Topic 7A: Descent with Modification
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
what is the most general taxon
domain
what is the most specific taxon
species
every living thing falls under 1 of which 3 domains
eukarya, bacteria (prokaryote), archae (prokaryote)
which two taxon are used as the scientific name for all organisms?
genus + species
who is Carolus Linnaeus
grouped similar species into increasingly general categories
developed taxonomy
binomial nomenclature
what is taxonomy
a branch of biology dedicated to the naming and classification on all forms of life
what is binomial nomenclature
a two-part naming system that includes the organism’s genus and species
who was Charles Lyell
developed the idea that the geologic processes that have shaped the planet have been uniform over a long period of time
important conclusion: the earth must be very old
what is each layer of rock called
a strata
deeper stratas are older
what was Jean-Baptiste de Lamarck use and disuse theory
more used parts of the body become larger and stronger, while less used parts deteriorate
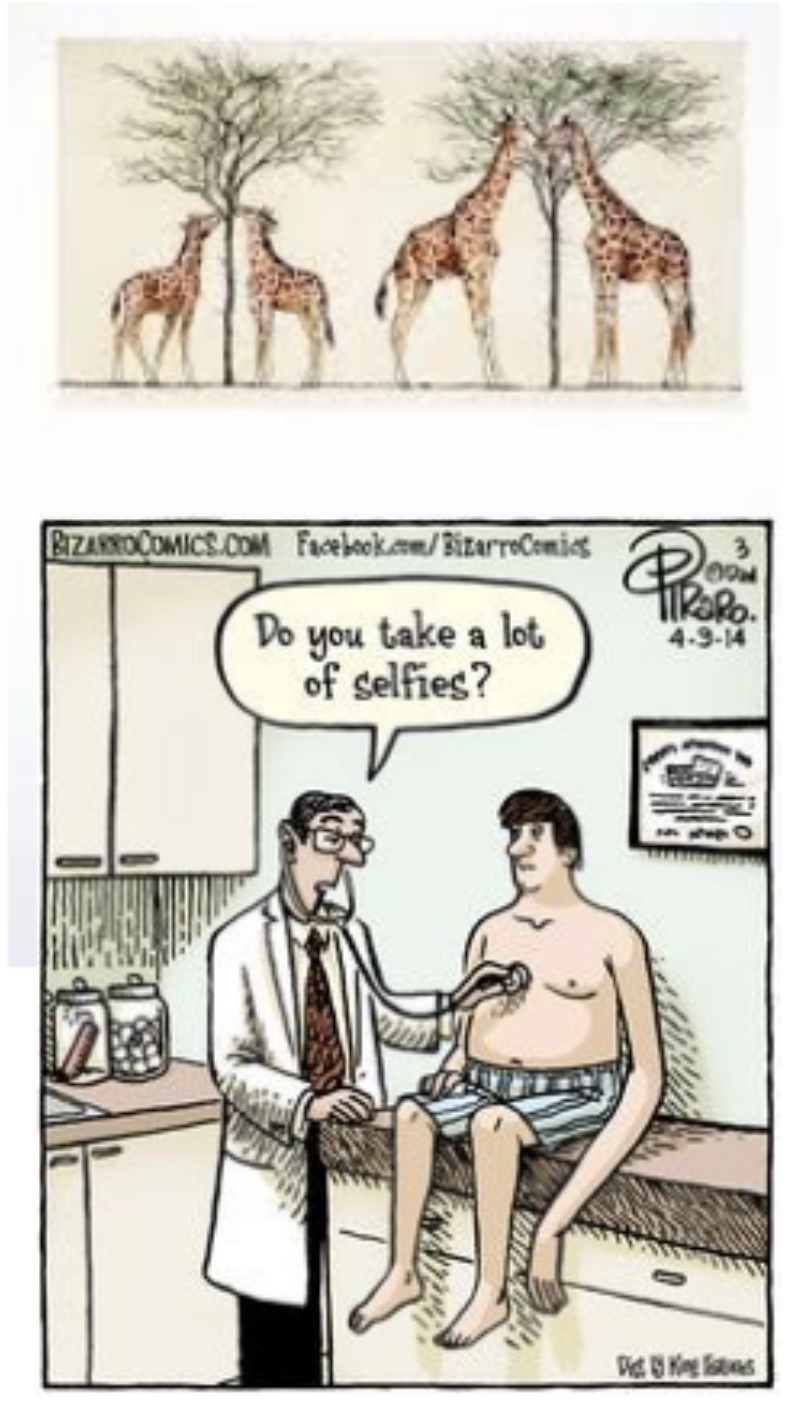

what was Jean-Baptiste de Lamarck’s inheritance of acquired characteristics theory
characteristics acquired during an organism’s lifetime could be inherited
what’s a way to memorize use and disuse theory
“if you don’t use it, you lose it”
what is Charles Darwin’s natural selection theory
explains how adaptations arise
adaptation: heritable characteristics that enhance organisms’ ability to survive and reproduce in specific environments
what does natural selection involve
individuals in a population vary in their traits, most being heritable
a population can produce far more offspring that can survive
individuals with inherited traits that are better suited to the local environment are more likely to survive and reproduce than individuals less suited
evolution occurs as the unequal reproductive success of individuals ultimately leading to adaptations of their environment
what is variation
there is genetic variation within a population which can be inherited
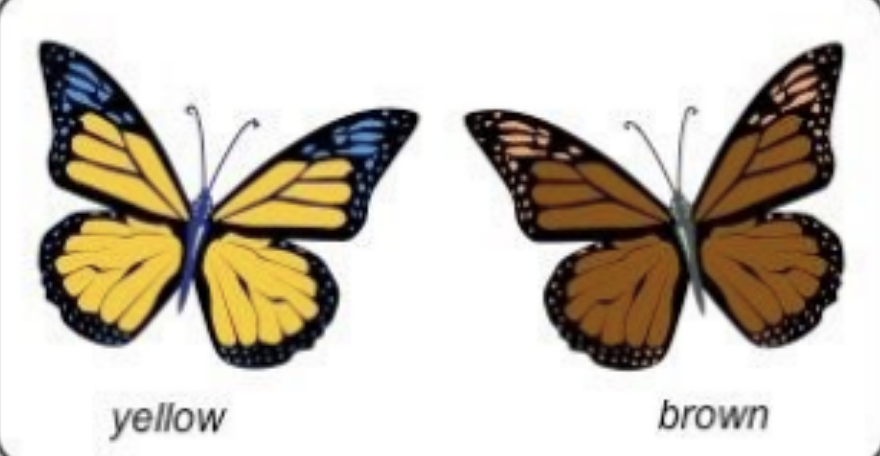
what is competition
overproduction of offspring leads to competition for survival
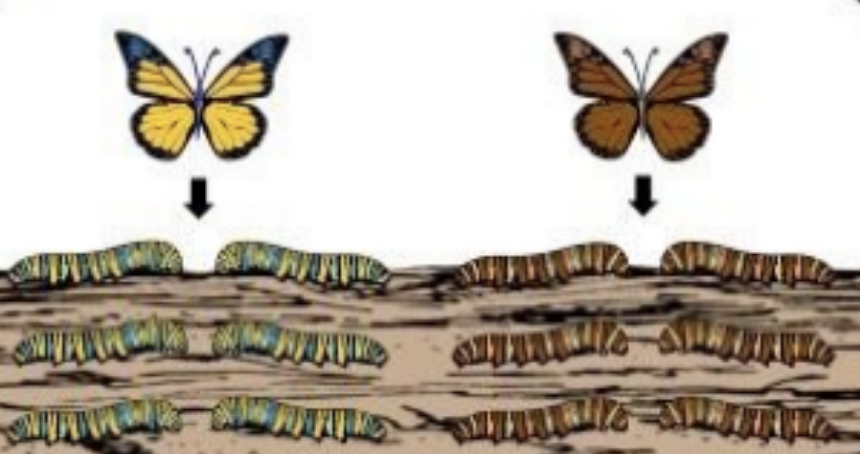
what are adaptations
individuals with beneficial adaptations are more likely to survive
what is selection
over many generations, there is a change in allele frequency (evolution)
Natural selection can lead to _____ and _____ _____
speciation; adaptive radiation
what is speciation
creation of a new species
what is adaptive radiation
the relatively fast evolution of many species from a single common ancestor
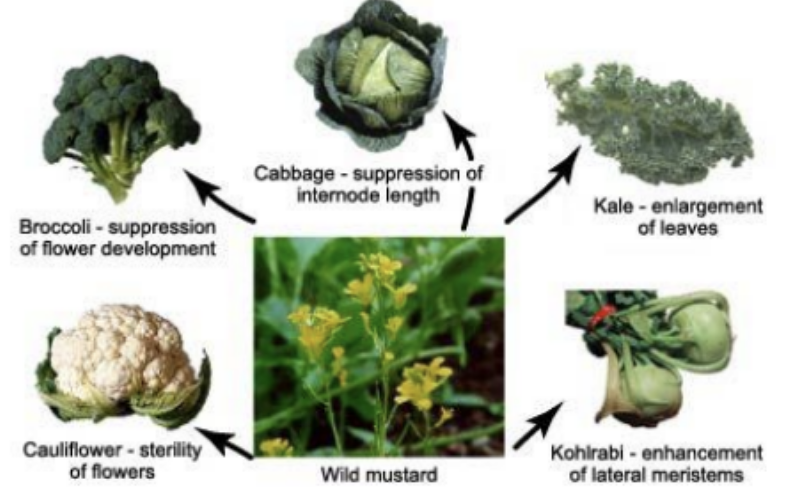
what is artificial selection
the process by which species are modified by humans
ex. Breeding dogs
Individuals do not evolve. ____ evolve.
Populations
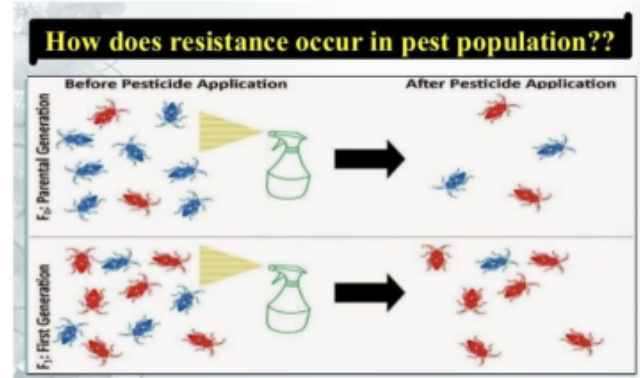
What Are Some Direct Observations of Evolutionary Change
Insect populations can rapidly become resistant to pesticides such as DDT
Evolution of drug-resistant viruses and antibiotic - resistant bacteria
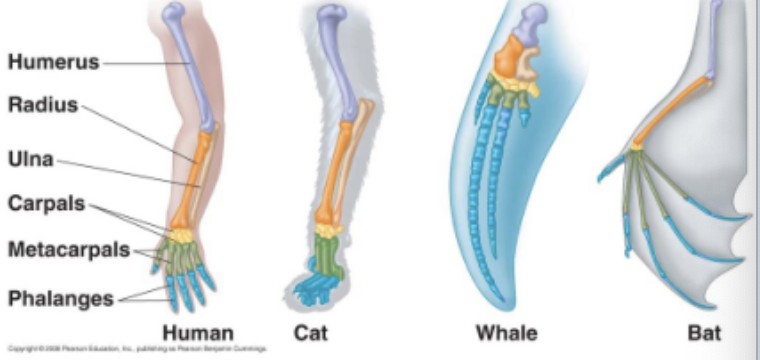
What is homology
characteristics in related species can have an underlying similarity even though they have very different functions
What are homologous structures
anatomical signs of evolution
same structure, different function
What are analogous structures
body parts
different structure, same function
goal is to adapt to the same environment
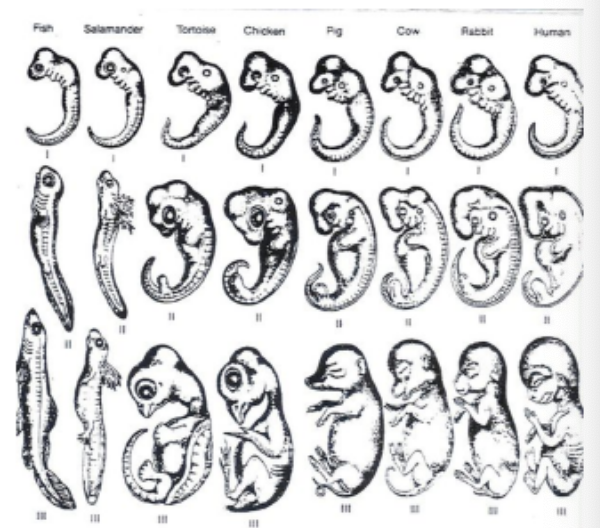
What are embryonic homologies
many anatomical homologies in embryos are not visible in adult organisms
ex. All vertebrate embryos have a post-anal tail and pharyngeal pouches
what are vestigial organs
structures with minimal, if not any importance to the organism
what are molecular homologies
shared characteristics on the molecular level
ex. Amino acid sequences coding for hemoglobin in primate species show great similarity, indicating a common ancestor.
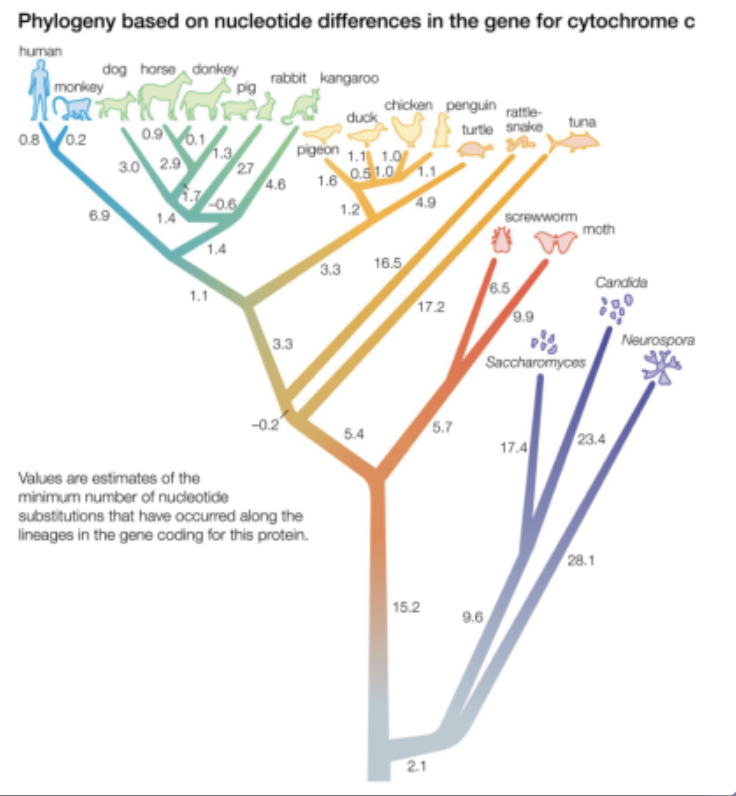
what is molecular biology
molecular similarities (similar DNA/proteins) provide evidence for the shared ancestry (common ancestor)
comparisons of DNA sequences can show how closely related or different two species are
what does convergent evolution explain
why distantly related species can resemble one another
this takes place when two organisms develop similarities as they adapt to similar environmental change
ex. torpedo shapes of penguin, dolphins and sharks are all solutions to movement to an aqueous environment
what is divergent evolution
two or more related species evolve into increasingly dissimilar forms
what is biogeography
the geographic distribution of species
species in a discrete geographic area tend to be more closely related to each other