W1 - Cells of the NS, Cerebral Cortex and White Matter
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
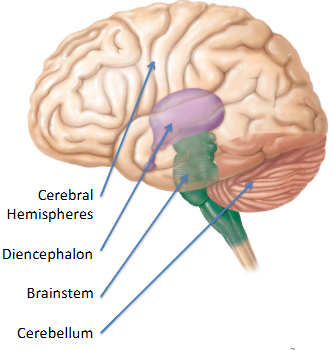
Composition of the Brain
R/L Cerebral Hemispheres (Cerebrum)
Diencephalon
Brainstem
Cerebellum
Cerebrum Composition
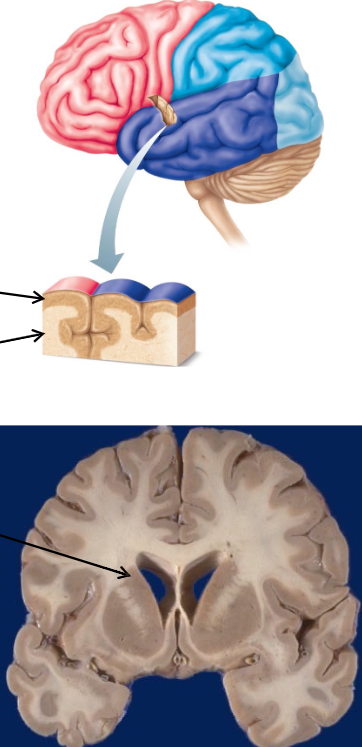
Cerebral Cortex = outer crust of cerebral gray matter, location of conscious mind
Cerebral White Matter = neuron fiber tracts deep to the cerebral cortex
Basal Nuclei (Basal Ganglia) = islands of gray matter buried within the white matter
Limbic System = gray and white matter structures dispersed thruout the cerebrum
Gross Anatomical Features of the Brain
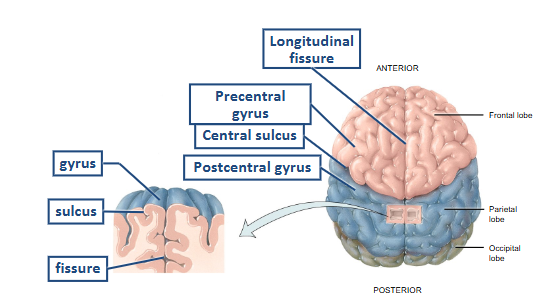
gyri = folds that increase SA, numerous
sulci = shallow grooves between the gyri
fissure = deep grooves that sep larger portions of the cerebrum
Lobes of the Cerebral Hemisphere
frontal
parietal
occipital
temporal
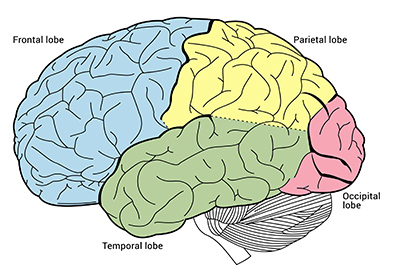
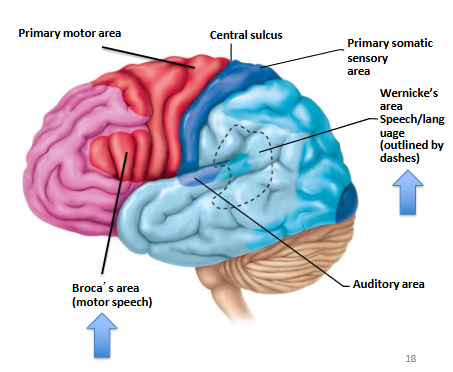
Frontal Lobe
contains primary motor cortex- voluntary control of skeletal muscles
Parietal Lobe
contains primary somatosensory cortex- conscious perception of touch, pressure, pain, vibration, temp
Occipital Lobe
contains visual cortex- conscious perception of visual stimuli
Temporal Lobe
contains auditory cortex and olfactory cortex- conscious perception of auditory and olfactory stimuli
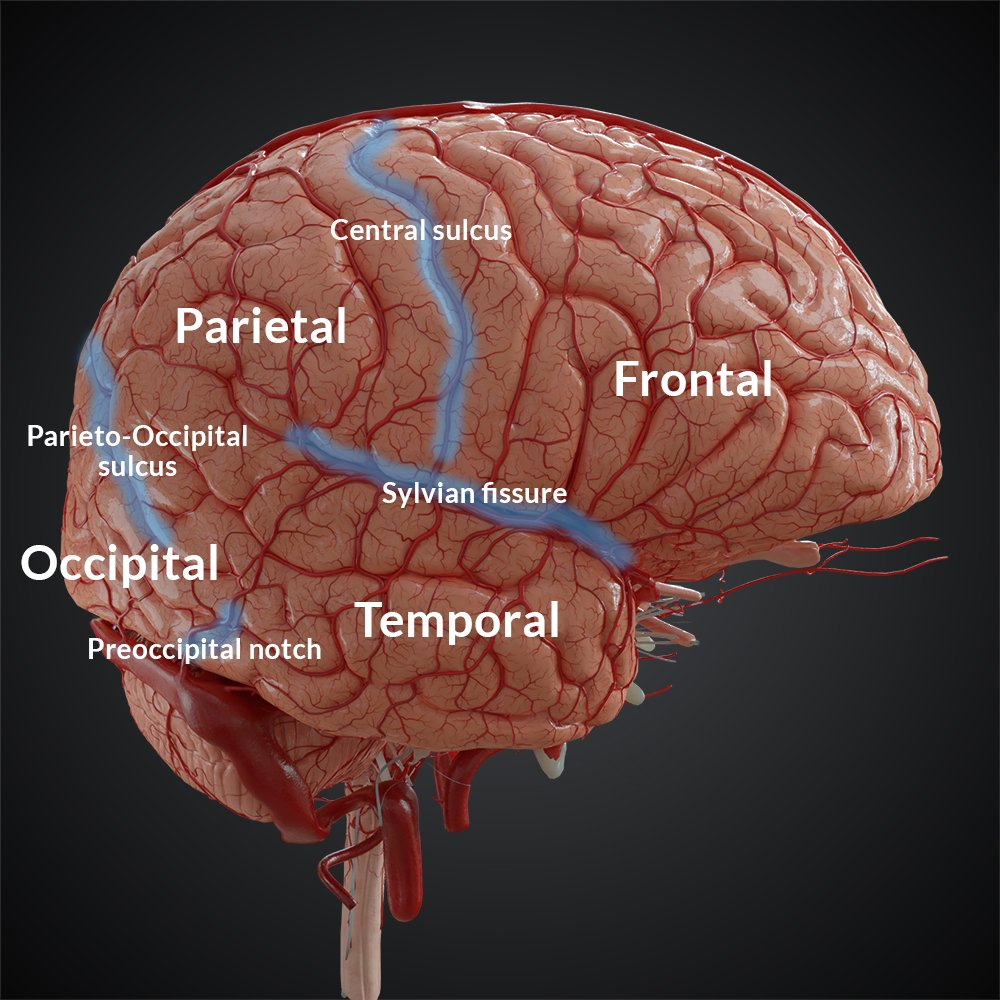
Fissures of the Brain (Sylvian fissure = Lateral Fissure/Sulcus)
Insula
located deep within the lateral fissure- involved in sensory processing, emotions and self awareness
Hemispheric Functionality
while both hems are involved in most functions, they are specialized
LT = language, numerical and scientific skills
RT = complex visual-spatial skills, communicate emotional significance to events and language, music perception
Pre/Post- Central Gyrus aka
primary motor/sensory cortex
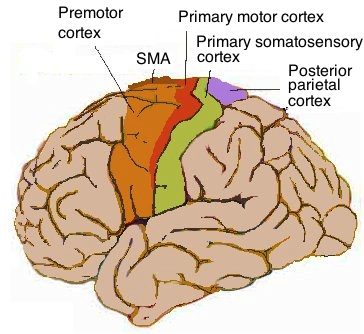
A lesion in the Somatosensory Area
causes contralateral loss of sensations, can perceive sensation but cannot tell the degree or origin
A lesion in the Primary Motor Area
contralateral paralysis
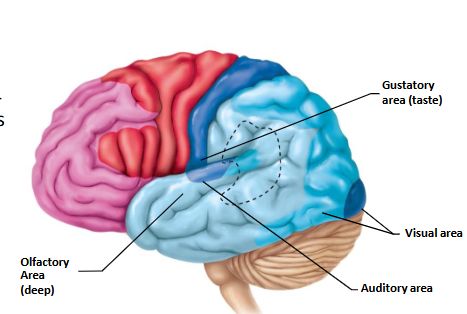
Special Sense Areas of the Cerebral Cortex
Insula = Gustatory (taste)
Occipital = Visual
Temporal = Olfactory, Auditory
Special Cerebral Cortex Areas for Speech and Language
Broca’s Area = speech muscles
Wernicke’s Area = permits recognition of spoken and written language, create plan of speech
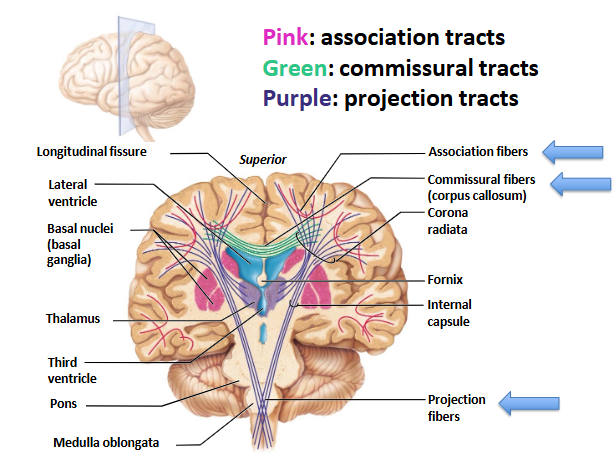
Types of Tracts within Cerebral White Matter
association = confined to the same hem
commissural = run between R/L hems
projection = project to and from the cerebral cortex and form asc/desc tracts
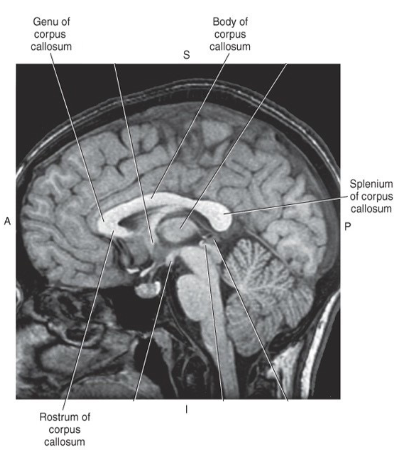
Corpus Callosum
important white matter commissural tract
components: rostrum, genu, body, splenium
Four Main Tissues
nervous
muscle
epithelial
connective
cells of the NS
neurons
neuroglia
neurons vs. neuroglia
neurons:
electrically excitable (AP)
cellular structures
cannot divide
neuroglia
not electrically excitable
supporting structures
can divide/multiply
layout of the NS
CNS
brain
spinal cord
PNS (Peripheral NS)
cranial nerves
spinal/peripheral nerves
nerve plexuses
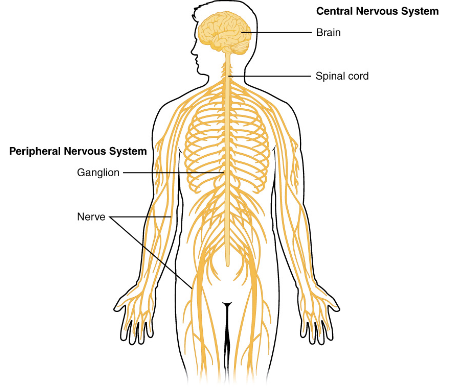
PNS
extension from the CNS
consists of all the nervous tissue outside of the CNS
Functions of the NS
sensory = detect changes thru sensory receptors
integrative = analyze sensory info, store info, make decisions
motor = respond to stimuli via effectors
PNS Function
acts as a communication line between
sensory receptors → CNS
CNS → effectors (glands, muscles)
Cranial and Spinal Nerves consist of
afferent neurons = sensory information from the periphery to the CNS
efferent neurons = motor information from the CNS to the periphery
Functional Divisions of the PNS
Somatic NS
Autonomic NS
Enteric NS
Flow of the NS
Sensory Components of the PNS (sensory receptors and neurons of the SNS, ANS, ENS) → CNS → Motor Components of the PNS (motor neurons) → Effectors (muscles, glands)
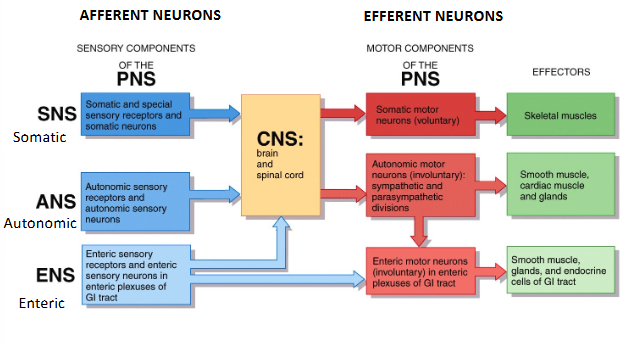
Sensory Components of the PNS (Afferent)
somatic sensory neurons
visceral sensory neurons
Somatic Sensory Neurons
carry sensory info that one is conscious of
temp
pain
touch
proprioception (sense of own movement/position in space)
muscle stretch
special senses
Visceral Sensory Neurons
carry sensory information that one is not conscious of
BP
blood gases
distension
change in pH
Motor Components of the PNS (Efferent)
Somatic Motor Neurons
Autonomic Motor Neurons
Somatic Motor Neurons
voluntary actions- conscious control of skeletal muscle contraction
Autonomic Motor Neurons
involuntary actions- unconscious control of smooth/cardiac muscles, gland secretions
ANS Subdivisions
sympathetic (fight or flight)
parasympathetic (rest and digest)
Functional Classification of Neurons
classified based on the direction of the AP propagation
afferent: to the CNS
efferent: from the CNS
interneurons/association (the CNS): process sensory info and elicit motor response
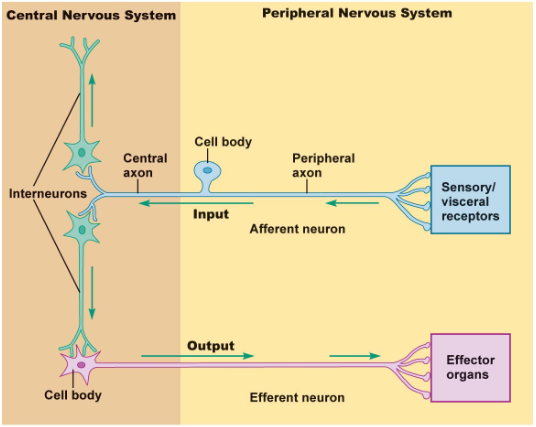
Cell Bodies of the Neuron Terminology
PNS
CNS
PNS = ganglia/ganglion
CNS = nuclei/nucleus
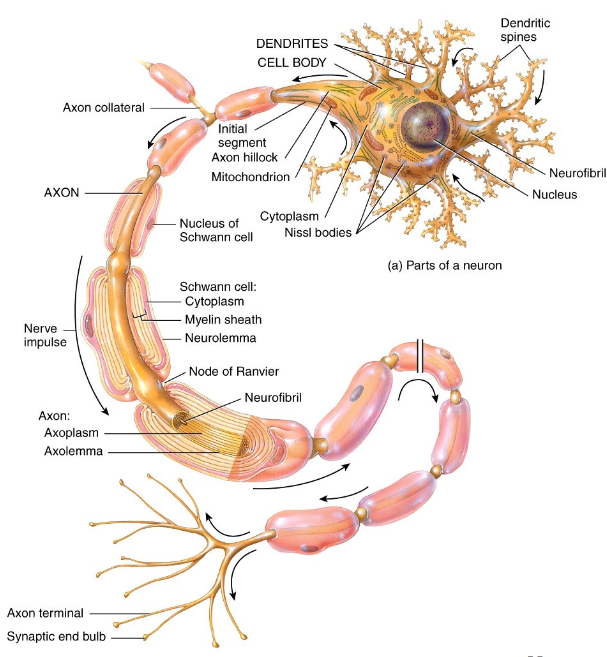
Components of the Neuron - Dendrites
multiple short and branches procesess off the cell body that receives input from neighboring neurons via neurual synapse
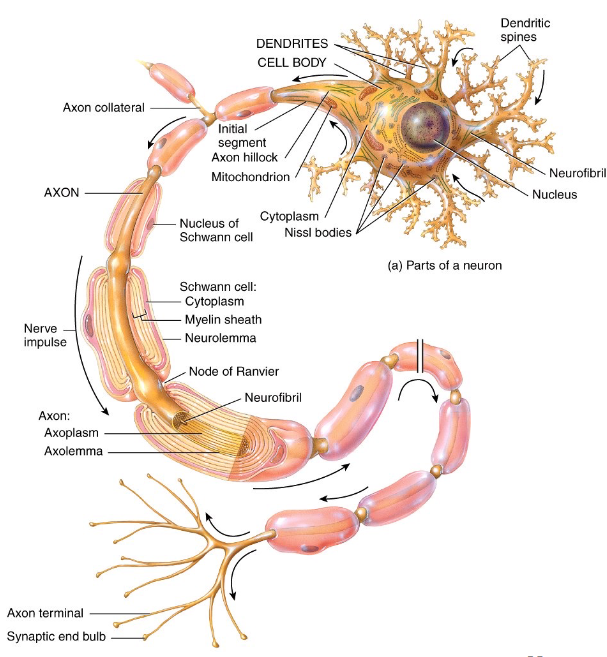
Components of the Neuron - Axon
single long cellular process that is connected to the cell body at the axon hilock
AP initiated at the initial segment → transmitted along the axon towards a another neuron/muscle fiber/gland cell
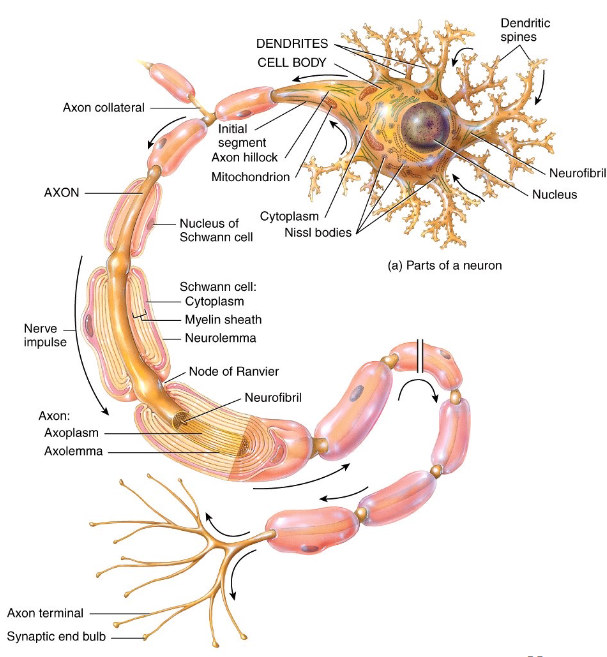
Components of the Neuron - Axon Terminals
division of axons
synaptic end bulbs contain synaptic vesicles that store neurotransmitters (molecules that excite or inhibit other neurons/muscle fibers/gland cells)
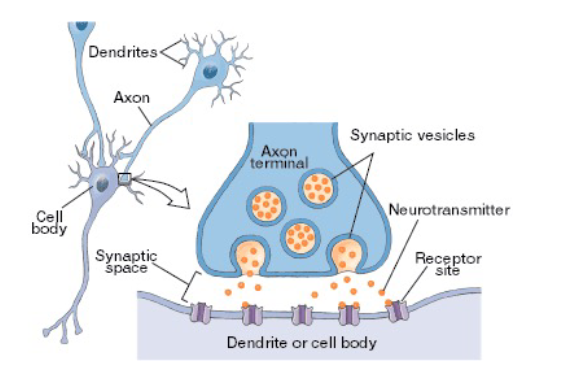
Presynaptic vs. Postsynaptic Neurons
the presynaptic neuron signals to the dendrites of the postsynaptic neuron at the neurual synapse
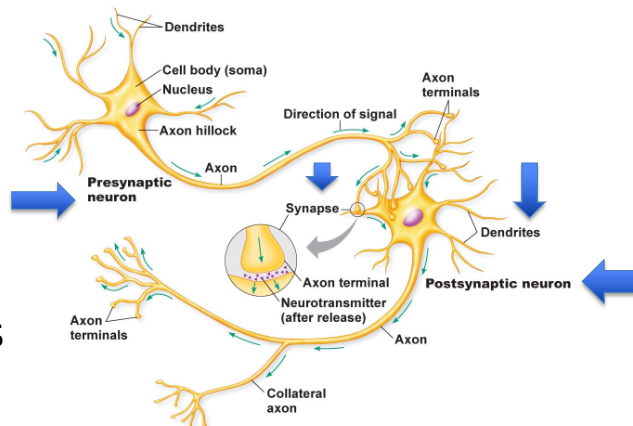
Axons of Neurons Terminology
PNS
CNS
PNS = nerves
CNS = tracts
Neuroglia in the CNS
astrocytes = strength/support, blood-brain barrier
microglia = phagocytes
ependymal cells = production of CSF
oligodendrocytes = myelination of axons of CNS neurons
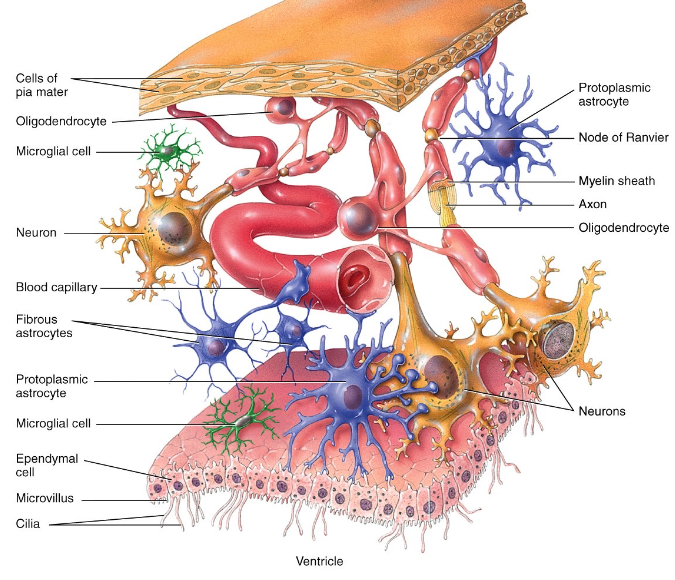
Neuroglia in the PNS
satellite cells = regulate extracellular environment of PNS neurons (like astrocytes in CNS)
schwann cells = myelination of axons of PNS neurons
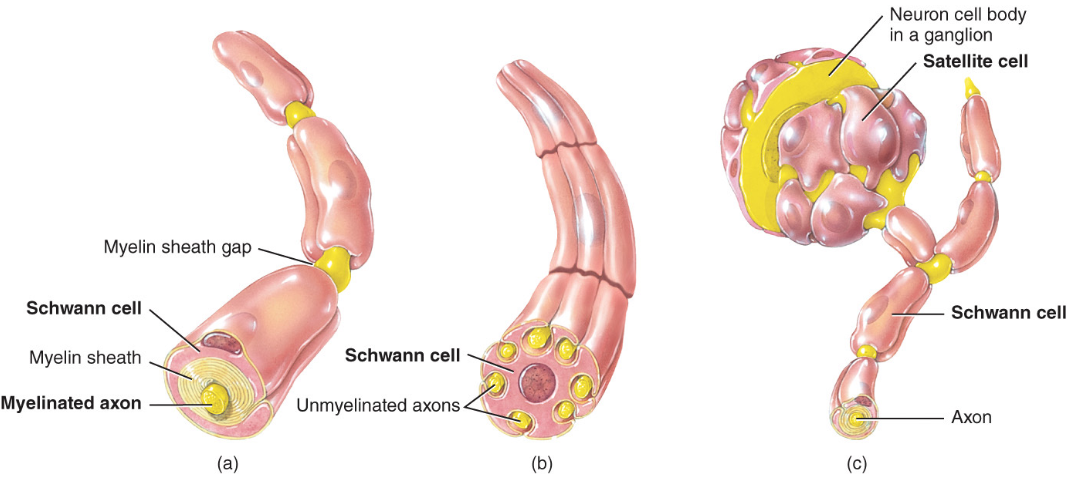
Myelination
a process which a fatty protein layer, called myelin sheath, forms around axons
provides electrical insulation of the axons, increases speed of AP conduction
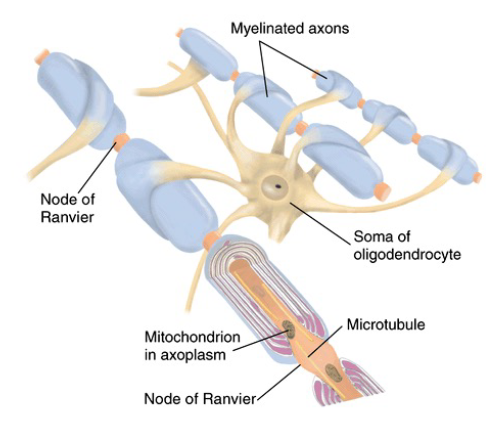
Nodes of Ranvier
gaps in myelin sheath along the axon
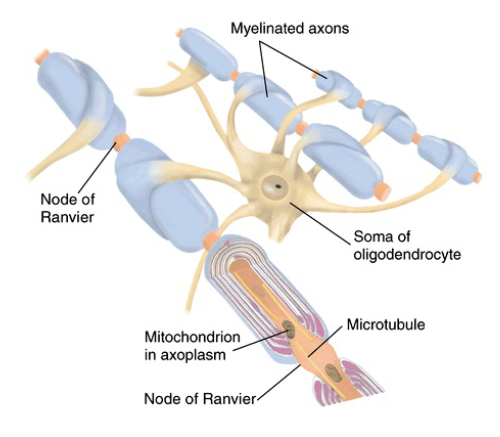
Two Types of Neuroglia that produce Myeline sheaths
oligodendrocytes (CNS)
Schwann cells (PNS)
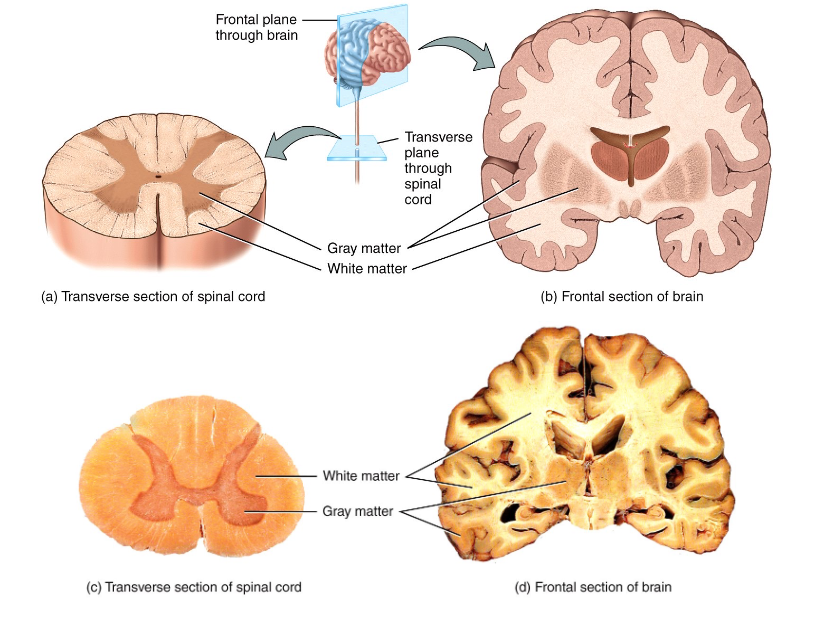
Gray vs. White Matter
gray = regions with many cell bodies and dendrites
white = regions with many axons