ENGT 2020 – Robotics Fundamentals : Ch 4 - 6
In ____ programming, the user specifies the goals of each task rather than the motions required to achieve the goal.
task-level
Which programming method allows a robot to remain in operation while a new program is written and debugged?
computer programming
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
In ____ programming, the user specifies the goals of each task rather than the motions required to achieve the goal.
task-level
Which programming method allows a robot to remain in operation while a new program is written and debugged?
computer programming
true or false : Manual programming does not require an operator skilled in the use of computers.
true
true or false : Off-line programming is performed using a computer that is not connected to the robot.
true
true or false : In continuous-path motion, an operator leads the robot through the various positions involved in an operation.
false
true or false : A manual rate control box translates high-level languages into machine code.
false
true or false : The first generation of industrial robots was controlled by means of programming languages.
false
true or false : Walk-through programming is used for continuous-path robots.
true
true or false : Using task-level programming, instructions are entered using menu-selected statements.
true
Three classifications of a robot’s pattern of movement are pick-and-place motion, ____ motion, and continuous path motion.
point-to-point
The ____ generation of robots evolved through the use of artificial intelligence.
third
true or false : Hierarchical control systems use sensory feedback to affect how the robot responds.
true
In ____ programming, each level accepts commands from the level above and generates simplified commands for the level below.
hierarchal control
In ____ programming, an operator adjusts end stops, switches, cams, wires, and hoses to set up the sequence of robot motion.
manual
A ____ is a set of instructions within a program that has a beginning and an end.
subroutine
The path of motion for ______________________________ robots is a series of straight lines between hundreds of possible programmed points to position the end effector at the correct spot.
point-to-point
With ______________________________ motion, the end effector follows a fixed pattern of movement and allows for two positions per axis.
pick-and-place
The ______________________________ level in hierarchical control programming receives commands for elemental moves.
third
Creating the instructions for a robot on a computer that is connected to the robot console is called ______________________________ programming.
online
With ______________________________ motion, control of the end effector’s path is more important than the end point positioning.
continuous path
A(n) ______________________________ program translates high-level languages into machine code.
compiler
Robots receive information about their surroundings from ______________________________ devices in the system.
sensing
______________________________ is the science and engineering of making machines perform operations commonly associated with intelligent human behavior.
artificial intelligence
In hierarchical control programming, ______________________________ are structured in levels.
commands
Using ______________________________ programming, the person programming the robot must be highly skilled in the precise motion required by the task.
walk through
Thousands of points may be recorded for fluid movement.
walk through programming
An operator leads the robot through an operation and records desired points into memory.
teach pendant programming
Only two positions are programmed for each axis.
manual programming
Engineering products with the robots that will assemble them in mind is called ______________________________.
designing for manufacturability
Safety devices that prevent unauthorized access to hazardous areas are ______________________________.
interlocks
The ______________________________ is different for each robot configuration and is defined by its type of joints and degrees of freedom.
work envelope
The two most important factors that influence operational speed are the desired accuracy and ______________________________.
payload
The closest distance between movements of a robot is ______________________________.
command resolution
true or false : Work station design should place control panels outside the robot’s work envelope.
true
true or false : Minimizing the number of parts required for a product makes assembly more complex.
false
The work envelope is defined by the type of joints a robot is equipped with and its ____.
degrees of freedom
The smallest incremental movement a robot can make is called ____.
resolution
true or false : Resolution expresses how precisely a robot’s hand is programmed to reach a predetermined point.
false
true or false : Service robots are mobile and can move to the work area to perform the necessary tasks.
true
The relationship of the ____ to work fixtures must be taken into account when designing a work station.
end effector
true or false : As speed increases, accuracy decreases.
true
The ____ is how precisely the end effector is programmed to reach a predetermined point.
accuracy
true or false : Plans to provide a safe working environment are considered only after a robotic system is designed and installed.
false
Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) use a ____ for navigation.
buried wire guide path, magnetic tape guide path, and global positioning system
true or false : Robots with six degrees of freedom can work anywhere within the work envelope.
true
Greater flexibility may be achieved by mounting a robot on the ____ within the work envelope, instead of the floor.
wall and/or ceiling
The accuracy of movement of a robot’s tool tip is described in terms of ____.
spatial resolution
rotation of the wrist
roll
movement of the vertical axis
waist
up and down movement of the wrist
pitch
extension and retraction of the arm
shoulder
up and down motion
elbow
side to side movement of the wrist
yaw
Machines that change the position or speed of a mechanical object.
servo systems
Signal a response to a particular form of energy.
sensing systems
Numeric instructions are changed into a series of on/off electrical signals.
digital systems
The combination of multiple subsystems.
synthesized systems
Ensure that all actions of an operation occur at a precisely defined interval.
timing systems
Continually at work making adjustments that alter machine operation.
control systems
Produce some form of mechanical motion.
mechanical systems
As the mechanical load on a dc motor increases, the motor speed ____.
decreases
true or false : Timing systems convert electrical energy into mechanical motion.
false
The ____ compares the feedback signal from the controlled element to a reference signal or standard.
comparator
In electrical systems, a ____ system signals a response to a particular form of energy.
sensing
A ____ dc motor has two sets of field windings.
compound wound
The difference between the synchronous speed and the rotor speed is called ____.
slip
true or false : Examples of loads include digital meters, pressure gauges, tachometers, and thermometers.
false
DC stepping motors are primarily used to change electrical pulses into ____.
rotary motion
true or false : In a mechanical system, control is accomplished by changing pressure, direction, force, and speed.
true
In a closed-loop system, the signal or data that provides information about interaction between the control unit and the load is called ____.
feedback
true or false : The counter electromotive force flows against the voltage coming into a dc motor.
true
true or false : In bifilar construction, three separate wires are simultaneously wound into the stator coil slots.
false
____ devices operate within the transmission path and alter the flow of power.
control
true or false : The transmission path provides a channel for the transfer of energy.
true
true or false : In an electric motor, the armature is an electromagnet.
true
A(n) ____ system transfers power from one point to another through mechanical motion that is used to do work.
electromechanical
true or false : In a series-wound dc motor, the armature and field circuits are connected in a series arrangement.
true
When subsystems are combined, the result is referred to as a ____.
synthesized system
The ____ is the rotating component of a motor and includes the armature, shaft, and associated parts.
rotor
The ____ unit of an industrial robot determines its flexibility and efficiency.
control
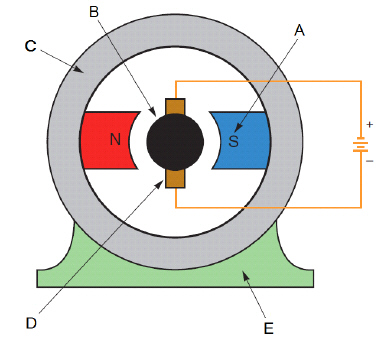
Identify the basic parts of a dc motor : field pole, stator, mounting, brush commutator assembly, and rotor
field pole : A
stator : C
mounting : E
brush commutator assembly : D
rotor : B
______________________________ occurs when energy is transformed into mechanical motion, light, heat, chemical action, or sound.
work
As the armature of a dc motor rotates, it generates its own voltage called ______________________________.
counter electromotive force
Changes in the field current result in corresponding changes in the ______________________________ of the electromagnetic field.
flux
______________________________ timing systems may include both interval and delay timing to provide energizing action in an operational sequence.
cycle
The ______________________________ receives data from both the input source and the output device, and determines if a correction signal should be sent to the actuator.
error detector
Flexible, fiber-optic rods that transfer light energy from its source to distant locations are called ______________________________.
light pipes
The ______________________________ rating of a motor represents the power of the motor.
horsepower
In a mechanical system, ______________________________ measure physical quantities, such as pressure, speed, and force.
indicators
A(n) ______________________________ motor is the only dc motor that can also be operated using ac power.
universal