5007PM - BURNS & SCALDS
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
what is a burn
Injury caused by thermal, chemical, electrical and radiation energy
what is a scald
A scald is a burn caused by contact with hot liquid or steam
Damage to skin caused by heat
how is the severity of a burn characterised
Extent of skin affected
Anatomical site
Depth of injury
Age of patient
Presence of coexisting disorders
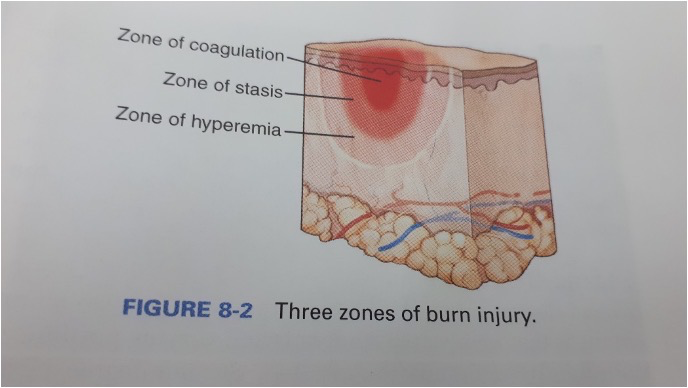
what are the three zone of a burn injury
zone of coagulation
zone of statsis
zone of hyperaemia
what is a 1st degree burn
burn to the superficial thickness
e.g sunburn
what is the presentation of a first degree burn
warm
red
painful
what is a second degree burn
burn to partial thickness
further classified- superficial or deep
superficial - epidermis only
deep - epidermis & dermis
whats the presentation of 2nd degree burns
Blistering
Painful
Glistening wound bed
how long does it take to recover from 2nd degree burns
2-3 weeks of wound care
what is a third degree burn
full thickness
deep into dermis
what is the presentation of third degree burns
leathery
white to charred
dead tissue
appearance- thick dry white
have pain from areas adjacent to burn site
what is the treatment for 3rd degree burns
Surgical intervention and intense period of rehabilitation.
what is a 4t degree burn
Not only to skin but also subcutaneous fat, muscle and bone
what are the types of burn
thermal
scald
radiation
electrical
chemical
non-accidental
what is a thermal burn
Caused by fire and heat
Direct injury to skin and tissue
what is a scald
Caused by hot liquid
Thicker the liquid and the longer the contact of skin = the greater the scald
what is radiation burn?
Exposure to radiation
Cell structure can be altered as the body responds to the radiation - causing cell mutations and cancer some times
what is an eletrical burn
Caused by currents of electricity
Usually deep
May cause severe damage to the skin and underlying tissue
Patients often have entry and exit wounds
how can electrical burns cause an arrest
Cardiac arrest due to the current passing through the myocardium.
Hand to hand worse than hand to feet.
how can electrical burns induce arrythmias
Mass destruction of muscles which then release potassium and myoglobin.
Potassium increases serum levels which can induce cardiac arrhythmias.
how can electrical burns damage kidney
When myoglobin is released into the bloodstream kidney damage may ensue
in this case urine may be coca cola or tea coloured.
what is a chemical burn?
Occurs when your skin or eyes come into contact with an irritant
Such as acid or a base
Be aware of cross contamination
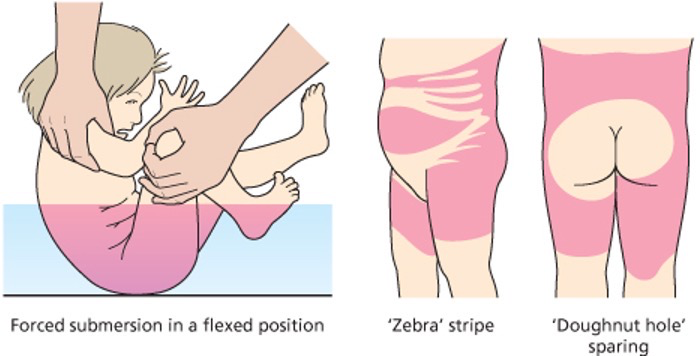
what is a non accidental burn
Forced submersion in a fixed position
Zebra striped
Doughnut hole sparing
what should you ask yourself if you expect a non accidental burn?
is the story consistent with injury?
Are there varying accounts of what happened?
does injury have a clean line of demarcation? signs of inflicted burn?
any other injuries?
why delay in medical attention?
aggressive bystander?
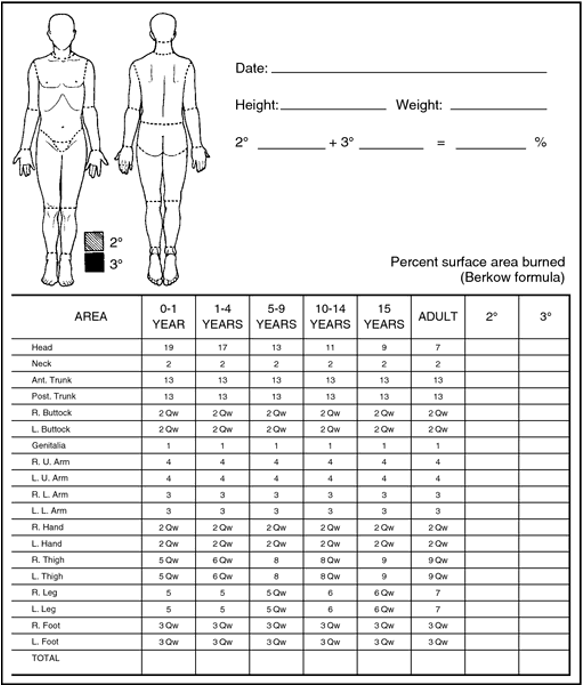
what are the assessment tools used for burn severity?
wallace rule of nine
lund and browder chart
patients palmer surface
mersey burns
what is the tool- wallace rule of nine?
9% - head and neck
9% - arm (each)
18% - trunk - each for anterior and posterior
1% for genitalia and perinueum
18% - leg (each)
what is the tool- patients palmer surface
The surface area of a patient's palm (including fingers) is roughly 0.8% of total body surface area.
what is the tool- Lund and Browder chart?
This is a good, quick way of estimating medium to large burns in adults.
The body is divided into areas of 9%
The total burn area can be calculated.
It is not accurate in children.
what is the presentation of TIME CRITICAL patients?
Major CAcBCD problems
Significant facial burns
Airway burns (soot or oedema around mouth and nose)
Hx of hot air and gas inhalation (appear well initially)
Resp distress
Circumferential burns of the chest, neck and limbs
Child >10% TBSA
Adult >15 TBSA
Presence of other major injuries
Preceding medical conditions
what % of burn is time critical in children
10%
what % of burn is time critical in adults
15%
what are the S&S of airway burns
Facial or neck burns
Soot in nasal or oral cavities
Productive cough - black sputum
Hoarseness
Dyspnoea - difficulty in talking
Dysphagia - difficulty in swallowing
Blistering round mouth and tounge
Scored hair, eyebrows and facial hair
Stridor/wheezing
Loss of consciousness
what is the management of burns?
large burns require fluids
elevate extremities
apply wet non adherent dressing
apply cling film (not on chemical)
cool/irrigant burn
how long should you cool burn for
20 mins
how long should you cool a chemical burn
up to an hour
what are the complications of having a burn injury
Inhalation injury
UTI
Clots in leg due to long lie
Infection
Hypovolemia and hypothermic shock - body regulates fluid and heat loss
Wound progression- swelling decreased blood flow lead to full thickness
Tetanus
what is a surgical circothyroidtomy
incision made through the skin and cricothyroid membrane to establish a patent airway during certain life-threatening situation