Lecture 9: Sensation and Perception
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Transduction
conversion of external energies or substances into a nervous system signal (inhibition or excitation)
Sense Receptors
transduce specific stimuli
Sensory adaptation
activation is highest when the stimulus is first detected, then sensory adaptation occurs
Perception
the process of organizing and interpreting sensory information
Psychophysics
the study of how we perceive sensory stimuli based on their physical characteristics
Absolute threshold
smallest stimulus energy needed for the nervous system to detect [50% of the time]
Gustav Ferchner
Suggests that human error increases as stimuli get weaker
Just noticeable difference
smallest change in intensity of a stimulus that we can detect 50% of the time
Weber’s law
the stronger the stimulus, the greater the change needed to detect
Signal detection theory
provides a way to detect and account for subjects’ biases
parallel processing
can attend to many senses at once
Bottom-up versus top-down processing (co-exist)
Bottom-up processing
sensory receptors register information about the external environment and send it up to the brain for interpretation
takes information and tries to make sense of it
Top-down processing
starts with cognitive processing in the brain
begins with some sense of what is happening and applies that framework to incoming information from the world
Perceptual sets
The relationship between a stimulus and its context
Perceptual constancy
size, colour, shape are consistent across conditions
Selective attention
process of focusing on on sensory channel and ignoring others
Filter theory of attention
theory that posits we can pay attention to important information while filtering out the rest
Dichotic listening task
Broadbent used this task to demonstrate his filter theory
Cocktail party effect
can pick out an important message in a conversation that does not involve us
Binding problem
how our brains take multiple pieces of information and combine them to represent something concrete
How light enters the eye
sclera
iris
Sclera
The white portion of the eye
Iris
opening that modifies the amount of light permitted through the pupil
Focusing light
Cornea
lens
Cornea
refracts light to focus it on back of eye
Lens
changes curvature (accommodation) to refract light onto back of eye
Changing light into neural activity
Retina
Fovea
Receptor cells (rods/cones)
Ganglion Cells
Retina
membrane at back of eye
Receptor cells
Contain photopigments that change on exposure to light
Rods: low levels of light
Cones: high acuity, colour vision
Ganglion cells
Axons leave the retina (at the blind spot), forming the optic nerve
Optic Nerve
propagates visual signals to the visual areas in the brain
Perception and the Visual Cortex
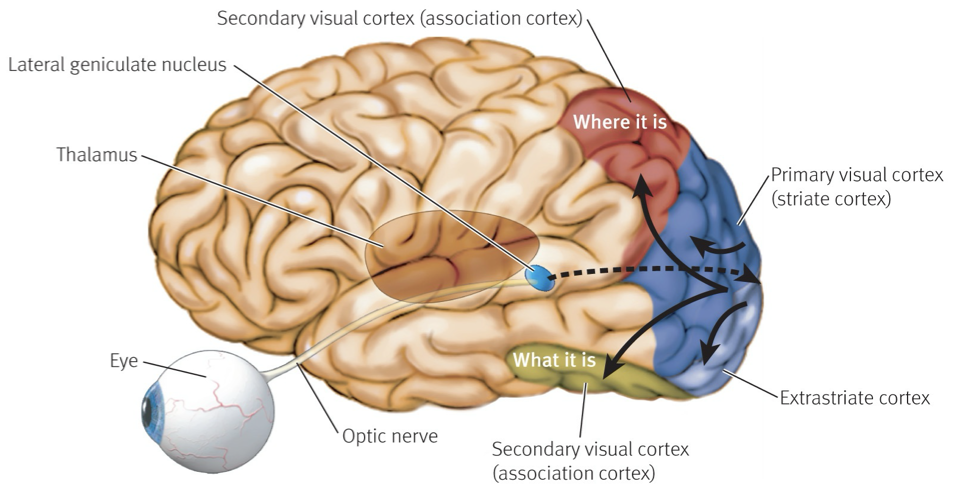
Visual Perception: Shape and Contour
Different cortical cells respond maximally to different types of stimuli
Detecting lines and edges
Simple cells and complex cells
Simple cells
Orientation-specific slits of light in a particular location
Complex cells
orientation-specific but less dependent on loaction
Feature detection
using minimal patterns to identify objects
Hierarchical model of processing
feature detector cells respond to increasing shape complexity with higher levels of cortical processing, from lines and edges to complex shapes and moving objects
Subjective contours
the brain fills in
Gestalt principles
the perception of objects as wholes within a context, not isolated lines and curves
We perceive objects as wholes when they display:
Proximity
Similarity
Closure
Symmetry
Figure-ground
Continuation
Pragnanz
Proximity
close together
Similarity
are similar
Closure
have missing contours
Symmetry
having symmetrical arrangement
Figure-ground
a central figure
Continuation
lines are seen as following the smoothest path
Pragnanz
reality reduced to the simplest form possible
Face recognition
extract key features, fill in from context and memory
cells in the lower temporal lobe fire in response to particular faces
Motion detection
brain compares visual frames
from there, it “estimates” what is moving
Colour
Theories of colour perception:
Trichromatic theory
Opponent process theory
Trichromatic theory
colour vision is based on our sensitivity to the three primary colours (red, blue, green)
Opponent process theory
colour vision is a function of complementary, opposing colours: red versus green or blue versus yellow
3D Relations
Monocular depth cues versus binocular depth cues
Monocular Depth Cues
Relative size
Texture gradient
Interposition
Linear perspective
Height in plane
Light and shadow
Motion parallax
Binocular Depth Cues
binocular disparity
binocular convergence
Present early in development
Infants between 6 and 14 months hesitate to crawl over the visual cliff used by Eleanor Gibson
Moon Illusion
the moon appears larger when it is near the horizon than when it’s high in the sky
The Ames Room
Trapezoidal room with slanted floor and ceiling, makes occupants appear to vary in height (exploits relative size principle)
Change Blindness
difficulty detecting obvious scene changes when eyes are moving, lights are flickering, or when watching a video
Synesthesia
a condition in which people experience cross-modal sensations