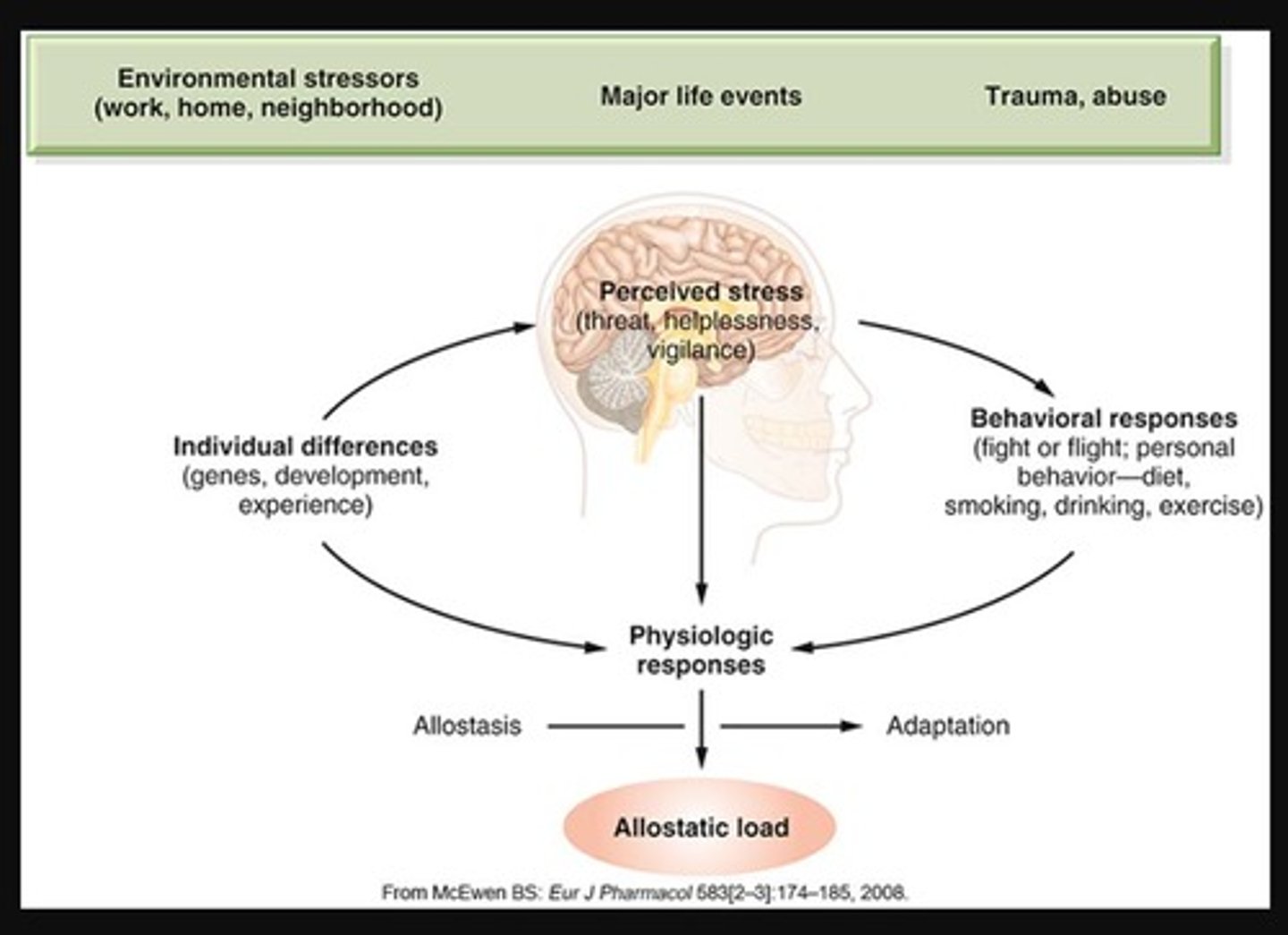
Describe the Alarm Stage
•Secretion of hormones and catecholamines to prepare for emergency reaction
Describe the Resistance stage
•Mobilization of body's resources to handle sustained challenge
Describe the exhaustion stage
•Overactivation of adaptive systems
•Leads to stress-related disorders
•Highly individualized
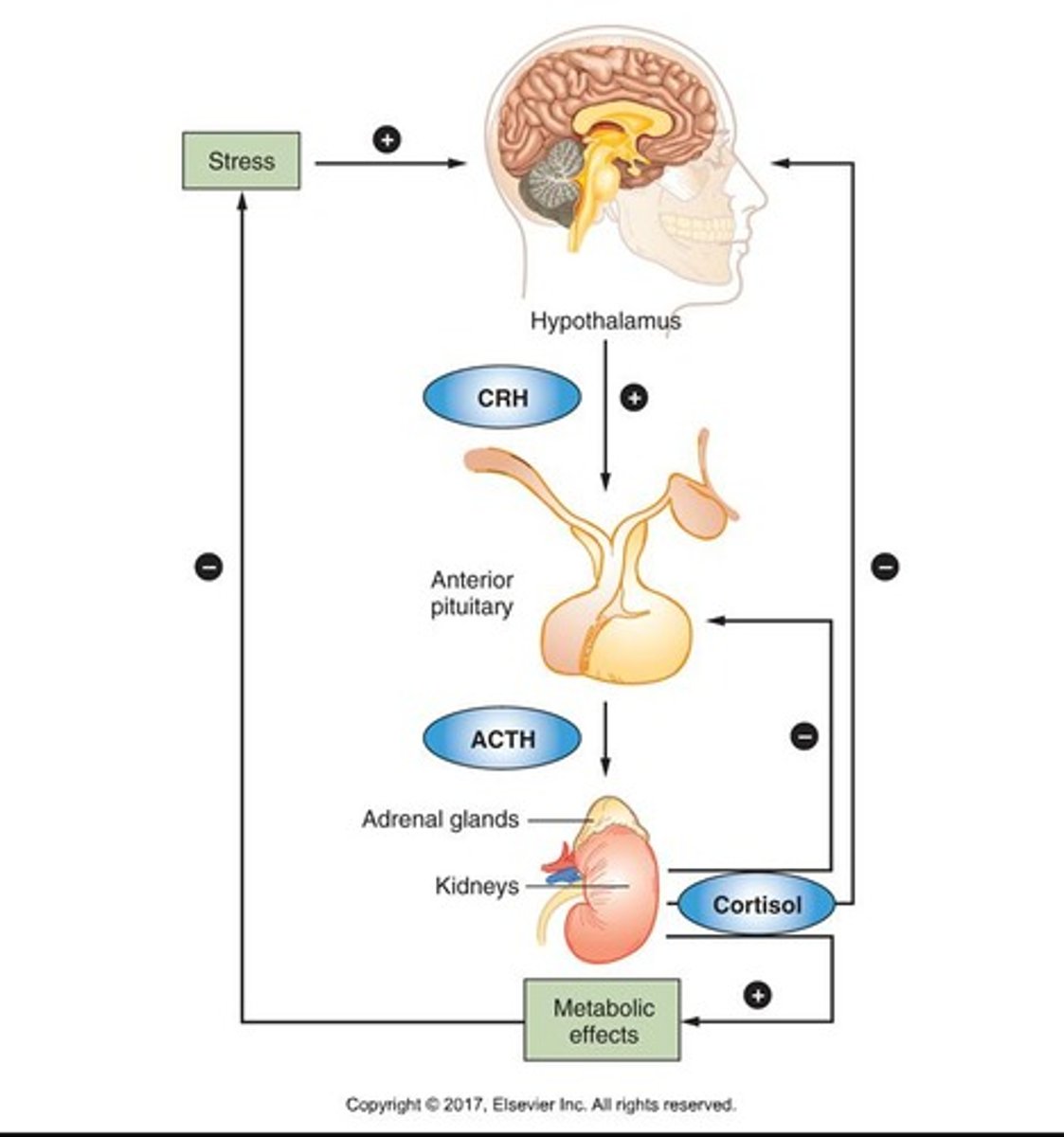
Stress response is regulated by the
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal (HPA) Axis
The Hypothalamus is
the control center for hormones including (corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH))
What hormone is primarily associated with stress responses?
Cortisol, which has widespread effects on the body during extended periods of stress.
What are the primary neurotransmitters involved in the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)?
Norepinephrine and acetylcholine.
Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction in both the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous system
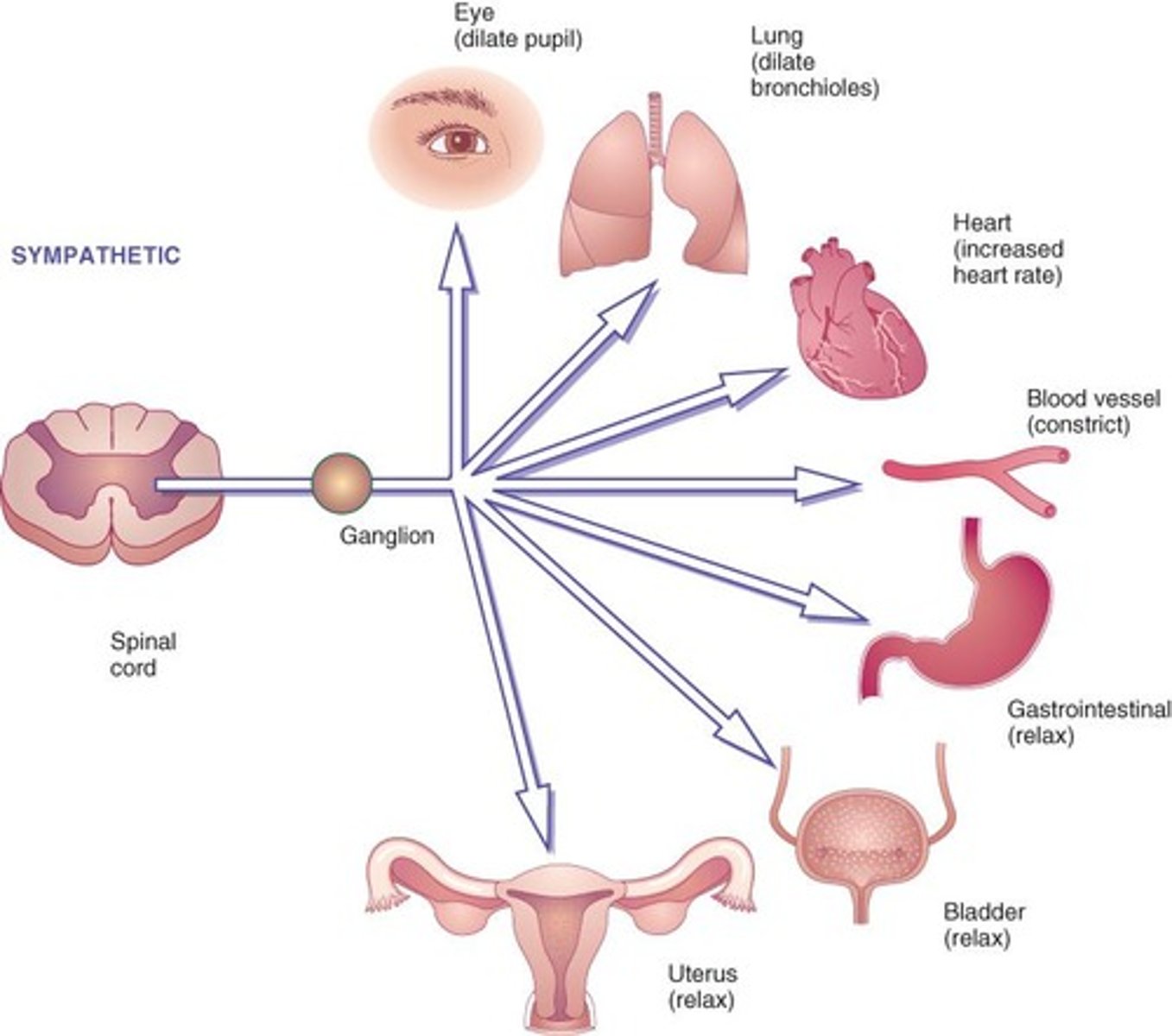
What is the role of adrenergic agonists in the sympathetic nervous system?
They stimulate adrenergic pathways, triggering the fight or flight response.
What are sympatholytics?
adrenergic antagonists
What are sympathomimetics?
adrenergic agonists
What are Parasympathomimetics?
cholinergic agonists
What are Parasympatholytics?
Anticholinergics
What is Anticholinesterase?
A drug that inhibits acetylcholinesterase
*parasympathetic effect
What are the actions of a Sympatholytic?
Decrease pulse rate
Decrease BP
Constrict Bronchioles
What are the actions of a Parasympatholytic?
Increase pulse rate
Decrease secretions
Decrease GI motility
Increase Urinary retention
Dilate Pupils
What are the four main sympathetic receptors?
Alpha1, Alpha2, Beta1, and Beta2 receptors.
Where are the adrenergic receptor sites?
•Heart, bronchi, GI tract
•Urinary bladder, ciliary eye muscles
Which neurotransmitters do adrenergic agonists stimulate?
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
What is the prototype drug for sympathomimetics?
Epinephrine, which acts as an adrenergic agonist.
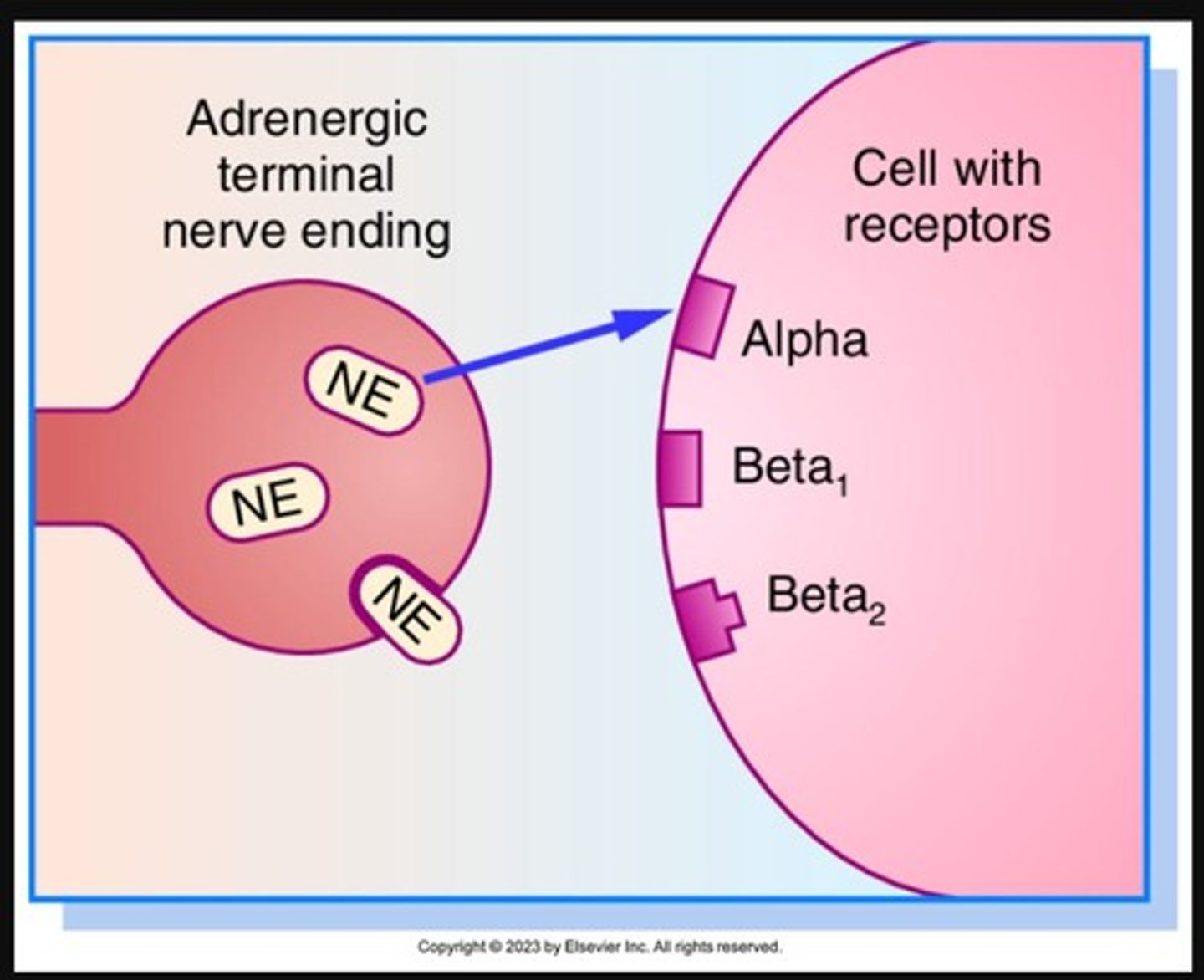
What are the effects of Adrenergic Alpha 1 receptors?
Increases cardiac contractility & Vasoconstriction
Dilates pupils
Increases blood pressure
Increases bladder relaxation & urinary sphincter contraction
What are the effects of Adrenergic Alpha 2 receptors?
Promotes vasodilation & decreased blood pressure
Decreases GI motility & tone
What are the effects of Adrenergic Beta 1 receptors?
Increases cardiac contractility
Increases BP & heart rate
What are the effects of Adrenergic Beta 2 receptors?
Bronchodilation, decreases GI tone & motility
Increases blood flow in skeletal muscles
Relaxes smooth muscles of uterus
Activates liver glycogenolysis & increases blood glucose
What do catecholamines cause?
sympathetic response
What are examples of Endogenous Catecholamines?
•Epinephrine, Norepinephrine, Dopamine
What are some examples of synthetic catecholamines?
Isoproterenol, Dobutamine
What are some examples of non-catecholamines?
•Phenylephrine, Metaproterenol, Albuterol
What are direct-acting Sympathomimetics?
Drugs that directly activate adrenergic receptors
Examples of direct-acting Sympathomimetics
epinephrine and norepinephrine
What are indirect-acting Sympathomimetics?
stimulate the release of norepinephrine from the terminal nerve endings
Example of indirect-acting Sympathomimetics
amphetamine
What are mixed-acting Sympathomimetics?
combine both direct and indirect actions
Examples of mixed-acting Sympathomimetics
ephedrine and pseudoephedrine
adrenergic agonist prototype drug
Epinephrine
Prototype Drug: Action of Epinephrine
-Increases vasoconstriction, BP, heart rate, and cardiac output
-Promotes bronchodilation
What conditions is epinephrine used for?
anaphylactic shock
Bronchospasms
Cardiogenic shock
Cardiac arrest
What are the side effects/ adverse reactions of epinephrine?
Cardiac dysrhythmias, palpitations
Tachycardia, hypertension
Dizziness, headache, paresthesias
Agitation, restlessness, tremors
Hyperglycemia, oliguria
What are the drug interactions of epinephrine?
Beta blockers decrease epinephrine action
Digoxin causes cardiac dysrhythmias
TCAs and MAOIs intensify and prolong effects
Concept of Adrenergic Agonists (CJMM)
Perfusion
Recognize Cues of Adrenergic Agonists (CJMM)
Record baseline vital signs for future comparisons.
Assess patient's drug history.
Analyze cues and prioritize hypothesis of Adrenergic Agonists
Decreased tissue perfusion, hypotension
Generate solutions of Adrenergic Agonists (CJMM)
Patient's vital signs will be within normal range.
Take Action for Adrenergic Agonists (CJMM)
Record patient's vital signs.
Report tachycardia, palpitations, tremors, dizziness, hypertension, increased BP and extra heartbeats
Monitor IV site for infiltration.
Avoid cold medicines and diet pills if hypertensive, diabetic, CAD, or has dysrhythmia.
Avoid continuous use of adrenergic nasal sprays.
What are the effects of adrenergic antagonists at alpha1 receptors(selective)?
They inhibit responses at alpha-adrenergic receptor sites, affecting vasodilation, dizziness, orthostatic hypotension, reflex tachycardia, pupil constriction, suppresses ejaculation.
What are the effects of adrenergic antagonists at beta1 receptors(nonselective)?
Decreases BP and HR
What are the effects of adrenergic antagonists at beta2 receptors(nonselective)?
•Bronchoconstriction
Bronchospasms
Contracts Uterus
Inhibits glycogenolysis (hypoglycemia)
•Use with caution in patients with COPD or asthma
What is the prototype drug for beta1 blockers?
Atenolol, which is an adrenergic antagonist.
What is atenolol used for?
Angina
acute myocardial infarctions
hypertension
What is the onset of atenolol?
1 hour
What is the peak of atenolol?
2-4 hours
What are the two types of cholinergic agonists?
Direct-acting and indirect-acting cholinergic agonists.
What are the types of cholinergic receptors?
nicotinic and muscarinic
Which neurotransmitter does cholinergic agonists mimic?
Mimic parasympathetic neurotransmitter acetylcholine
Where are muscarinic receptors found?
Heart, GI, GU, glands
What is the cholinergic prototype drug?
Bethanechol chloride
What does Bethanechol chloride do?
increase urination
What conditions is Bethanechol chloride used for?
treat non-obstructive urinary retention, neurogenic bladder
What are side effects/adverse reactions of Bethanechol chloride?
•Hypotension, diaphoresis, miosis
•Increased salivation & gastric acid
•Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps
What are the life threatening effects of Bethanechol chloride?
Bronchospasm, wheezing
What are the contraindications of Bethanechol chloride?
•Bradycardia, hypotension, peptic ulcer
•Parkinsonism, hyperthyroidism
Urinary tract obstruction
What is the prototype drug for direct-acting cholinergic agonists?
Bethanechol, which promotes bladder contraction.
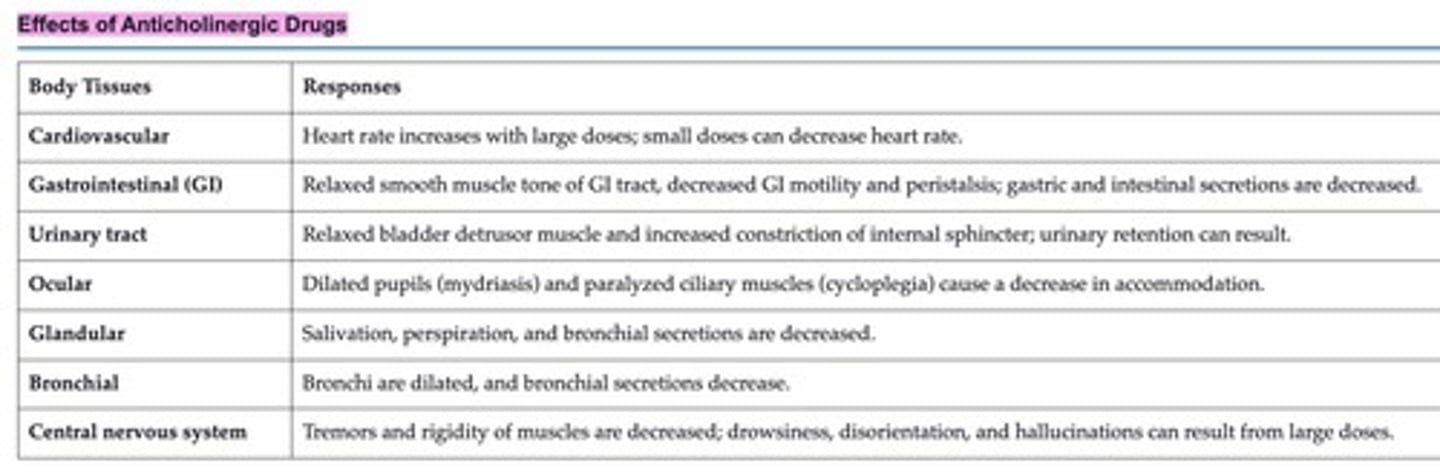
What are the side effects of anticholinergics?
hot as hare, blind as a bat, mad as a hatter, red as a beet, dry as a bone..... Can't SEE PEE SHIT SPIT!!!
Mydriasis → pupil dilation
(when you're crazy, mad as a hatter, your eyes get BIG)
BRONCHODILATION! (ANTIcholinergics are ANTI bronchospasm)
Anticholinergics are the rhymes... rhymes are weird... we are ANTI rhymes
What is the function of atropine?
It is an anticholinergic that:
Increase heart rate
promotes pupil dilation
decreases GI motility
spasms
peristalsis
salivary and gastric secretions
What are the common uses of atropine?
-Reduce Salivation
-Increase HR during bradycardia
What are the side effects of atropine?
dry mouth, decreased perspiration, blurred vision, tachycardia, constipation, and urinary retention
what are the adverse effects of atropine?
Tachycardia, paradoxical bradycardia, angina, ileus, seizures
Life-threatening: Dysrhythmias, laryngospasm, coma
What is the function of Benztropine?
•Decreases involuntary movement, tremors, & muscle rigidity
What disease is Benztropine used to treat?
Parkinson
What are the side effects of Benztropine?
Anticholinergic side effects, which include dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, urinary retention, and memory impairment.
What is Tolterodine Tartrate used for?
Decrease urinary frequency, urgency, and nocturia not related to a urinary tract infection (OBS)
What are the side effects of Tolterodine Tartrate?
Drowsiness, dizziness, dry mouth and eyes, headache, blurred vision, confusion, diarrhea, abdominal pain, constipation, dyspepsia, dysuria, fatigue, weight gain, arthralgia, hallucinations, and urinary retention
What are the adverse effects of Tolterodine Tartrate?
Angioedema, chest pain, tachycardia, peripheral edema
What are the life threatening effects of Tolterodine Tartrate?
Life threatening: Stevens-Johnson syndrome
What is the most common cause of lower urinary tract infections (acute Cystitis)?
E. coli
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Klebsiella
Proteus, Pseudomonas
What is the most common cause of upper urinary tract infections (acute pyelonephritis)?
•Most common organism, E. Coli
What is the prototype drug for urinary antiseptics/biotics?
Trimethoprim
trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
What is a urinary analgesic used for?
to relieve the pain, burning, and discomfort caused by infection or irritation of the urinary tract
What are the prototype drugs for Urinary analgesic?
•phenazopyridine hydrochloride
What are the symptoms of acute cystitis in females?
Symptoms may include frequent urination, urgency, and pelvic pain.
What is the prototype drug for urinary anticholinergics?
Solifenacin succinate, which helps relieve urinary frequency and urgency.
What is Solifenacin succinate used to treat?
treat overactive bladder and urinary incontinence
What are the side effects of treat Solifenacin succinate?
-Blurred vision, dizziness, fatigue, cough, pharyngitis, dry mouth
•nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation, dyspepsia
•cystitis, urinary retention, peripheral edema
What are some adverse effects of solifenacin succinate?
Tachycardia, hypertension, angioedema, GI obstruction
What are some life-threatening adverse effects of solifenacin succinate?
Life threatening!- dysrhythmias, hyperkalemia
What are some contraindications of solifenacin succinate?
•glaucoma, gastroparesis, GI obstruction or urinary retention
What should be monitored in patients receiving urinary anti-infectives?
Vital signs, lab results, and signs of infection.
What is the role of cholinergic antagonists?
They block the action of acetylcholine, affecting various bodily functions.
What is the difference between sympathomimetics and sympatholytics?
Sympathomimetics stimulate the sympathetic nervous system, while sympatholytics inhibit it.
What is the clinical judgment process for adrenergic agonists?
Recognize cues, record baseline vital signs, assess drug history, and monitor for adverse effects.
What are the effects of beta-adrenergic antagonists?
They decrease heart rate and contractility, reducing blood pressure.
What is the significance of the fight or flight response?
It prepares the body to respond to perceived threats through physiological changes.
What are the potential side effects of adrenergic agonists?
Tachycardia, palpitations, tremors, dizziness, and hypertension.
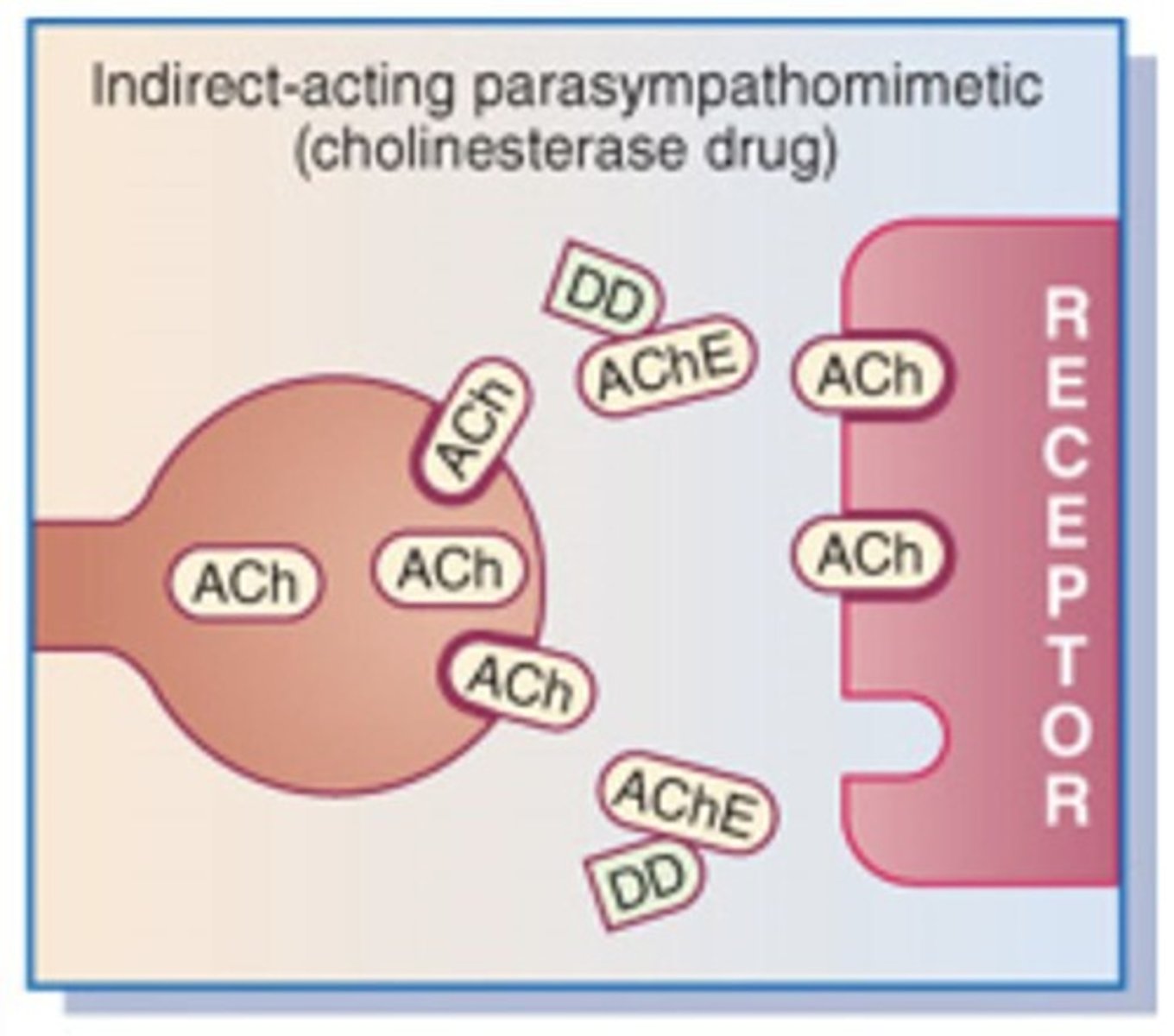
What is the role of indirect-acting cholinergic agonists?
They inhibit the breakdown of acetylcholine, prolonging its action at receptor sites.