1.6 The Periodic table 🔍
1/40
Earn XP
Description and Tags
GCSE CCEA Specification GCSE Chemistry Double Award Science, Triple Award Science Unit 1: Structures, Trends, Chemical Reactions, Quantitative Chemistry and Analysis
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
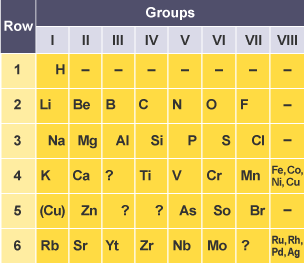
Differences of Mendeleev’s periodic table
arranged elements by increasing atomic weight, modern uses atomic number
left gaps for undiscovered elements and predicted their properties, modern includes all known elements
did not include noble gases
contains significantly less elements
altered order to group elements with similar observed properties
has no blocks of lanthanides and actinides, which are present today
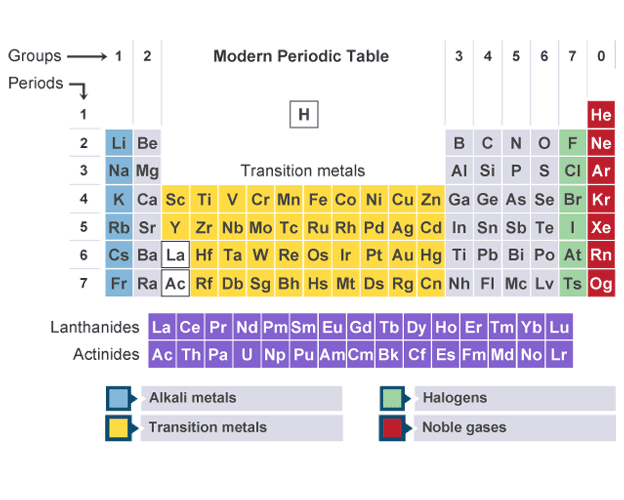
Periodic table
organised list of all known elements arranged by atomic number
Element
substance that consists of only one type of atom and cannot be broken down into anything simpler by chemical means
Structure of periodic table
made up of groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows)
Position of metals in periodic table
separated by ‘stepped line’ running below boron to astatine
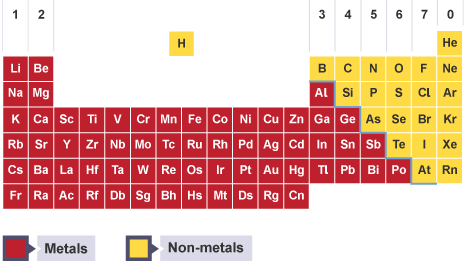
Properties of metals
good conductor of electricity and heat
generally high melting points
ductile and malleable
sonorous (makes a ringing sound when struck)
all solids other than mercury
Properties of non-metals
poor conductor of electricity
generally low melting points
brittle (breaks when hammered)
not sonorous
mostly gases other than solids C, P, S, Se, I and liquid Br
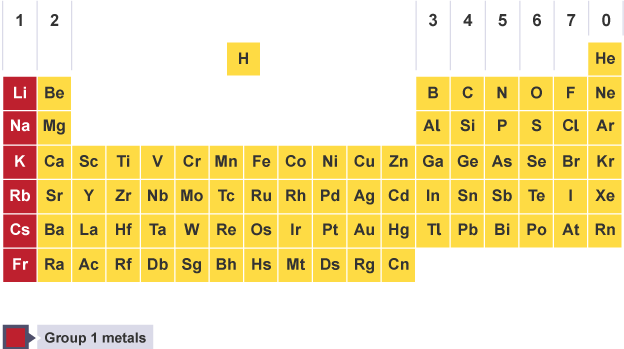
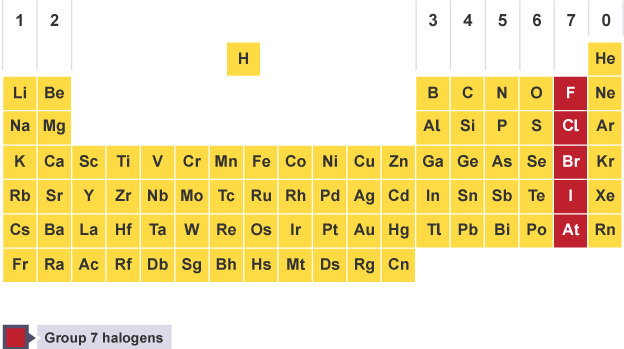
Names of groups in periodic table
1- Alkali metals
2- Alkaline earth metals
7- Halogens
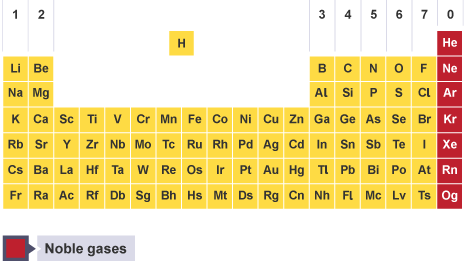
0- Noble gases
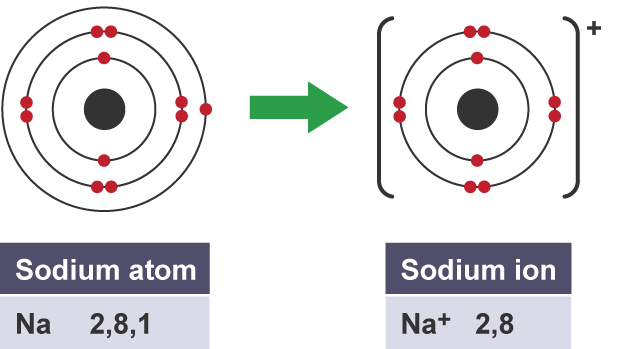
Why elements with similar properties appear in the same group
same number of valence electrons to gain or lose to form an ion with stable electronic configuration
Properties of alkali metals
low density, first 3 floating in water
very soft and easily cut with a knife
shiny when cut but tarnish rapidly in air
low melting points, decreasing down the group
conduct electricity
Colour of alkali metals
white compounds and colourless solutions
Alkali metals in water equation
alkali metal + water→ alkali metal hydroxide + hydrogen
Observations of lithium in water
floats on surface of water
moves about on surface
fizzing
heat is released
metal disappears
colourless solution formed
Observations of sodium in water
same observations as lithium
metal melts into silvery ball
sometimes orange flame produced
Observations of potassium in water
same observations as lithium
rapidly metal melts into silvery ball
lilac flame produced
small explosion/ crackling noise
Safety precautions with alkali metals
Use tweezers when lifting
Safety screen and wear safety glasses
Small piece of metal
Large volume of water (trough)
store under oil to prevent reaction with oxygen/ moisture
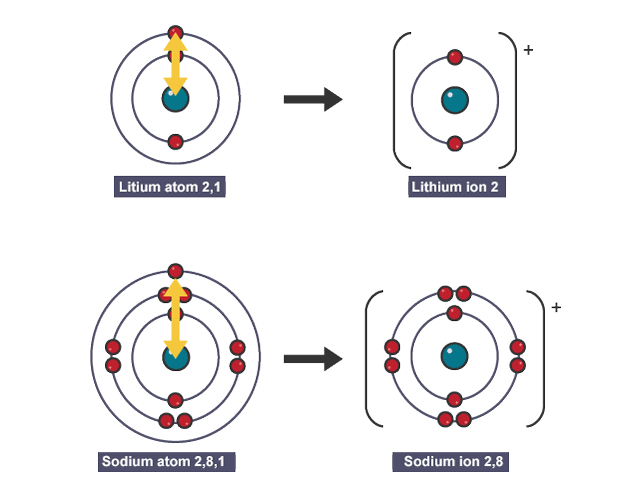
Why do alkali metals so vigourously
all have one electron in outer shell which is easy to lose
Pattern of reactivity in alkali metals
reactivity increases going down group
Why reactivity changes
atomic radius increases causing nuclear attraction to decrease
easier to lose/ harder to gain an electron
shielding from electrons between shells
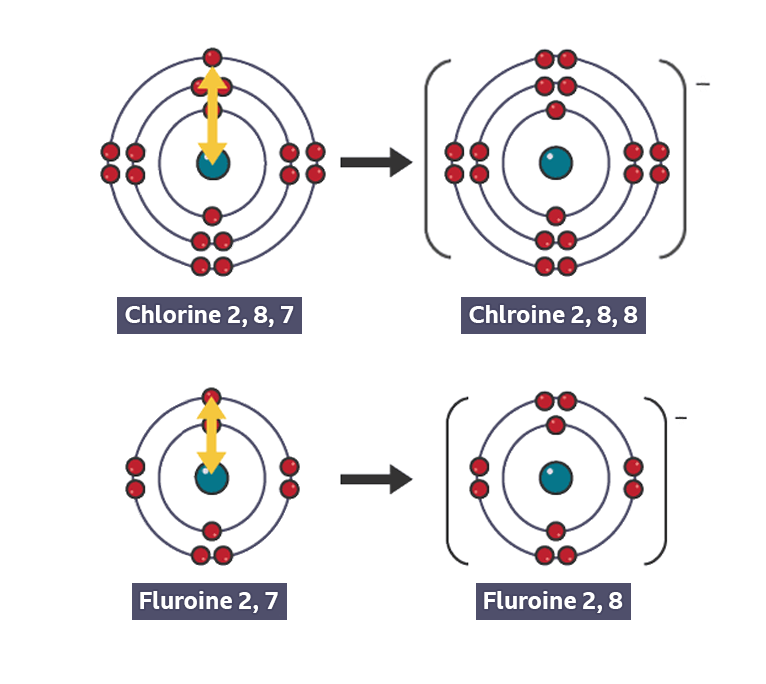
Properties of halogens
diatomic, linked by single covalent bond
toxic so use fume cupboard when storing
very reactive
do not conduct electricity
Fluorine
yellow gas
Chrloine
yellow-green gas, colourless solution
Bromine
red-brown liquid, orange solution
Iodine
grey-black solid, brown solution
Pattern of state in halogens
darker in colour and change from gas to liquid to solid
Reason for state changes in halogens
melting point increases going down group
Pattern of reactivity in halogens
reactivity decreases going down
Why reactivity decreases
atomic radius increases causing nuclear attraction to decrease, harder to gain an electron, and shielding from electrons between shells
Sublimation
change of state from solid directly to gas on heating, without passing through the liquid phase
Iodine sublimation
turns from grey-black solid to purple gas
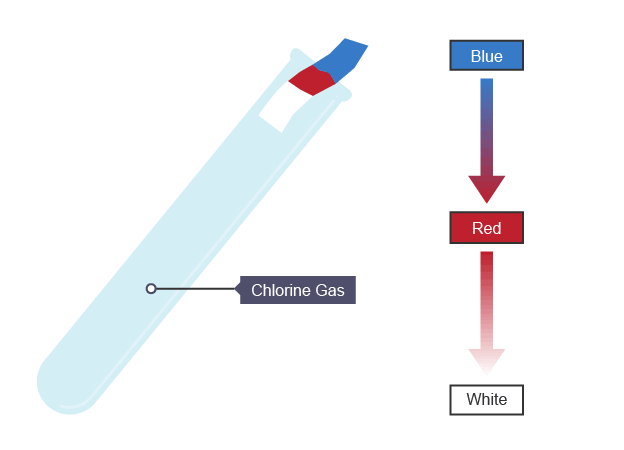
Test for chlorine gas
damp universal indicator paper turns red, then bleaches white if present
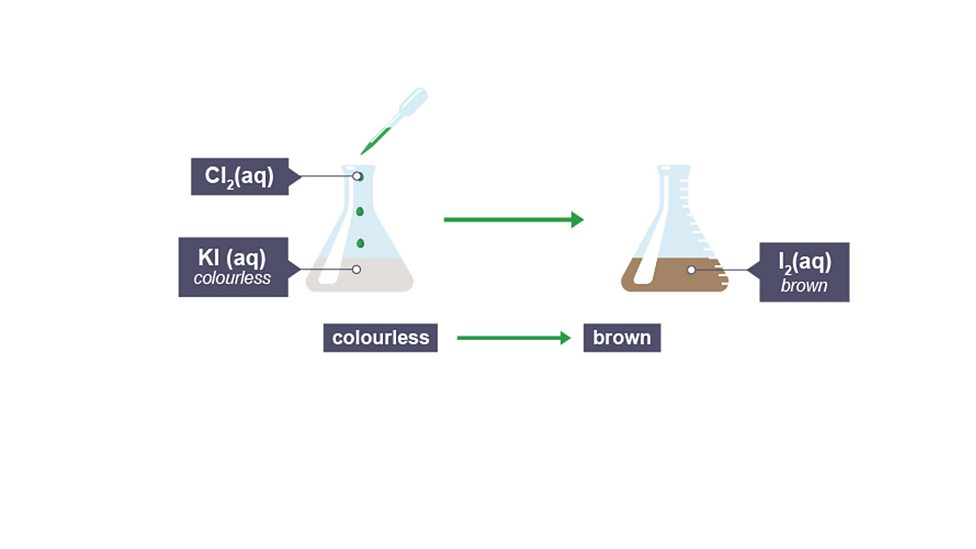
Displacement
more reactive element displaces (pushes out) less reactive from compound,
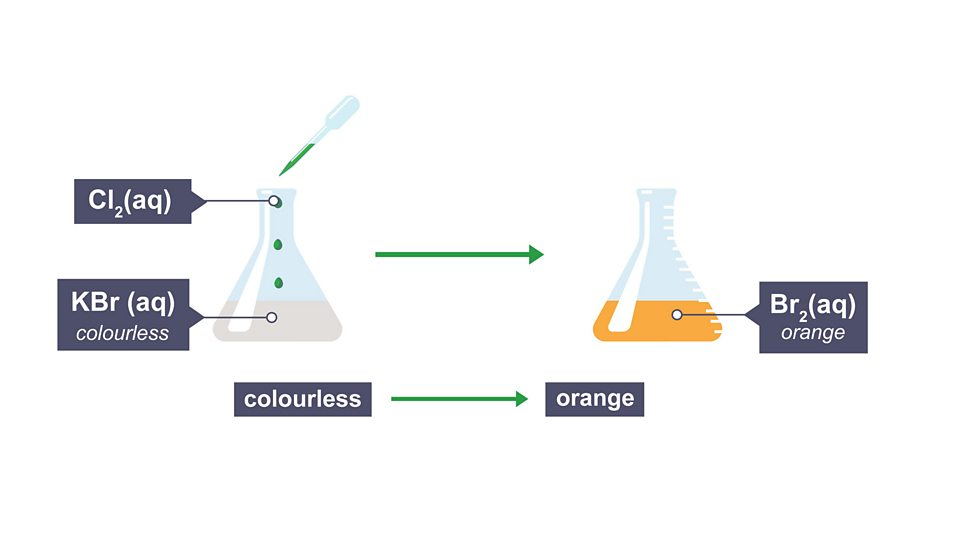
Colours of halogen displacement reactions
starts with colourless solution (as is a salt) and result reflects halogen that’s been pushes out
Properties of noble gases
inert (unreactive)
colourless gases
low boiling points
boiling point increases going down group
Why are noble gases unreactive
stable electronic configurations as they have full outer shell
Why boiling points of noble gases decrease
forces of attraction between smaller atoms is very weak so the bigger the atom the stronger the force
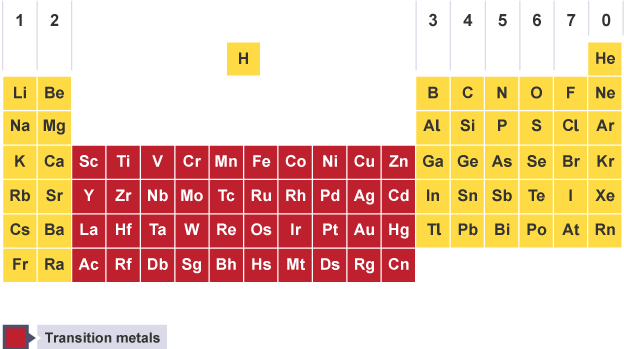
Properties of transition metals
High melting point (except mercury)
High density
Low reactivity with water
React to form ions with different charges
Form coloured compounds
Colour of copper(II) oxide
black solid
Colour of copper(II) carbonate
green solid
Colour of hydrated copper(II) sulfate
blue crystals
Colour of any copper(II) salt in solution
blue solution