Unit Two (s): Liberalism
1/377
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
378 Terms
Political Life Before Liberalism
Governments were absolute monarchies‐ kings or queens with complete control over all decisions.
How was the Divine Right of Kings abused?
Monarchies often abused their power and restricted individual rights and freedoms to ensure their order and stability.
(Freedom, Speech, Property)
How was there limited mobility before liberalism?
Strict Class Structure

Humanists
Sought meaning and purpose in love, beauty, art and the development of the self, answered many of life's questions based on reason rather than faith.
(14th Century)
Renaissance
(14-16th century)
Sparked a belief in the importance of the individual in society (instead of just focusing on the afterlife). (Artwork)
Protestant Reformation
(1517)
Reflected the belief that reason was as significant as faith for the believer in Christianity.
The Enlightenment
(17th-18th Century)
Promote the beliefs of classical liberalism that congealed into the liberal ideology of the 19th century.
Humanists, renaissance, the protestant reformation, and the enlightenment all represent what?
An emergence of a modern spirit of individualism in Europe
Hobbes
Concerned with social and political order; felt only way to ensure security of all individuals was to sacrifice individual sovereignty to strong monarch
Locke
Role of government to limit itself to protecting individual liberty; natural rights
Rousseau
General will (consensus)
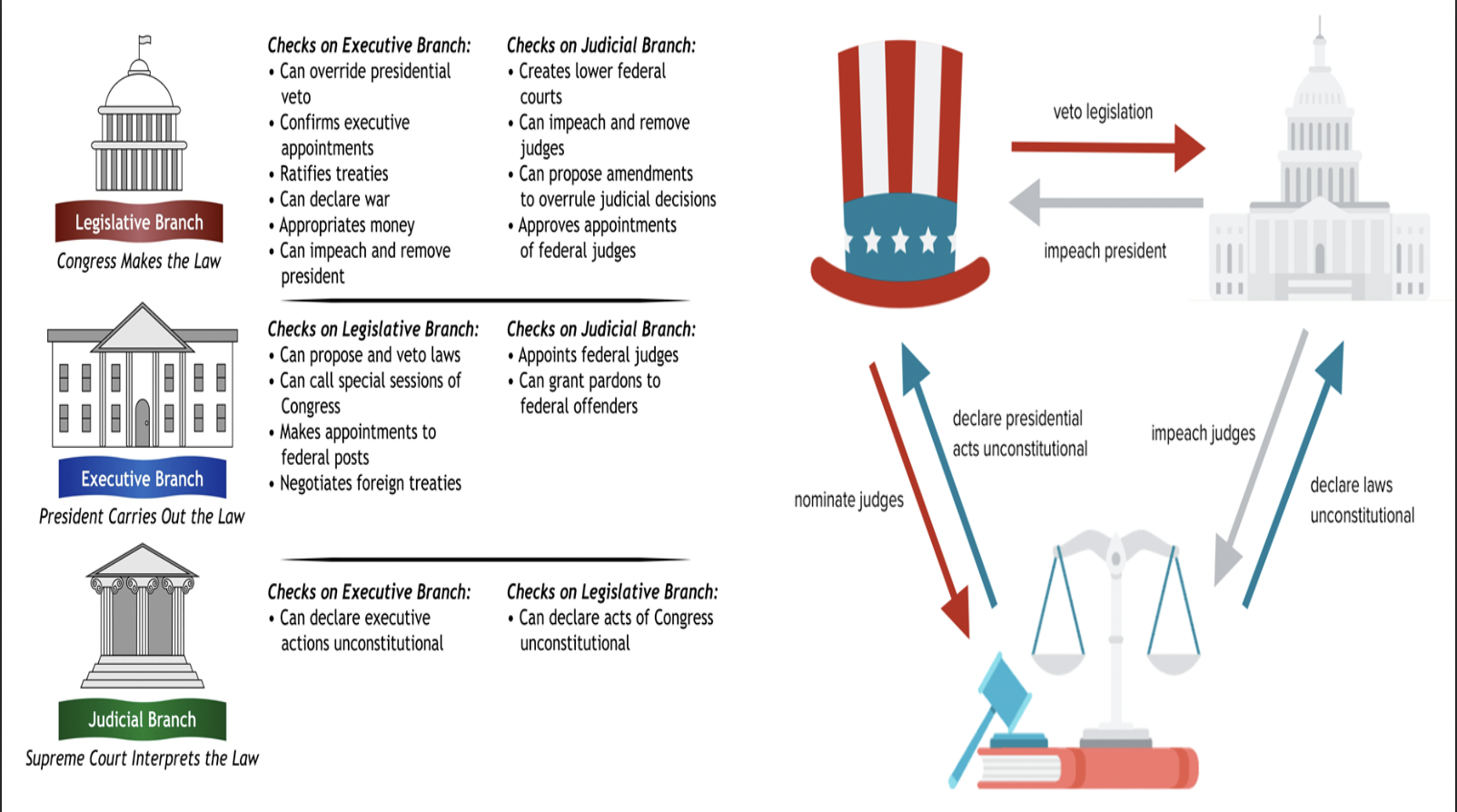
Montesquieu
Need to have checks and balances on the three branches of government; no one branch is too powerful
Smith
Limited government to keep society stable in order to encourage capitalist trade; laissez-faire
Mill
Wanted political freedom for all people, including rights for women
Charles de Secondat, Baron de Montesquieu
French Enlightenment thinker whose writings were banned by the Catholic church

What did Montesquieu believe in?
In the worth of the individual, the equality of individuals, and the accountability of the government.
Believed strongly in the separation of powers in government (executive, legislative, and judicial).
What would be within Montesquieu’s system?
Checks and Balances
Each branch would be both separate from and dependent on one another so that no one branch became too powerful.
In order for this system to work, people needed to be involved in government-a democracy.
John Stuart Mill
Advocate for personal liberty (freedom)

What did Mill believe was the government’s role?
•Preserve rule of law
•Protect private property
•Ensure physical security of each person
Should deal with consequences of bad choices, not try to prevent them
The Harm Principle
Believed that the only limitations that should be placed on the individual were those that would protect others (i.e. The only restrictions on people should be those that prevent harm to others)
Five influential ideas from the Enlightenment
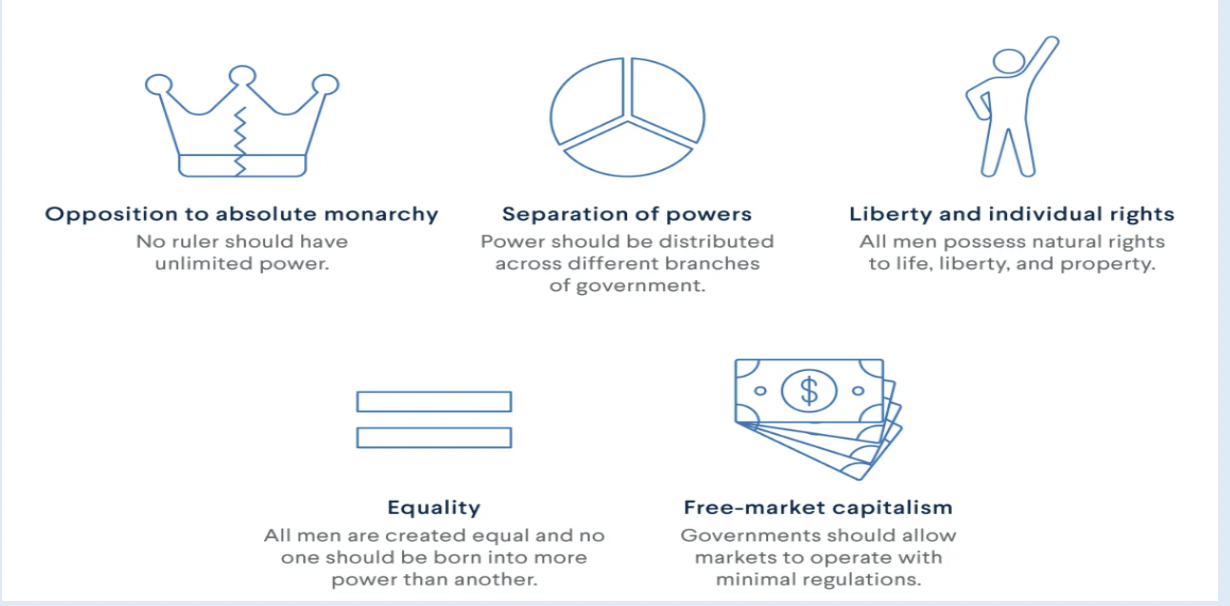
Classical Liberalism focuses on?
Supporting freedom of speech and freedom within actions.
Advocates for Limited Government and embraces the principles of individualism.

Negative Freedoms
Refer to the idea of being free from interference or restriction by others, especially the government.
Having the space to do what you want without someone else getting in your way.
What are examples of negative freedoms?
Freedom of speech or the right to privacy are considered negative freedoms because they protect you from outside interference in your choices and actions.
Classical Liberalism Beliefs
Primacy of individual rights and freedoms, to be exercised in the individual’s self-interest.
Belief that humans are reasonable and can make rational decisions that will benefit both themselves and society as a whole.
Economic freedom, involving the ownership of private property and free markets (markets with limited government intervention)
The protection of civil liberties
Constitutional limitations on the government
1750-1900
What emerged from the Industrial Revolution & Classical Liberalism Period and what got destroyed?
Throughout the 17th century, order in society faced many challenges such as the emergence of new ideas (liberalism & nationalism) and the breakdown of the old feudal economic order.
During 1750-1900, Classical liberalism developed from?
The thinking of individuals such as Locke, Montesquieu, Smith, and Mill, who were concerned with protecting the rights and freedoms of citizens.
The development of classical liberalism led to what?
Emergence of Classical Liberal ideas where government involvement became less desired and individual rights and freedoms became more important.
During the Industrial Revolution & Classical Liberalism Period What did People want During This Time?
Meritocracy (you earn what you get on merit)
Individual Freedoms & Rights to be protected
The ability for individuals to make decisions freely
Economic Freedom
The ability to live life according to individual rational thoughts & decisions
Ability to participate in Government
Classical Liberal Thought in ACTION examples
American & French Revolutions were attempts to implement the ideas of liberal thought.
(1775) American Revolution: 47 000 citizens.
(1789) French Revolution: 27 million citizens.
Liberalism gradually evolved into an ideology as?
As the ideas of the Enlightenment thinkers were applied to specific situations.
The American Declaration of Independence and the French Declaration of Rights of Man were important documents because?
They placed individual rights and freedoms at the forefront for the first time.
Indigenous Influence on Liberal Governments
Political structure of the Haudenosaunee confederacy is believed to have influenced the development of modern liberal democracies.
Haudenosaunee Confederacy
Political alliance of six Indigenous nations located in what is now New York State, USA and Ontario, Canada.
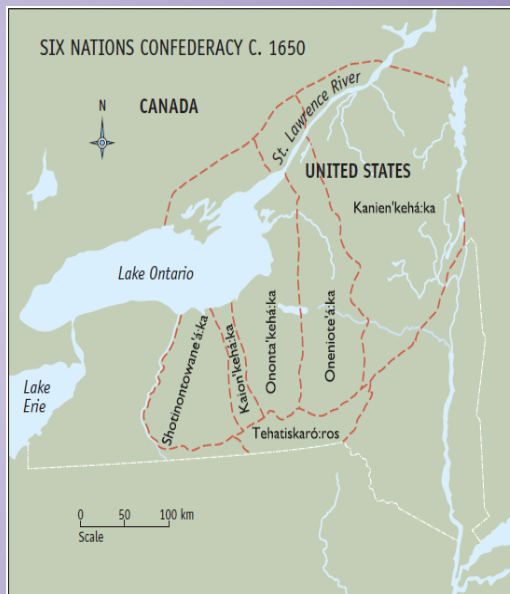
Features of the Haudenosaunee Confederacy “The Great Law of Peace”
Consensus decision-making
Separation of powers: Different councils responsible for different areas of governance.
Importance of respect for individual rights and freedoms, including the rights of women
Influence of the Haudenosaunee Confederacy on America & Canada
Some people believe that the founding fathers of the United States (the guys that wrote the American Constitution) were influenced by the Haudenosaunee Confederation.
Thomas Jefferson and Benjamin Franklin had a lot of exposure to the Haudenosaunee and expressed admiration for their political system.
So Europeans Were Kicking off Absolute Monarchies with Classical Liberal ideas - now what?
Economic system changes
They begin to reject Mercantilism (the economic system used by Monarchies to enrich themselves only).
What replaced the economic systems of monarchies
Adam Smith’s Free Market Capitalism.
Feminism
Belief that ‐ men and women are to be treated equally in all respects.
1860s Suffragists
Began to argue for the right to vote, feeling that political power was the only way to achieve their goals.
Achieving the right to vote allowed what for women?
Led to more equality rights for women in society
ie. the right to hold public office, more equal rights in marriage,divorce and abortion.
Luddites
Army of redressers, reactionary individuals that strongly opposed machinery as it decreased job opportunity.
Led to Luddism
How did the government respond to Luddites?
Government responds to their actions by making machine breaking illegal (Protecting Property)
Sends in Army to Luddite Hotspots
Who were the Chartists and what did they fight for?
(REFORMERS)
• Universal suffrage for all men over 21
• Equal-sized electoral districts
• Voting by secret ballot
• An end to the need for property qualifications for Parliament
• Pay for Members of Parliament
• Annual elections
For what main principle of liberalism were the Chartists fighting to have recognized?
Right to vote!
Were the chartists succesxful?
No as in 1839 they present a Charter to HOC with 1.25 million signatures and in 1842 they present second petition with 3 million signatures but in 1848 The third Petition is rejected
Who is associated with classical conservatism?
Edmund Burke
Edmund Burke was horrified by what?
Extremes of French Revolution (Highlighted flaws of individualism, equality & Freedom)
What did Edmund Burke believe in?
Believed change should take into account the past and the future, not just the present, therefore change could not come from the whims of the present generation
What did Edmund Burke believe in, in regards to institutions?
Need established institutions run by EDUCATED people (Against democracy) (Also, against Tyrannical government)
What were Burke’s core beliefs?
Government should be led by the capable, not the masses.
Government should represent not just the living but also past and future generations. Change should be slow and honor tradition rather than be dictated by the present generation.
Values tradition, stability, and hierarchy.
When and how was socialism developed?
Developed in Europe in the early 19th century as a response to the declining social and economic conditions of the working class during the Industrial Revolution.
When was their movement towards socialism? What was it based on?
In the 1800s which was based around the idea of a fair distribution of wealth and equal opportunities for all
Poor conditions that led to embracing socialism occurred because of what?
Practice of classical liberal ideas, such as individualism and laissez-faire capitalism, which created a vast inequality between the working class and the business-owning class.
Draw a diagram of the values of socialism and liberalism
:)
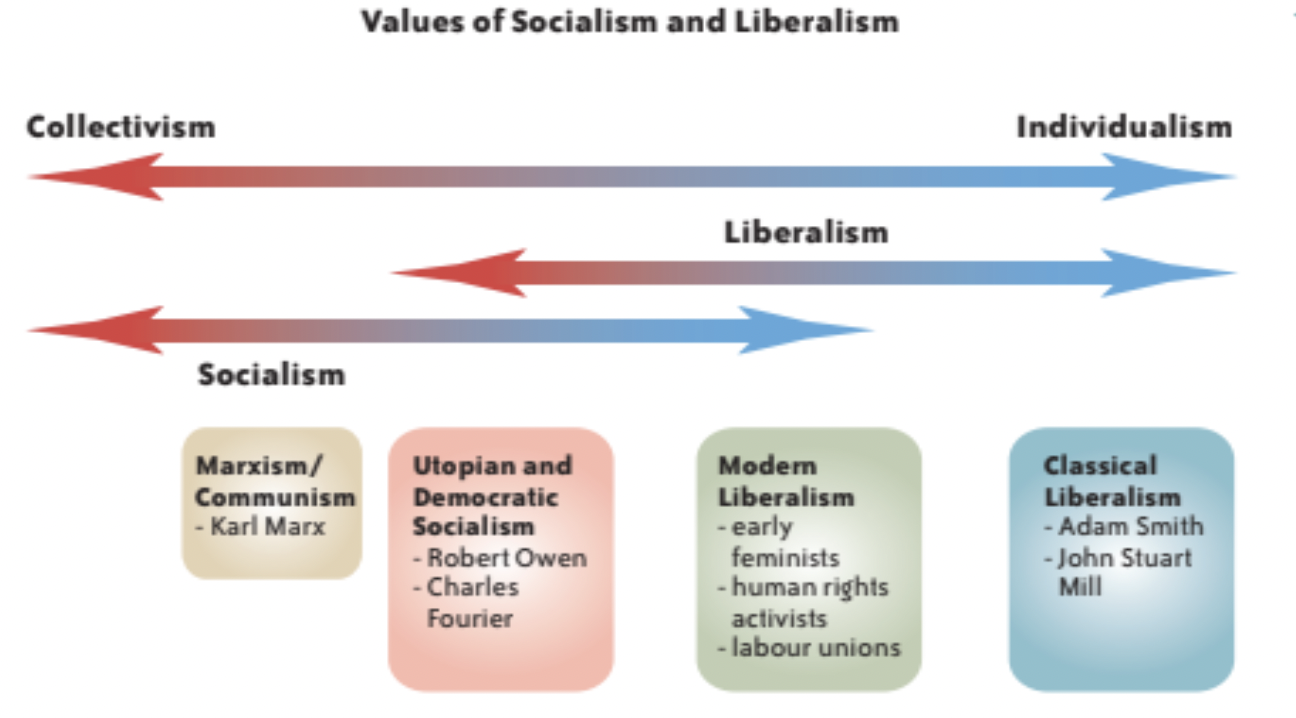
Who was a Utopian Socialist?
Robert Owen
Principles of Utopian Socialism
Embraced ideas of humanitarianism (rejected the harsh conditions of the Industrial Revolution)
Operated factories that had vastly improved living and working conditions
Fewer working hours, better wages and no child labour (under age 10)
Factory Acts were built upon Owen’s business
Other Utopian Socialists
Titus Salt and Charles Fourier
Titus Salt’s ideas/actions
Noise and pollution from the factory was reduced through innovative practices (modern flues, burying the factory shafts underground)
Churches, public schools, libraries were all built for the enjoyment of the residents
Charles Fourier ideas/actions
Envisioned self-sufficient, cooperative communities called phalansteries.
Work assigned based on personal interests rather than necessity.
In a sense Worker Cooperatives!
Phalansteries
Where people would live and work together in harmony.
Democratic Socialism
Believe that the government should be a force that actively promoted the collective interest of society through public ownership of key industries and social programs (i.e. health care)
How is Democratic Socialism a mix?
While embracing classic liberal values like democracy, individual freedoms and rights, they believe that capitalism creates economic inequality that must be addressed for the benefit of society
Marxism
Radical form of socialism.
Also termed scientific socialism or communism.
Marx and Engles wrote what together?
Communist Manifesto, 1848
What did Marx strongly believe in?
Private Property Leads to Exploitation. Abolish Private Property
The Famous Five
Were five prominent Canadian suffragists who advocated for women and children: Henrietta Muir Edwards, Nellie McClung, Louise McKinney, Emily Murphy, and Irene Parlby

What were the Famous Five also known as?
The Valiant Five and initially as The Alberta Five
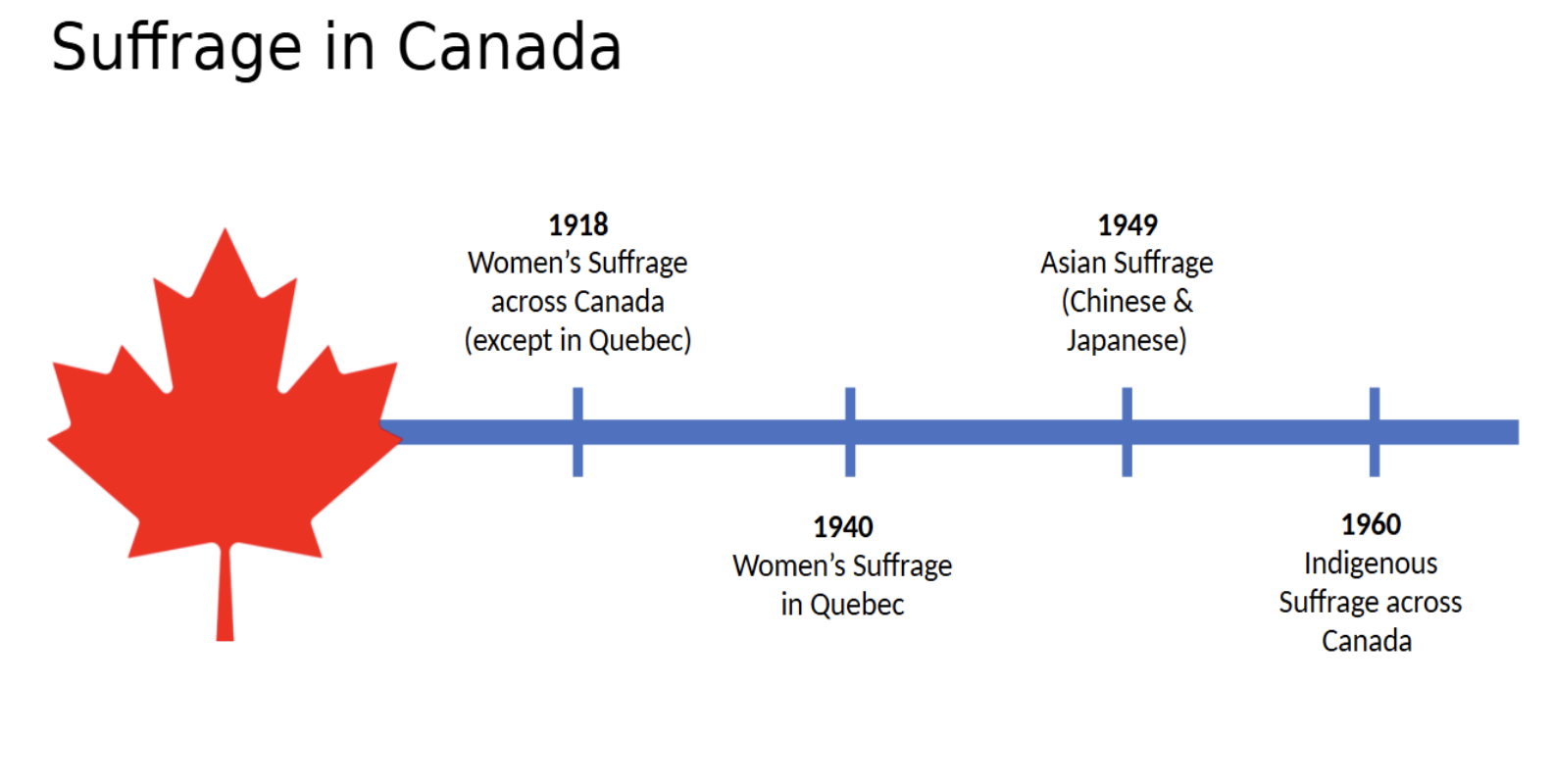
How has universal suffrage changed over time?
:)

How has suffrage in Canada evolved?
:)

What is this, and what freedoms does it include?
A foundational text in the history of human and civil rights, the Declaration consists of 30 articles detailing an individual's "basic rights and fundamental freedoms"
Includes Negative and Positive Freedom
Sundown Towns
Showcased extreme inequality as Blacks were not allowed to be outside when it became dark, or else they would suffer from assault or potentially death.
Civil Rights Act, 1964

Welfare capitalism
Initiatives by industrialists to provide non‐monetary rewards to workers for their loyalty and to stave off labour unions (USA)
Welfare capitalism is a classical liberal economic system combined with?
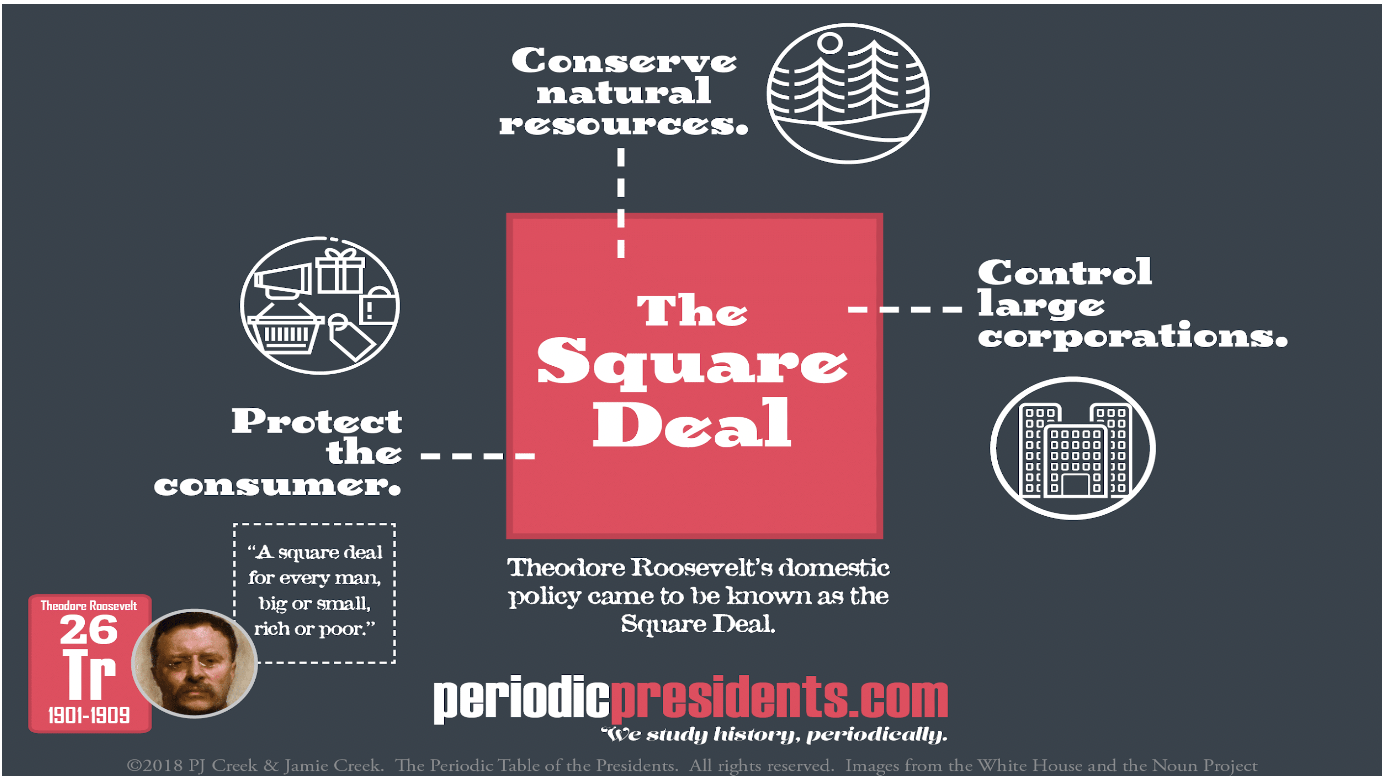
A government that used legislation to give workers protection such as limited working hours and a minimum wage, and a safety net with features like pensions and medical insurance (The Square Deal)
The Square Deal
Factory Act Examples: Laws Between 1800-1900’s
The master or mistress of the factory must observe the law all rooms in a factory are to be lime-washed twice a year and duly ventilated.
The hours of work of apprentices are not to exceed twelve a day, nor commence before six in the morning, nor conclude after nine at night.
Factor Act Laws went against what?
Classical liberal economic values ‐ it upheld basic political liberal values like individual rights and freedoms.
Britain: Factory Acts
1810
Decreasing working hours, regulating the age of child workers and regulating # of hours women and children could work.
How has Germany employed Factory Acts?
Introduced a law providing for illness and maternity leave. Later workplace insurance and old age assistance. 1883,4

At the time of Germany established factory acts how was there a gradual shift?
At the time, these government regulations were not viewed by capitalists as necessary and capitalists DID NOT welcome the changes.
Over time, these regulations grew, became more popular and became known as labour standards as classical liberal societies began evolving into modern liberal ones.
Unions
Recognition of a new right—the right to organize and bargain collectively.
Triangle factory
Collective actions brings a stronger voice

UN Human Right Declaration ‘4
Everyone has the right to form and to join trade unions for the protection of his interests.

The Progressive party, believing that no people can justly claim to be a true democracy which denies political rights on account of sex, pledges itself to?
The task of securing equal suffrage to men and women alike.
The supreme duty of the Nation is?
Conservation of human resources through an enlightened measure of social and industrial justice.
The Progressive party pledges to work unceasingly in State and Nation for:
Effective legislation looking to the prevention of industrial accidents, occupational diseases, overwork, involuntary unemployment, and other injurious effects incident to modern industry; – The fixing of minimum safety and health standards for the various occupations
The prohibition of child labor;
Minimum wage standards for working women, to provide a “living wage” in all industrial occupations;
The progressive party states we favour the union of all the existing agencies of the Federal Government dealing with?
Public health into a single national health service...to perform efficiently such duties in the protection of the public from preventable diseases.
The National Progressive Party was formed because of?
An unresponsive political structure in the United States at the time.
Welfare state

The movement from welfare capitalism to the welfare state was spurred by the?
Great Depression
How did the Great Depression influence the shift to welfare state?
Widespread business failures and impoverishment called laissez-faire principles into question
Depression became a catalyst for change, and what began to emerge was modern liberalism as we know it today.
Business cycles
Recurring pattern of economic expansion and contraction in an economy, moving through four main phases: expansion, peak, contraction, and trough
Consequences of the Great Depression
Bank runs, business failures, unemployment, dust bowl, rise of extremism
Bank runs
Too many people wanting to withdraw their savings for financial institutions at the same time causing it to go bankrupt.
Business failures
Governments responded by imposing tariffs to protect home businesses, but this had the reverse effect (increasing prices for consumers who in turn bought less and pushed more businesses to the brink).
Unemployment
Jobless and poverty rates increase ‐ by 1933, the rate was 25% in the USA (some countries it was as high as 35%) and incomes were 54% (HALF!) of what they were in 1929.
Dust Bowl
Farmers faced a decade of drought and dust and farm bankruptcies
Rise of extremism
Germany (and many other places - including many in North America) turned to extreme ideologies as a response to the Depression.
Why did the Ottawa Trek in (1935) happen?
•Gov’t sponsored relief camps set up in BC (worked small jobs in return for wages)
•Inadequate conditions (poor conditions, low pay) protested by residents of camps