2.1 Potential Energy of Bonds
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
bonding
chemical bond formed between atoms or ions when valence electrons are transferred or shared
valence electrons
electrons that can be found in their outermost shell of the atoms. They are the electrons used for bonding.
electronegativity
measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of elctrons
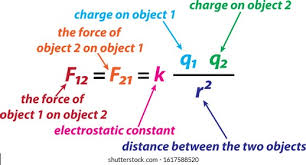
Coloumbs law
Q1(2)/r²
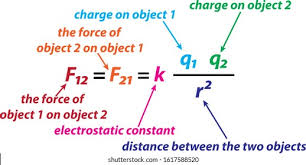
Coulombic Attraction
attractive force between oppisitely charged particles, such as the positive and negative electrons within in atom
What coulombs law tells us
the attractive force between charged particles increased with an increase in charge and decreases with an increased in the distance
Why does electronegativty decrease down a column
as there is a greater distance from the nucleus and because there is more electron shielding (btw columns are vertical)
Why does electronegativity increase as you move across a period
This is because the protons increase, leading to a stronger nucleur charge which increases attraction for electron bonding.
what is an ionic bond and its characteristics
a bond formed between two or more atoms or ions
-electronegativity different so great that more electornegative element steals the electron from the less electronegative element
-strongest ytpe of bond
-tends to happen between metal and nonmetal
-electronegativity difference between elements must be greater than 1.7
what is a covalent bond
-bond formed between 2 atoms or ions
-electronegativtiy difference so low that atoms share the electrons instead
-usually happens between nonmetals
what is a polar covalant bond
-stronger than nonpolar covalanent bond
-happens when electrons are shared unequally
-difference in electronegativity usually 0.5-1.7
-one atom shares electrons more closely, making it slightly more negative
what is a nonpolar covalant bond
-when difference in electronegativity is so mall that the elements share the electrons equally
what is metallic bonding and its characteristics
-weakest type of bond
-valence electrons move freely between the different metal atoms.
-described as sea of electrons throughout the metal
What is the shielding effect?
The shielding effect is the reduction in the effective nuclear charge on an electron due to repulsive forces from other electrons in lower-energy inner shells.