Basic Measurements in Epidemiology
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Epidemiological Tools
1- rates
2-ratios
3-proportion
Rate
A rate measures the occurrence of some particular event in a population during a given time period
Note
A rate measures the occurrence of some particular event in a population during a given time period
Rate Comprises 4 Elements {Components}
Numerator
Denominator
Time Specification
Multiplier
Numerator
It is the number of times an event has occurred in a population , during a specified period
Denominator
this can be :
A - related to the population ,and this include
B- related to total event
related to the population ,and this include
Mid-year population
Population at risk
sub-groups of the population
Types of the rates
crude {unstandardized} rates
specific rates
standardized rates
crude {unstandardized} rates
These are the actual observed rates ,e.g. birth and death rates
specific rates
These are the actual observed rates :
1- due to specific causes ,e.g. TB
2- occurring in specific groups , e.g. age
3- during specific time period , e.g. annual ,monthly rates.
Ratios
This expresses a relation in size between two random quantities

Note
The numerator is not a component of the denominator
In The Ratio
Proportion
This refers to the ratio which indicates the relation in magnitude of part from the whole.
Note
Here the numerator is always included in the denominator
In The Proportion
Morbidly
Any departure , subjective or objective , from a state of physiological well-being.
Importance of morbidity data
Description of the extent and nature of the disease load in the community ,and so assist in the establishment of priorities .
Provision of more comprehensive and accurate information about patient characteristics than those obtained from mortality data , and thus it is essential for basic research.
The data serve as starting point for etiological studies , and thus play an essential role in disease prevention
These data are needed for monitoring and evaluation of disease control activity.
Importance of morbidity data
The data provide insight into the community's disease burden to help set health priorities.
offer detailed patient information crucial for research.
support the identification of disease causes for prevention
essential for monitoring and evaluating disease control efforts.
The morbidity ratios measure 3 aspects of morbidity , which are
1. Frequency :
this is measured by the incidence and prevalence rates.
2. Duration :
this is measured disability rate
3. Severity :
this is measured by case fatality rate
Incidence
It is defined as the number of NEW cases occurring in a defined population during a specified period of time.
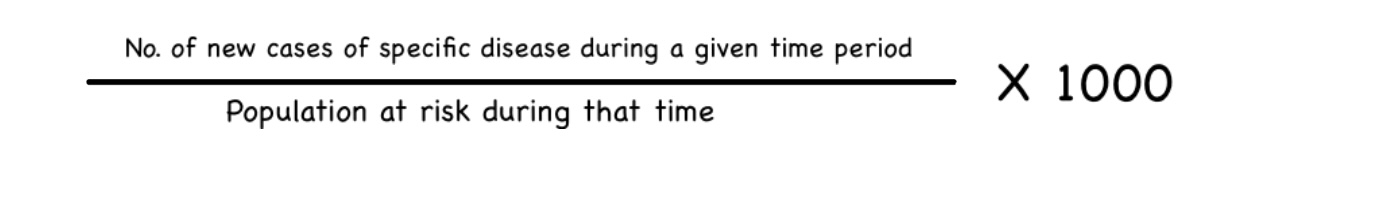
Special incidence rates
Attack rate
Secondary attack rate
Incidence density
Attack rate
It is the incidence rate used only when the population is exposed to risk for a limited period of time .e.g. ,during an epidemic

Secondary attack rate
This is the number of exposed persons
developing the disease within the range of the incubation period following exposure to a primary case .
• In other words , it is the incidence of the disease among the contacts
Incidence density
Here the denominator is the total person — time of follow up
Incidence rate is important (Uses of incidence)
1. Controlling the disease .
2. For research into etiology and pathogenesis ,distribution of disease ,and efficacy of preventive and therapeutic measures
Prevalence
It refers to all current cases {old and new} existing at a given point in time, or over a period of time in a given population

Types of prevalence ratios
1. Point prevalence .
2. Period prevalence .
Uses of prevalence
It helps to estimate the magnitude of health/disease problems in the community, and identify potential high risk population
It is useful for administrative and planning purposes ,e.g., hospital beds, manpower needs, facilities …etc.
Relationship between prevalence and incidence
Prevalence depends on two factors:
1- incidence 2- duration
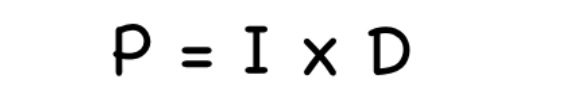
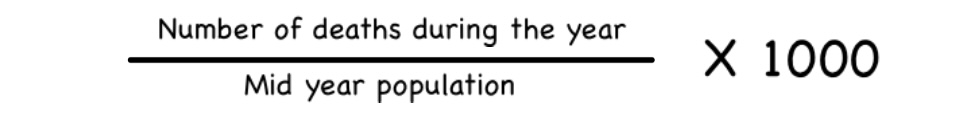
Measurements of Mortality
1. Easily to obtain & reasonably accurate.
2. Crude death rate
Specific death rates
A/ Disease specific
B/ Age specific
C/ Gender Specific
D/ Combination.
Case Fatality Rate
• It is the killing power of disease.
• It is ratio of deaths to cases.
• Used in acute infectious diseases.

Maternal mortality rat
The death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy, irrespective of duration & site of pregnancy.
Child Mortality Rates
Infant mortality rate : Number of deaths of children below one year of age per 1000 live births during the same year and in the same area.
Neonatal mortality rate : Newborns 1- 28 days.
Under 5 mortality rate : 1 day up to less 5 years.
Disease reporting
1. Immediate Notification.
2. Weekly reporting.
3. Monthly reports.
4. Annual reports