UARK CHEM 2 Exam 3
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Adding reactant (which makes Q < K) causes
the reaction to shift to the right
Adding product (which makes Q > K) causes
the reaction to shift to the left
Removing reactant (which makes Q > K) causes
the reaction to shift to the left
Removing product (which makes Q < K) causes
the reaction to shift to the right
Decreasing volume causes
a reaction to shift in the direction with fewer moles of gas
Increasing volume causes
a reaction to shift in the direction with more moles of gas
Adding an inert gas to a mixture at a fixed volume
does not affect equilibrium (no shift)
When a reaction has equal number of moles of gas on both sides of a chemical equation,
a change in volume does not affect equilibrium (no shift)
In an exothermic reaction,
heat is a product
increasing the temp causes the reaction to shift left
decreasing the temp causes the reaction to shift right
In an endothermic reaction
heat is a reactant
increasing the temp causes the reaction to shift right
decreasing the temp causes the reaction to shift left
Binary acids
composed of hydrogen and a nonmetal

Oxyacids
contain hydrogen and an oxyanion
Oxyanions ending with -ate
-ate goes to -ic
ex. sulfate to sulfuric acid

Oxyanions ending with -ite
-ite goes to -ous
ex. sulfite to sulfurous acid

Acid-base reaction
an acid reacts with a base and the two neutralize each other, producing water or in some cases a weak electrolyte
Titration
a substance of known concentration is reacted with another substance of unknown concentration
Equivalence point
just enough titrant has been added to completely react with the analyte
indicator
used to identify the equivalence point
Acid
a substance that produces H+ ions in aqueous solution
Base
a substance that produces OH- ions in aqueous solution
Single arrow indicates
complete ionization
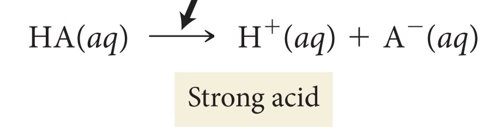
Double arrow indicates
partial ionization
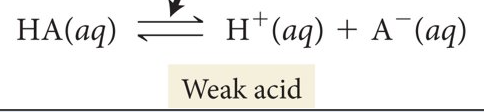
Bronsted-Lowry Definition of Acids
donates a proton (H+ ion) and becomes a conjugate base
Bronsted-Lowry Definition of Bases
accepts a proton (H+ ion) and becomes a conjugate acid
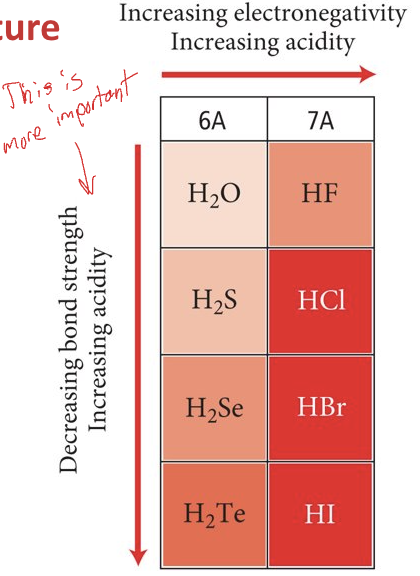
For Binary acids
acidity increases as electronegativity increases
For binary acids pt. 2
acidity decreases as bond strength increases
In a column,
bond strength has a greater effect than electronegativity on acidity
For oxyacids,
electronegativity increases, acidity increases
For oxyacids pt. 2
as the # of oxygen atoms attached increases, acidity increases
What are the 6 strong acids
Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
Hydrobromic acid (HBr)
Hydriodic acid (HI)
Nitric acid (HNO3)
Perchloric acid (HClO4)
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4, diprotic)
What are the 6 weak acids?
Hydrofluoric acid (HF)
Acetic acid (HC2H3O2)
Formic acid (HCHO2)
Sulfurous acid (H2SO3, diprotic)
Carbonic acid (H2CO3, diprotic)
Phosphoric acid (H3PO4, triprotic)
The strength of an acid can be measured by
using its ionization equation
ex.
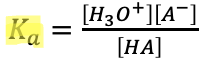
The weaker the acid,
the smaller the Ka value and the less the acid ionizes in the solution
Water is
amphoteric- it can act as an acid or a base
Water can undergo
autoionization- it acts as both an acid and bas to itself
Ion product constant for water
Kw
At 25 C Kw is equal to 1.0×10^-14
In a neutral solution, like pure water,
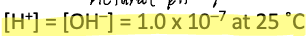
In an acidic solution,
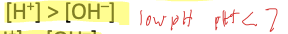
In a basic solution,
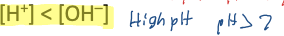
The strenght of an acid and its conjugate base are
inversely related
the stronger the acid, the weaker the conjugate base
Equation for pH
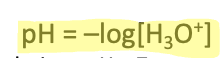
Equation for pOH
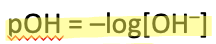
The pH scale
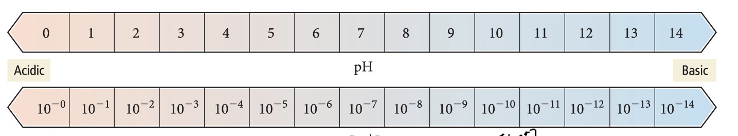
The pOH scale
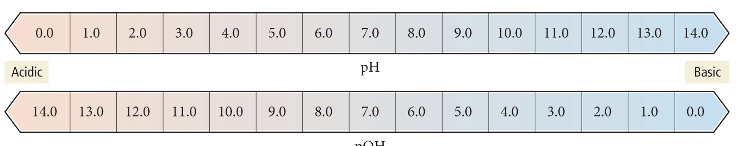
A strong base
completely dissociates to produce OH-
Ka x Kb =
Kw = 1 × 10^-14. at 25 C
The strength of an acid and its conjugate base are
inversely related
The stronger the acid,
the weaker the conjugate base
Anions
Conjugate base of a strong acid generally produces a neutral solution
Conjugate base of a weak acid produce a basic solution
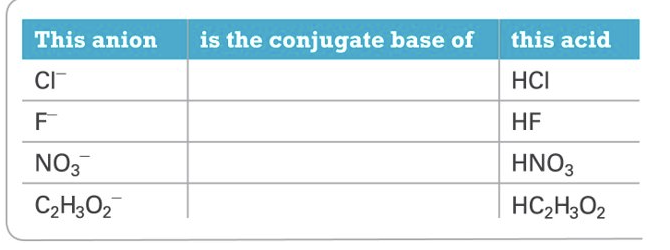
Cations
Cations that are counterions of strong bases
ex. NaOH, Ca(OH)2, KOH
produce a neutral solution
Cations pt.2
Cations that are the conjugate acids or weak bases produce an acidic solution
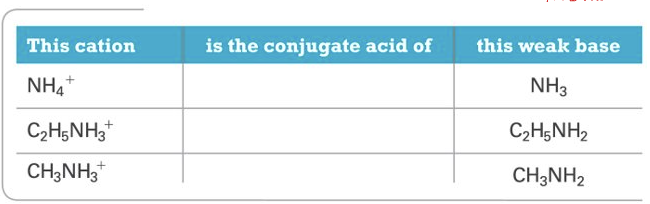
Cations pt.3
Cations that are small, highly charges metals produce an acidic solution
ex. Fe3+, Al3+
Salts in which neither cation nor anion acts as an acid or base
form a neutral solution
ex. NaCl
Salts in which the cation does not act as an acid, but the anion does act as a base
form a basic solution
ex. KF
Salts in which the cation does act as an acid, but the anion does not act as a base
form an acidic solution
ex, NH4Br, FeCl3
Salts in which the cation does act as an acid, and the anion does act as a base
Acidity or basicity depends on relative strengths
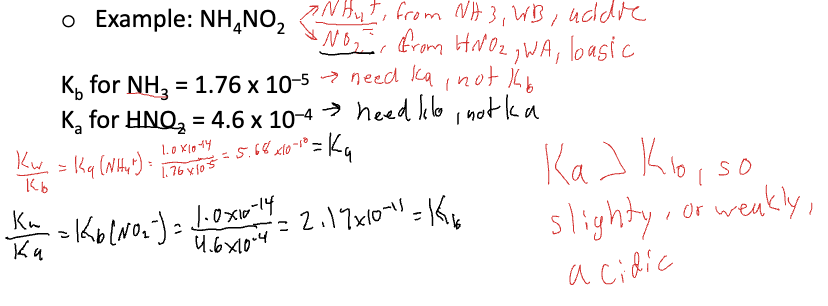
Polyprotic acids
ionize in successive steps, each with its own Ka
successive Ka, values get smaller
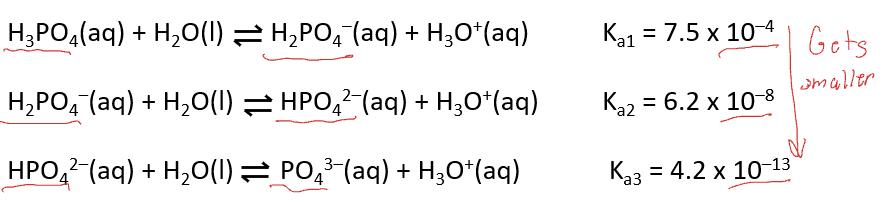
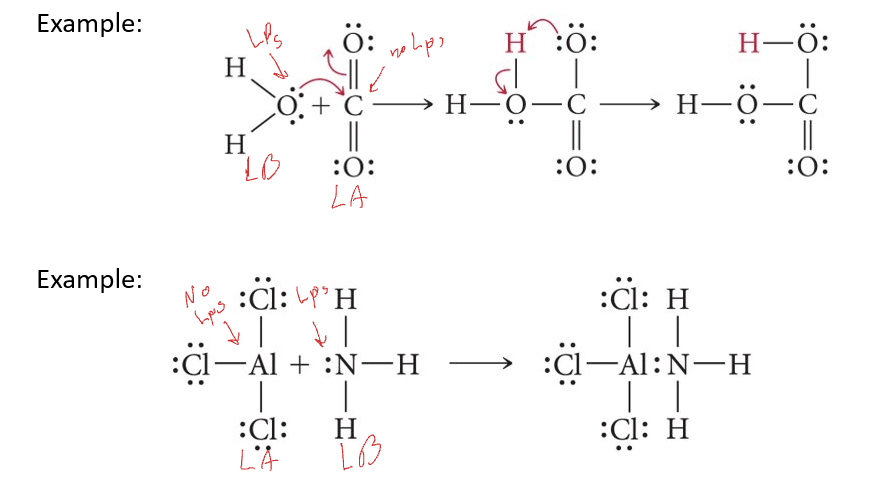
Lewis acid
electron pair acceptor
doesn’t have lone pairs, so it accepts lone pairs
ex. BF3
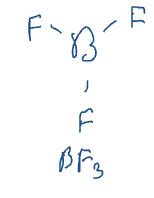
Lewis base
electron pair donor
Has lone pairs, so it donates them
ex. NH2
Examples of Lewis Acids and Base
Buffer
resists pH change by neutralizing added acid or base
A buffer contains significant amounts of either
a weak acid and it conjugate base
a weak base and its conjugate acid
The Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
the equation holds as long as the x is small approximation is valid
the initial concentrations of acids and conjugate bases should be at least 100 to 1,000 times greater than the equilibrium constant

What color should your titration be?
A very light pink
Dark pink means you overshot
For titrations,
the acids and bases need to be in moles for the RICE table
What is the pH at the equivalence point in a SA and SB titration?
pH of 7
Before the equivalence point in a SA and SB titration,
H3O+ is in excess
After the equivalence point in a SA and SB titration,
OH- is in excess
Solubility-product constant
Ksp
a measure of the solubility of a compound
Molar solubility
moles of a compound that dissolve in 1 L of liquid
Know that…
molar solubility doesn’t equal Ksp
When comparing solubility, you cannot compare Ksp values directly unless
the two compounds produce the same number of ions from their formula unit
In general, the solubility of an ionic compound is…
lower in a solution containing a common ion than in pure water
In general, the solubility of an ionic compound with a strongly basir or weakly basic anion increases with
increasing acidity (decreasing pH)
If Q < Ksp,
the solution is unsaturated and more ionic compound candissolve in the solution
If Q = Ksp,
the solution is saturated; the solution is holding theequilibrium amount of dissolved ions
If Q > Ksp,
the solution is supersaturated