methane and feed
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
H2 accumulation
impaired digestion
acetic acid
h2 source
proprionic acid
h2 sink
butyric acid
h2 source
acids in the rumen
acetic, propionic, butyric acid
methane: relative to co2
short term effect, so that the effect is higher on the low term
methan half year life
12 years, so reduce methane production then cleraeance rate from atmosphere
nutritional strategies to decrease enteric methane
- Intake and diet composition
o Level of intake
o Roughage quality / nutritive value
o Level of starch, fibre, fat etc
- Specific methane inhibitors
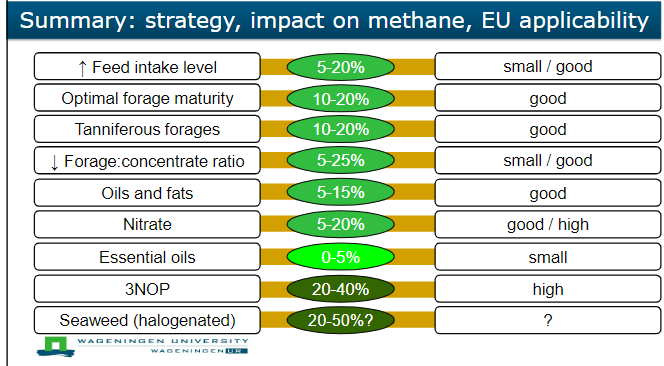
impact on methane
increase feed intake level
optimal forage maturity
tanniferous forages
decrease forage: concentrate ratio
oils and fats
nitrate
essential oils
3no
seawead
Increasing feeding level
- Directs nutrients to milk or weight gain
o Inrease absoulate methane emission )g/head/day) + 18 degrees Celsius
o Decrease methane yield (g/kg feed): -8% (-4 to -12%)
o Decrease methane intensity (g/kg product): -17% (-9 to -23%) (milk)
- How to increase feed intake?
o High quality management (hygiene, feeding frequency etc)
o Avoid situations insufficient forage
o Deitary deficiencyes (lack of protein, minerals, etc)
- Trade-off
o Decreased fibre digestibility, due to the greater feed intake level, retention time has an effect on the fibre
decreasing grass maturity
- The key for thi is high quality grass, more mature, more fibre
- Yung grass, better digestibile, shift fermentation process in the rumen to more probiotics, lower hydrogen, more digestible nutrients, more milk, per unit of milk lower methane
- Shifts rumen fermentation and increases production (milk/growth)
- Increse methane emission (g/head/day): +7% (1-17%)
- Decrease methane yield (g/kg feed) -4% (-1 to -8%)
- Decrease methane intensity (g/kg product): -13% (-7 - -18%) (milk)
- Good applicability
- Trade offs:
o Increased nitrogen (N) excretion
o More intense management
increasing harvest maturity of whole plant maize silage
- At the highest maturity, more starch, more slowly degradblae starch, methane emissions are lower
- Inclusion of taniferous forages, opzoeekn
- - tannis are plant secondary compounds rich in phenols
- Inhibit rumen methanogens and protozoa; shift rumen fermantion
- Decrease absolute methane mission
- Decrese methane yield
- Decrease methane hield
- Promising species include buschclover, birdsfoot trefoil, leucaena
- Commercial tanning etracts available
concentrate ratio
- Increase concentrate, may increase feed-food competition
oil/fats
negative effects
3nop and mcr
- Huge effects, varible effects
- Less efficient with high fibre high fat
- Depends on type of diet