General + Phylum Apicomplexa (Coccidia) (Cram)
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Common name for parasites of the Kingdom Protista
Protozoans
Are protozoans multicellular or unicellular?
Unicellular
Kingdom Protista parasites do not have ova, what are the eggs called?
Oocysts
How are the different Phyla of Kingdom Protista divided?
Based on movement
What are the three Phyla of Kingdom Protista of veterinary medicine significance?
Phylum Apicomplexa
Phylum Sarcomastigophora
Phylum Ciliophora
What kind of motility do Phylum Apicomplexa parasites have?
Non–motile
True or false: All members of Phylum Apicomplexa are parasitic
True
Are parasites of Phylum Apicomplexa intracellular, extracellular, or intercellular?
Intracellular, they cause disease by destroying cells from within
What are the two most important groups within Phylum Apicomplexa?
Coccidia
Hemosporidians
Coccidia develop in the epithelial cells of the gut and cause _______ (coccidiosis)
enteritis
How are coccidia typically transmitted?
Fecal contamination
What are the six important coccidia genera? Remember: Every Cat Secretely Craves Nonstop Touch
Eimeria
Cystoisospora
Sarcocystis
Cryptosporidium
Neospora
Toxoplasma
Are coccidia typically host specific or not?
Typically host specific
What are the two Eimeria species specific to cattle?
Eimeria zuernii
Eimeria bovis
What is the Eimeria species specific to rabbits?
Eimeria stiedae
What are the three Cystoisospora species specific to dogs, cats, and pigs respectively?
Dogs – Cystoisospora canis
Cats – Cystoisospora felis
Pigs – Cystoisospora suis
True or false: A host cannot be parasitized by multiple species of coccidia simultaneously, the species will compete with each other
False. A host can be parasitized by multiple spieces of coccidia (ie. Eimeria bovis and Eimeria zuernii in cattle)
Clinical symptoms are important for the diagnosis of coccidia, what else is a diagnosis based on?
Identification of oocysts in the host's feces
Is replication of coccidia species sexual, asexual or both?
Both
Which genera sometimes uses paratenic hosts, Cystoisospora or Eimeria?
Cystoisospora
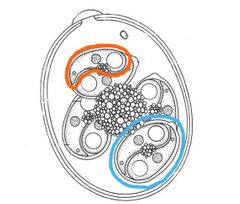
What are the structures outlined in orange and blue called?
Orange – Sporozoite
Blue – Sporocyst
What is the infective stage of coccidia?
Sporozoites
Sporozoites are liberated from the oocyst and the sporocyst in the host and invade the host's intestinal cells to asexually reproduce. What is the term for the asexual reproduction of sporozoites?
Shizogony
As sporozoites mature they can look for other cells to invade or may undergo sexual reproduction. What is the term for the sexual reproduction of sporozoites?
Gametogony
What is the prepatent period of coccidiosis in dogs and cats?
7–14 days
Drug that slows or weakens coccidia, but does not kill them
Coccidiostatic
Drug that kill coccidia
Coccidiocidal
What is the genus species of coccidia that affects cats, and poses a zoonotic risk especially to pregnant women?
Toxoplasma gondii
What are the intermediate hosts of Toxoplasma gondii?
Almost every mammal and bird
What is the site of Toxoplasma gondii in the definitive host?
Small intestine
What is the site of Toxoplasma gondii in the intermediate host?
Muscles (also liver, lung, eye, and brain)
Term for the rapidly multiplying stages of Toxoplasma gondii in sporulated oocysts
Tachyzoites
Term for the slowly multiplying stages of Toxoplamsa gondii that form tissue cysts within the muscle of the IH
Bradyzoites
Can cats also have bradyzoites?
Yes
What are the two ways a cat can become infected with Toxoplasma gondii?
Paratenic host (usually rodent)
Oral ingestion (infective oocyst)
The prepatent period of Toxoplasma gondii depends on the life stage ingested. Between bradyzoites and oocysts/tachyzoites. Which PPP is longer?
Oocysts and tachyzoites are longer (up to 3 weeks)
What are the two types of Toxoplasma gondii infections in humans?
Acquired
Congenital
What are the three stages of Toxoplasma gondii ingested by a human that can cause acquired toxoplasmosis?
Bradyzoites
Tachyzoites
Sporozoites
What stage of Toxoplasma gondii needs to be ingested by a pregnant woman to cause congenital toxoplasmosis in the fetus?
Sporozoites
What are some symptoms of congenital toxoplasmosis in humans?
Abortion (early pregnancy), stillbirth, blindness, retardation, learning difficulties
What can be done to protect pregnant women from Toxoplasma gondii?
Pregnant women do not clean litter boxes, litter boxes are deep cleaned frequently, wear gloves while gardening, wash hands after handling cats
Fecal testing is ineffective when testing for Toxoplasma gondii, cats only release oocysts once in their life for 1–2 weeks. What test is done instead?
Serological testing
What are the two Cryptosporidium species that affect mice and calves and just calves respectively?
Mice and calves – Cryptosporidium muris
Calves – Cryptosporidium parvum
What age of calf do C. muris and C. parvum affect respectively?
C. muris – Older than 3 months
C. parvum – 1–3 weeks old
What type of calf do Cryptosporidium species affect more: beef or dairy calves?
Dairy calves
What is the site of Cryptosporidium in the definitive host?
Small intestine
At what stage are Cryptosporidium infective?
Oocysts, don't need to be sporulated
Are Cryptosporidium species zoonotic?
Yes
What is the genus species of coccidia that affects the nervous system of horses?
Sarcocystis neurona
What is the definitive host of Sarcocystis neurona?
Opossum
What are some of the intended intermediate hosts for Sarcocystis neurona, the parasite will form sarcocysts in the host's skeletal muscles
Cats, ferrets, raccoons, sea otters, skunks, and seals
What kind of host is a horse when infected with Sarcocystis neurona?
Dead end host
What is the name of the neurological disease caused by Sarcocystis neurona in horses?
Equine protozoal myeloencephalitis (EPM)
What are some clinical signs of EPM in horses?
Ataxia, head tilt, recumbency, muscle atrophy of hindlimbs, and dysphagia
How many sporocysts and sporozoites are present in a sporulated Sarcocystis neurona oocyst?
Sporocysts = 2
Sporozoites (per sporocyst) = 4
What is the genus species of coccidia that causes abortion in cattle?
Neospora caninum
What is the definitive host of Neospora caninum?
Dogs and wild dogs
What are some intermediate hosts of Neospora caninum?
Cattle, sheep, goats, bison, moose, and white–tailed deer
What life stage of Neospora caninum can intermediate hosts and sometimes definitive hosts harbour in their tissues?
Bradyzoites
Is Neospora caninum zoonotic?
No
What can be done to prevent dogs from becoming infected with Neospora caninum?
Fence off cattle and don't allow dogs to ingest cow's placental tissue