2) Aufbau, Hund's Rule. Pauli Exclusion Principle & Periodicity
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What is E*n?
E*n closer together if…
Energy levels
n increases
For hydrogen, what does orbital energy depend on?
For atoms with more than one electron, what does orbital energy depend on?
Hydrogen: n
Multi electrons: n & l
What is a ground-state atom?
In describing ground-state electron configuration, what is the guiding principle?
GSA: an isolated atom of an element that is in its lowest energy or unexcited state.
The guiding principle is to keep the total energy of the atom as low as possible.
What are 2 rules of the Aufbau Principle?
Add the number of protons & neutrons to the nucleus.
Add the number of electrons in a way that gives the lowest total energy.
Orbitals are filled in order of increasing energy with the lowest energy orbitals being filled first
State 2 further rules of Aufbau Principle.
Electrons are assigned to orbitals in order of increasing values of n + l.
For subshells with the same value of n + l, electrons are added to the subshell with the lowest values of n. E.g.,

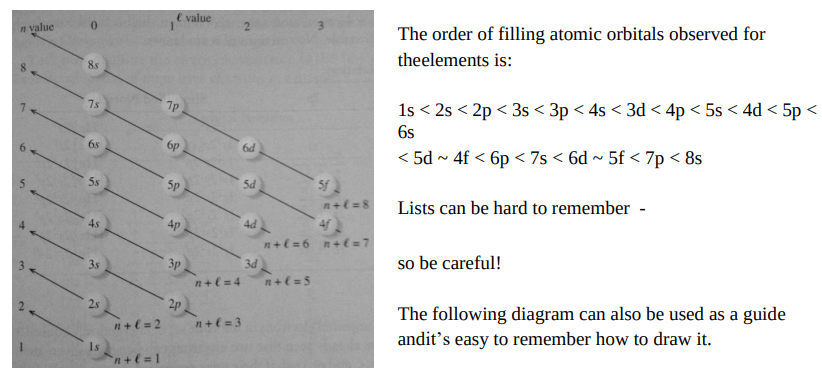
Remember, more on back.

What is Hund’s rule? (2)
Electrons occupy all of the orbitals of a given subshell singly before pairing begins.
The unpaired electrons have parallel spins.
What does the Pauli Exclusion Principle state?
State 2 rules for this.
States that no 2 electrons in an atom can have identical sets of 4 quantum numbers.
Two electrons in the same orbital must have different spins. Two electrons in one orbital are said to be spin paired, one electron in an orbital is said to be unpaired.
Define Valence Electrons and Core Electrons.
Valence: electrons beyond the nearest noble gas (leftover).
Core: electrons summarised by noble gas.
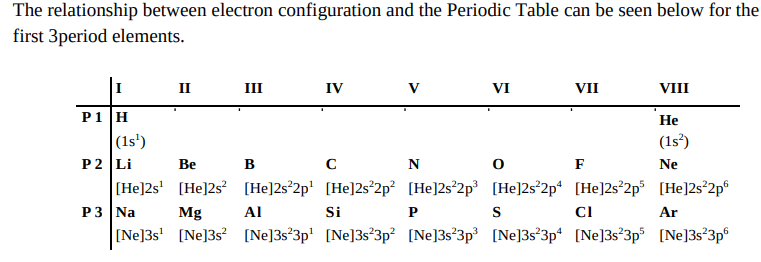
What does this table tell us about valence electrons?
What does it tell us about the VDWs radii?
What does it tell us about electronegativity?
Valence: same configuration down each group (hence similar reactivity).
VDWs radii: atoms get smaller from left to right due to stronger pull from nucleus.
Electronegativity: decreases down group (increasing n = more layers of electrons so positive pull felt less strongly by external electrons).