rad tech-upper extremity
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
kVp used
speed. low-mid range of 60-80 on digital systems
mAs used
amount of radiation. varies depending on system. Looking for good trabecular bony details; and soft tissue margin visualization
SID
subject to image distance, 100-115cm (40-46 inches)
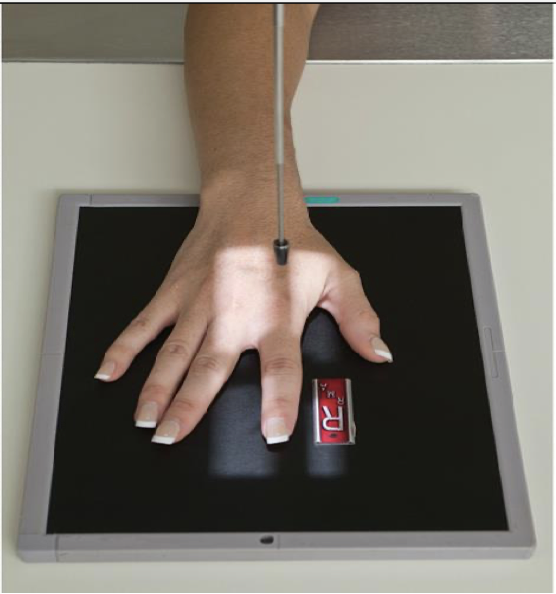
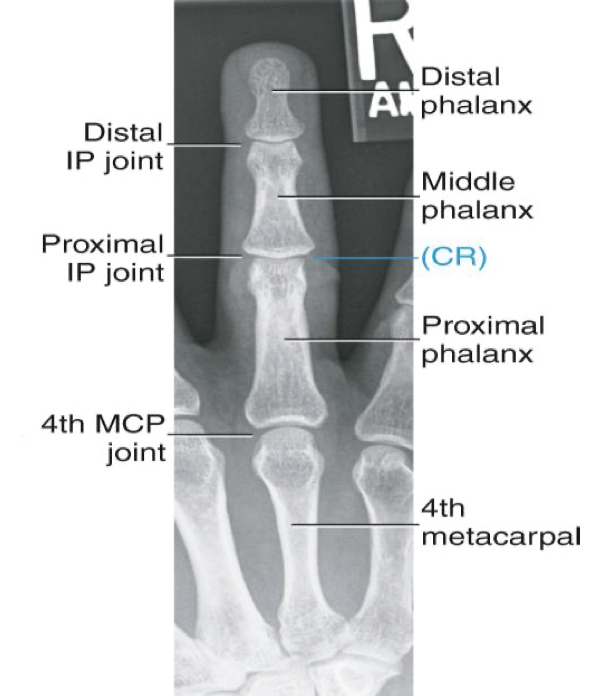
PA Finger ( 2nd-5th Digit)
patient position:
Sitting at side or end of table
Arm (humerus) is abducted
Elbow is flexed 90 degrees
Forearm is resting on table
part position:
Finger is not medially or laterally rotated
Fingers are slightly spread to prevent soft tissue overlap
CR:
Perpendicular to IR
Centered to proximal IP joint
Collimation:
X-ray beam collimated to include entire finger and at least ⅓ of the metacarpal

Evaluation Criteria for PA Finger
• Entire finger and minimum ⅓ of metacarpal demonstrated
Some technologists will choose to include entire metacarpal on image
• Center field at PIP joint
• No rotation of phalanges
Equal concavity of both sides of phalanges
Equal amounts of soft tissue demonstrated on both sides of bone
• IP and MCP joints are open spaces
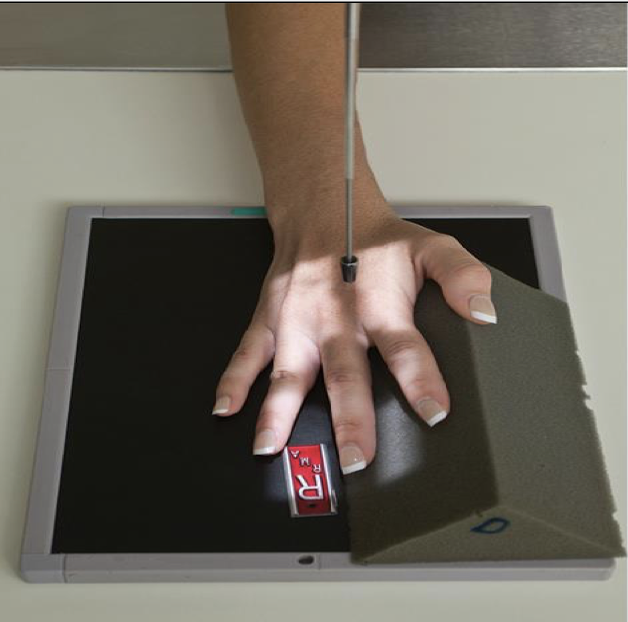
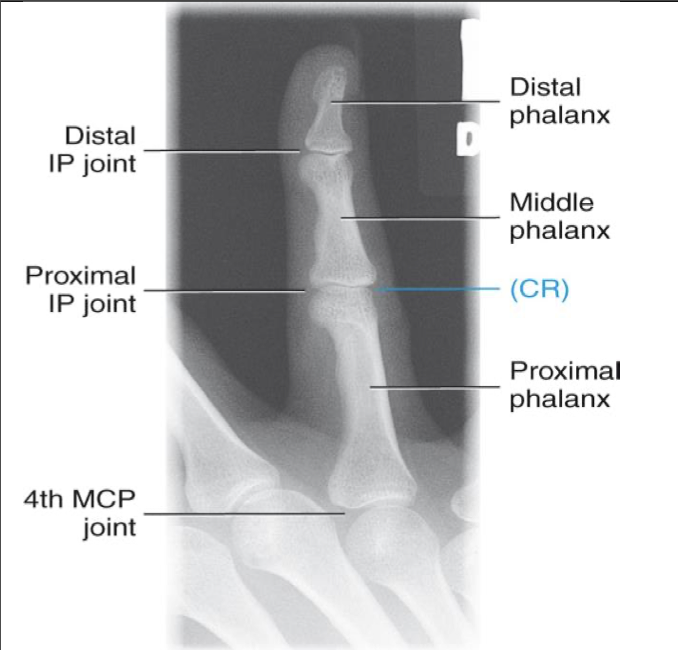
PA 45 °Oblique Finger ( 2nd-5th Digit)
Patient Position
Sitting at side or end of table
Arm (humerus) is abducted
Elbow is flexed 90 degrees
Forearm is resting on table
Part Position
Finger is rotated 45 degrees externally (thumb side up)
2nd digit can be medially rotated instead
Fingers spread slightly
Finger remains parallel to image receptor
Can use a positioning sponge
CR
X-ray beam collimated to include entire finger and at least ⅓ of the metacarpal

Evaluation Criteria for PA 45° Oblique Finger
• Entire finger and MCP joint demonstrated
• Increased concavity of lateral (thumb side) aspect of phalange
• Decreased concavity of other aspect
Note: opposite will be true for the 2nd digit if it was rotated internally rather than externally
• Center field at PIP
• IP and MP joints are open spaces
• Soft tissue demonstrated
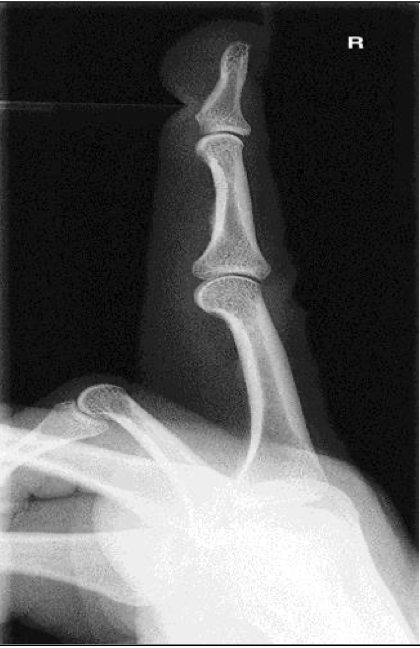
Lateromedial or Mediolateral- Finger ( 2nd-5th Digit)
Patient Position
Sitting at side or end of table
Arm (humerus) is abducted
Elbow is flexed 90 degrees
Forearm is resting on table
Part Position
Affected finger is straight with other fingers placed in a loose fist
May need a positioning aide to keep affected finger straight
Affected finger in a lateral position (“side- on”) and parallel
2nd finger may be positioned “thumb side” against the IR (mediolateral)
3rd-5th usually positioned with medial aspect of hand against the IR (5th finger against IR)
CR
Perpendicular to IR
Centered to proximal IP joint
Collimation
X-ray beam collimated to include entire finger and at least ⅓ of the metacarpal

Evaluation Criteria for Lateral Finger
• Entire finger and MCP joint demonstrated
• CR centered at PIP
• Collimation includes entire finger and at least MCP joint
• True lateral position
Anterior aspect is concave
Posterior aspect is straight or slightly convex
• Digit parallel to IR
IP and MP joints are open spaces
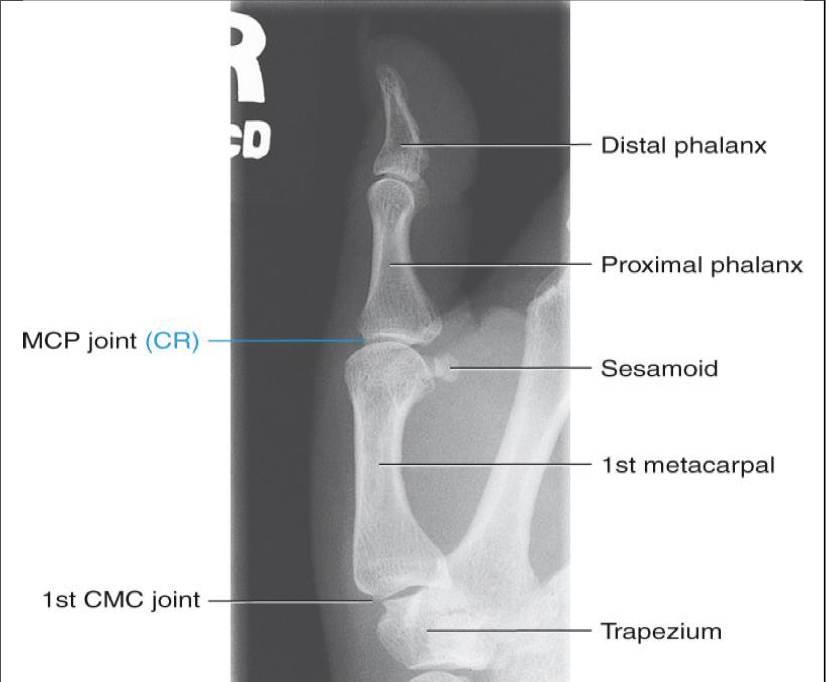
AP Thumb ( 1st Digit)
Patient Position
Sitting facing the table
Arm is extended and in extreme internal rotation
Part Position
Posterior surface ( back) of thumb is in contact with the IR
Fingers may need to be held back by other hand
CR
CR is perpendicular to first MCP joint
Collimation
Collimation to include entire thumb and trapezium

PA thumb
PA Projection: Alternative to AP if required

Evaluation Criteria for AP (PA) Thumb ( 1st Digit)
• Entire thumb demonstrated (including first CMC joint)
• No soft tissue overlapping MCP
• Center field at first MCP joint
• Must include trapezium
• No rotation of phalanges
• Equal concavity and soft tissue
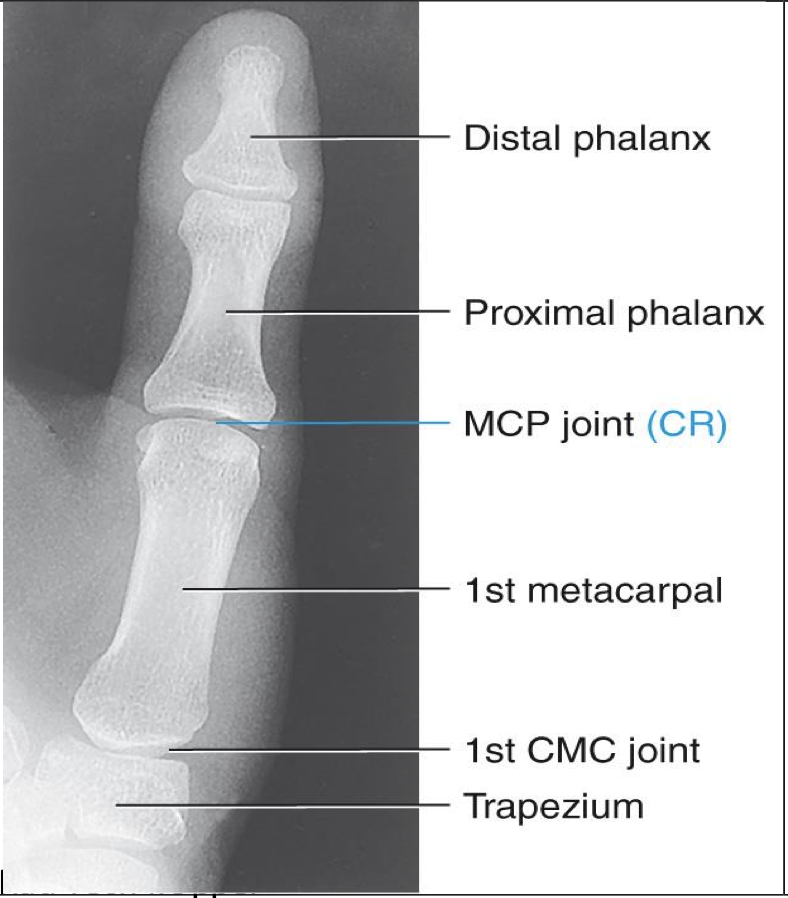
PA 45° Oblique Thumb ( 1st Digit)
Patient Position
Same as AP thumb or same as finger
Sitting facing table or alongside table
Part Position
Hand is placed palm down on the IR (pronated)
This naturally places the thumb in a 45 o oblique
Hand must be flat with no flexion in the fingers
Thumb is slightly abducted
CR
CR is perpendicular to 1st MCP joint
Collimation
Collimate to include all of thumb and trapezium
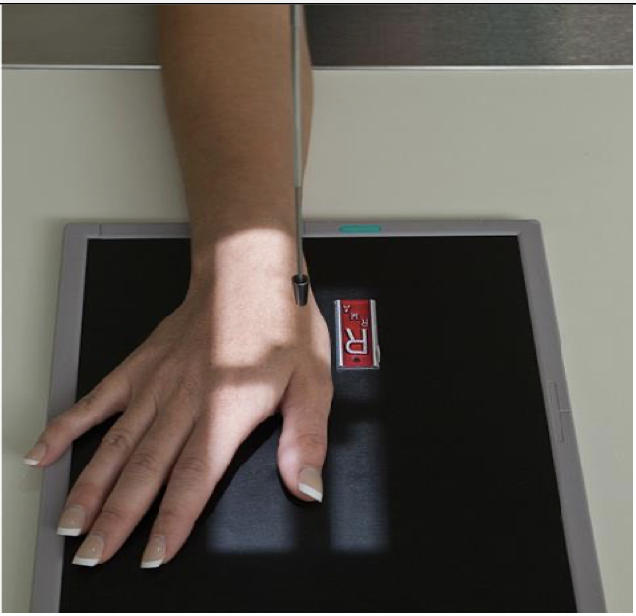
Evaluation Criteria for PA 45° Oblique Thumb ( 1st Digit)
• Entire thumb demonstrated including trapezium and CMC joint
• Joints partially open as in 45° oblique
• Increased concavity of phalanges on side facing fingers
• Center of field at first MCP joint
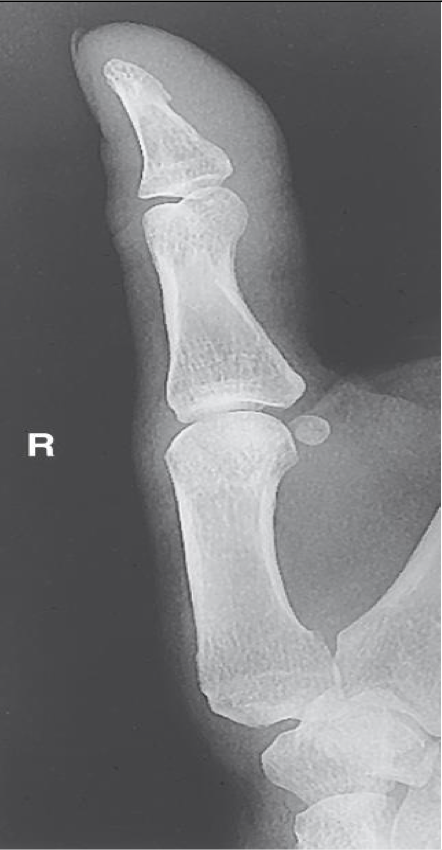
Lateral Thumb ( 1st Digit)
Patient Position
Same as PA & Oblique
Part Position
Place hand flat on IR ( same as oblique) and flex the fingers to “roll” thumb to a lateral position
Hand may be positioned in a loose fist as well
Rotate hand medially to place thumb in a true lateral
Thumbnail is the profile
Abduct thumb slightly
CR
Center to 1st MCP
Collimation
Collimate to include entire thumb and trapezium
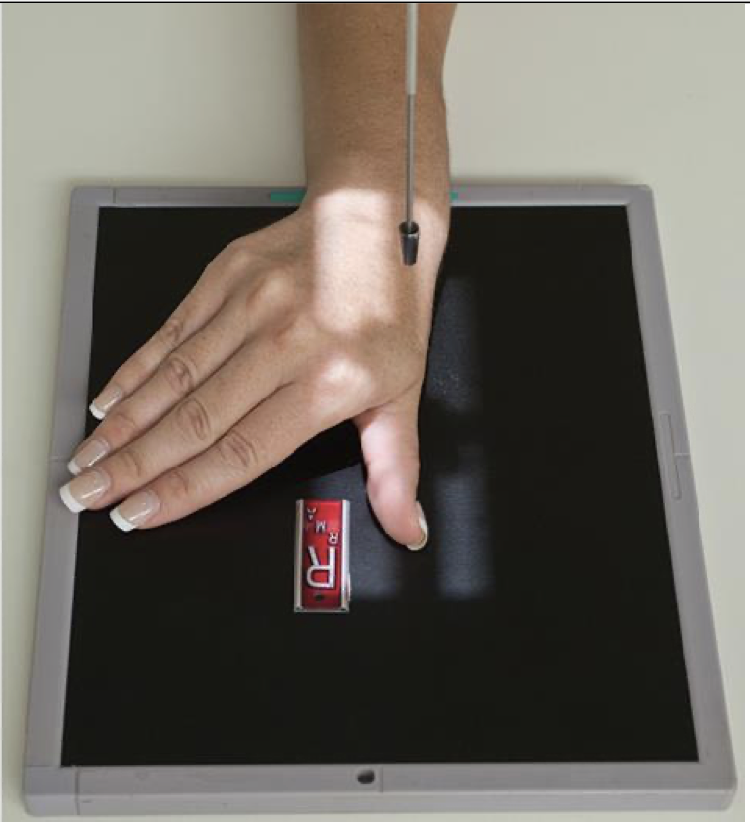
Evaluation Criteria for Lateral Thumb ( 1st Digit)
• Entire thumb demonstrated including trapezium
• Minimal overlap of bases of 1st and 2nd metacarpals
• Center of field at first MCP joint
• Increased concavity of phalanges on anterior (finger) side
• Decreased concavity on posterior side
PA Hand
Patient Position
Sitting at side or end of table
Humerus abducted; elbow flexed 90 degrees
Forearm resting on table
Part Position
Hand is placed palm down on IR ( pronated)
Fingers slightly spread
No rotation of hand
CR
Centered to 3rd MCP joint
Collimation
Include all carpals, metacarpals, phalanges and distal portion of radius and ulna

Evaluation Criteria for PA Hand
• Entire hand and carpals demonstrated
• Center of field at 3rd MCP joint
• MCP and IP joints are open
• Equal concavity of phalanges and metacarpals
• Slight overlap of bases of the 2nd to 5th metacarpals
• No overlap of heads of the 2nd to 5th metacarpals
• Minimum of 2.5cm (1”) of radius & ulna included
PA (external) 45 degree Oblique Hand
Patient Position
Sitting at side or end of table
Arm (humerus) is abducted
Elbow is flexed 90 degrees
Forearm is resting on table
Part Position
Hand is obliqued 45 degrees externally ( pinky down)
Fingers should be kept parallel to IR
When fingers are not of interest; fingers may be flexed and placed on IR
CR
Centered to 3rd MCP joint
Collimation
Include all carpals, metacarpals, phalanges and distal portion of radius and ulna
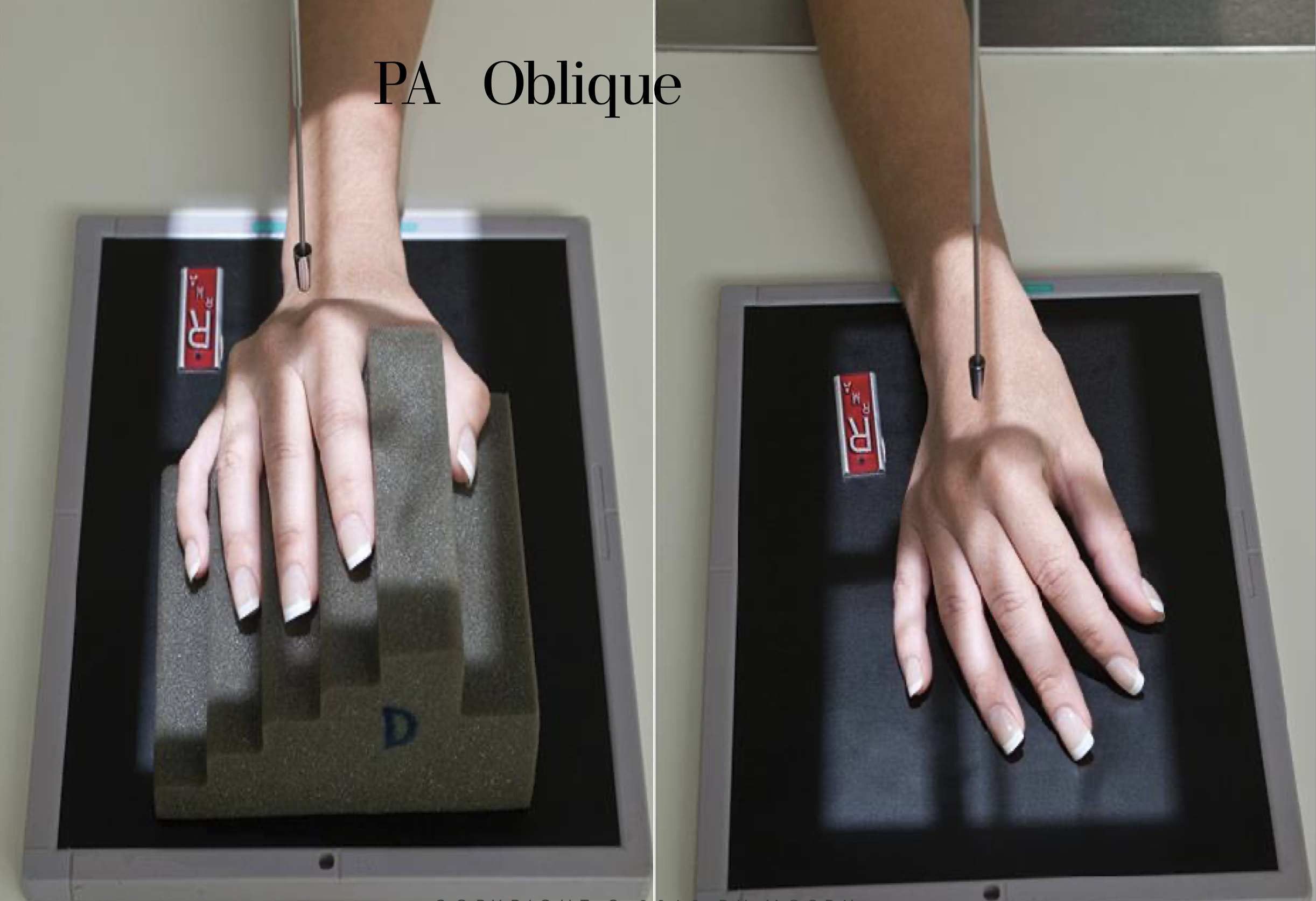
Evaluation Criteria for PA 45 degree Oblique Hand
• Entire hand and carpals demonstrated
• Midshafts of metacarpals should not overlap
• Heads of 3rd,4th,5th metacarpals are slightly overlapped
• Minimal overlap of heads of 2nd & 3rd
• MCP and IP joints are open ( if fingers were kept parallel)
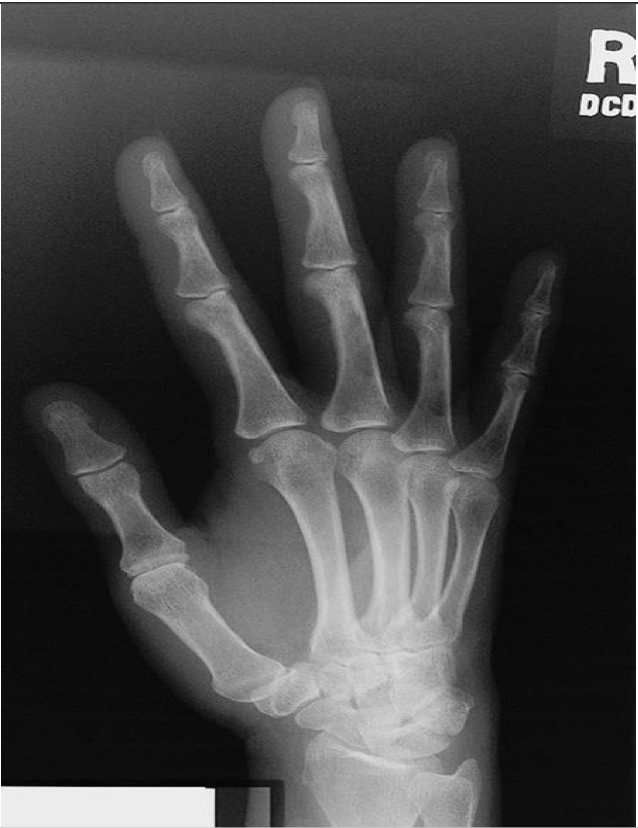
Lateral ( fan) Hand-Lateromedial Projection
Patient Position
Sitting at side or end of table
Arm (humerus) is abducted
Elbow is flexed 90 degrees
Forearm is resting on table
Part Position
Hand is placed in a lateral position with the medial aspect ( pinky side) of hand on the IR
Fingers & thumb are spread out like a “fan”
Phalanges are kept parallel to IR
Metacarpals are superimposed
** Use metacarpals to judge accuracy of positioning not the radius and ulna
CR
CR centered to 2nd MCP
Collimation
Include all carpals, metacarpals, phalanges and distal portion of radius and ulna
Evaluation Criteria for Lateral Hand
• Entire hand and carpals demonstrated as well as at least 2.5 cm ( 1”) of radius & ulna
• Centered at second MCP joint
• Fingers equally separated
• Metacarpals superimposed
• Radius and ulna superimposed or ulna is slightly posterior
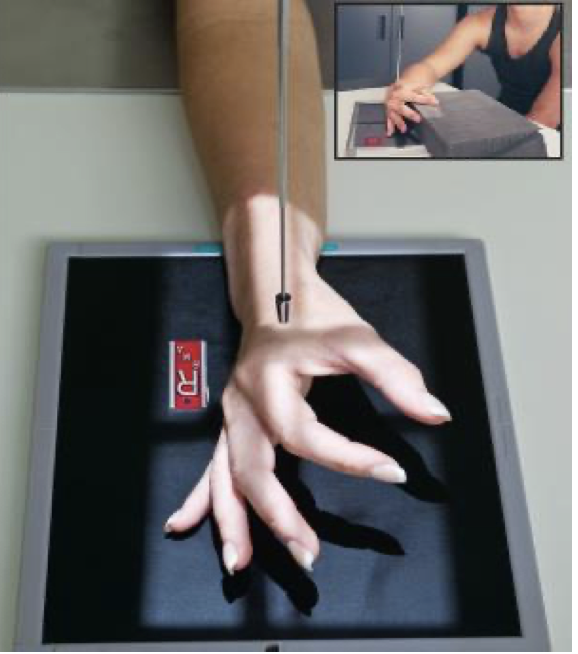
Lateral Hand- Extension/Slight Flexion
Same basic positioning and centering as “fan” lateral
Fingers are extended and superimposed
May be used for detection of foreign bodies or to better visualize anterior/posterior displacement fractures of the metacarpals
Fingers can be flexed slightly if extension is too painful
Thumb is in a PA

Bilateral AP Oblique hands “ Ball Catchers”
- Special projection for early detection of rheumatoid arthritis and fractures at the base of the 5th metacarpal
- Both hands are imaged together
- This projection is usually substituted for the PA oblique
Patient Position
Sitting facing the table
Part Position
Both hands ;with posterior aspect against the IR
Hands internally obliqued 45⁰
Fingers extended ( can be slightly flexed)
Thumb slightly abducted to prevent superimposition over metacarpals
Note: this can be difficult for patients with advanced disease
CR
Centered between hands @ level of MCP’s
Collimation
Same as PA /PA Oblique
Evaluation Criteria for “ Ball Catchers”
• Bilateral hands in 45° oblique position
• Midshafts of second to fifth metacarpals and base of phalanges not overlapped
• Thumb not superimposed over metacarpals
• MCP joints should open
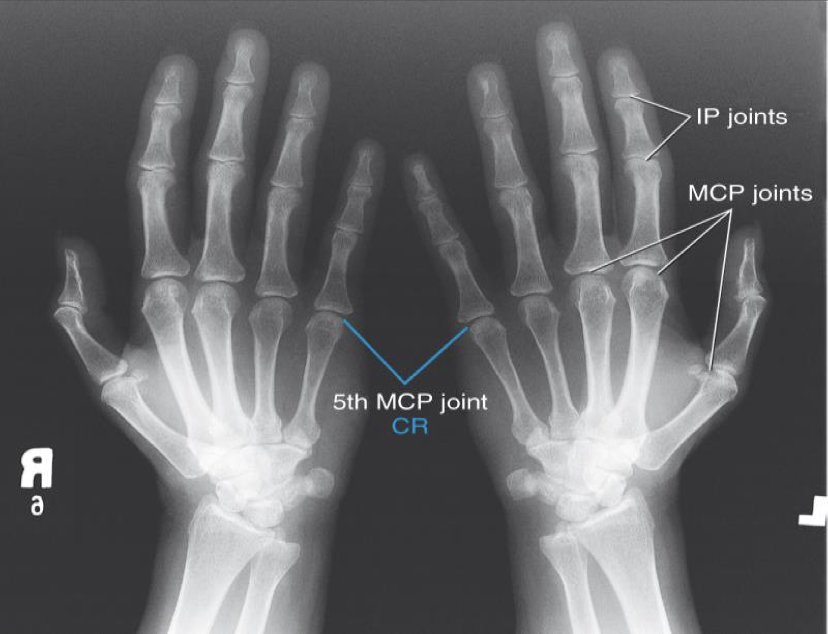
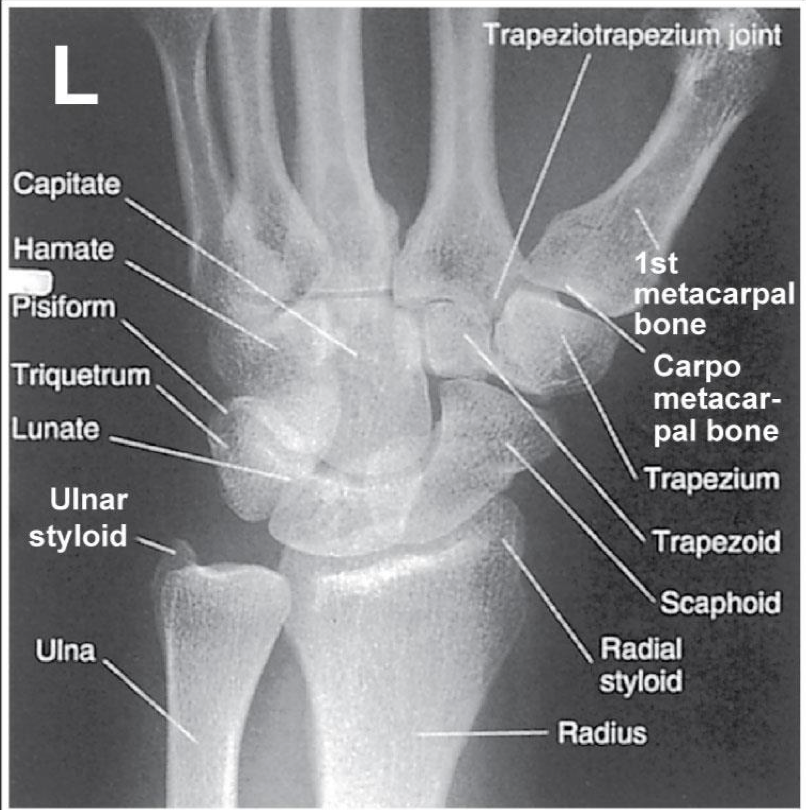
PA Wrist
Patient Position
Sitting alongside or end of table
Humerus abducted & elbow flexed 90 degrees
Elbow, forearm, wrist and hand are resting on table
Shoulder and forearm/wrist should be at the same level
May need to raise the table or support the IR on a sponge etc
Part Position
Wrist is placed on the IR with hand pronated
Mid-carpal area centered to the IR
Arch hand slightly(10-15 o ) to place carpal area in close contact with the IR
CR
Perpendicular to IR
Centered to mid carpal area
Collimation
include all carpal bones, distal radius & ulna and proximal metacarpals
1/3 of metacarpals and 1/3 of forearm included
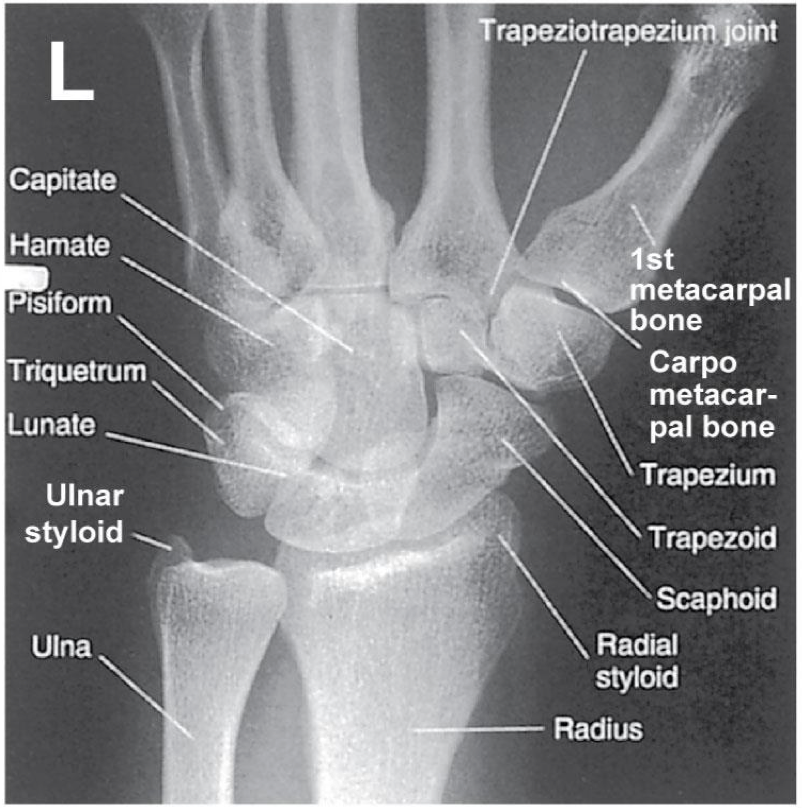
Evaluation Criteria for PA Wrist
• Distal radius/ ulna and carpals demonstrated
• Ulnar styloid process in profile
If humerus is not abducted & elbow flexed: the ulnar styloid process will not be in profile
• Open (or near open) radioulnar joint
• Center of field at midcarpals
• Long axis of 3rd metacarpal in line with long axis of forearm
• No rotation
• Exposure factors
Good soft tissue
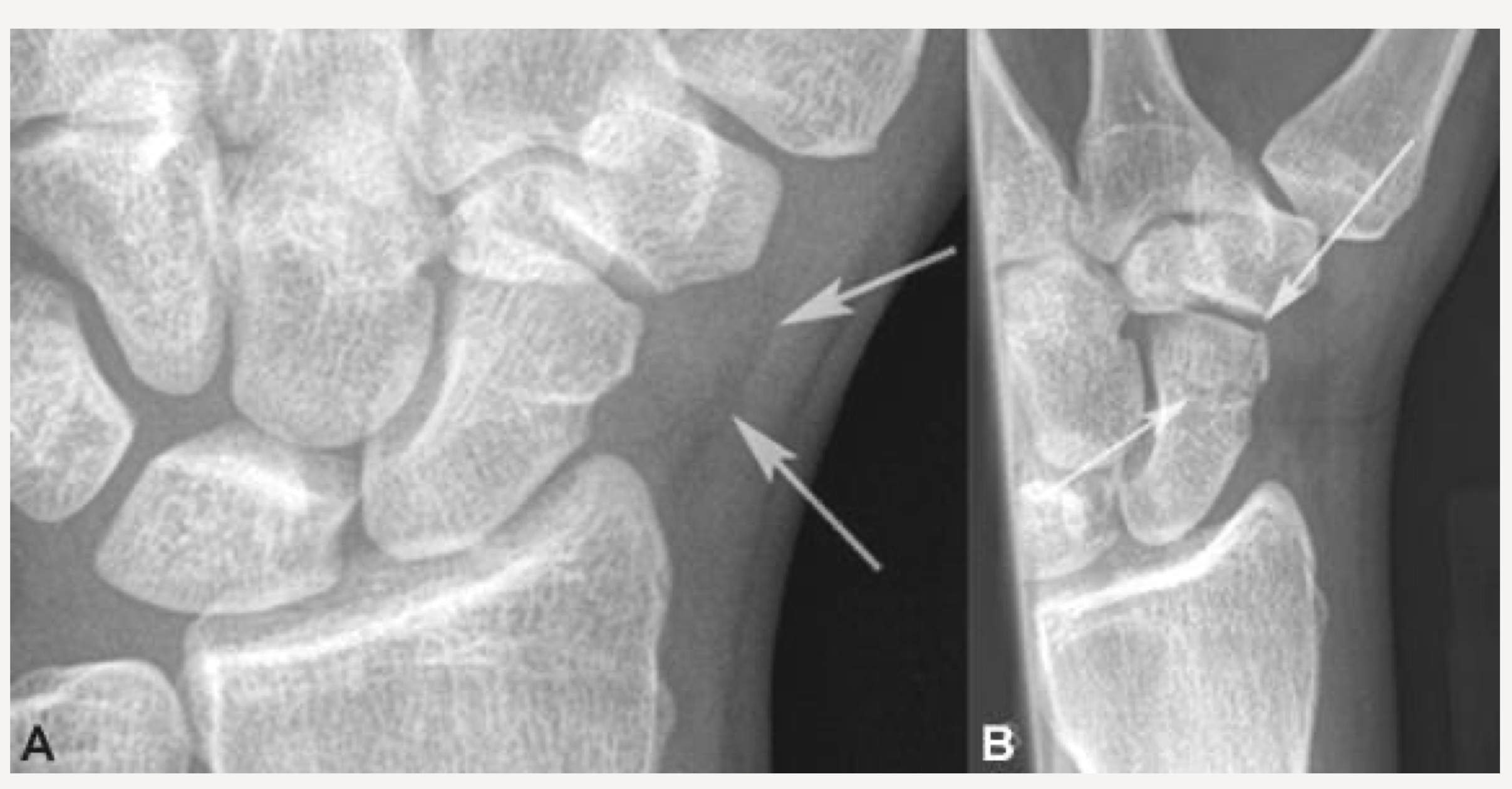
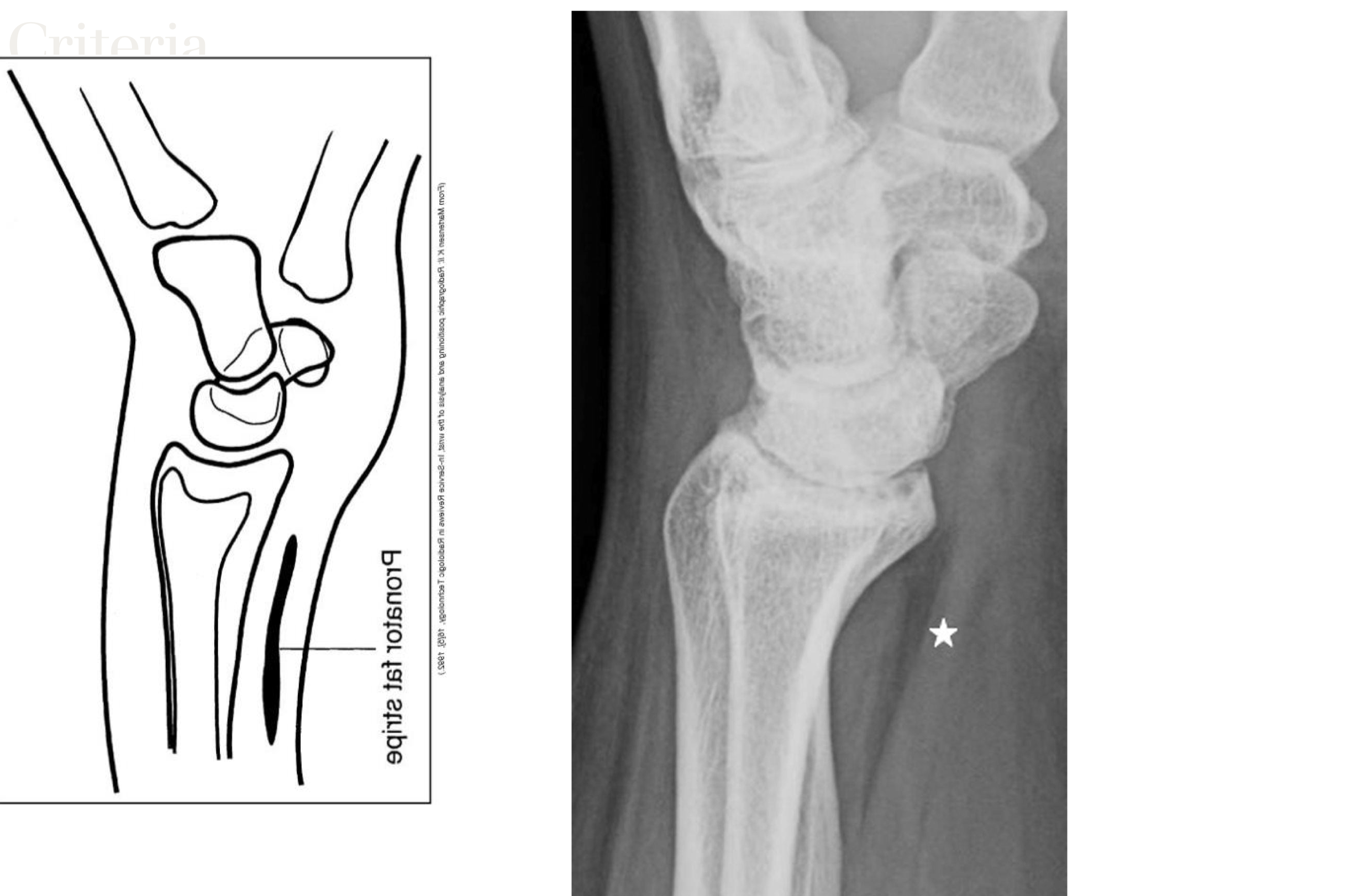
Should demonstrate scaphoid fat stripe
scaphoid fat stripe
looks black, sign of fracture or dislocation. On PA and oblique wrist projections
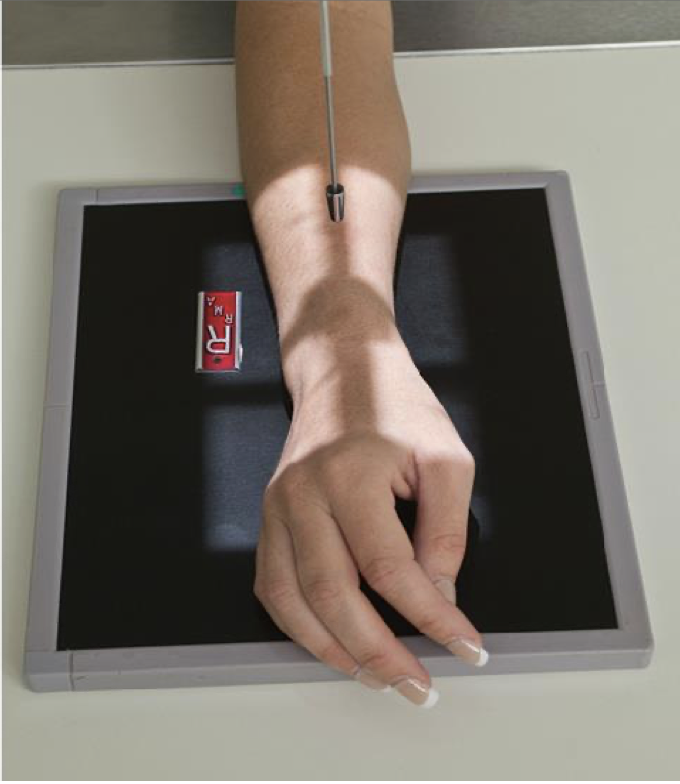
PA 45 degree Oblique Wrist
Patient Position
Same as PA Wrist
Part Position
Hand is pronated and wrist is rotated 45 o laterally
Thumb side “up”
Hand should be arched slightly
Long axis of 3rd metacarpal in line with long axis of forearm
CR
Centered to mid-carpal region
Collimation
Same as PA Wrist
Evaluation Criteria for PA 45 degree Oblique
• Distal radius, ulna, and carpals demonstrated
• Radius & ulna partially superimposed
slight overlap of metacarpals
• Center of field at midcarpals
• Trapezium and trapezoid seen in its entirety
• Scaphoid is minimally superimposed by trapezoid & capitate
• Exposure factors: soft tissue + bony detail
3rd metacarpal lines up with middle of wrist
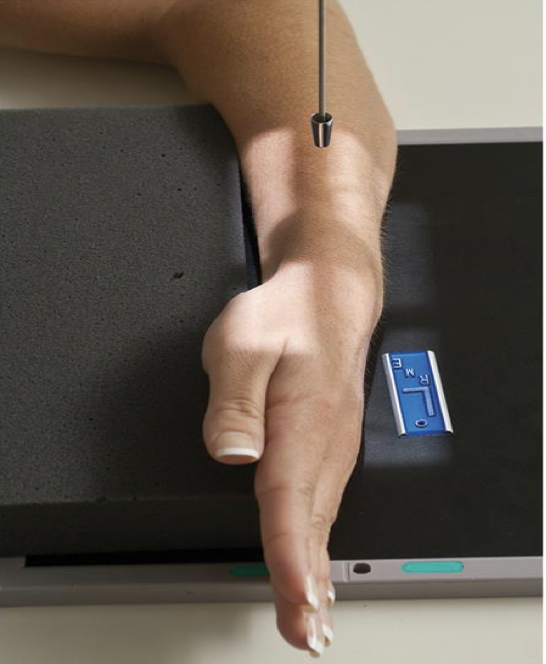
Lateral Wrist-Lateromedial Projection
Patient Position
Same as PA & PA Oblique Wrist
Part Position
Wrist is placed on the IR in a true lateral with thumb side up ( lateromedial)
Use the radius & ulna to determine “true” lateral ; not the hand
First metacarpal is parallel to forearm
CR
Centered to mid-carpal region
Collimation
Same as PA Wrist
Evaluation Criteria for Lateral Wrist
• Distal radius, ulna, and carpals demonstrated
• Radius and ulna are superimposed
• Metacarpals nearly all superimposed
• Ulnar styloid in profile posteriorly
• Distal margins of scaphoid and pisiform are aligned
• Center of field at midcarpals
• First metacarpal parallel to radius/ulna
• Exposure factors demonstrate the pronator fat stripe
pronator fat stripe
on prone/anterior side. Always present
FOOSH
fall on outstretched hand, often causes scaphoid fracture
why does a fractured scaphoid become more apparent after it occurs
it can cut off the blood supply. Also once bony callus starts to form
PA/PA Axial Scaphoid-Ulnar Deviation
Patient is positioned same as PA wrist except hand is flat on IR
Wrist is in ulnar deviation
Forearm remains stationary
Hand is deviated towards the ulna
1st metacarpal is aligned w/ radius
CR centered to scaphoid
2cm distal & medial to radial styloid process
- Base of anatomical “snuff box”
Collimation can be closer than for “regular” PA wrist
CR may be angled toward the elbow
10-15 o or 20° (Stetcher Method)
Other Positioning Modifications for Scaphoid
Clenched fist (done at QEH, make fist to straighten scaphoid, and ulnar deviate)
Elevated Hand/Wrist
Multiple CR angles
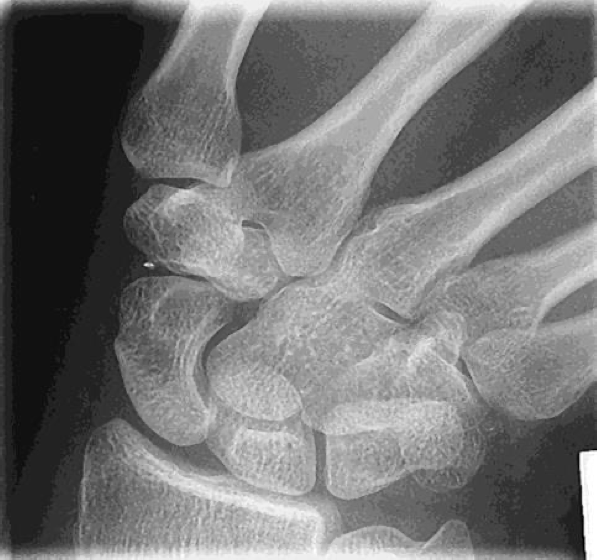
evaluation criteria for PA/PA Axial Scaphoid-Ulnar Deviation
Scaphoid clearly seen without superimposition
10° to 15° CR angle (elongates scaphoid)
Scaphoid fat stripe demonstrated
1st metacarpal is aligned with the long axis of the forearm
Indicates proper ulnar deviation
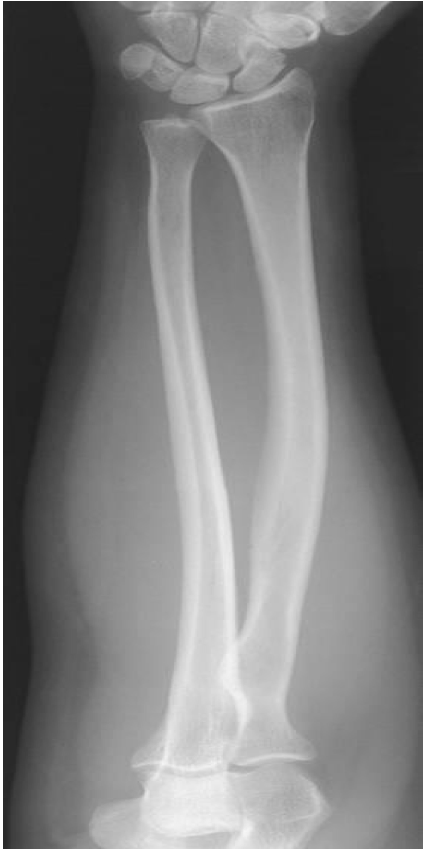
AP Forearm
Patient Position
▪ Sitting at side or end of table
▪ Arm extended straight out from body with palm up
▪ Entire upper limb should be at same height
Part Position
▪ Place forearm on IR with hand supinated
▪ Lean patient slightly laterally to place forearm in true AP
CR
▪ Perpendicular to mid-forearm
Collimation
▪ Include carpals and distal humerus
▪ 3-4 cm (1-1.5 in) of distal wrist and humerus included
Evaluation Criteria for AP Forearm
• Carpals to distal humerus included
• Humeral epicondyles are in profile.
• Only slight, if any, superimposition of distal radioulnar joint
• Radial head, neck and tuberosity are slightly superimposed over the proximal ulna
• Open space b/w shafts of radius and ulna
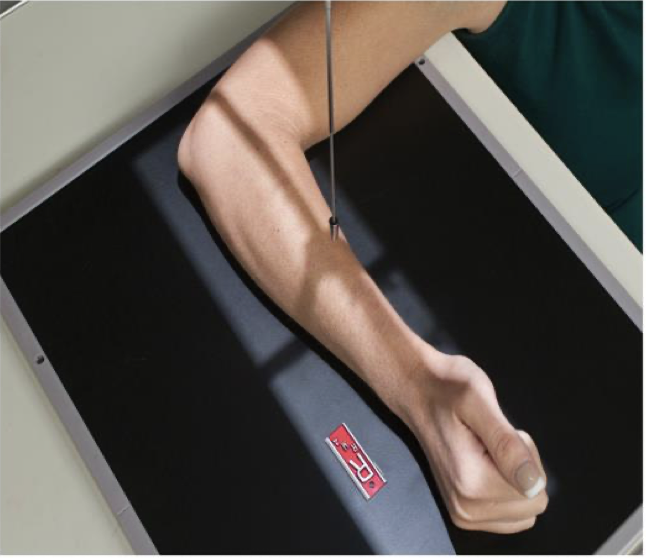
Lateral Forearm -Lateromedial Projection
Patient Position
Similar to wrist
Patient sitting at side or end of table
Humerus abducted, elbow flexed 90 o
Entire upper limb at same height
Part Position
Wrist is placed in a lateral
Thumb side up (lateromedial)projection
CR
To midforearm
Collimation
o Same as for AP projection
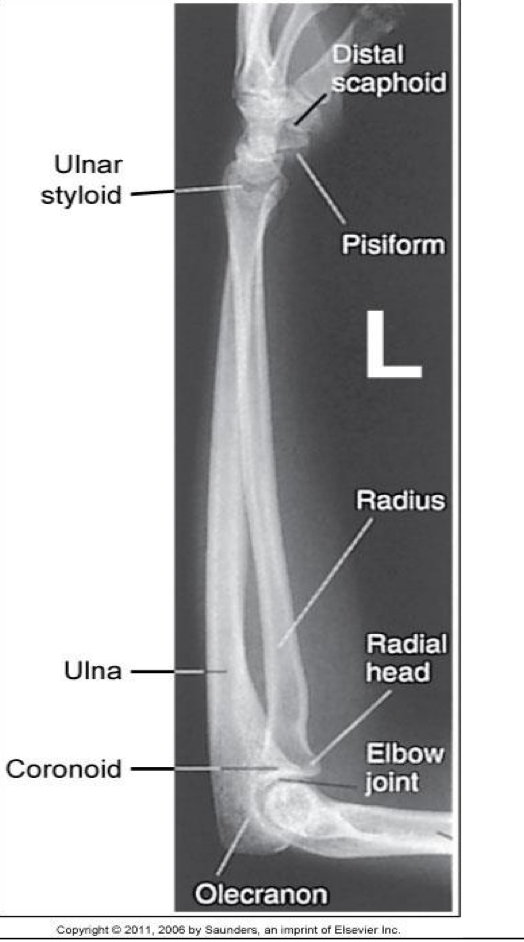
Evaluation Criteria for lateral forearm
• Carpals and distal humerus included
• Elbow flexed 90°
• Head of ulna superimposed over radius
• Radial head superimposed by coronoid
• Radial tuberosity is superimposed over medial radial shaft
• Humeral epicondyles are superimposed
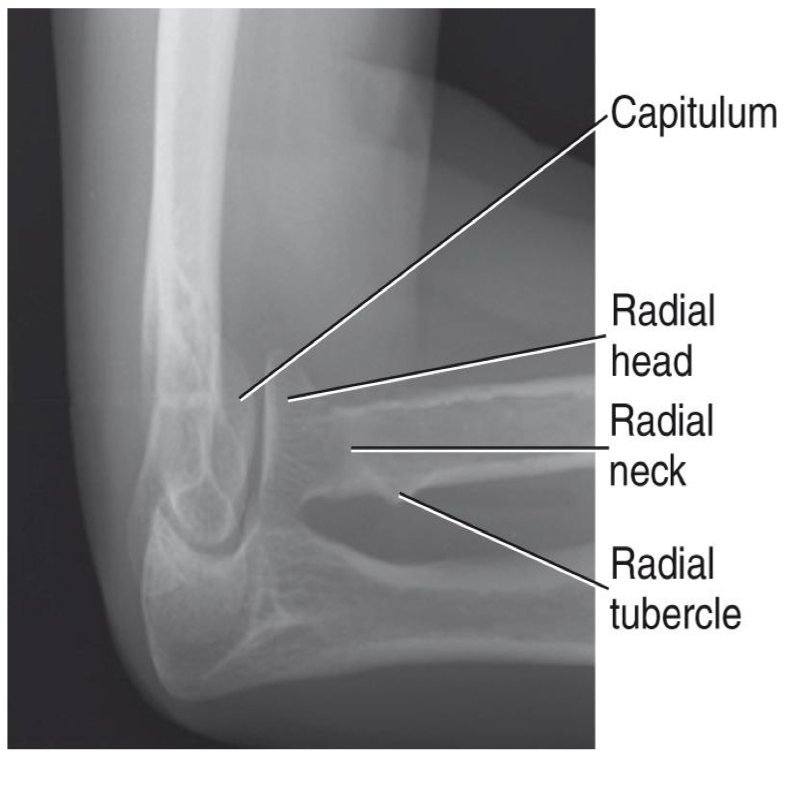
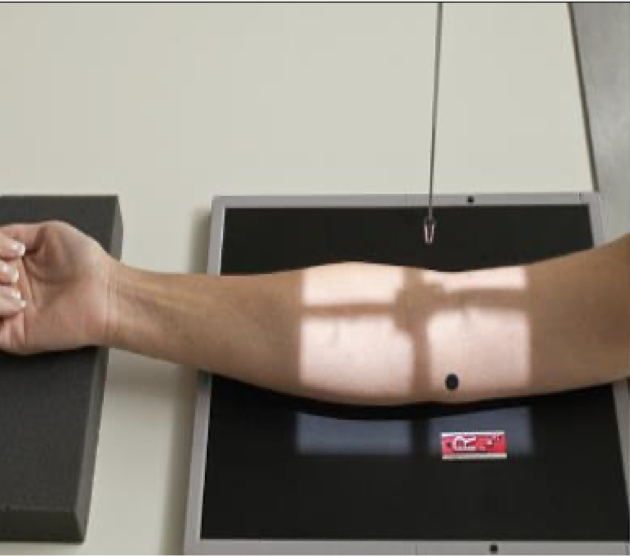
AP Elbow
Patient Position
▪ Sitting at end or side of table
▪ Arm fully extended; hand supinated; entire upper limb at same height
▪ If hand is not supinated: radius & ulna are crossed
Part Position
▪ Place elbow on IR in a true AP – Humeral epicondyles equal distances from the
IR
▪ Patient may need to lean laterally
CR
▪ Perpendicular to elbow joint
Collimation
▪ To include distal humerus and proximal radius/ulna
Evaluation Criteria for AP elbow
• Radial head, neck& tuberosity are slightly (approx. 0.6 cm) superimposed over the proximal ulna
Medial rotation causes too much superimposition
Lateral rotation causes too little superimposition
• Radial tuberosity in profile medially
• Olecranon located in the olecranon fossa
• No rotation of humeral epicondyles
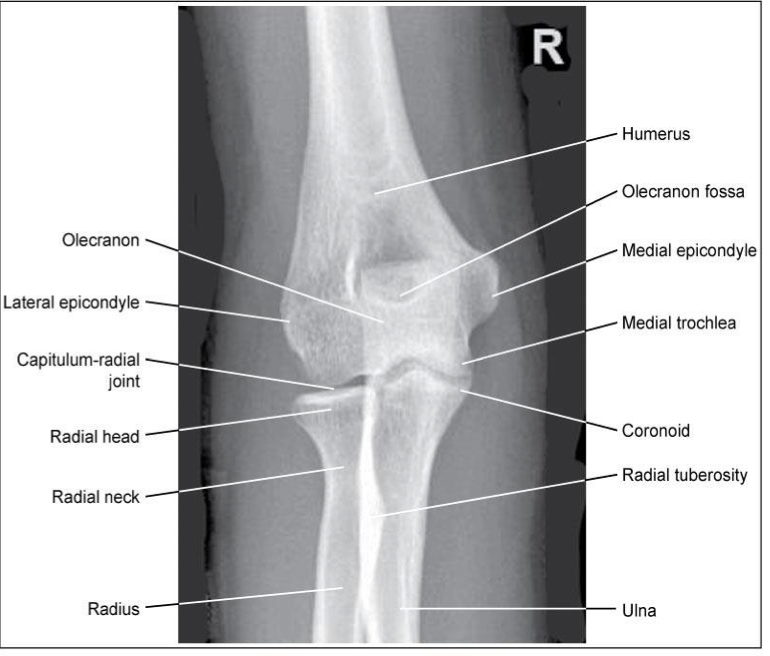
Lateral Elbow -Lateromedial Projection
Patient Position
▪ Sitting alongside or end of table
▪ Humerus abducted
▪ Entire upper limb must be at same height
Part Position
▪ Elbow flexed 90
▪ If elbow is not flexed 90, the posterior fat pad is visible**
▪ Wrist in a lateral; thumb up
▪ May need to elevate wrist slightly to keep elbow lateral
CR
▪ To elbow joint (4cm medial to olecranon process)
Collimation
▪ Same as AP
▪ MUST include soft tissues of entire elbow
Evaluation Criteria
• Three concentric arcs visible on distal humerus
Trochlear sulcus ( small, central arc)
Capitulum ( mid-sized arc)
Medial trochlea ( largest arc, outermost)
• Olecranon process in profile
• Humeral epicondyles superimposed
• Radial head partially superimposed over coronoid
• Radial tuberosity is superimposed over medial radial shaft
• Appropriate exposure factors
• Fat pads must be visible
• Elbow flexed 90
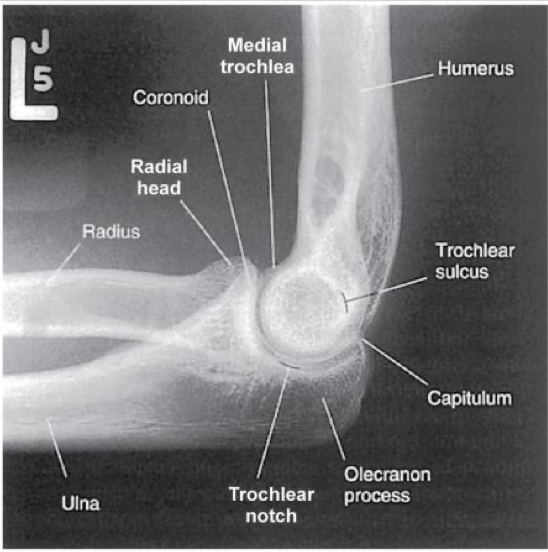
what are the 3 concentric arcs seen in a lateral elbow
trochlear sulcus (innermost), Capitulum, and trochlea (outermost)
Lateral Elbow- Fat Pads
▪ Three fat pads of interest on a lateral elbow
▪ These soft tissues structures play a vital role in accurate image interpretation
▪ Improper positioning can distort these fat pads
▪ Anterior fat pad & supinator should be visible on all lateral images
▪ Distortion of these fat pads may indicate joint injury
▪ Posterior fat pad is not visible on normal lateral elbow
▪ If visible, this can indicate joint injury
▪ Improper positioning may also result in visualization - Elbow MUST be flexed 90⁰!
▪ The posterior fat pad sits within the olecranon fossa when elbow is flexed 90°
▪ Swelling or bleeding from an injury forces the fat pad out of the olecranon fossa (see
below)
D= Posterior Fat Pad
C= Anterior Fat Pad
E= Supinator Fat Pad

Medial Oblique elbow -Internal Rotation
moure superimposed
• Coronoid process in profile
• Trochlea and medial epicondyle in partial profile
• Radial head superimposed on ulna

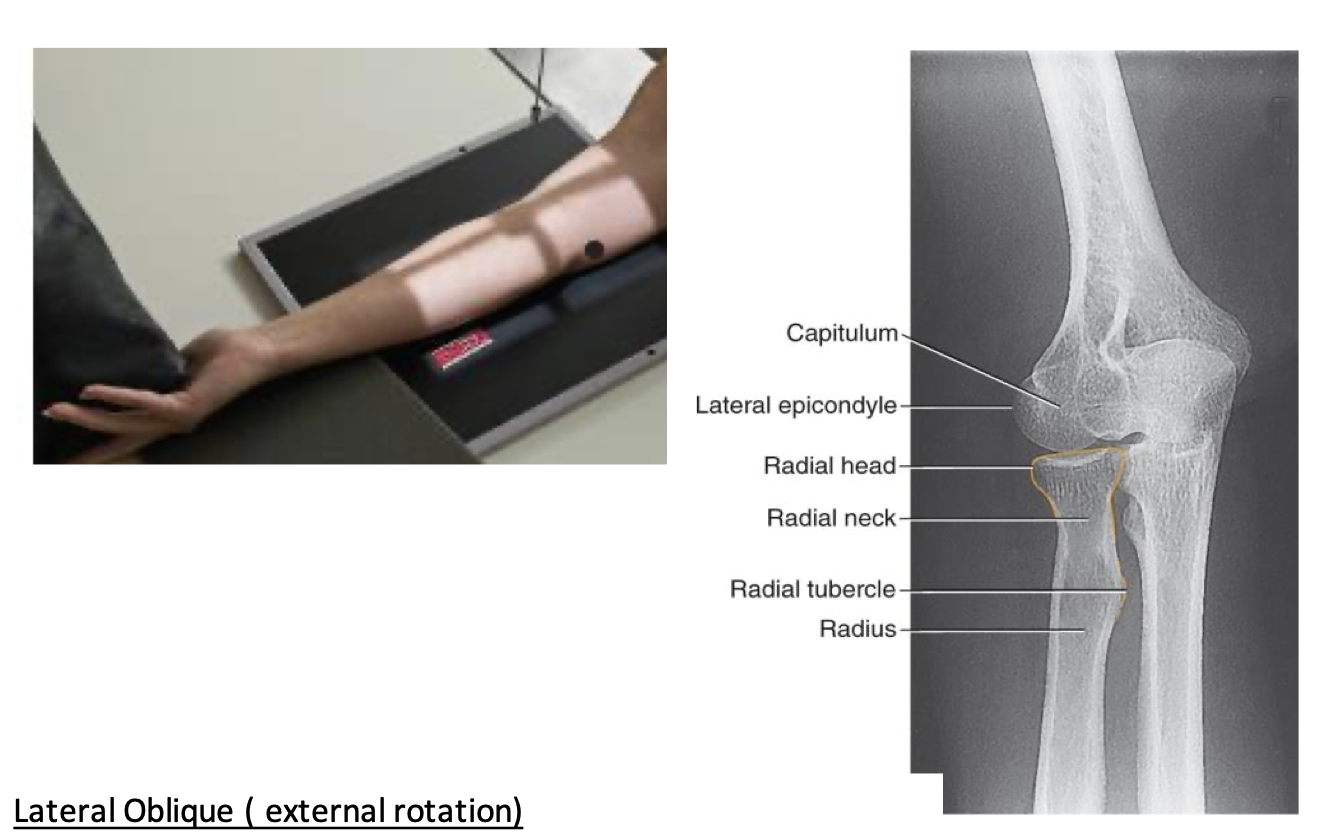
Lateral Oblique-External Rotation
• Radial head, neck, and tuberosity in profile and free of superimposition
• Lateral epicondyle and capitulum in profile
Lateral Elbow- Radial Head - Four Position Method
• Patient position
o Same as lateral elbow
• Four images acquired ( all on the same IR if possible) to show entire circumference of radial head
• Hand positions
supinated (maximum external location)
Lateral
3. Pronated
4. Internal rotation

Axial Lateral Elbow- Radial Head Coyle Method
• Patient and part positioned as for a lateral elbow
• Hand is pronated NOT lateral
• CR 45° toward the shoulder
• For radial head
• Useful in trauma and when patient cannot oblique elbow
Evaluation Criteria for radial head
• Open joint space between radial head & capitulum
• Radial head, neck & tuberosity nearly free of superimposition
• Radial tuberosity facing posterior (indicating the hand is pronated)
• Humeral epicondyles will be distorted due to the CR angle