Lecture 17: Pentose Phosphate Pathway
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What can glucose be used for?
Synthesis of structural polymers (ECM and cell wall plysaccharides)
Storage (Glycogen, starch, sucrose)
Oxidation via PPP (Ribose 5-phosphate)
Oxidation vis glycolysis (pyruvate)
What is Pentose?
Sugar with 5 carbons
Can be linear or cyclic
What is DNA?
Where genetic information is encoded.
Template for identical DNA molecules
What is a Nitrogenous base/nucleobase?
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
What is a Nucleosid?
Ribose sugar AND Nitrogenous base
What is a Nucleotide?
Phosphate AND Sugar AND Nitrogenous base
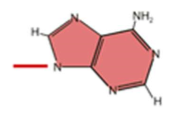
What is this Nucleobase?
Adenine
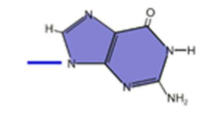
What is this?
Guanine
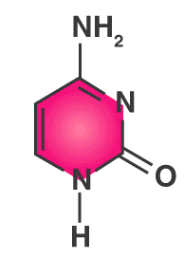
What is this?
Cytosine
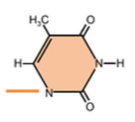
What is this?
Thymine
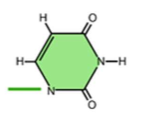
What is this?
Uracil
What is the purpose of the PPP?
Alternative pathway for glucose oxidation
What does the PPP yield?
2 NADH/glucose
Pentoses to synthesize nucleotides
Reduced cofactors to synthesize amino acids, fatty acids, sterols, etc
What is an important intermediate for the PPP?
Glucose 6-phosphate
What cells/tissues use the PPP?
Rapidly dividing cells (need more DNA)
Tissues that carry out fatty acid synthesis
Tissues that synthesize cholesterol and steroid hormones (liver, adrenal glands, gonads)
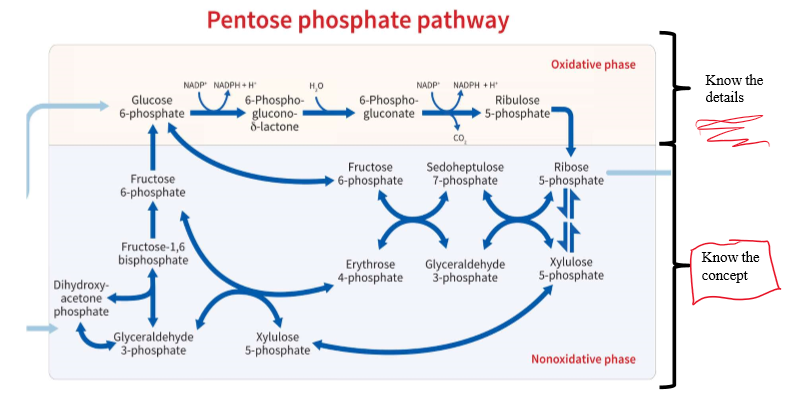
What reactions make up the PPP?
Oxidative and non-oxidative
What steps are irreversible?
1st and 3rd oxidative reactions
What steps are reversible?
nonoxidative reactions
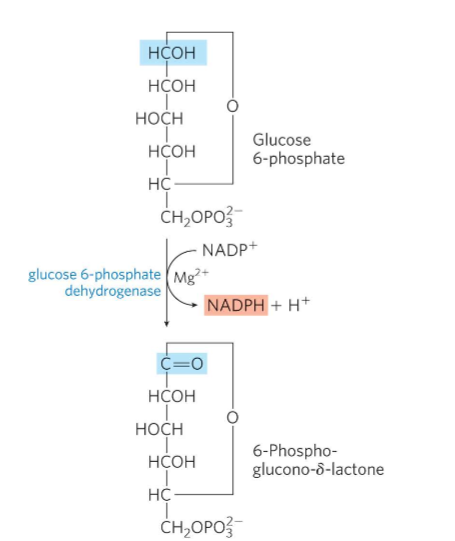
What is Oxidative Step 1?
Glucose 6-phosphate to 6-phosphoglucono-delta-lactone.
Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) Oxidizes and uses NADP+ as electron acceptor
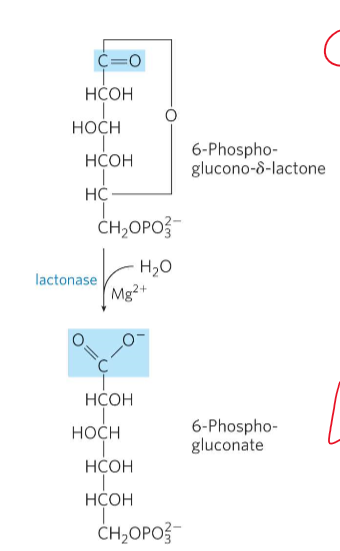
What is Oxidative step 2?
6-phospho-glucono-delta-lactone to 6-phosphogluconate
LACTONASE does this
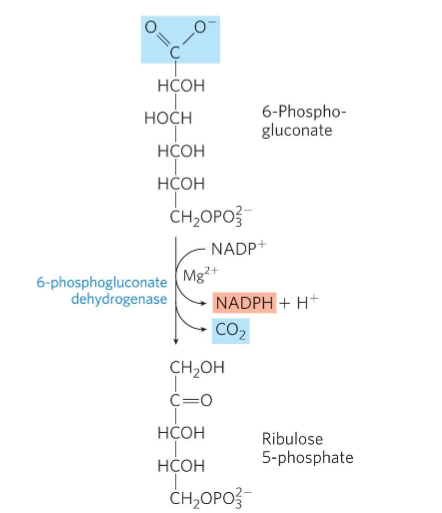
What is Oxidative step 3?
6-phosphogluconate forms ribulose 5-phosphate and NADPH
6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase oxidizes and decarboxylates
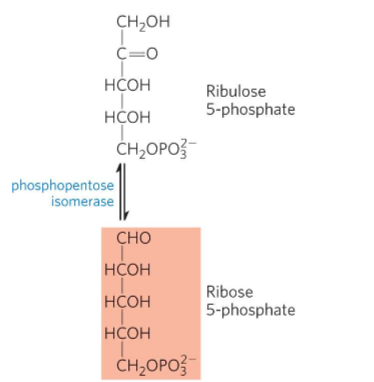
What is Oxidative step 4?
Ribulose 5-phosphate to ribose 5-phosphate
Phosphopentose isomerase converts
What does nonoxidative phase of the PPP do?
Recycles pentose phosphates to glucose 6-phosphate
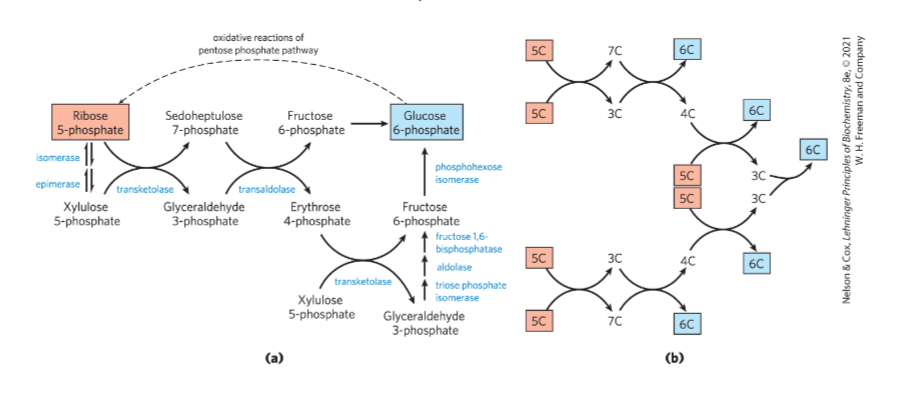
What is this?
Nonoxidative PPP reactions
What is the overall equation of the PPP?
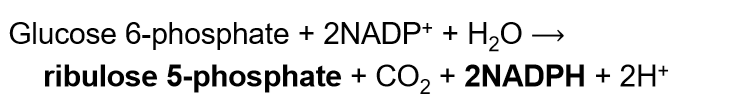
What does the Reductive Pentose Phosphate pathway do?
Converts hexose phosphates to pentose phosphates
Reversal of the nonoxidative reactions of the pentose phosphate pathway
How is the PPP inhibited?
NADPH inhibits the PPP
Why does NADPH inhibit the PPP?
Concentrations of NADP+ and NADPH determine whether glucose 6-phosphate enters glycolysis or the PPP
If there is too much NADPH, glucose 6-phosphate can continue through Glycolysis