Physicochemical Properties
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is matter?
Any object that has weight and takes up space
What are the 3 states of matter?
1. Solid
2. Liquid
3. Gas
Molecules in the solid state are held together by ______?
intermolecular forces
↑ Temperature = (increase/decrease) energy?
increase (disruption of the lattice solids)
What is the triple point of a phase diagram?
point where all three phases (solid, liquid, gas) are in equilibrium
What is the process of freeze drying called?
Sublimation/Lyophilization (solid → gas; no heat applied)
Gas molecules collide with...?
- one another
- wall of container
How does gas exert pressure?
rapid motion of the molecules colliding
1. Volume increase = (increase/decrease) pressure
2. Volume increase = (increase/decrease) temperature
3. Temperature increase = (increase/decrease) pressure
1. decrease
2. increase
3. increase
What is Boyle's Law?
- relationship between volume & pressure
- PV = k
What is Charle's Law?
- relationship between volume & absolute temperature
- V = Tk
What is Gay-Lussac's Law?
- relationship between pressure & absolute temperature
- P = Tk
What is the Ideal Gas Law?
- relationship between pressure, volume, and absolute temperature
- refers to an ideal situation where no intermolecular interactions exist, collisions are perfectly elastic, no energy exchange
- PV = nRT
How would you find molecular weight from Ideal Gas Law?
1. substitute n = weight (g) / molecular weight (M)
2. PV = (g/M)(RT)
3. M = gRT / PV
Cooling a gas leads to a loss of...?
kinetic energy
Applying/Increasing pressure to a gas leads to what?
- turning into a liquid
- interaction increases and encourges Van der Waals interactions
T/F: Presence of Van der Waals forces means liquids are considered denser than gas?
True
Explain Vapor Pressure?
1. liquid is placed at a constant temperature
2. molecules break away from the surface of the liquid
3. pass into gaseous state
What is equilibrium/saturated vapor pressure?
- rate of molecules evaporating from liquid surface equals the rate of molecules condensing back into the liquid
- leads to boiling
- saturated vapor pressure = atmospheric pressure
What are the two types of solids?
1. crystalline
2. amorphous
T/F: Liquids have higher density than solids?
False (solids > liquids due to strongest molecular forces)
What are crystalline solids?
molecules are arranged in a fixed geometrical pattern (lattices; ex. NaCl, ice, diamond)
What are polymorphism?
- Crystalline solid occur in more than one crystal form (ex. albuterol)
- Will have different physical properties (melting point & solubility)
- Same molecule just different crystalline structure
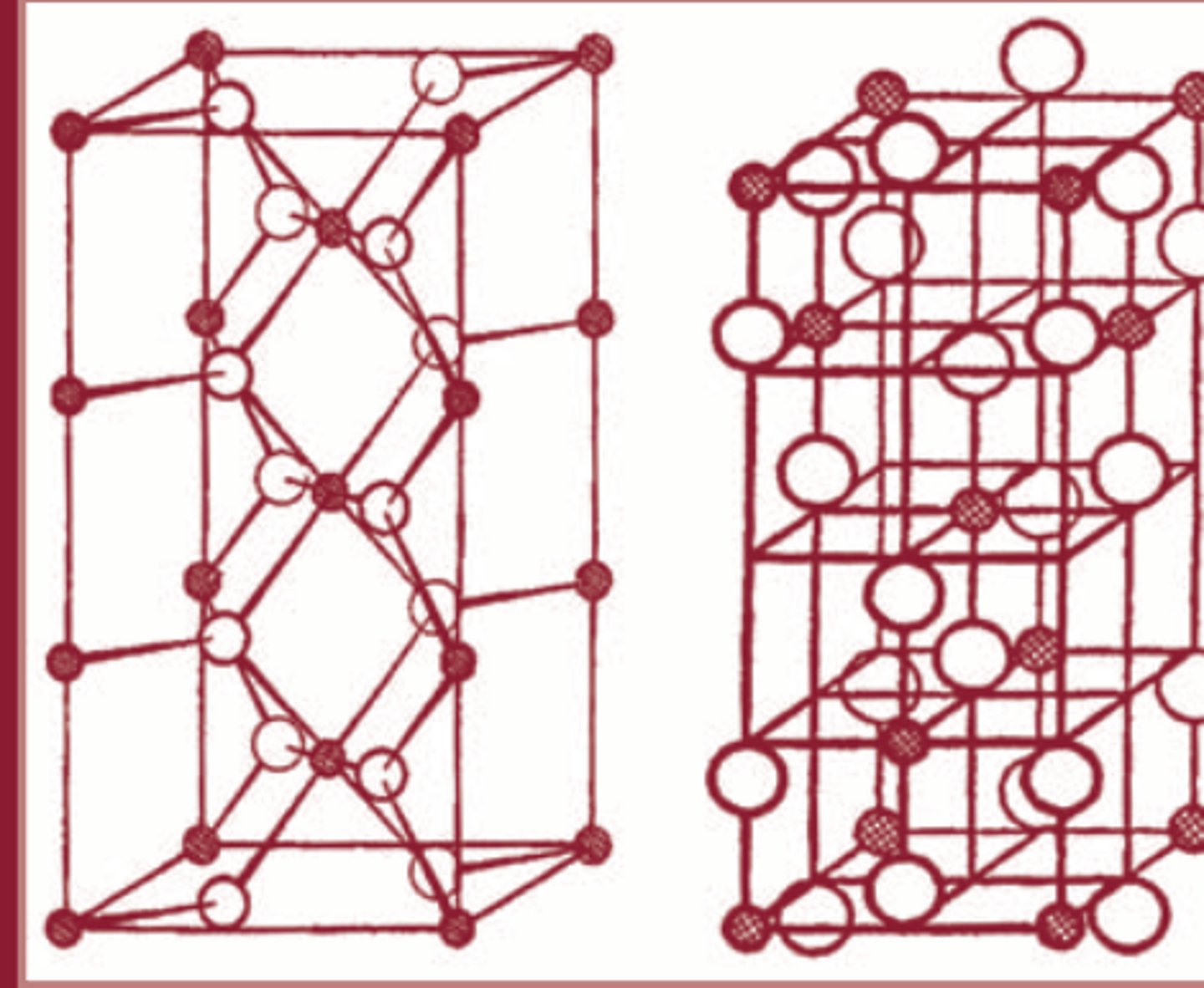
What are amorphous solids?
- molecules are arranged randomly (no lattices)
- also known as super-cooled liquids
- are not physiocochemically stable as crystals
- ex. graphite (amorphous form of diamonds)
Which one would be better if you desire quick onset of action, crystalline or amorphous solids?
amorphous