Understanding Obesity: Physiology and Interventions
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What is obesity defined as?
An excess of subcutaneous fat compared to lean body mass.
What is the estimated prevalence of obesity among US adults by 2030?
1 in every 2 US adults will have obesity.
How is Body Mass Index (BMI) calculated?
BMI = Weight (kg) / height (m)² or Weight (lbs) * 703 / height (inches)².
What are the sensitivity and specificity characteristics of BMI in diagnosing obesity?
BMI has low sensitivity (issues diagnosing obesity) but high specificity (good at ruling out obesity).
At what level is BMI most accurate?
BMI is accurate at the higher ends of obesity, such as morbidly obese.
How does BMI perform at the population level compared to the individual level?
BMI is better at a population level than an individual level.
What are some genetic components influencing obesity?
Genetic components include responses to overfeeding, control of food intake, fat storage, and energy expenditure.
How does aging affect fat storage patterns?
Growth hormone and gonadal hormone decrease with age, leading to increased visceral fat storage.
What role does leptin play in obesity physiology?
Leptin is released from fat cells, helps with satiety, and is often upregulated after a meal.
What is the function of ghrelin in the body?
Ghrelin is an appetite-increasing gut hormone that stimulates the drive for carbohydrate intake.
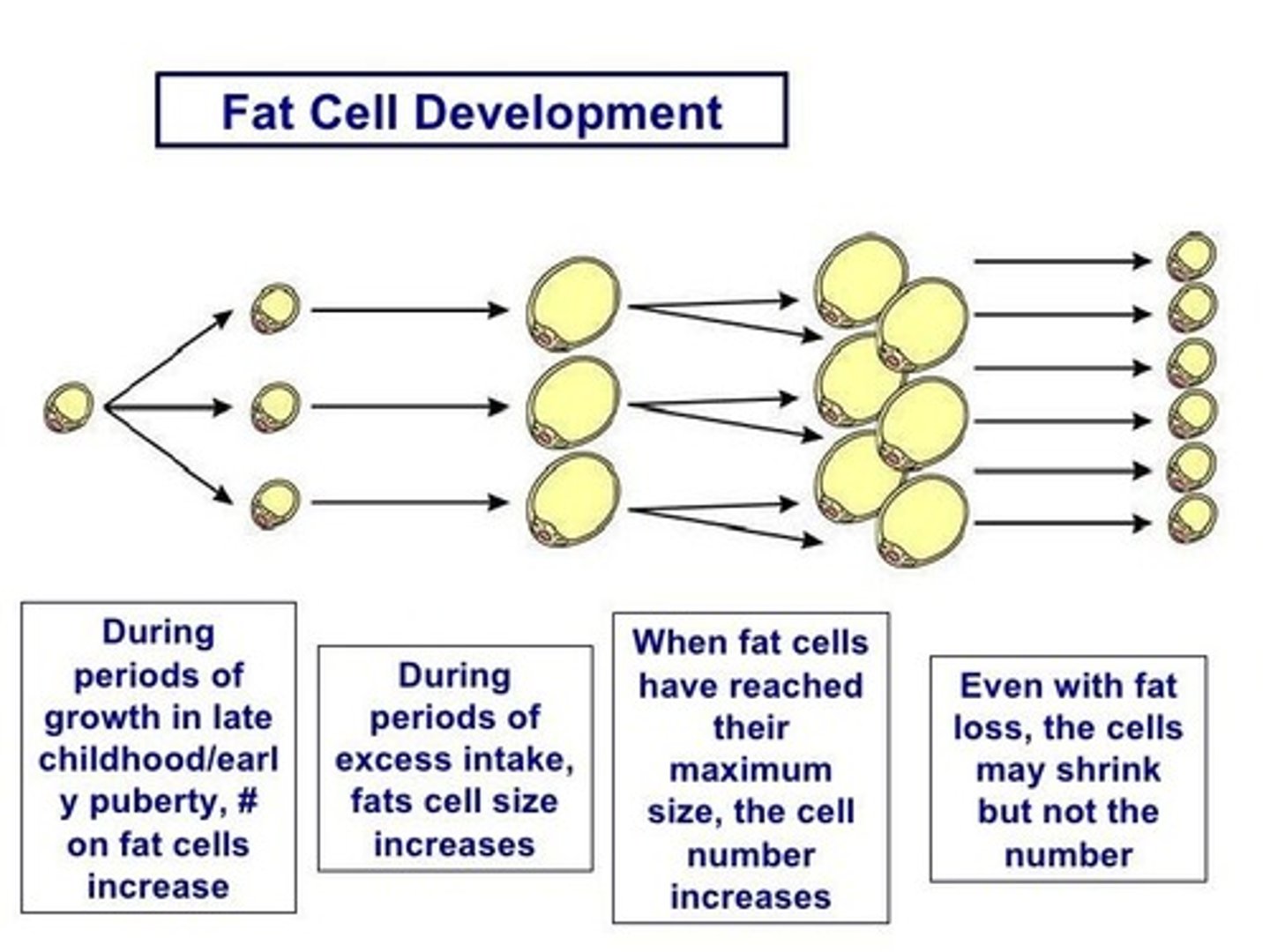
What happens to the number of fat cells during weight loss?
Even if weight is lost, the number of fat cells remains the same; they can only shrink in size.
What is set-point theory in relation to weight?
Set-point theory suggests the body is resistant to changes in homeostasis, particularly weight loss.
What did the study by Fothergill et al. (2016) reveal about weight loss?
It highlighted the challenges and physiological responses related to weight loss.
How does metabolic rate change with age?
Metabolic rate generally decreases with age.
What are some diet intervention strategies for obesity?
Strategies include meal replacements, lower-fat higher-carb diets, higher-fat lower-carb diets, and decreased glycemic load diets.
What is Roux-en-Y-gastric bypass?
A surgical procedure that restricts food intake by limiting stomach reservoir and may alter hormone regulation.
What is the role of exercise in managing obesity?
Exercise can show short-term improvements and should be combined with diet therapy for long-term results.
How does resistance training impact metabolic rate?
Resistance training increases basal metabolic rate (BMR) by increasing muscle mass.
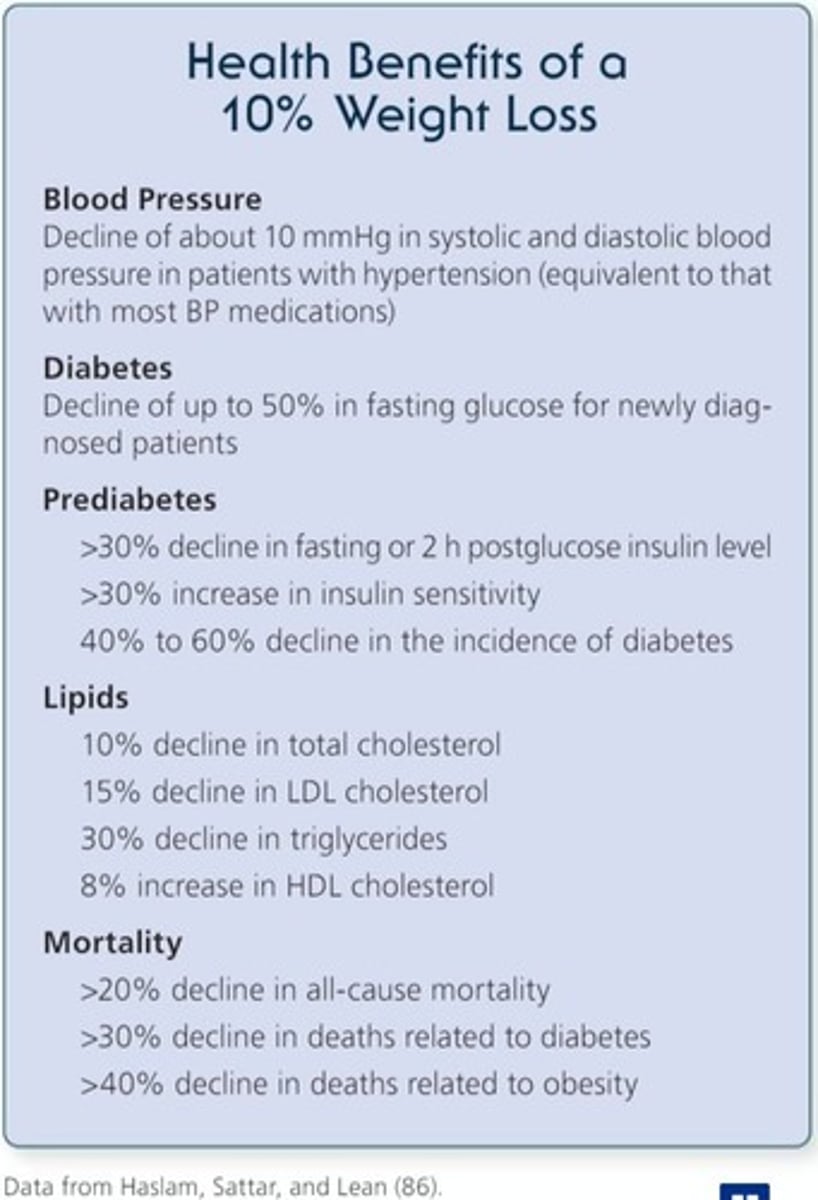
What amount of weight loss is associated with significant health improvements?
A 10% weight loss can accomplish various health benefits.
What is a common misconception about managing obesity?
The oversimplified approach of just telling patients to eat less and run more is ineffective.
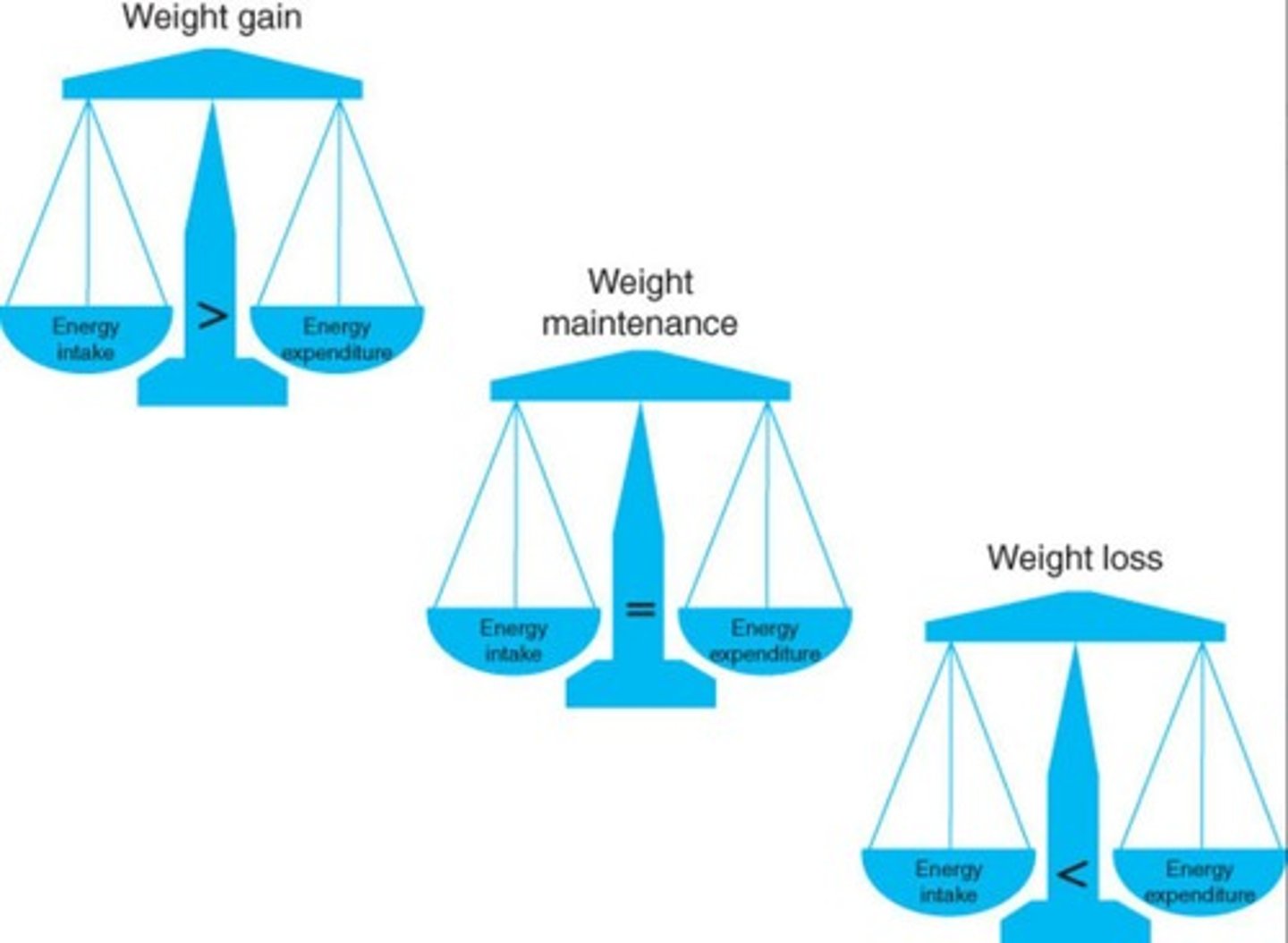
What is the first law of thermodynamics in relation to obesity?
It states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, but the complex physiology of food intake and calorie expenditure complicates this.