Neuroscience 1 (copy)
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Central nervous system
consists of the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system
A division of the nervous system consisting of all nerves that are not part of the brain or spinal cord.
superior colliculus
receives visual sensory input
Inferior colliculus
auditory reflexes
enteric nervous system
the nervous system of the digestive tract
temporal cortex
Brain region that processes information about sound and is involved in consciously remembering past events, and for facial recognition.
parietal cortex
Provides higher levels of sensory information, such as map of the external world, that is important for planning and carrying out movements; spatial reasoning and processing sensations
frontal cortex
The front part of the cortex of the brain. Divided left and right into the two frontal lobes, this part of the brain is associated with cognitive functioning such as planning, foresight, and understanding.
ventral tegmental area
stimulates amygdala for pleasure and reward center
olfactory bulb
the brain center for smell, located below the frontal lobes
Hippocampus
a neural center located in the limbic system; helps process explicit memories for storage
Limbic System: Amygdala
controls emotion
Pons
sleep and arousal
Medulla
controls heartbeat and breathing
Amygdala
A limbic system structure involved in memory and emotion, particularly fear and aggression.
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
Occipital cortex
Brain region that processes visual information.
Cerebellum
Balance and coordination
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
Thalamus
the brain's sensory control center, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
Sensation
the detection of environmental stimuli
Perception
awareness of what we sense
Functional pathway
Sensory receptors, thalamus, primary sensory cortex
Sensory receptor cells
sensation through transduction
Thalamus
relay that can modulate attention
Primary Sensory Cortex
perception
Primary Sensory Cortex
sends information on to “association cortex”
•Basis for cognition
Sound
pressure waves in the air
Sensory receptor cell for auditory system
Hair cells
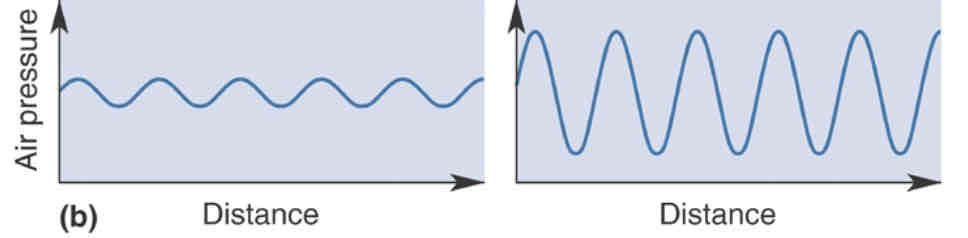
Frequency
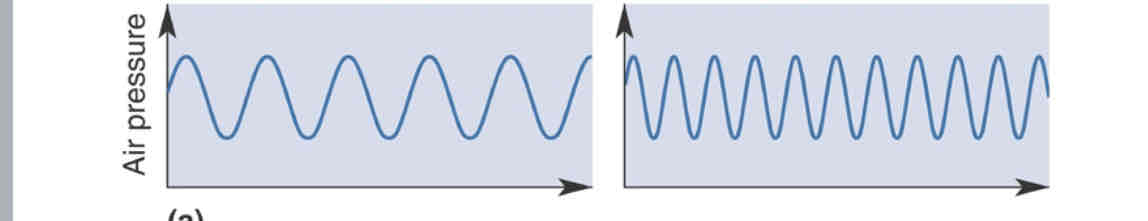
Intensity
Outer ear
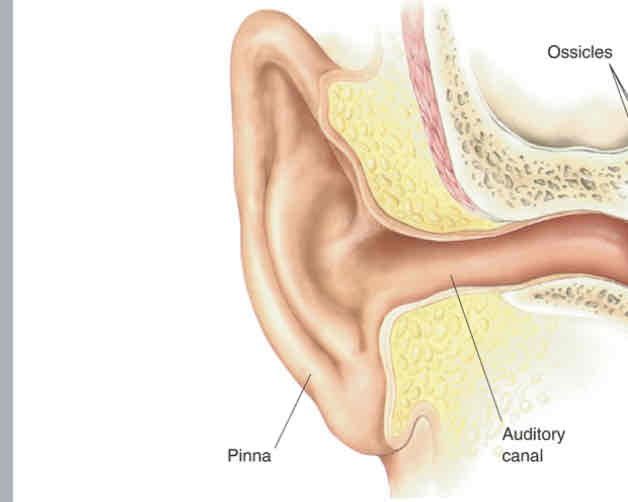
Middle ear
Inner ear
Pinna
Auditory canal
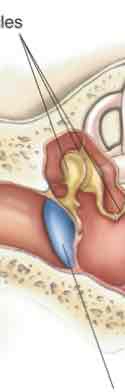
Ossicles
Three bones in the ear: stapes malleus, incus
Tympanic membrane
Ear drum connected to ossicles
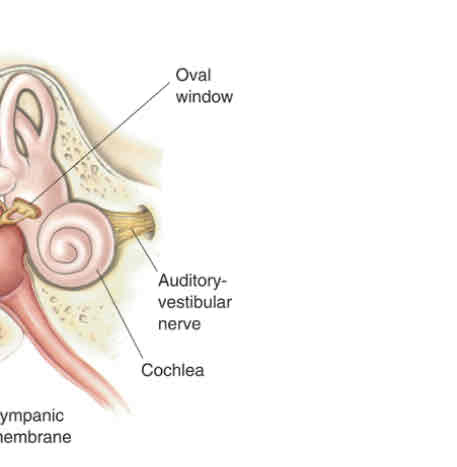
Oval window
Section of the cochlea that connects to ossicles or the stapes
Cochlea
Snail shell shaped part of the inner ear
Primary auditory cortex
Located in the temporal lobe of the cerebrum
Association cortices