Envirothon Aquatics Quizlet
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
How much of Earth is covered by water?
2/3
How much of Earth's water is soil moisture?
3.8%
Unsaturated zone/Vadose zone/Zone of Aeration:
above the water table, pores filled with air
Water Table
the top of where the pores are filled with water, highest level of groundwater
Capillary Fringe
above water table, pores are somewhat filled b/c of adhesion + cohesion
Saturated zone/Phreatic zone
the region below the water table where pore space is filled with water
Porosity
Empty Pore Space/Total volume of geologic formation, affected by grain sorting, shape, compaction
Permeability
Rate at which water can flow through
-depends on size + connectivity of pore spaces
Aquifer
body of rock/unconsolidated sediment that stores water, permeable & porous. Saturated
-best aquifer is well sorted, well rounded, large particles
Unconfined Aquifer
no boundary, water table free to rise/fall
Confined/Artesian Aquifer
Aquifers covered by an impermeable and confining layer impeding water flow in or out, specific recharge zones, often under pressure
Aquitard
saturated, intermediate water holding capacity/permeability
Aquiclude
Saturated, relatively impermeable/low water holding capacity
Artesian Well
A well in which water rises because of pressure within the aquifer
Infiltration
water enters subsurface
Percolation
water flows through the ground
Interflow
subsurface runoff - sideways movement of water in unsaturated zone
Throughflow
interflow that returns to the surface
Hydraulic head
mechanical energy available, Elevation head + Pressure head
Potentiometric surface
surface that water would rise too if no pressure/confining surface
Soil Water
Water in unsaturated zone
As soil dries,
it is harder to remove water from it
The smaller the particles,
the more surface area = the more tension for equal amount of water
Field Capacity/drained upper limit
soil moisture left in soil after being drained for a few days.
Wilting point
soil water content when plants start to wilt
Plant Available water
field capacity - wilting point
Soil moisture deficit
amount of water (in mm) needed to fill soil back up to field capacity
Catchment/Watershed
area for which all the water flows into one waterbody
Divides
highest ridges that separate different catchments
Lotic
moving waters (rivers, streams)
Lentic
still waters (lakes, ponds)
Ephemeral
only flows after rainfall
Intermittent
only flows when water table is high (late spring-early summer)
Perennial
flows year round
Fastest location in a stream
just under the surface
Fastest location in a meandering stream
Thalweg/cut bank side of stream just under surface
Discharge
velocity x cross sectional area, Affected by gradient, channel size and shape, channel roughness and amount of water
Substrate
type of substance on the bottom of the stream
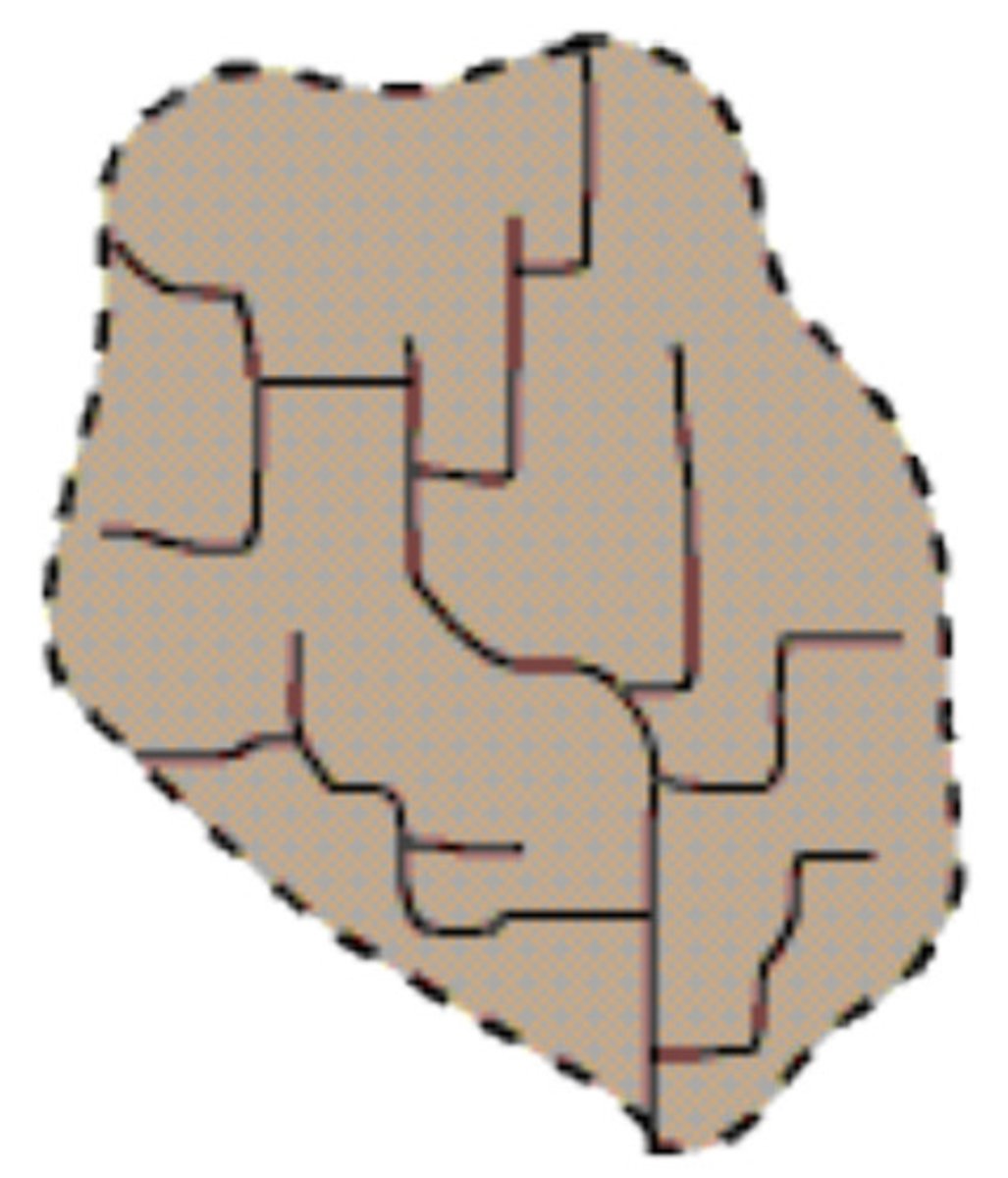
Rectangular
on substrate with rectangular joint
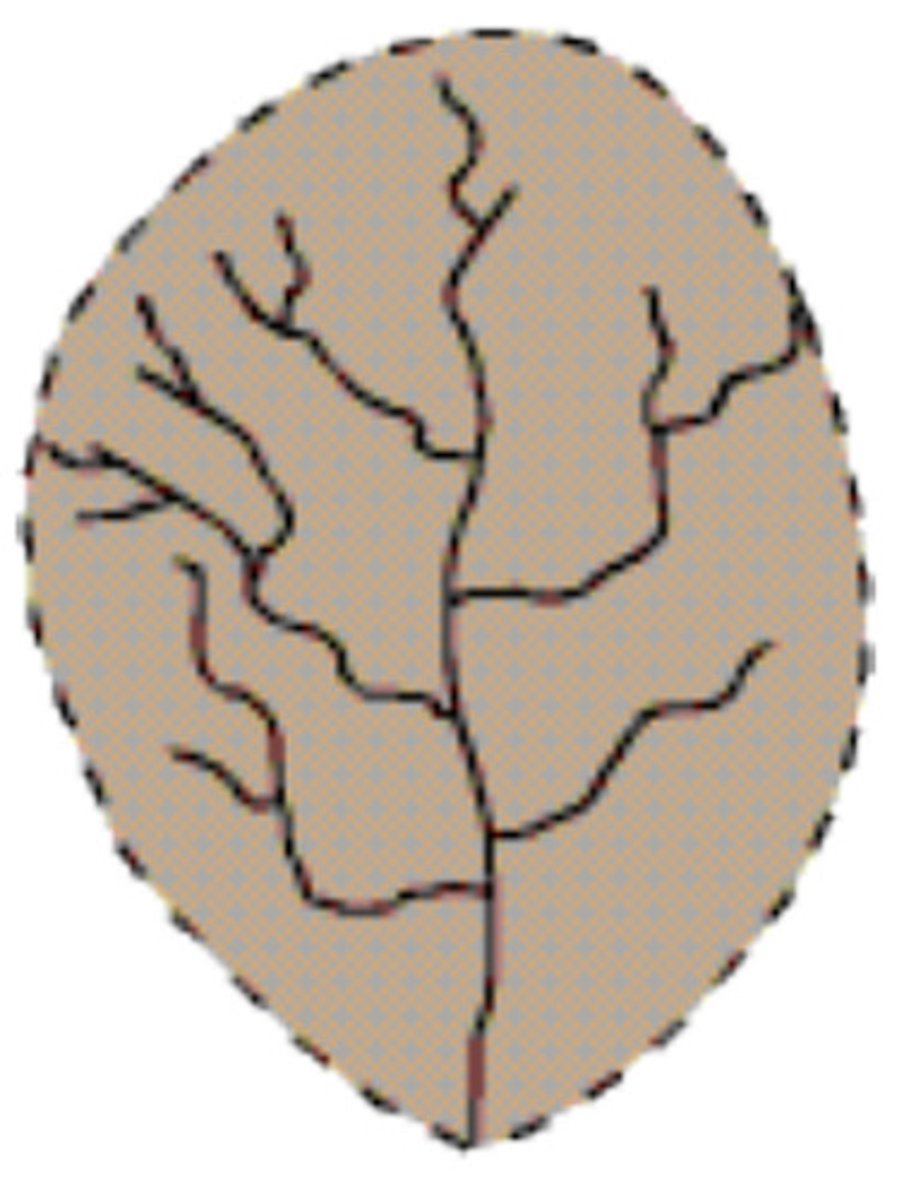
Dendritic
on uniform substrate with a gentle slope
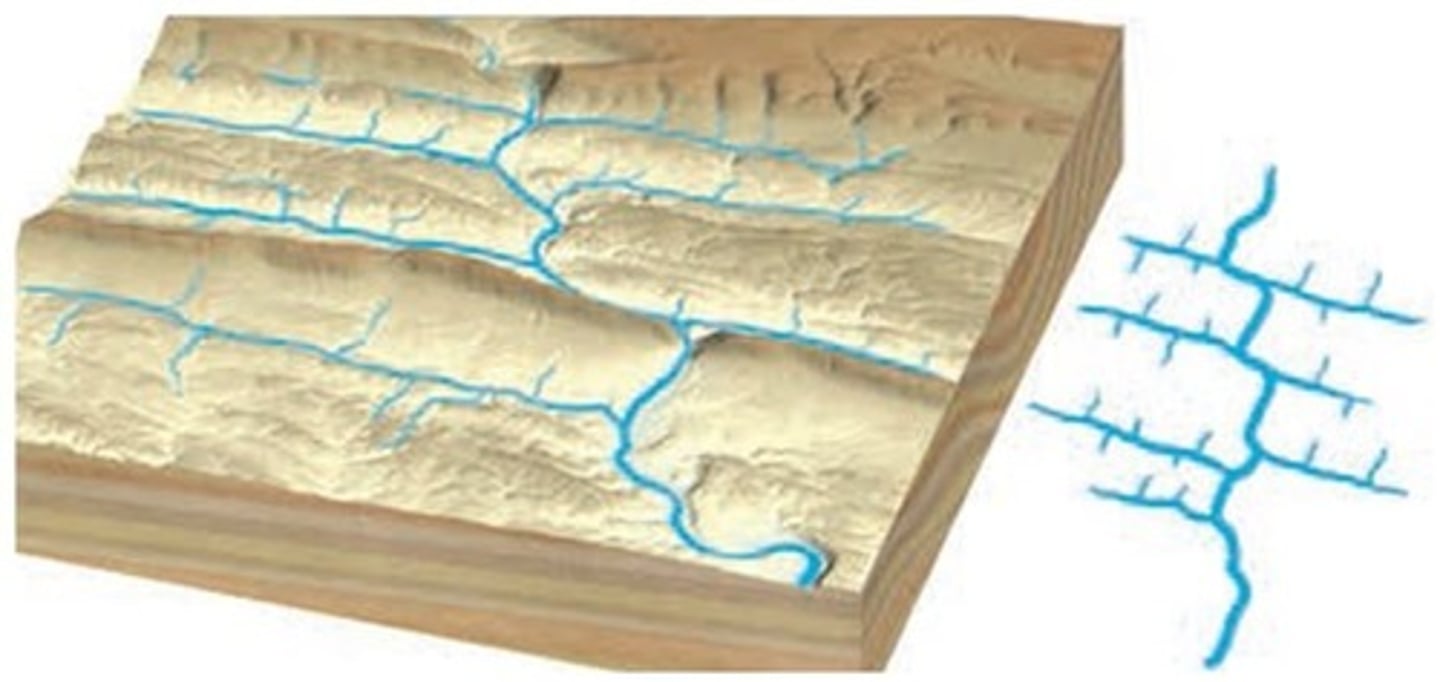
Trellis
substrate with parallel ridges/valleys from folding
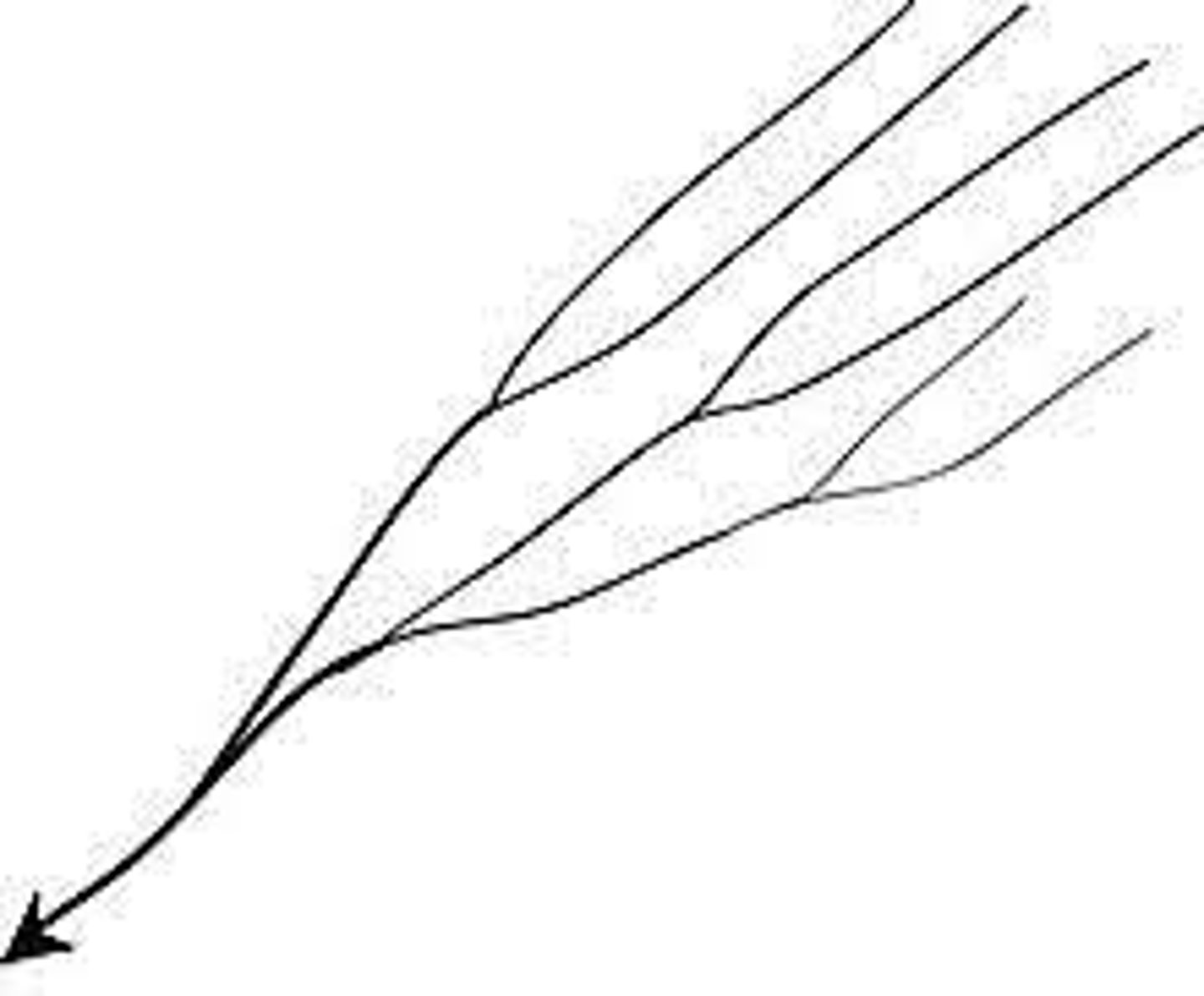
Parallel
on uniform steep slopes with weak substrate and no vegetation
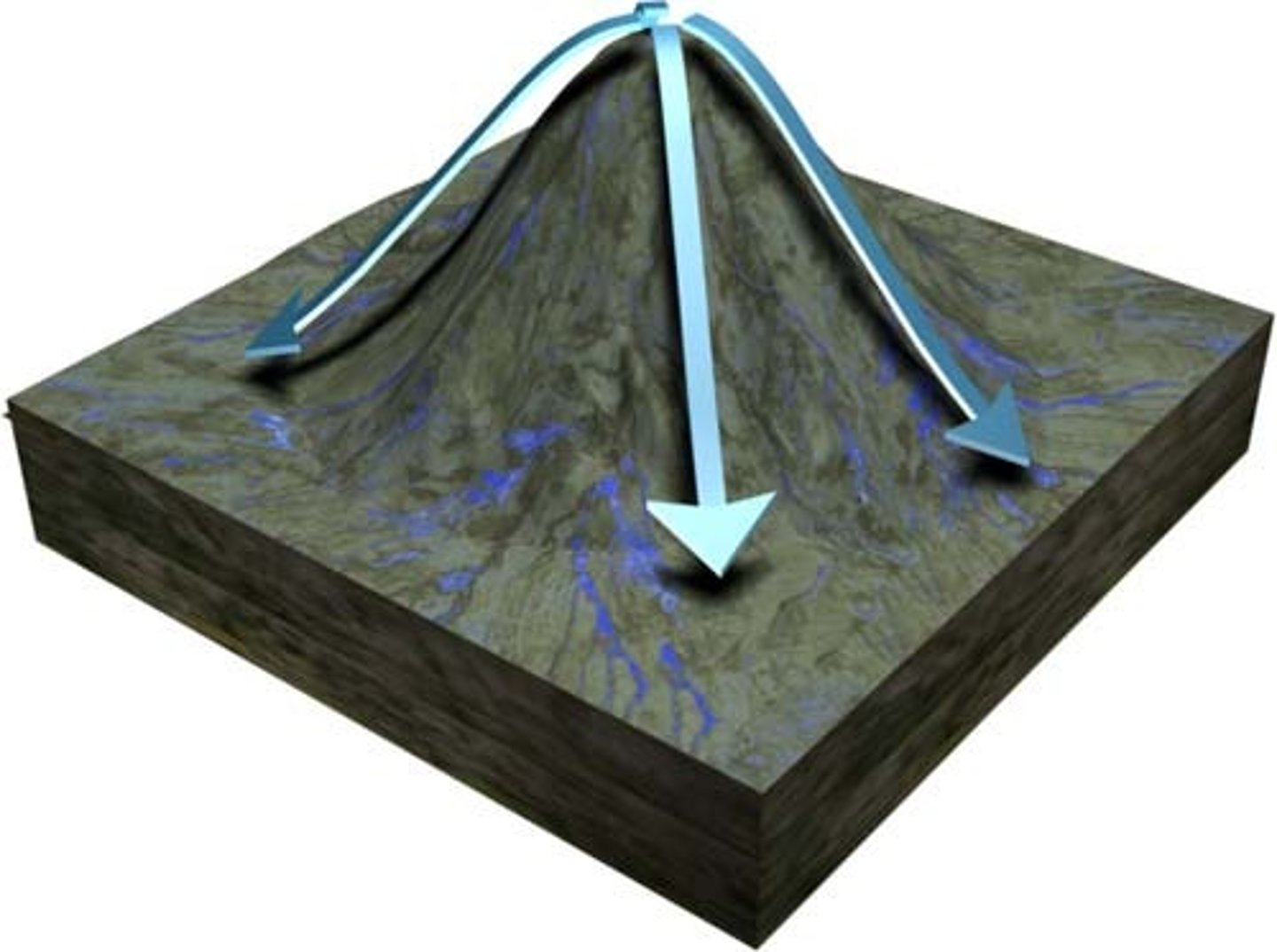
Radial
generally on volcano
Braided channel
generally high sediment load, lots of bars that shift
Meandering channel
most mature streams, Straight
Ways streams can erode
Scour (from abrasion w/suspended sediment), Breaking and Lifting, Attrition, Dissolution
Attrition
process of erosion that occurs during rock collision and transportation
Stream carries sediment via
Dissolved Load, Suspended Load, Bed Load (saltation)
Competence
largest size particle river can carry. Dependent only on velocity
Capacity
total volume of particle river can carry. Depends on discharge
When does deposition happen?
river no longer has the competence to carry sediment
Headwaters
erosional zone, streams are fast and cut v-shaped valleys
Transfer zone
amount of erosion= amount of deposition
Depositional zone
at low elevations, sediment deposited and river meanders
Base level
how far down stream can erode. Ultimate base level = the ocean
Does discharge and velocity increase/decrease as you go downstream?
increase
Photic
sunlit upper waters-> light dims to 1% of surface
Aphotic
no light
Littoral
near shore, emergent plants
Limnetic
well-lit, open surface waters farther from shore, depth to which sunlight can penetrate the water
Benthic
lake bed
Lakes in the Northeast are generally...
DIMICTIC - they mix once in fall and once in spring.
Lake temperature layers
epilimnion, metalimnion, hypolimnion
Lakes in Summer
surface is heated. Lake stratified into three layers by temperature
Lakes in Fall
surface is cooled. lake becomes isothermal and overturns
Lakes in Winter
surface is cooled and ices over. Coldest water & ice at top, warmer water at bottom
Lakes in Spring
surface is warmed to 4C, lake becomes isothermal, overturns
Water is densest at what temperature?
4C
Isothermal
having a constant temperature
Consequences of Stratification
deeper waters (hypolimnion) can become hypoxic or anoxic, can accumulate toxic gases (ie H2S as a result of anaerobic decomposition)
Overturning
mixes the water, giving the deeper waters oxygen, and bringing nutrients to the shallow waters.
-If this happens to fast, could kill life because the toxic gasses are introduced too quickly
What are wetlands (Clean Water Act definition)
areas inundated by surface or groundwater, long and frequent enough such that it supports vegetation adapted for saturated soil
What are wetlands (Manual definition)
land that is saturated for at least part of the year, with hydric soils and a special vegetational type
What makes a wetland?
Hydrophytic vegetation
Hydric, gleyed soil( <2 chroma)
look for water @ the surface, channels, etc. <6.6 ft of water
How are wetlands formed
Either paludification or terrestrialization
Paludification
generally with bogs, moss grows and traps water
Terrestrialization
eutrophication
Swamps
Wooded Wetland
-wet for part of year
-trees often dormant
Bogs
spongy peat deposits & Sphagnum moss
-Anaerobic, slow decomposition
-Nutrient poor, low in oxygen -> carnivorous plants, good for preservation
-Very acidic. Fed only by precipitation
Fens
Similar to bogs, but less acidic and more nutrients because also partially groundwater fed.
-carex and ephiorum moss
Marsh
dominated by grasses, wet the entire year
Vernal pool
temporary pools that form in springtime. Important nurseries for amphibians
-fairy shrimp + blue spotted salamander
Wetland benefits
-Improved water quality: filters out pollutants
-Reduces sedimentation
-controls erosion
-Flood Control: wetlands slow water and store it
-Water Supply: helps recharge groundwater
-Habitat: provides habitat for many endangered species., Important nurseries for fish and resting areas for migratory birds,
-Economic Benefits: timber, mammals, birds, shellfish,
-Recreation: for people (a lot of birders help economy), education, research
-Important in nutrient cycling, provides an anaerobic environment which is needed for many processes
Estuary
Where saltwater meets freshwater
Mudflats, tidal marshes, mangrove swamps, etc
TYPES OF ESTUARIES by geology/formation
Tectonic Estuaries
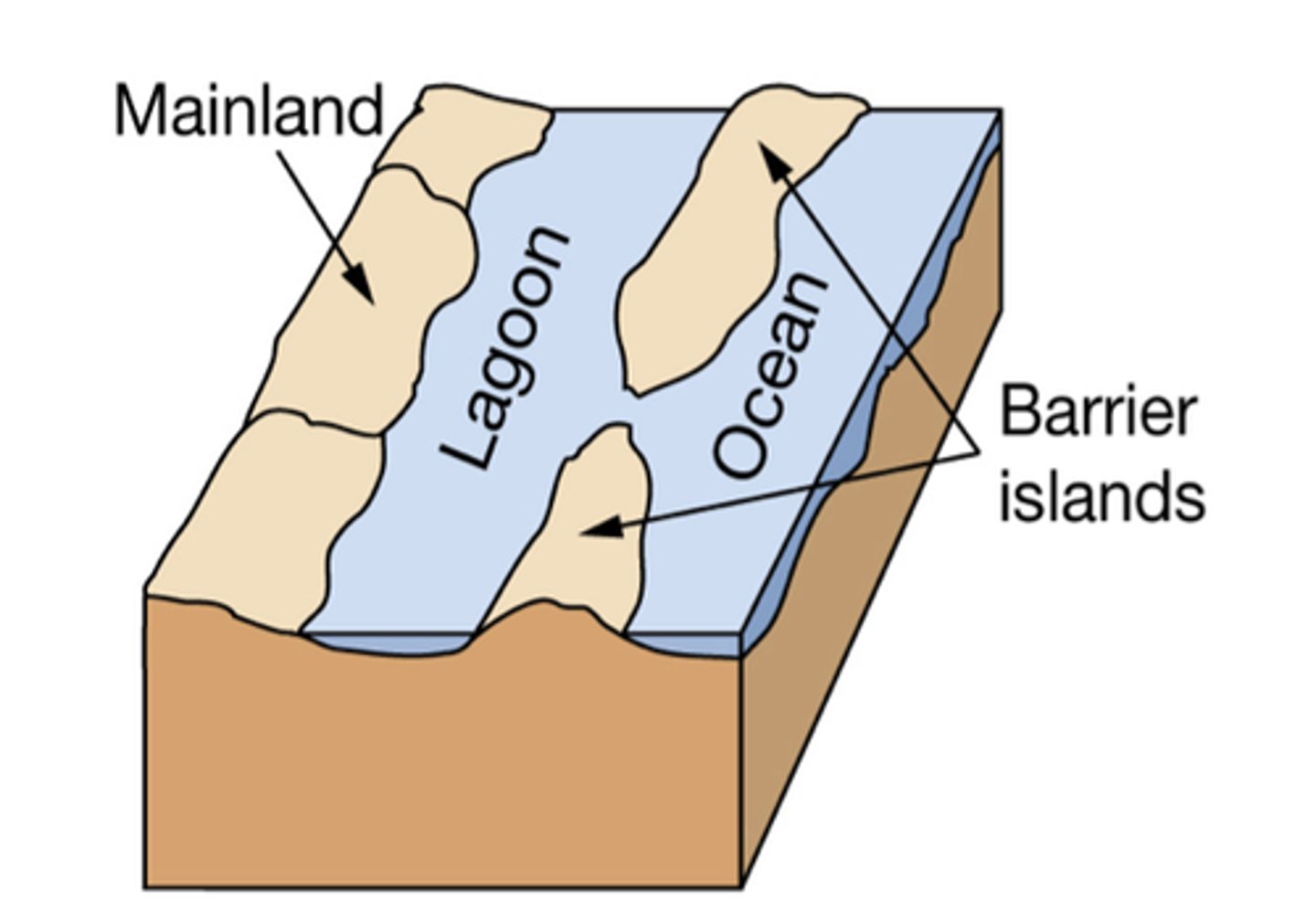
Bar Built Estuaries (lagoons)
Fjord-Type/Glacial
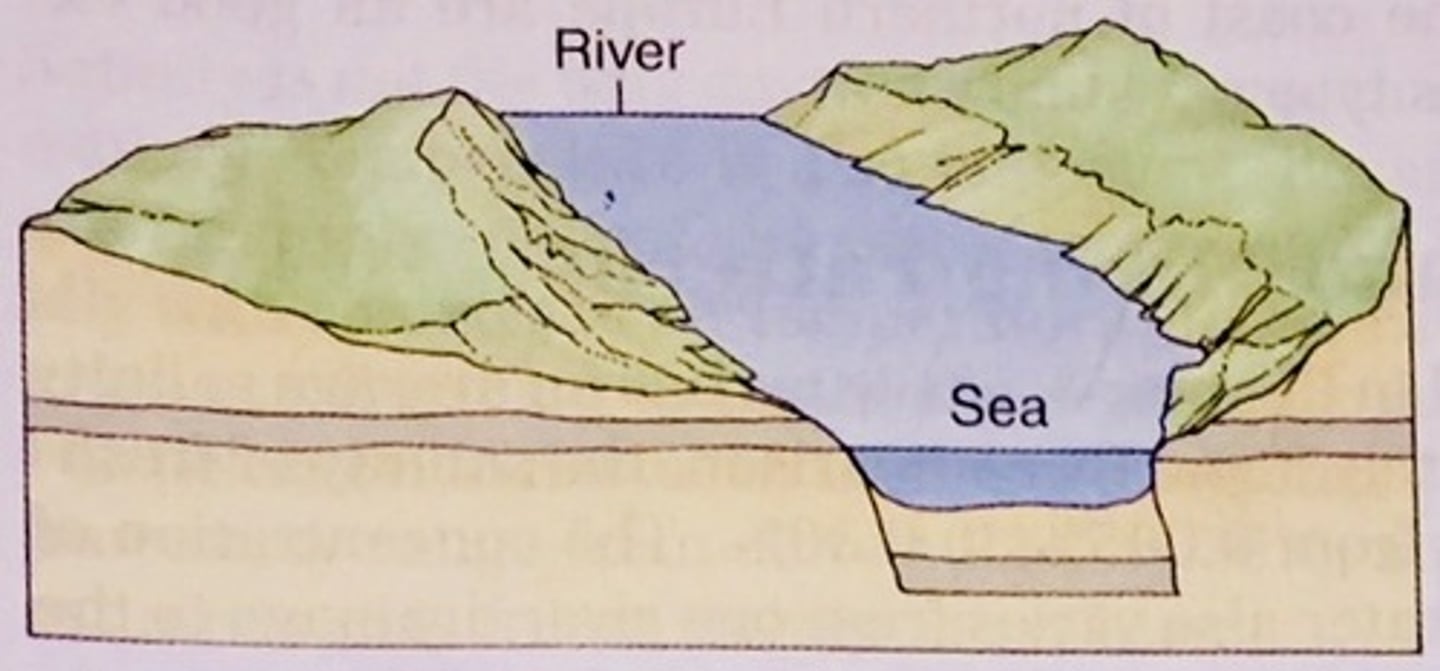
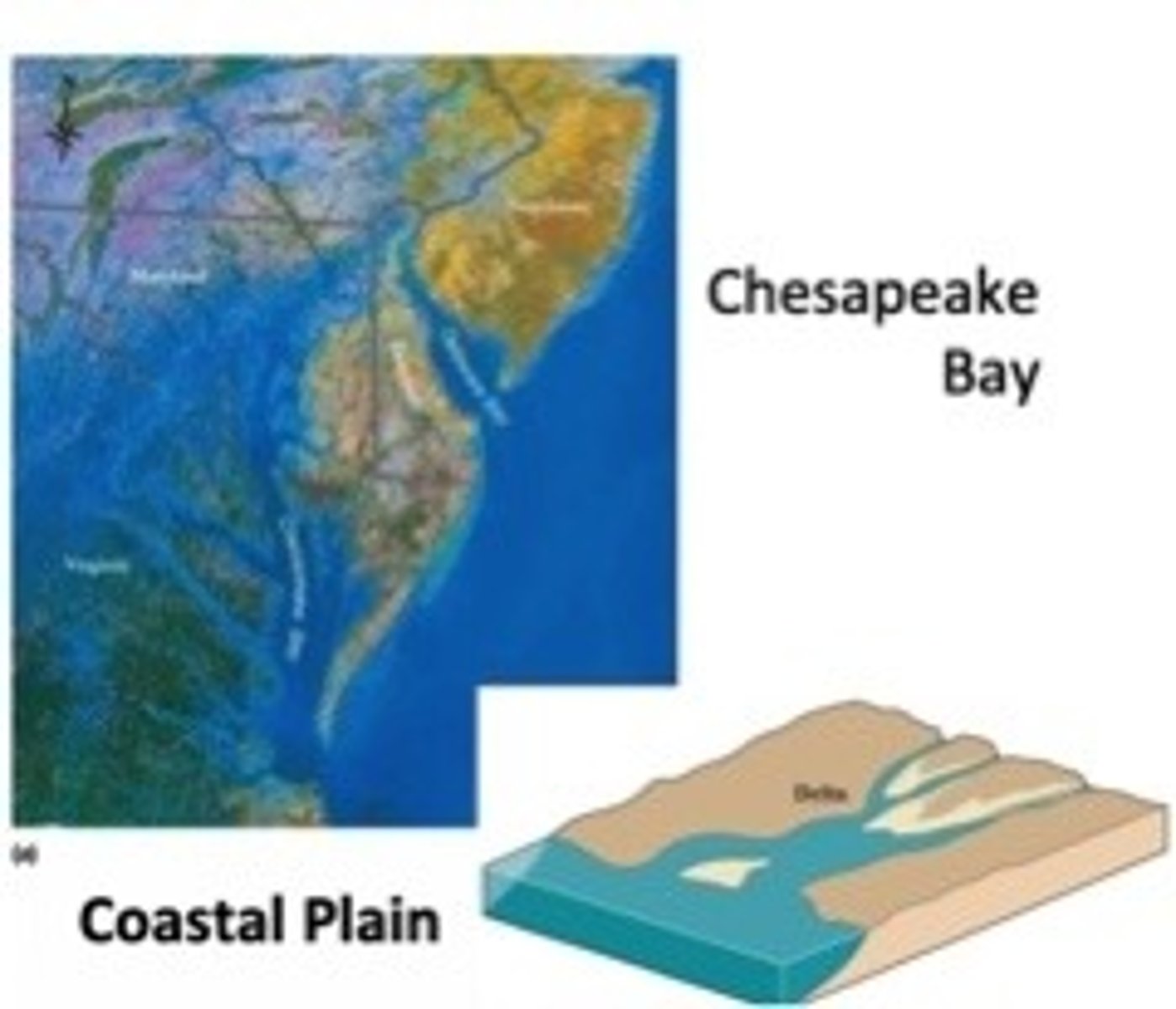
Coastal Plain/Drowned River Valley
TYPES OF ESTUARIES by stratification
Vertically Mixed
Partially Mixed
Stratified Salt Wedge
Stratified Fjord Type
Hypersaline
Estuarine Circulation
freshwater flows at surface from head to mouth, saltwater flows subsurface from mouth to head.
Tectonic estuary
formed when a depression along a fault line fills with water (e.g. San Francisco Bay)
Bar-built estuary
lagoon separated from ocean by sand bar or barrier island
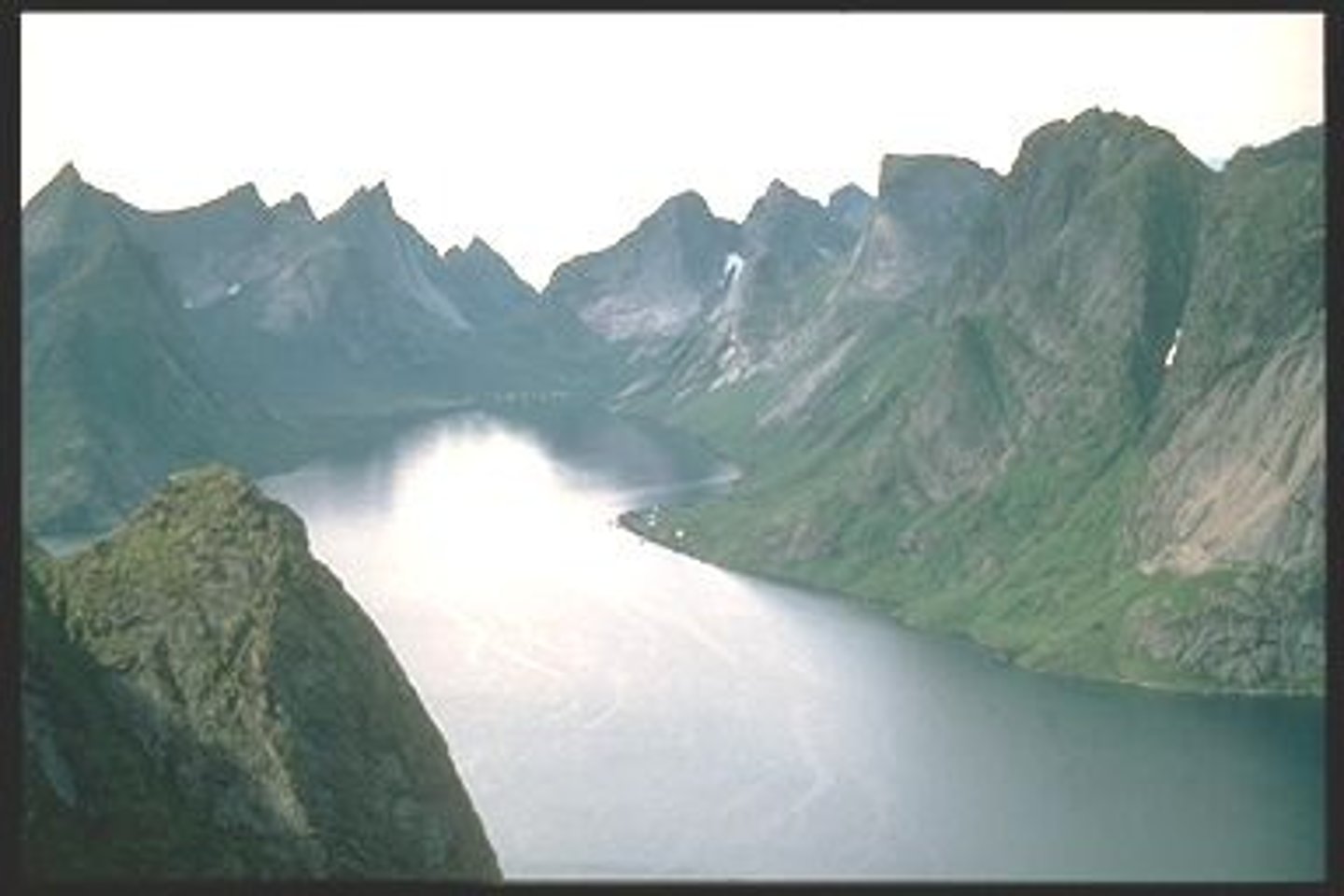
Fjord
a narrow inlet of the sea between cliffs or steep slopes

coastal plain/drowned river valley
formed when sea levels rise + fill existing river valley, most common type
Pelagic
open water in the middle of a lake
Profundal Zone
deep water below light penetration level
photic
sunlit upper waters from surface to where light dims to 1% of the surface
lake ontogeny
lake successional process
What percent of water on earth is ocean/freshwater?
96.5%, 2.5% (other saline water = 0.9%)
What percent of freshwater is ice caps/glaciers?
68.7%
What percent of freshwater on earth is groundwater?
30.1%
What percent of freshwater on earth is surface freshwater?
1.2%
What percent of surface freshwater is lakes?
20.9%