vm 602 anatomy joints of the thoracic limb
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
"fleshy" attachment of the thoracic limb to the trunk
synsarcosis
-formed by 2 or more bones
-cavity between bones
-cartilaginous articulations
-joint capsule
-synovium: produces synovial fluid
-stabilized by muscles and/or ligaments
synovial joints
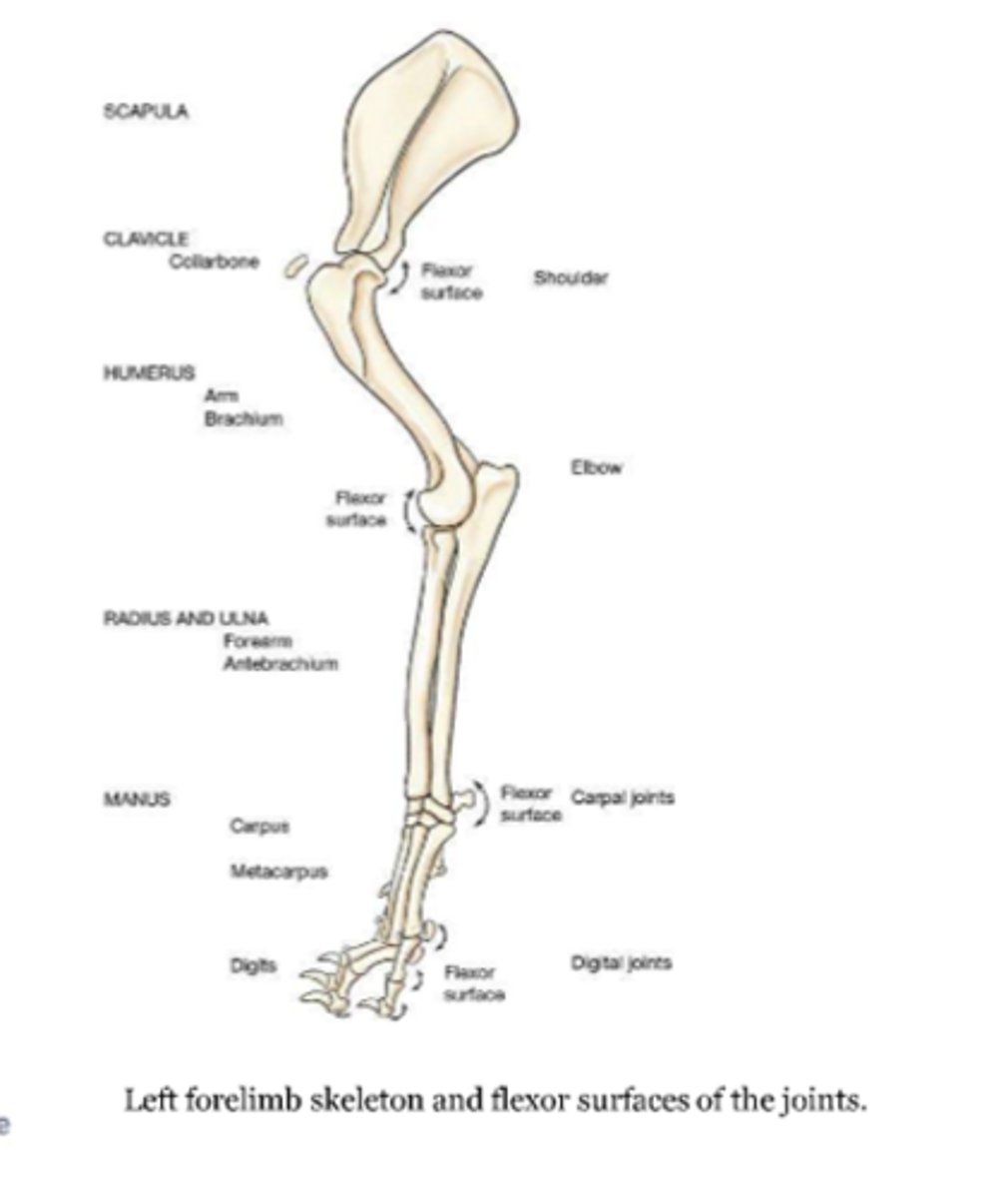
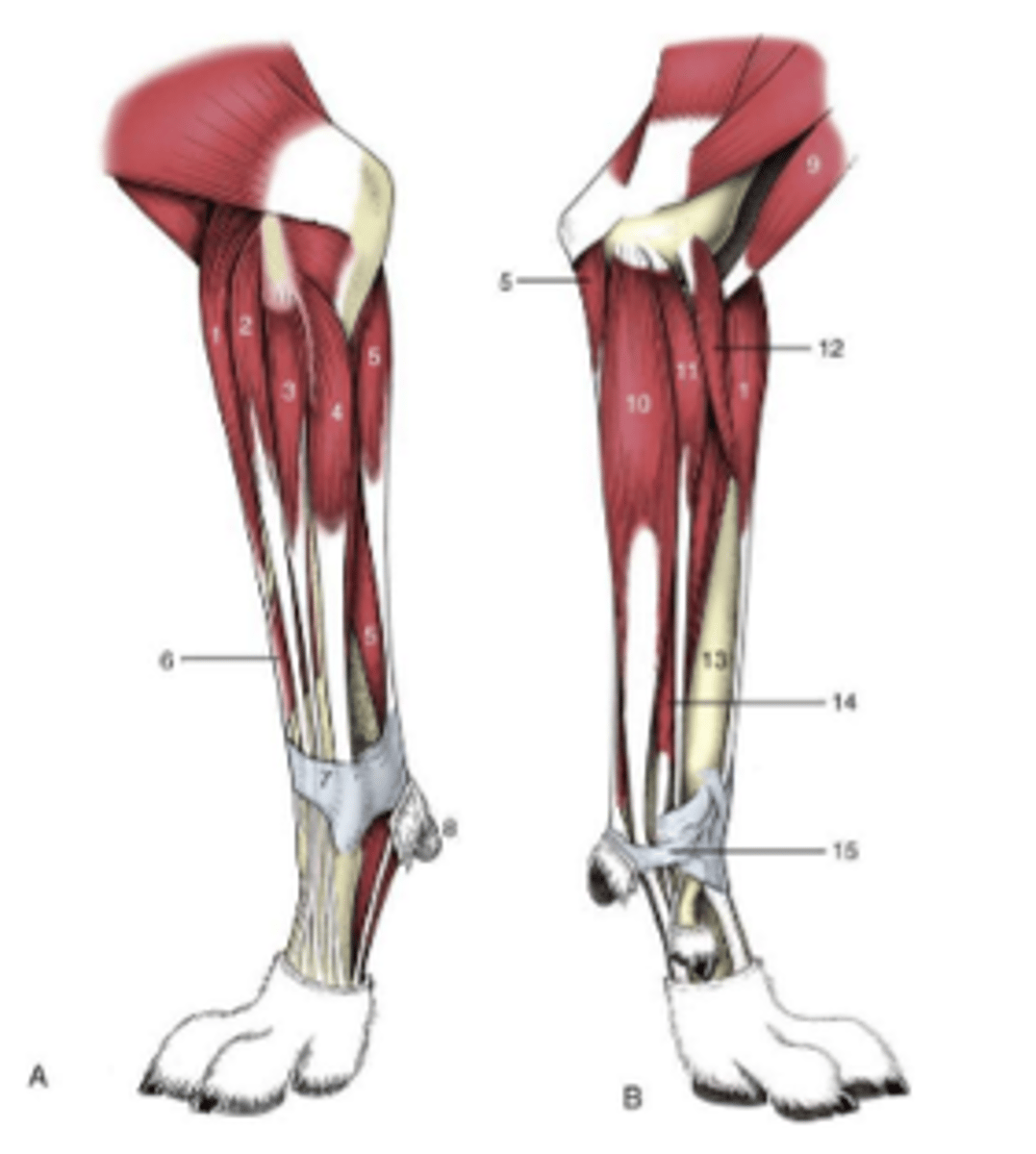
joints of the thoracic limb and flexor surfaces
-shoulder joint
-elbow joints
-carpal joints
-digital joints:
metacarpophalangeal joint
proximal interphalangeal joint
distal interphalangeal joint
-filled with synovial fluid
--viscous fluid
--nourishes and lubricates the joint
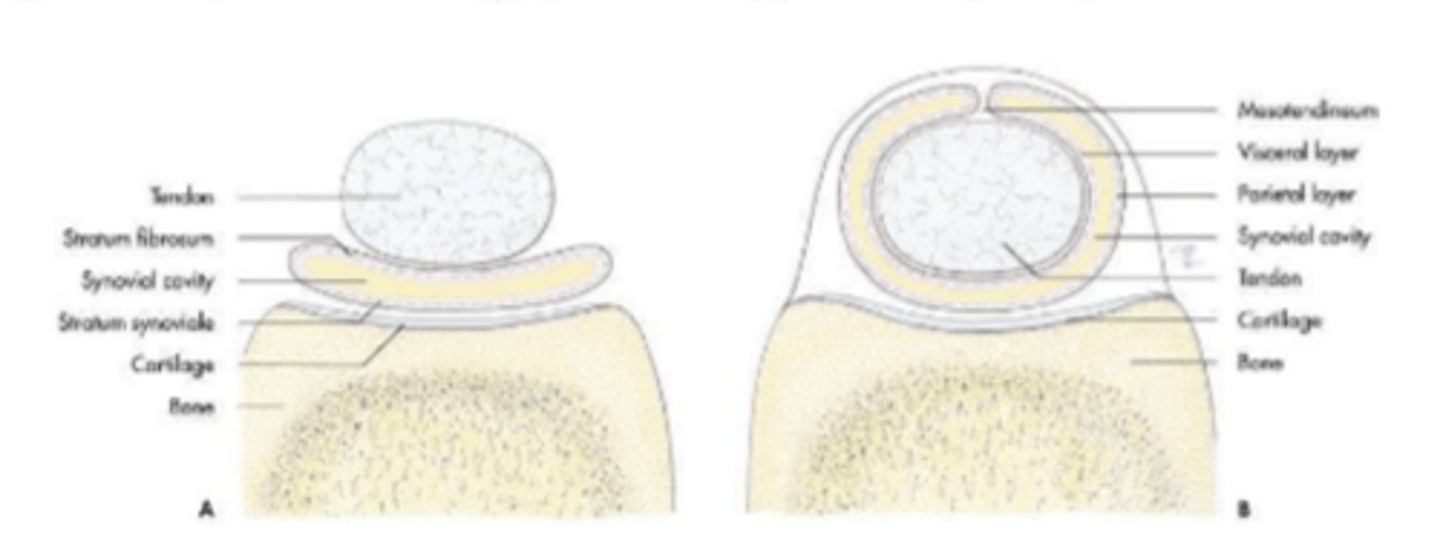
synovial structures
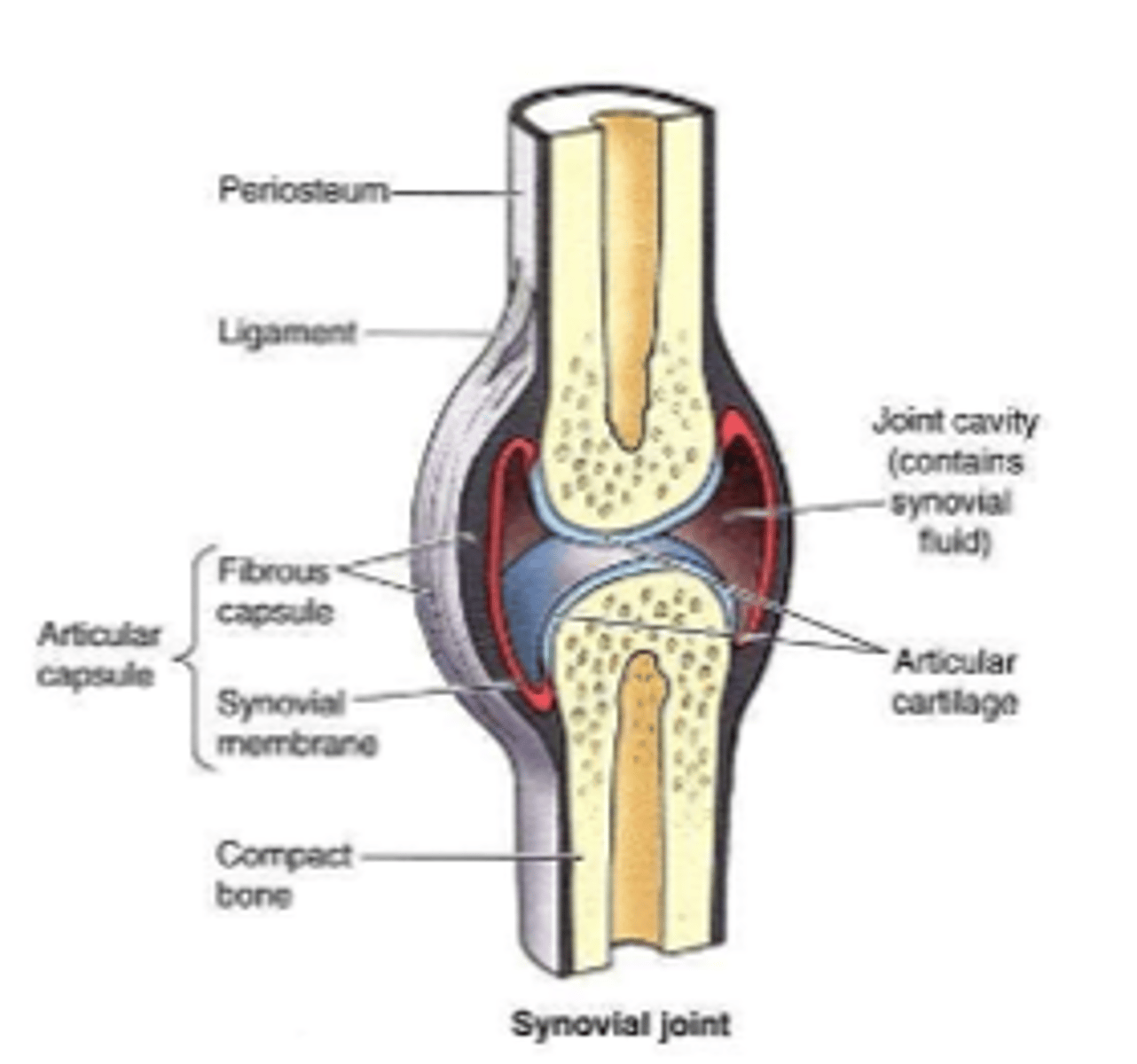
-synovial envelope that encloses a joint
-fibrous: can restrict movement
-puches
synovial joint capsule
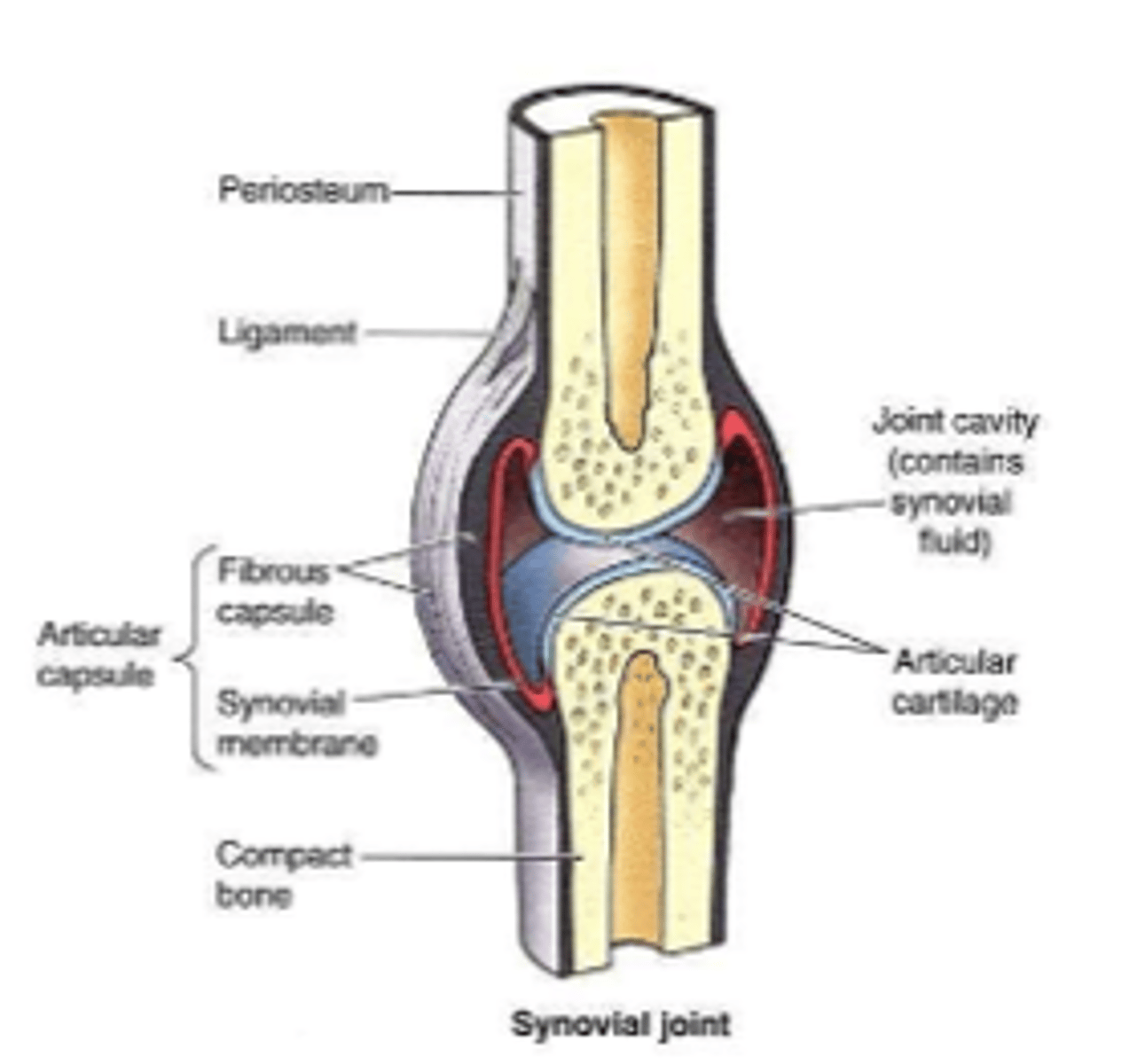
synovial sac lying between a tendon or muscle and an adjacent bony prominence
synovial bursae
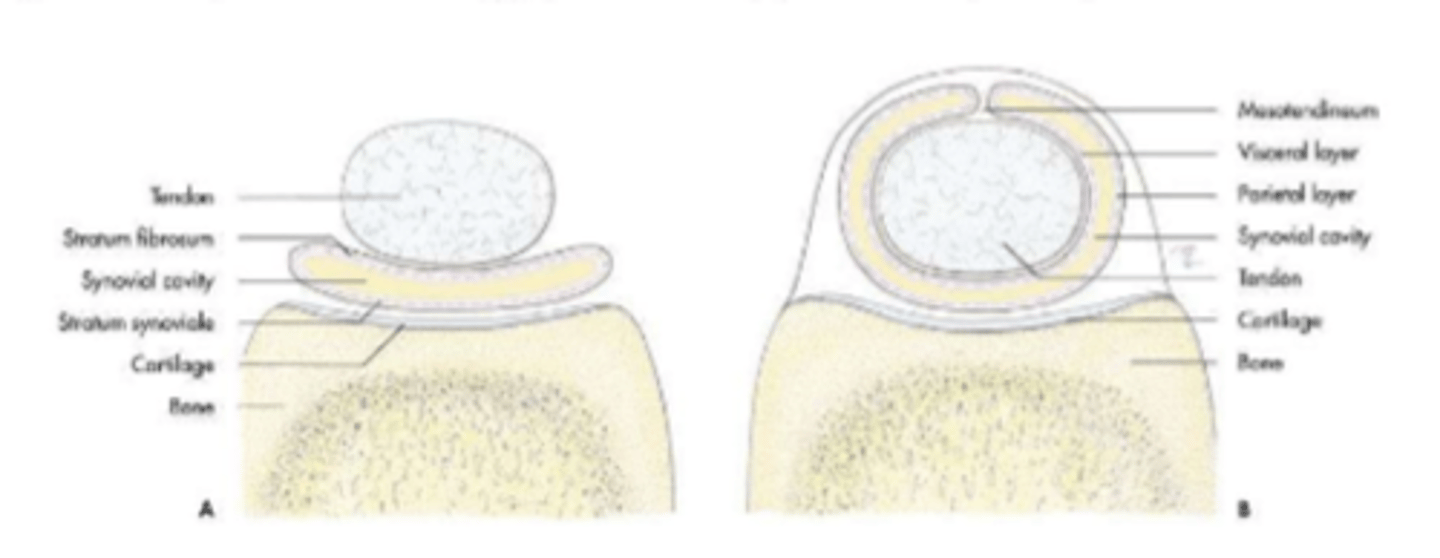
synovial sac that completely surrounds a tendon
tendon sheaths
synovial structure diagram
attach bone to bones
stabilize and support the joints
type I collagen
ligaments
fibrous band of connective tissue that bind tendons
retinacula
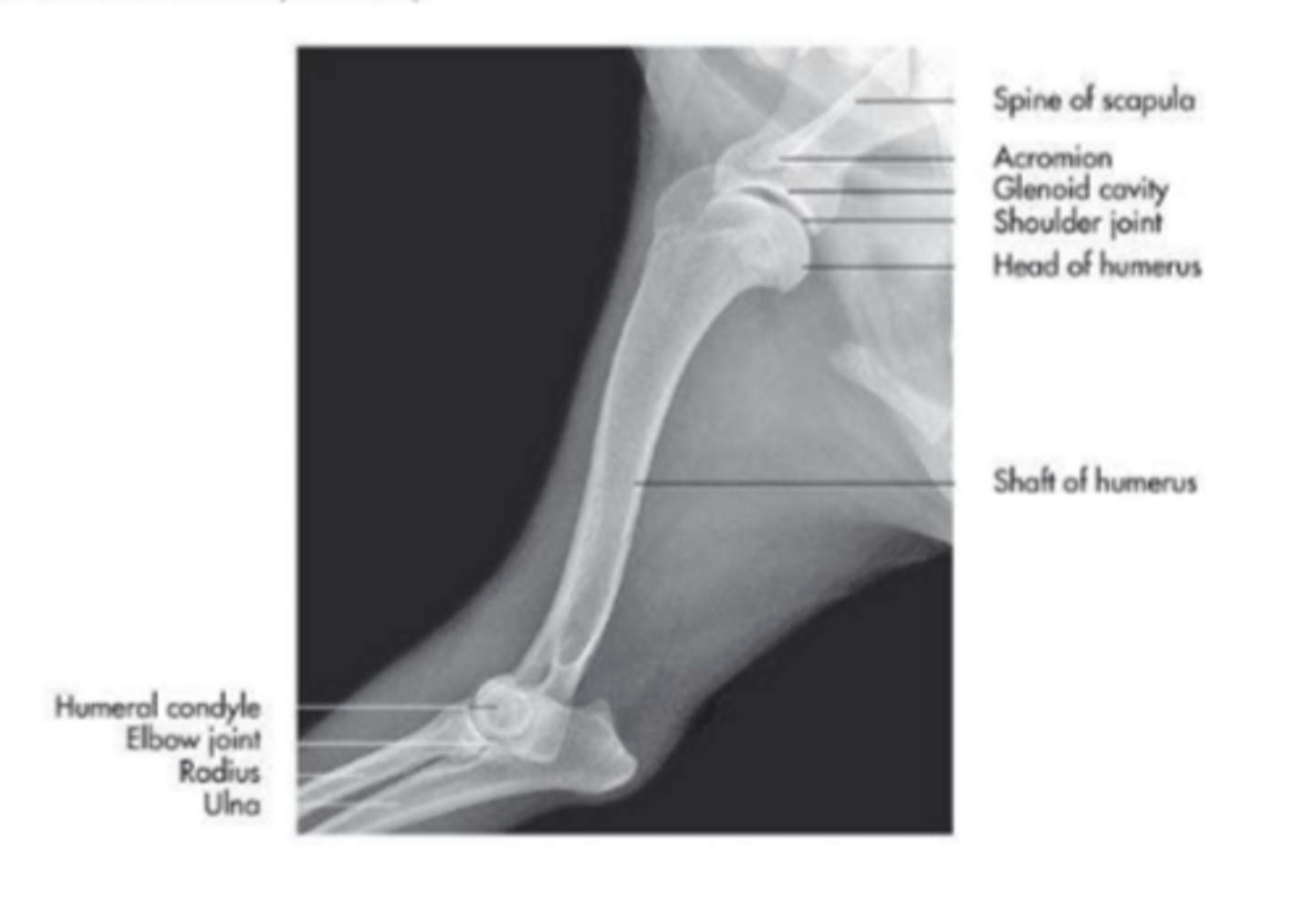
articular surfaces: glenoid cavity of the scapula
humeral head
range of motion: flexion and extension
supporting ligaments: none, joint is stabilized by muscles
-supraspinatus, infraspinatus, and subscapularis mm
glenohumeral (shoulder) joint
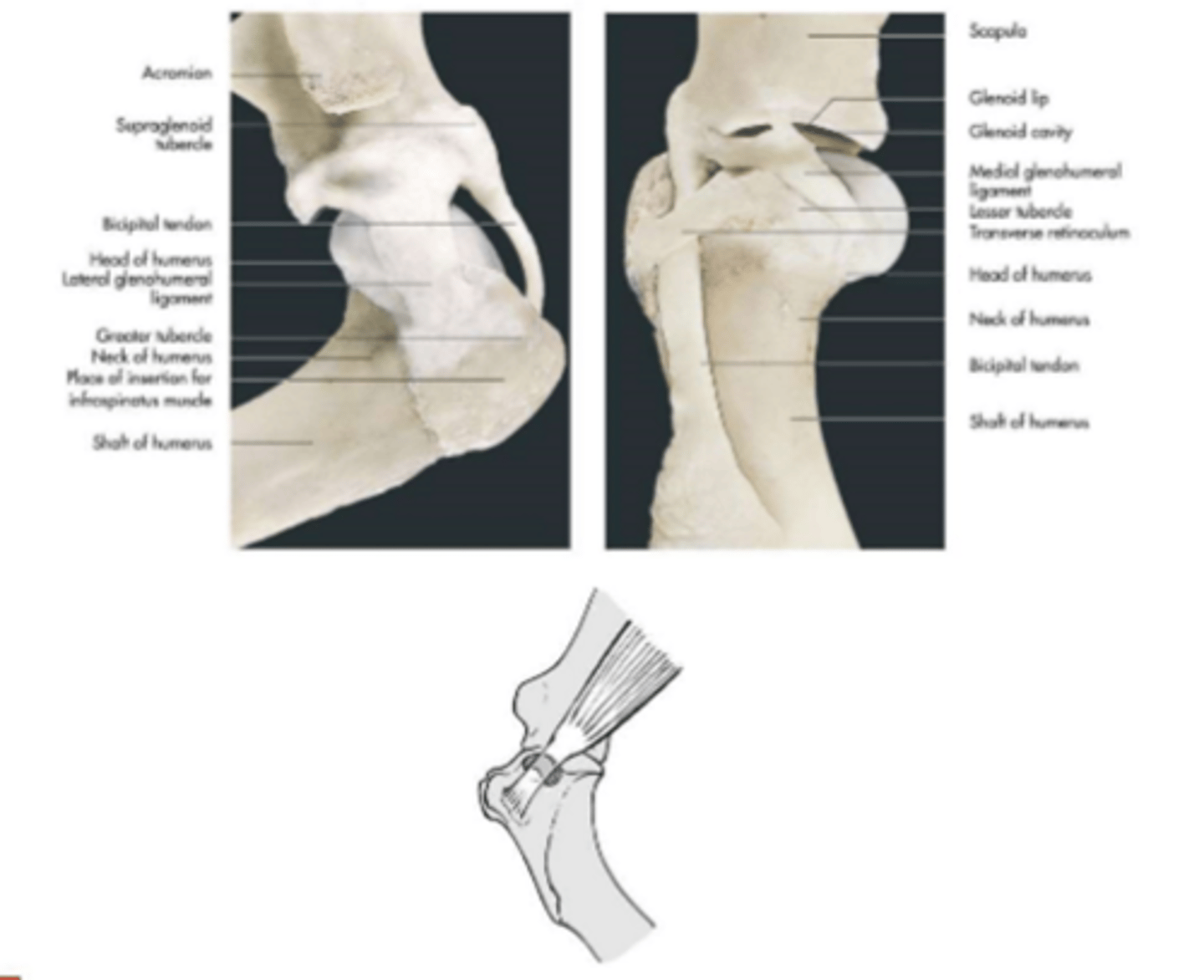
associated structures of the shoulder joint
glenohumeral ligaments
-medial and lateral
---thickening of the joint capsule
transverse humeral retinaculum
-holds biceps tendon in the bicipital groove
synovial structures
-infraspinous bursa
-tendon sheath of bicipital tendon
-bicipital bursa
---synoviocentisis
articular surfaces:
-humeral condyle
-head of radius and trochlear notch of the ulna
-articular circumference of the radius and radial notch of the ulna
range of motion:
flexion and extension
supporting ligaments:
medial and lateral collateral ligaments
synovial structures:
caudodorsal pouch
cubital (elbow) joints
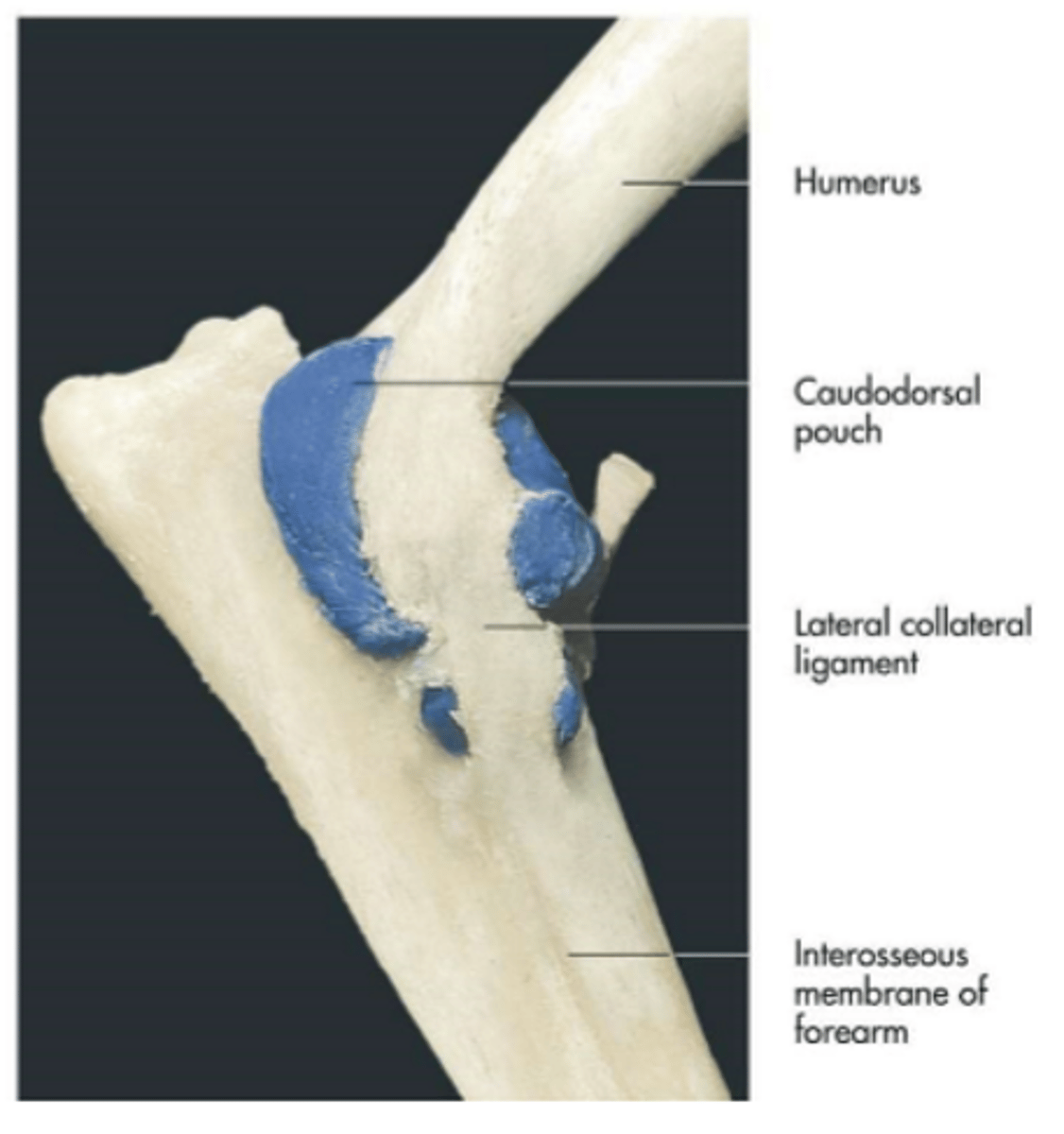
a site for arthrocentesis
-can access or inject joints
caudodorsal pouch
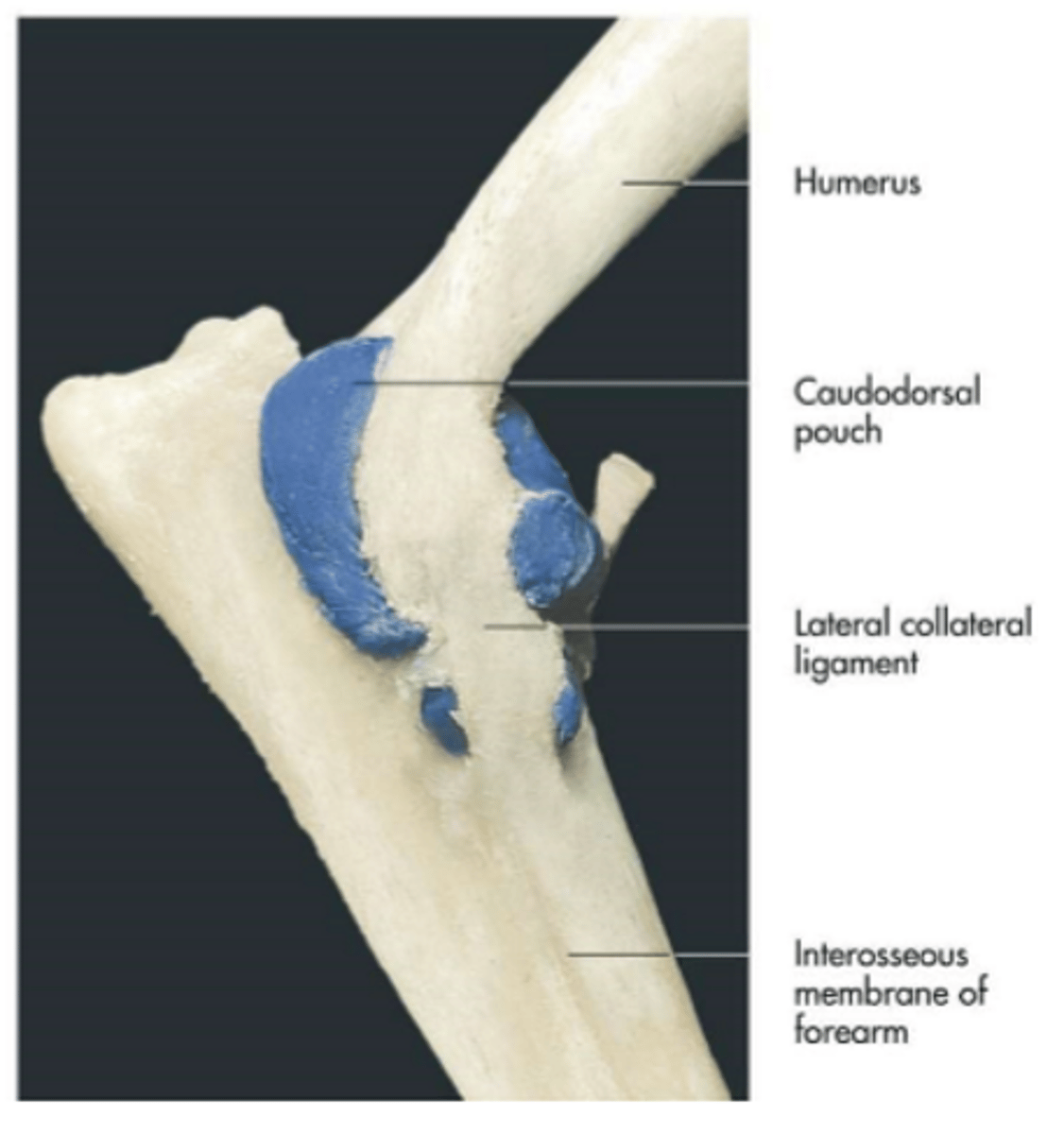
Articular surfaces:
-articular circumference of the radius and radial notch of ulna
-articular circumference of ulna and ulnar notch of radius
range of motion:
supination and pronation
supporting ligaments:
interosseous ligament
radioulnar joint
(relevant mostly in carnivores)
composite articulations:
-antebrachiocarpal joint
-middle carpal joint
-intercarpal joint
-carpometacarpal joint
range of motion:
-flexion and extension
--antebrachiocarpal and middle carpal
supporting ligaments:
-medial and lateral collateral ligaments
-palmar carpal ligament
-short ligaments
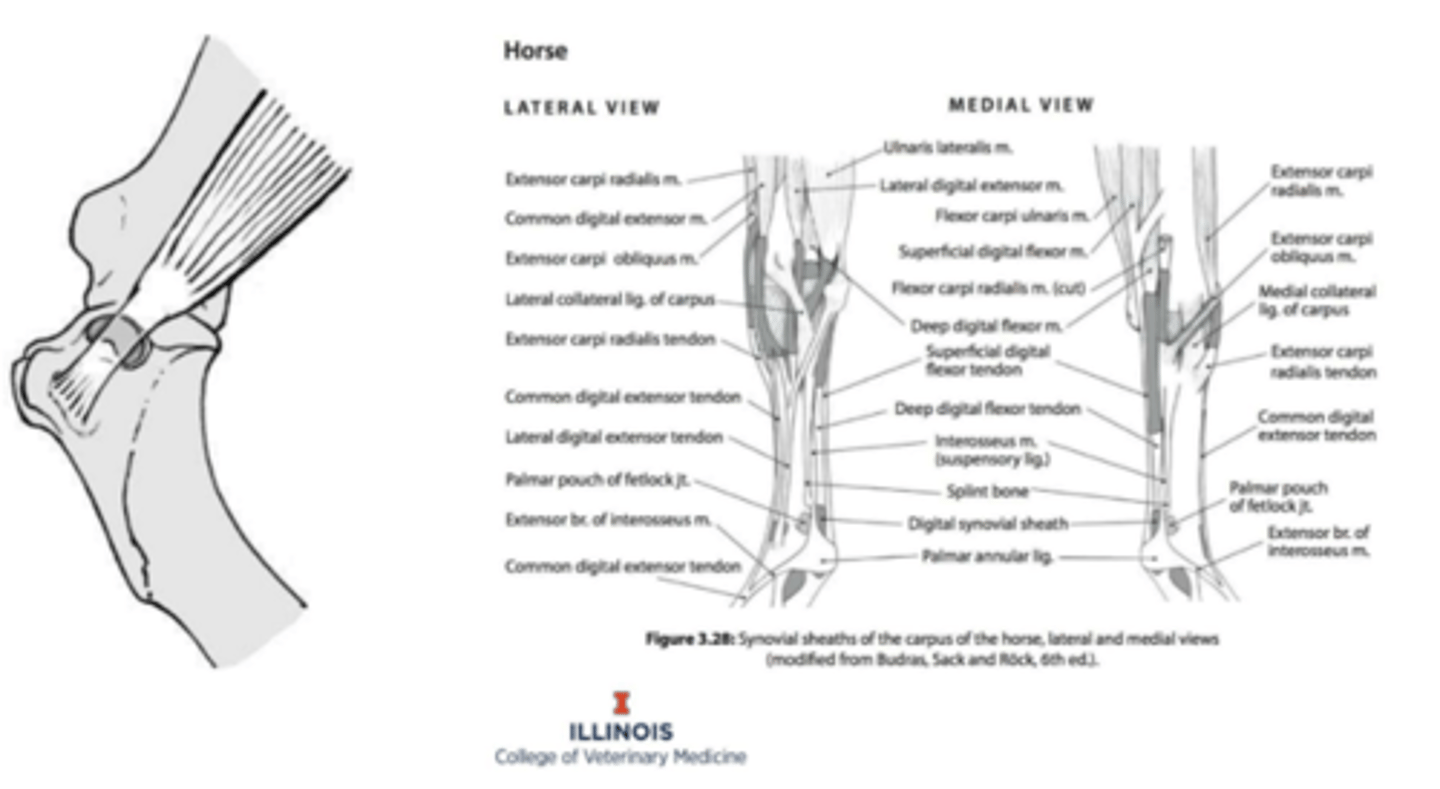
carpal (wrist) joint
carpal joints that are less movable
intercarpal and carpometacarpal joint
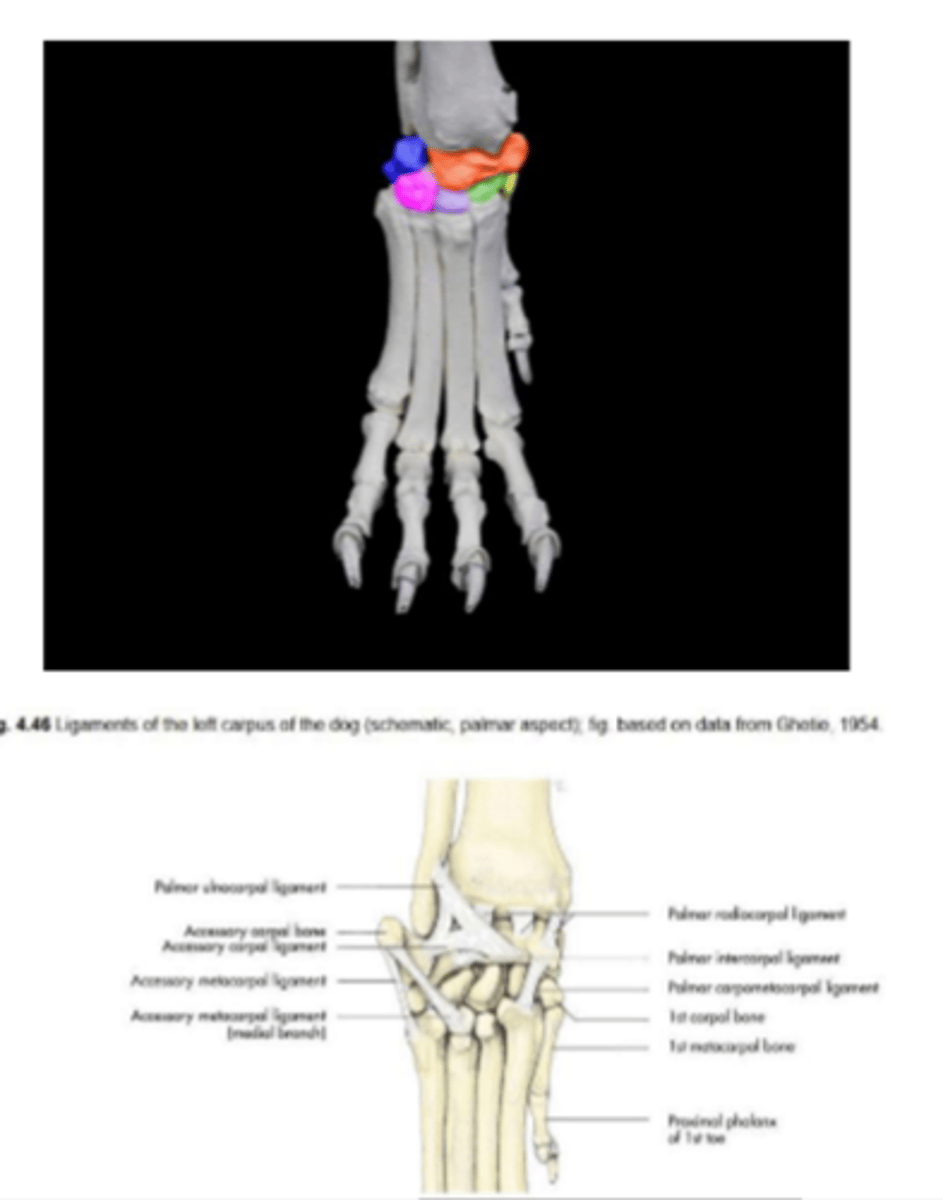
associated structures of the carpal joint
synovial structures
-common joint capsule
--separation between synovial compartments
--exception: middle carpal joint communicates with carpometacarpal joint
tendon and tendon sheaths of extensor and flexors
retinacula
-extensor retinaculum
-flexor retinaculum
clinical application: carpal injection
separation between synovial compartments means they do not communicate and need to inject them separately
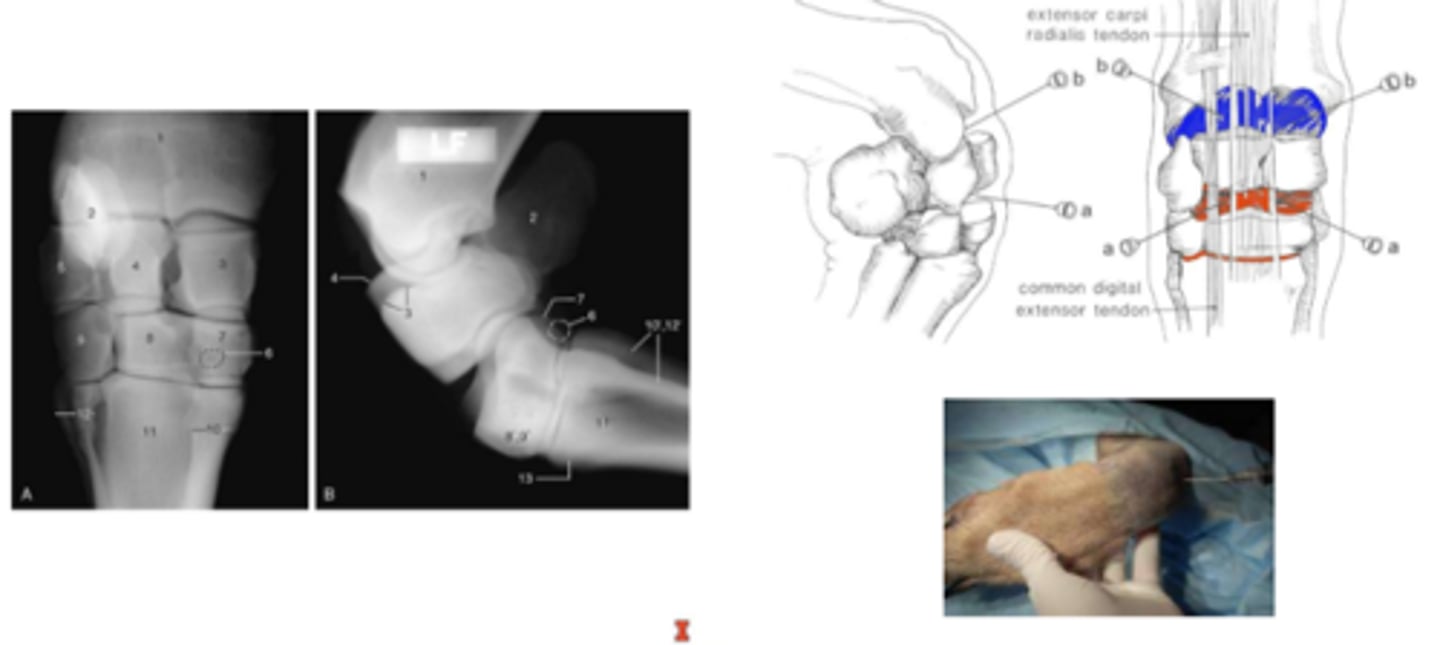
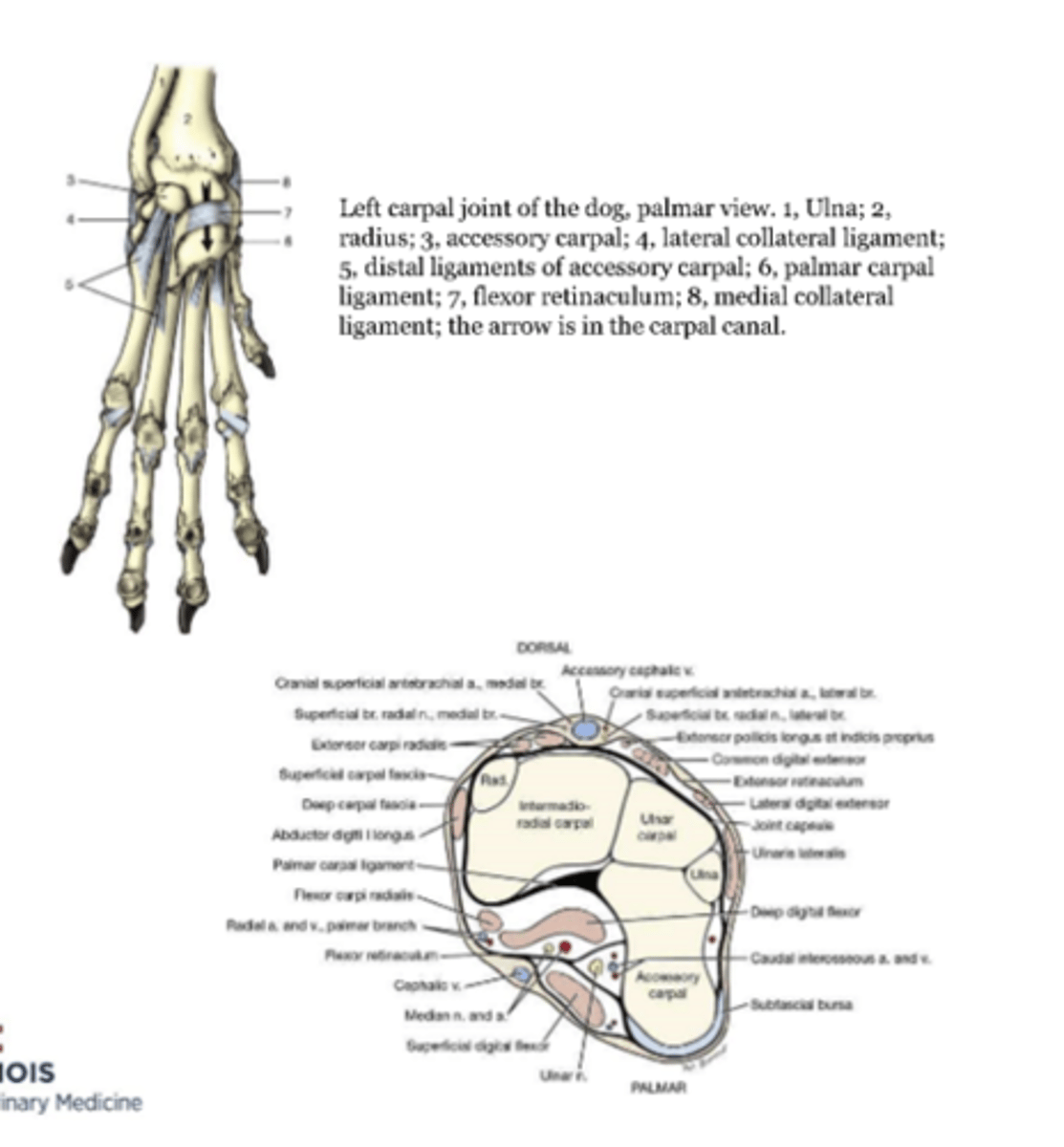
"passageway"
-flexor carpi radialis m
-digital flexor tendons and their synovial sheaths
---SDF
---DDF
-blood vessels and nerves
---median and radial aa
---median and ulnar nn
boundaries
-palmar carpal ligament
-flexor retinaculum
-accessory carpal bone
carpal canal
joint:
-metacarpophalangeal joint (fetlock): distal extremity of the metacarpal bone and proximal extremity of the proximal phalanx
-proximal interphalangeal joint (pastern): distal extremity of the proximal phalanx and proximal extremity of the middle phalanx
-distal interphalangeal (coffin): distal extremity of the middle phalanx and proximal extremity of the distal phalanx
range of motion:
flexion and extension
supporting ligaments:
-medial and lateral collateral ligaments (horse)
-annular ligaments
digital joints
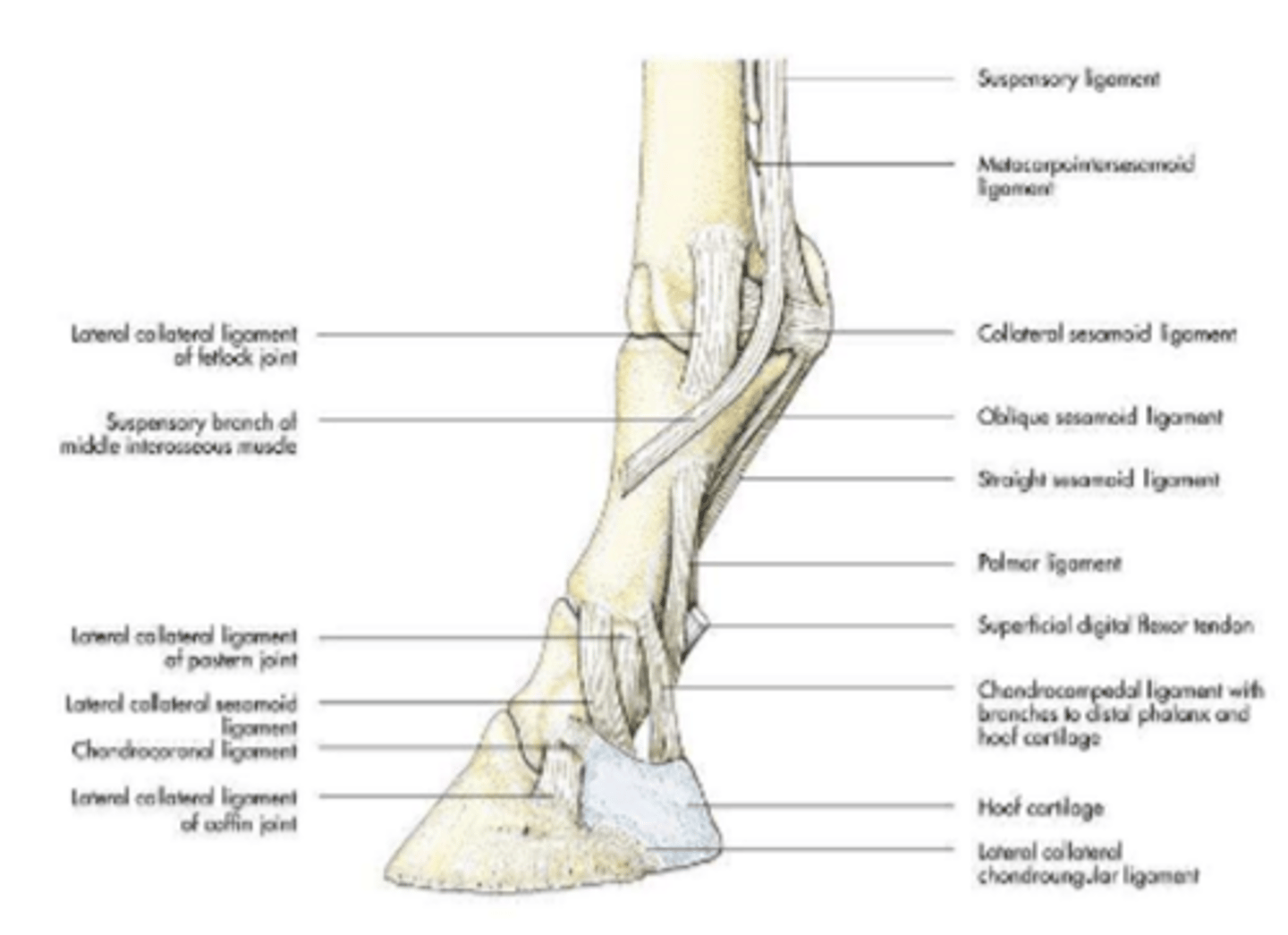
fetlock joint
metacarpophalangeal joint
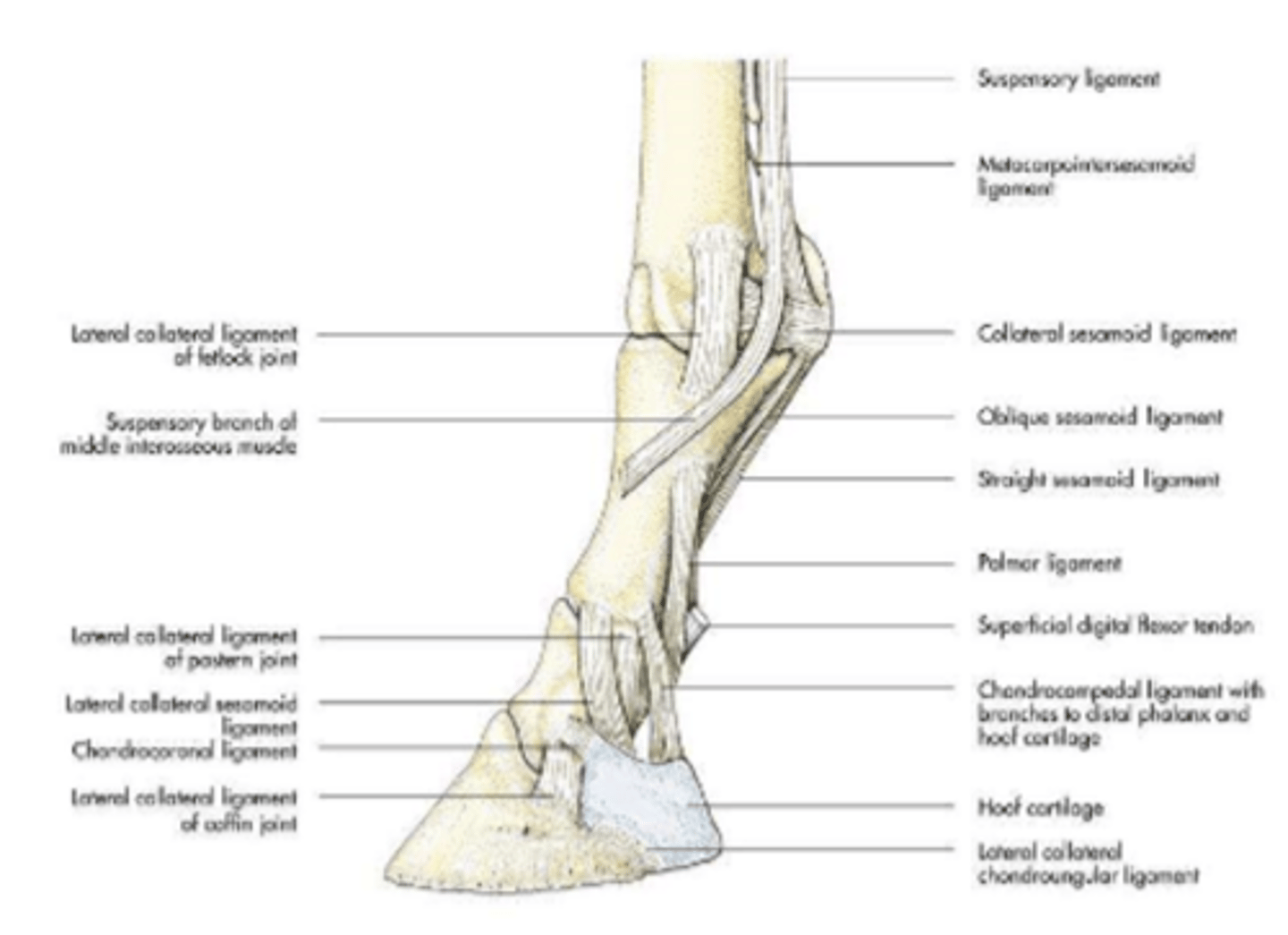
pastern joint
proximal interphalangeal joint
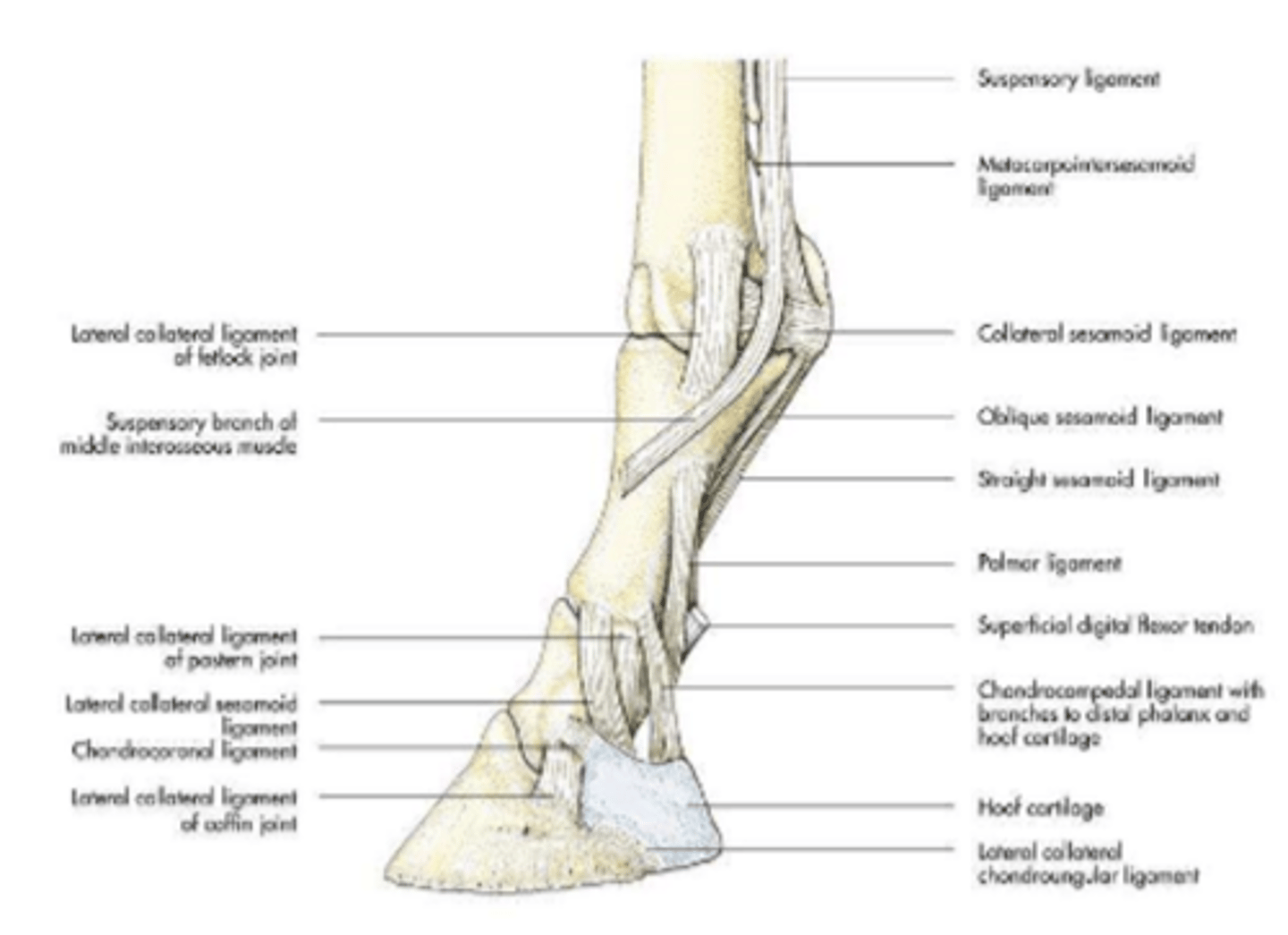
coffin joint
distal interphalangeal joint
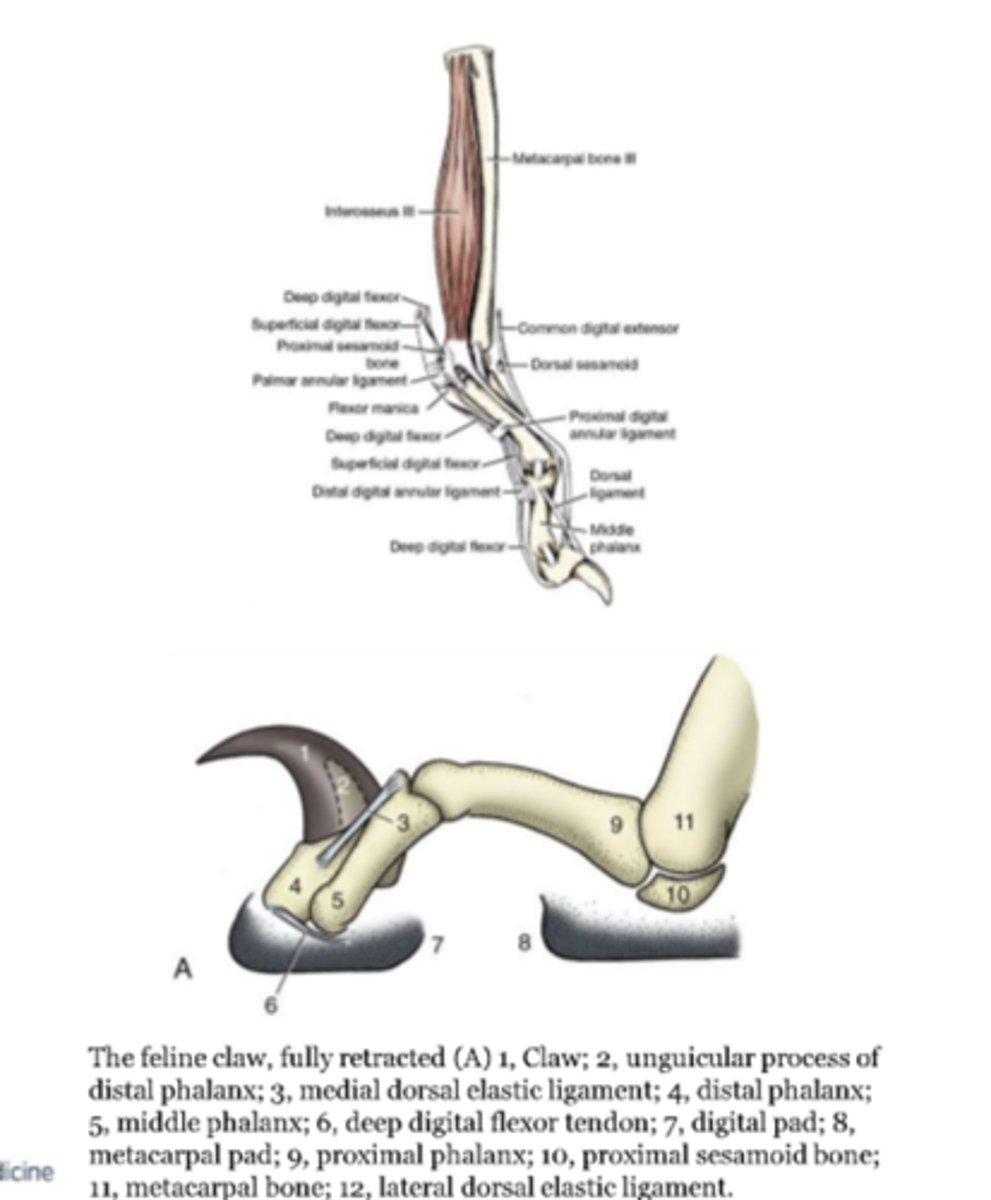
located on each side of the common digital extensor tendon
keeps claws retracted (works more in cats than dogs)
claws are protruded by simultaneous contraction of the deep digital flexor
dorsal elastic ligaments
brace the digital flexor tendons
-proximal digital and distal digital
-looks like an X in horses
annular ligaments
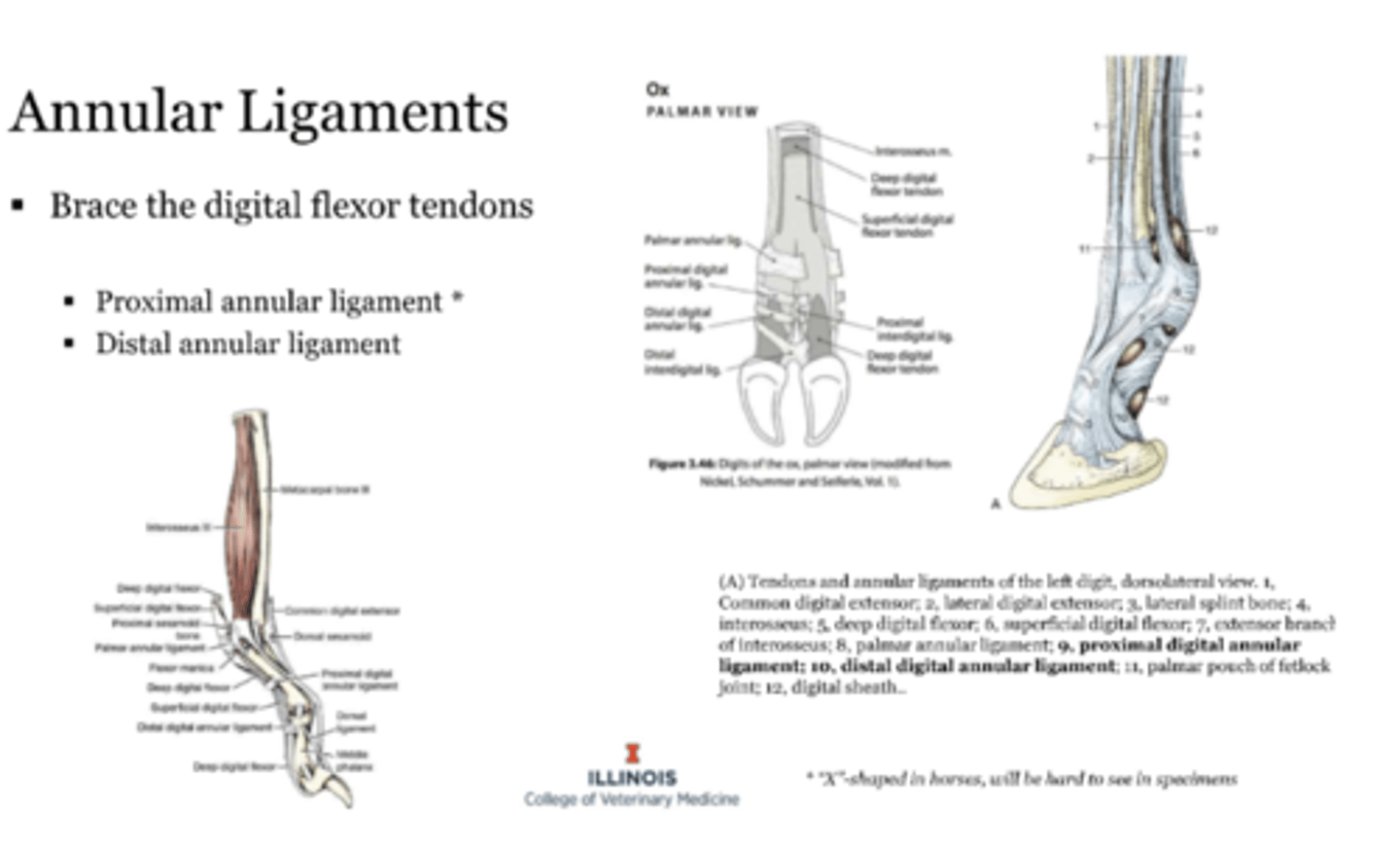
in ruminants
support the digits and prevent the digits from spreading
-proximal and distal
interdigital ligament
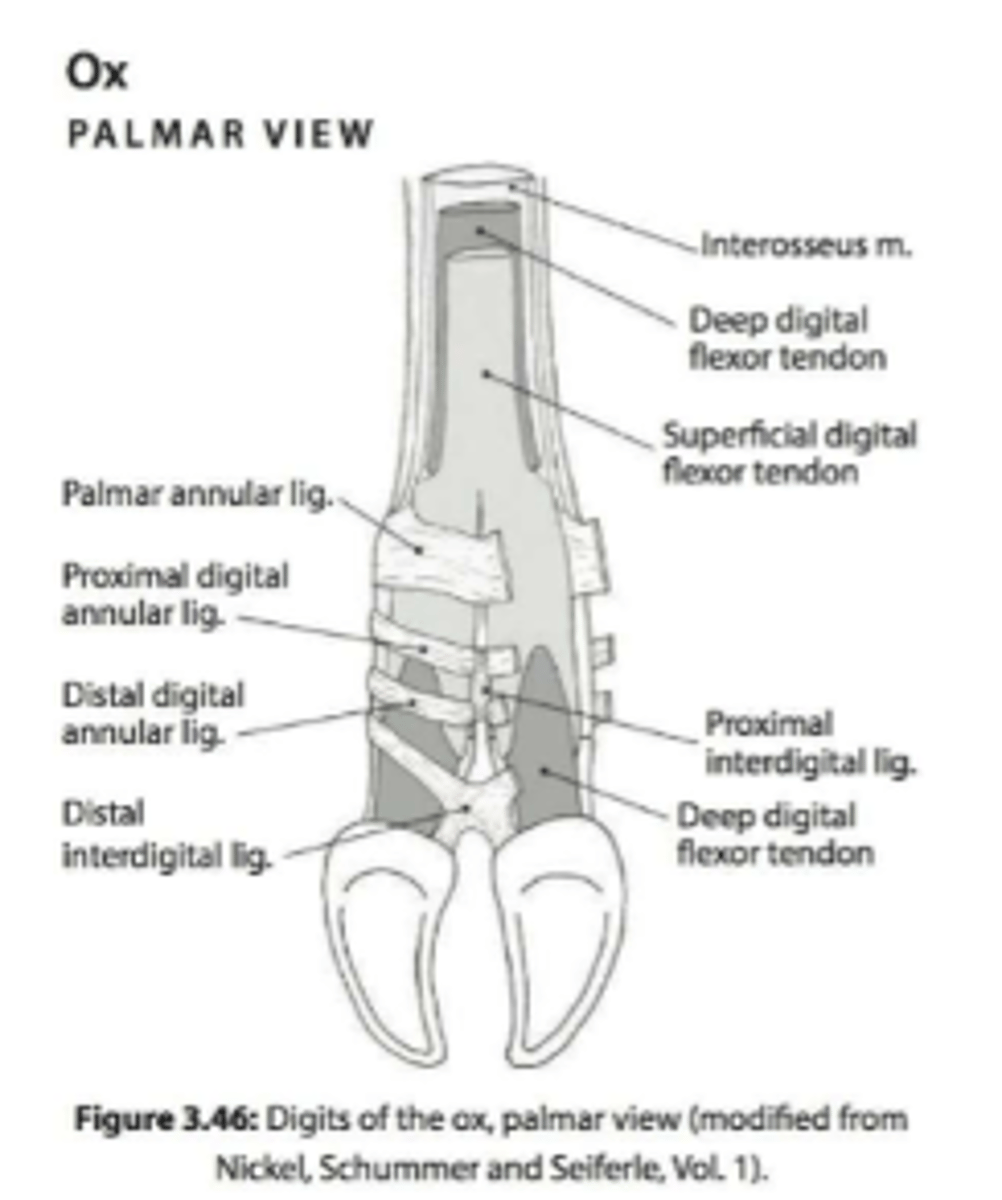
in horses
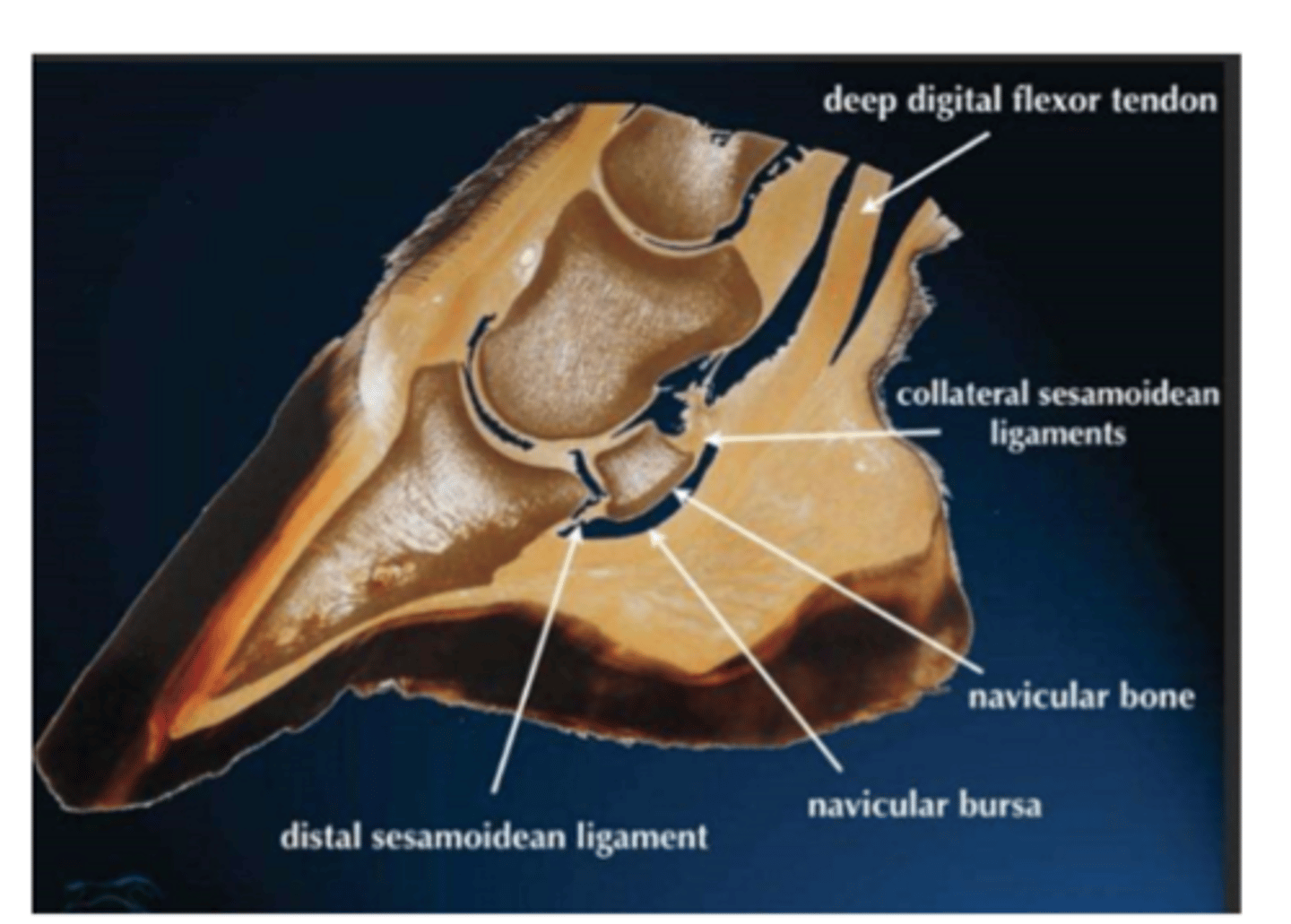
located between the navicular bone and deep digital flexor tendon
clinically- relevant: bursitis due to injury (puncture is most common)
navicular bursa
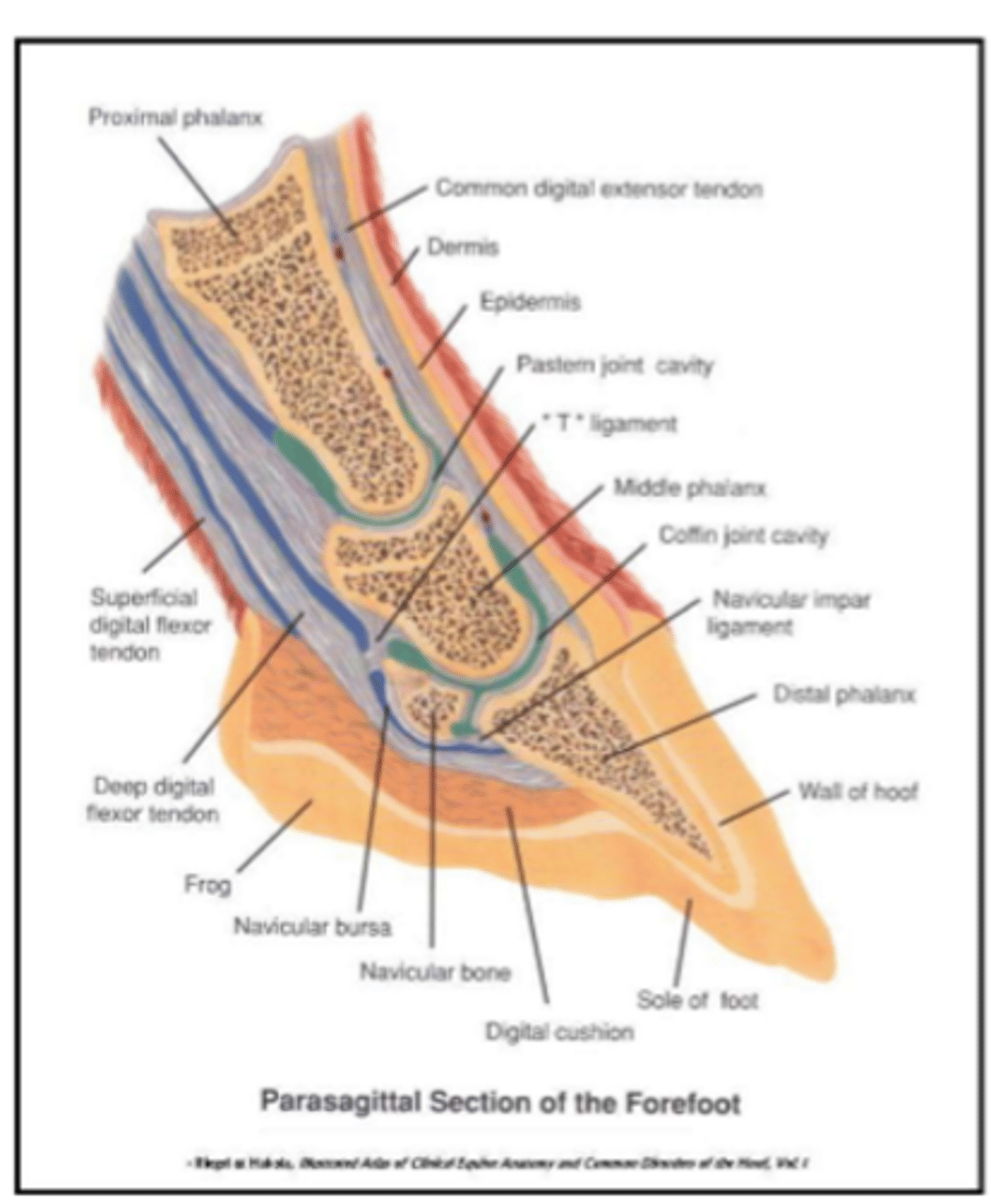
picture of navicular bursa