MSE 3030 - Thermodynamics - Prelim 1
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is a thermodynamic engine?
Always returns to the same state in a cyclic manner
Has to convert thermodynamic heat and work into other forms of thermodynamic heat and work
It can always be in the exact same state
Change in state variables over the entire engine is zero
Q: Does a thermodynamic engine have to have the change in entropy be zero? If no, then why does a thermodynamic engine not have to be reversible?
A closed system vs. a closed path
How do you find the net work of a cycle?
The area enclosed by the cycle (delta W = line integral of PdV)
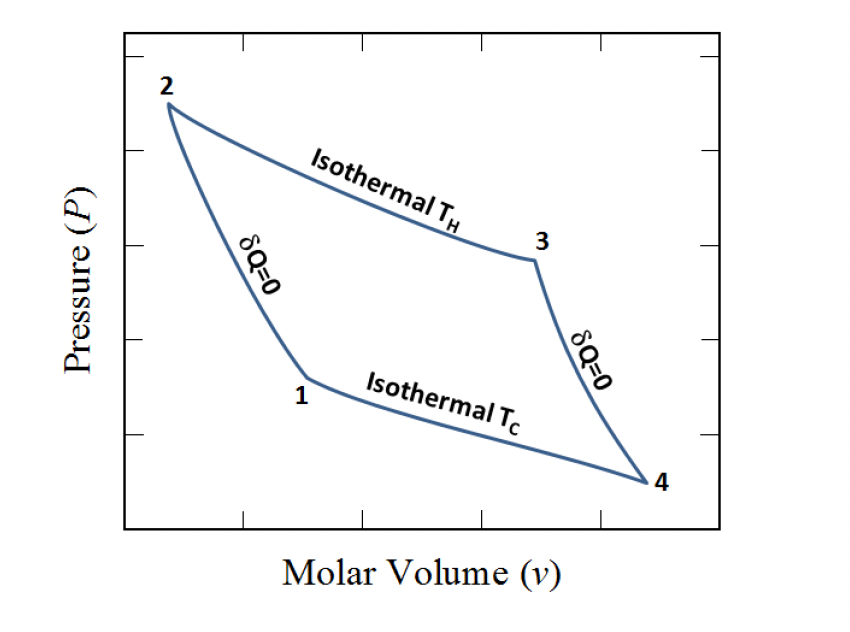
Define the sign of the work in different steps of this carnot cycle
1 → 2: Work is negative, energy is leaving the system
2 → 3: Work is positive, the environment is doing work on the system and energy is entering the system
3 → 4:
4 → 1:
How does what heat measure physically distinguishable from temperature?
Temperature: in the units of K, F, or C. An intensive property, increasing the size of the system will not increase the temperature.
Heat: A type of energy, in the units of Joules. Heat is an extensive property. Increasing the size of the system does increase the heat! Describes the thermal energy transfer between two systems and what happens in between states.
For reference, think of increasing the system of the system to be “replicating” the system.
How does the equipartition help us derive the heat capacities at constant pressure and volume? What EOS does this apply to, with what conditions?
The following only applies to ideal gasses at high temperatures.
What are the conditions to be able to use PV = nRT? Why do these conditions have to be true?
Perfectly elastic conditions
Molecules are infinitely far apart/non-interacting
All particles are point particles/occupy no volume
Low pressure & high temperature
These equations have to be true because ….
What does the ability to extract work from a system say about its reversibility?
Nothing. But, being able to extract the maximum possible work is a characteristic of a reversible process. In an irreversible process, some work is lost to increasing the entropy of the system. Gibbs’s free energy is useful for describing the amount of work available to extract.
In what cases do the different potentials apply? (dG, dH, dA, dU)
What is the difference between an open and closed system? Does a closed path exist, and if it does, what is it?
Give the formulas for the change in each relevant potential (U, H, A, G)
dH = TdS - PdV
dH = TdS + VdP
dA = -SdT - PdV
dG = -SdT + VdP