module 5 - price floors and ceilings
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
non-binding price floor
minimum price set by the government that is below the current market equilibrium price (no real effect on the market)
binding price floor
a government imposed minimum price that is set above the market equilibrium price, which does affect the market by preventing prices from falling to the natural equilibrium level
non-binding price ceiling
a max price set by the government that is above the market equilibrium price, so it has no effect on the market
binding price floor
a government imposed max price that is set below the market equilibrium price, meaning it does affect the market by forcing prices down and causing a shortage
unemployment and minimum wage
debated however:
raising the wage increases labor costs, leading to higher unemployment
result in less workers, cutting hours, etc
price control
government laws to regulate prices instead of letting market forces determine prices
consumer surplus
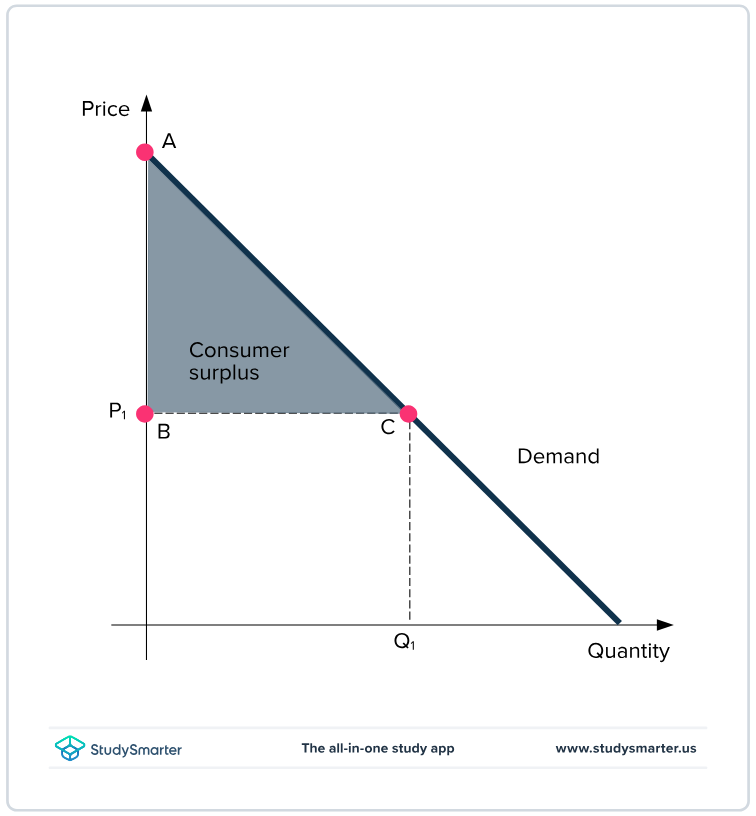
buyers’ willingness to pay for a good minus amount they actually pay, and it measures the benefit buyer get from participating in a market. can be computed by finding the area below the demand curve and above the the price
producer surplus
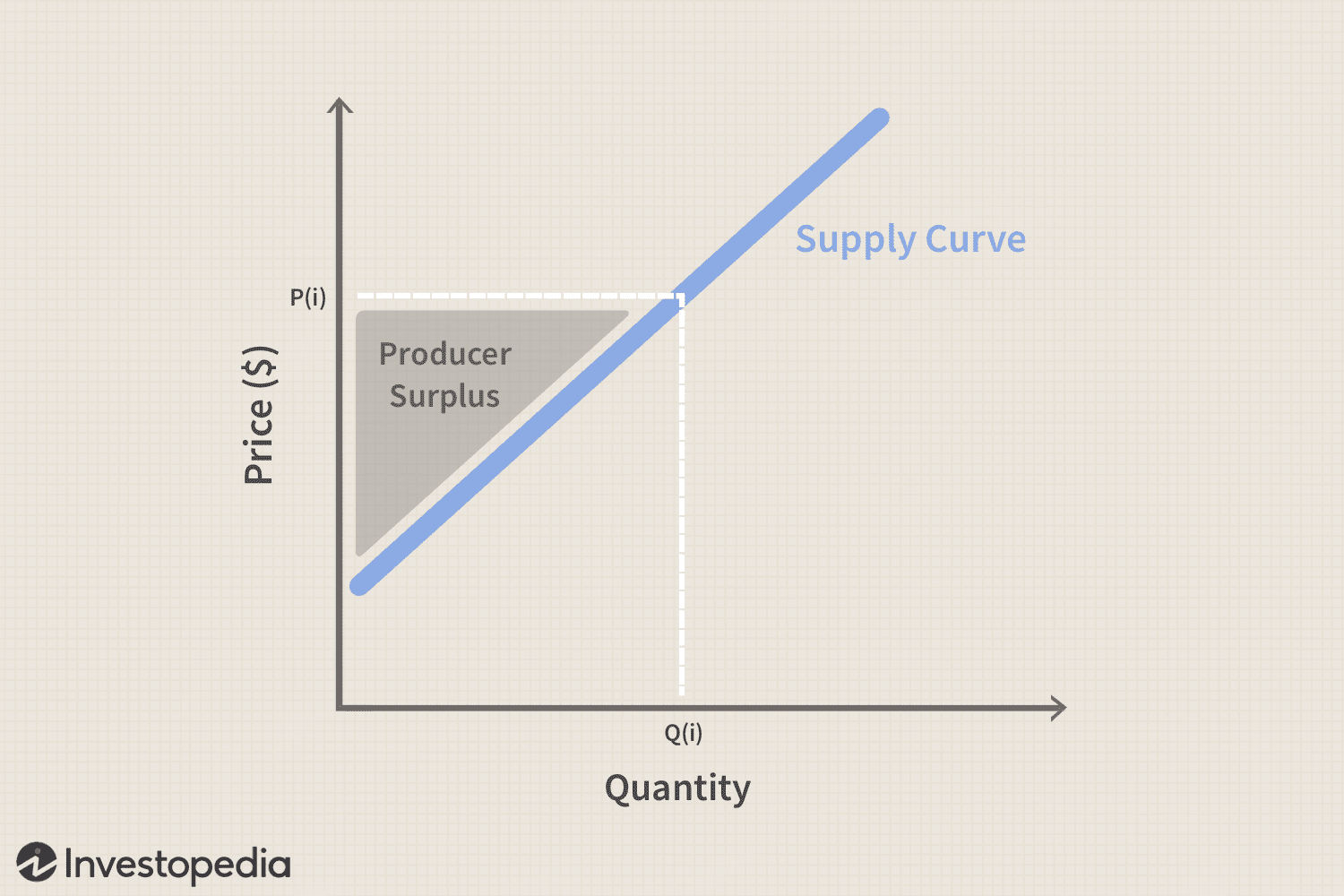
the amount sellers receive for the goods minus their costs of production, and it measures the benefit sellers get from participating in a market. can be computed by finding the area below the price and above the supply curve
allocation of resources
maximizes total surplus (sum of consumer + producer surplus) is efficient
often concerned with efficiency as well as equality
equilibrium of supply and demand
maximizes total surplus
invisible hand in market leads buyers and sellers to allocate resources efficiently
markets and allocation
does not do this efficiently in the presence of failures, such as market power or externalities