AP Physics 2
1/150
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is a work in progress
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
environment
anything outside the system
boundary/interface
separates the system and the environment
kinetic theory of matter
all matter is composed of small particles which have space between them and are in random motion
evaporation
water molecules collide and get knocked off
atomic number
number of protons
the number of electrons is equal to the number of ___ if neutrally charged
protons
atomic mass is sum of
protons and neutrons
assumptions of an ideal gas
All collisions, both between the molecules themselves, and between the molecules and the walls of the container, are perfectly elastic. (That means that there is no loss of kinetic energy during the collision.)
There are no (or entirely negligible) intermolecular forces between the gas molecules.
Gases are made up of molecules which are in constant random motion in straight lines.
The volume occupied by the molecules themselves is entirely negligible relative to the volume of the container.
pressure
particle collisions with the wall or container
source of temperature
average kinetic energy of an objects atoms
heat and temperature ____ the same thing
are NOT
heat
transferring or exchanging thermal energy (between system and environment)
temperature is directly proportional to
P*V
maxwell distribution area meaning
more area means more particles
names of the 4 special gas processes
Isobaric - pressure constant
isothermal - temperature constant
isochoric - volume constant
adiabatic - no heating (Q=0)
0th law of thermodynamics
thermal equilibrium is based on temperature. If two systems are in thermal equilibrium with a third system, then they must be in thermal equilibrium with each other
1st law of thermodynamics
there are two ways to change the thermal energy of a system, heating and work2n
2nd law of thermodynamics
Heat flows spontaneously from hot to cold. Entropy (disorder) of an isolated system is always increasing
3rd law of thermodynamics
kinetic energy of particles at absolute zero is zero. Entropy is zero
gas expands
positive work done by gas to environment
loss of energy means ___ will go down because the ___ decreases
temperature, speed
gas contracts
environment doing positive work on gas
heat engines
convert thermal energy into mechanical energy
specific heat
a characteristic of matter that describes how difficult it is to change temperature. AKA amount of energy required to raise 1kg of a substance by 1 kelvin
Methods by which heating can occur
Conduction, convection, radiation, evaporation
radiation
heat transferred by electromagnetic waves
as heat (Q) is transferred into or out of an object, its temperature will change unless
there is a phase transition
heating takes
time
insulator
charge remains localized
conductor
allows electric charges to flow through it
Grounding
our body is a conductor so charges are conducted through our body to the earth
3 ways to charge an object
friction (rubbing), conduction (touching), induction (not touching)
superposition for electrostatics
net force on one charge is vector sum of all other electrostatic forces
electric field
describes the force a positive charge would feel
electric field lines
never cross, closer together means larger magnitude, start on positive charges and end on negative charges
electric field inside a conductor
is zero everywhere unless there is a point charge inside it
electric potential
how much potential energy a charge would have if it was in the empty spaceec
electric potential energy
energy stored in a charge based on where it is in space
potential difference
work done per unit charge in moving from two equipotential surfaces
synonyms for potential difference
voltage, emf (electromotive force)
positive charges move from ___ electric potential to ____ electric potential
high, low
negative charges move from ___ electric potential to ____ electric potential
low, high
capacitor
two parallel plates that have an equal and opposite amount of charge. purpose is to store and be able to quickly dump energy
capacitance of a capacitor
ratio of charge on either plate and the potential difference between the plates, essentially it measures the capacitors ability to store charge
a point charge inside a metal sphere would
polarize the sphere but the overall charge of the sphere would remain the same
do electrons or protons move during conduction
electrons
if two points have a potential difference between them and they are connected with a conductor, negative charges will flow from ____ concentration to a ______ concentration
higher, lower
electric current
measures the amount of charge passing a given point every second
battery
supplies a potential difference to maintain a continuous flow of charge
we say that current is the ____ flow of charges but in reality it’s actually ____ charges
positive, negative
resistor
function is to use up voltage
voltmeter
measures potential difference between two points, high resistance
ammeter
measures current, is like a flow meter, low resistance
are light bulbs ohmic
NO
omh’s law is valid as long as
the temperature remains constant
junction rule
conservation of charge, total current coming into a junction must equal the total current leaving the junction
loop rule
conservation of energy, total voltage drops and gains must total to zero as you travel around a closed loop
parallel branches have the same
potential difference
short circuit
path of no resistance
resistors in series
add resistances togetherr
resistors in parallel
inverse of the summation of the inverse resistances
ideal battery
no internal resistance
internal resistance
usually modeled as an ideal source in series with a small internal resistor
capacitor in series
inverse of the summation of the inverse capacitances
capacitor in parallel
add the capacitances together
for a capacitor in series what is the same for all plates
q
what is the same for capacitors in parallel
potential difference
an empty capacitor behaves like
an ideal wire
a full capacitor behaves like
an open switch
current is
undiminished throughout a circuit, same amount of current everywhere unless there are parallel branches
like poles ____ unlike poles ____
repel, attract
what happens if a magnet is broken into two
both pieces has a pair of poles (magnetic poles never appear in isolation)
compass needle will align itself ____ to the external _____ _____
tangent, magnetic field
magnetic field lines
always form complete loops (N→S outside) (S→N inside)
where is the magnetic field strongest for a bar magnet
inside the magnet
sources of magnetic fields are _____ ______
moving charges, and in turn these magnetic fields exert forces only on other moving charges
all charges produce ____ fields
electric
moving charges produce ____ fields
magnetic
magnetic force and magnetic field (are/are not) in the same direction
are not
magnetic forces cannot perform work because of their
perpendicularity
if the velocity and magnetic fields are perpendicular the path of the charge is
a circle
the right hand rule is used for ____ charges
positive
the left hand rule is used for ___ charges
negative
3 different RHR’s
thumb in direction of current, the way the fingers curl gives magnetic field direction
Fingers pointing towards velocity or current, curl B, thumb is direction of the force
curl current, thumb gives magnetic moment
magnetic moment
points in the direction of the B field that the object created, not the one it’s experiencing. Is a measure of how much torque a dipole will feel in a magnetic field
into/out of page symbols
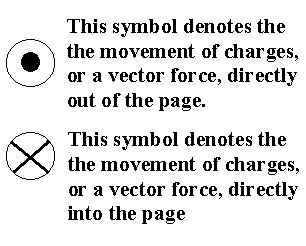
permeability
the ability to be magnetized
solenoid
loop stretched out to form a spiral
describe magnetic field of a solenoid
uniform inside the solenoid, zero outside
current carrying wires carrying currents in the same direction will ___ while current carrying wires carrying currents in the opposite direction will ____
attract, repel
magnetic particles never change an objects ____
speed (they only turn them)
electromagnetic induction
a magnetic field can be used to induce current in a wire. source of the current is the establishment of motional emf due to the CHANGE in magnetic flux
magnetic flux
measurement of how much magnetic field penetrates a surface
Lenz’s Law
the flux is ____ and it is ____. therefore the loops B field will be (opposite)
reflection
ability of light to bounce off of a surface
two types of reflection
specular: smooth surface θi=θr
diffuse: surface is rough/uneven, light rays are scattered
angle of incidence is measured to the
normal
refraction
apparent bending of light
in phase
waves of light match up peak to peak and trough to trough
wave speed depends on the
medium