Pharynx and Esophagus
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Pharynx
Posterior to nasal cavity and oral cavity
Extends past the larynx
Buccopharyngeal, Muscular, Mucous membrane
What are the 3 layers of the pharynx?
Buccopharyngeal layer
Layer of the pharynx
Most external
Covers pharynx
Continuous with pretracheal fascia
Muscular layer
Layer of the pharynx
Outer circular
Inner longitudinal
Mucous membrane layer
Layer of the pharynx
Submucosa contributes to pharyngobasilar fascia
Posterior portion lies against the prevertebral layer of deep cervical fascia
Nasopharynx, Oropharynx, Laryngopharynx
What are the 3 regions of the pharynx?
Nasopharynx
Region of the pharynx
Posterior of the nose and inferior to soft palate
Oropharynx
Region of the pharynx
Posterior of the mouth
Laryngopharynx
Region of the pharynx
Posterior of the larynx
Lateral wall of nasopharynx
Opening of the pharyngotympanic tube
Superior: Torus tubarius
Inferior: Ridge of levator veli palatine
Salpingopharyngeus muscle
Raises the pharynx during swallowing
Opens the orifice of the pharyngotympanic tube
Equalizes pressure in pharynx
Choanae
Two openings found at the back of the nasal passage between the nasal cavity and the pharynx
Soft palate, base of the tongue, palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches
Boundaries of the oropharynx
Oropharynx
Extends from the superior border of the soft palate to the superior border of the epiglottis
Epiglottic valleculae
Depression that temporarily stores saliva to avoid triggering swallowing reflex
Pharyngeal lymphatic ring
The Waldeyer Ring is also known as the (?)
Waldeyer Ring
An aggregate of lymphatic tissue around the pharynx which includes palatine, lingual, pharyngeal, and tubal tonsils
Piriform fossa
Contains the branches of the internal laryngeal and recurrent laryngeal nerves
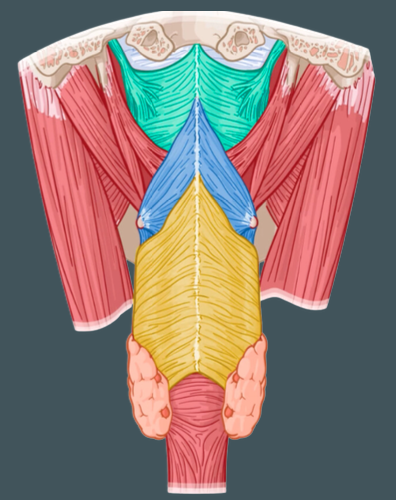
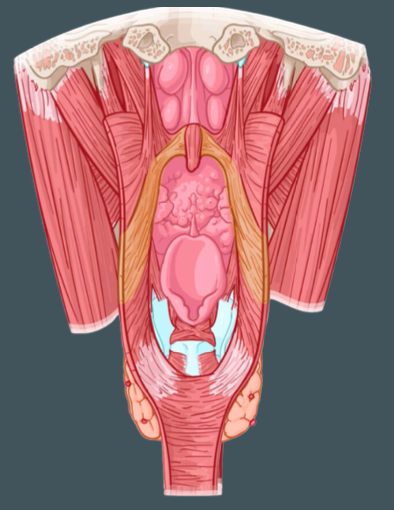
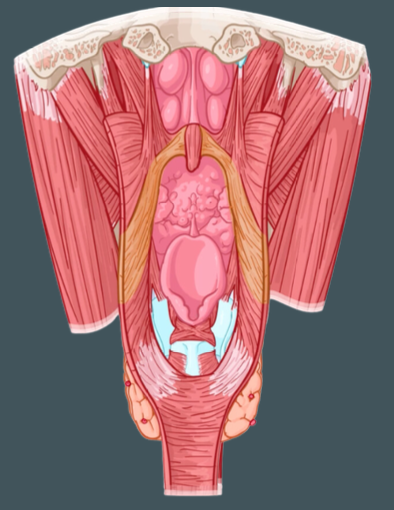
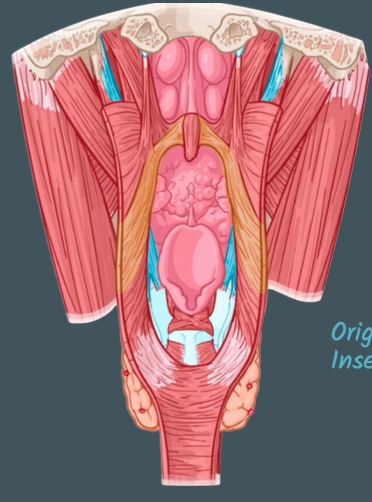
Pharyngeal constrictor muscles (Superior, Middle, Inferior)
External circular muscles that contract in sequence during swallowing to constrict the pharynx
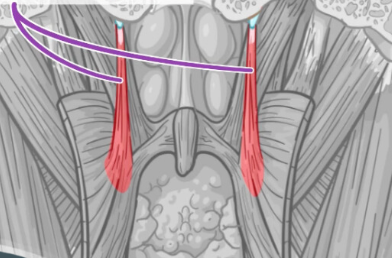
Pterygomandibular raphe
Origin of the superior pharyngeal constrictor
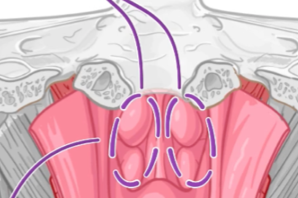
Stylohyoid ligament; lesser and greater horns of hyoid
Origin of middle pharyngeal constrictor
Oblique line of thyroid cartilage and side of cricoid
Origin of inferior pharyngeal constrictor
Pharyngeal raphe
Common insertion of the constrictor muscles
Pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve
Innervation of laryngopharynx muscles
Vagus, glossopharyngeal, sympathetic nerves
Pharyngeal plexus
Palatopharyngeus, Stylopharyngeus, Salpingopharyngeus
Internal longitudinal muscles of the laryngopharynx that elevate larynx and shorten pharynx during swallowing and speaking
Hard palate and palatine aponeurosis
Origin of palatopharyngeus muscle
Thyroid cartilage and pharyngeal wall
Insertion of palatopharyngeus muscle
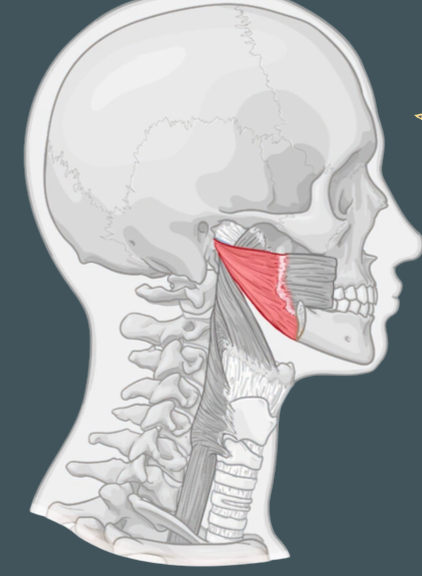
Styloid process
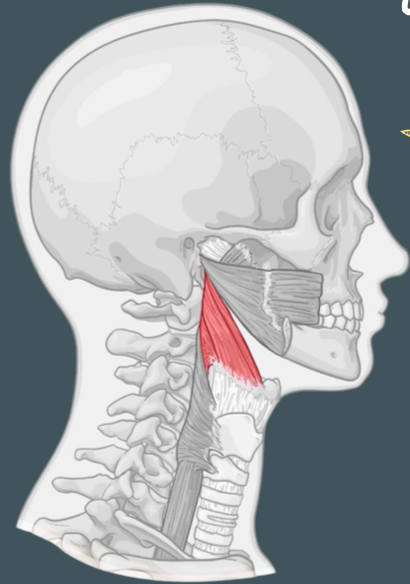
Origin of stylopharyngeus muscle
Thyroid cartilage
Insertion of stylopharyngeus muscle
Pharyngotympanic tube
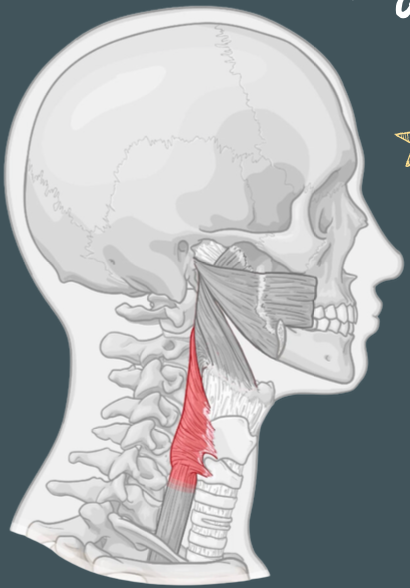
Origin of salpingopharyngeus muscle
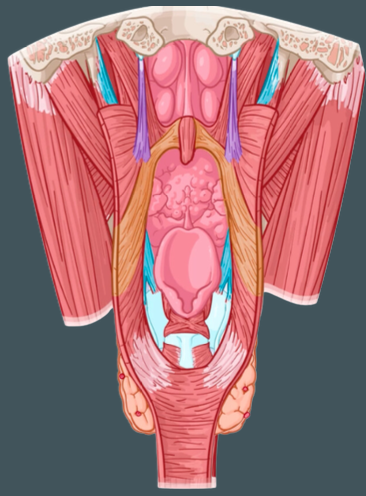
Thyroid cartilage and pharyngeal wall
Insertion of salpingopharyngeus muscle
Pharyngeal branch of Vagus nerve and pharyngeal plexus
Innervation of palatopharyngeus and salpingopharyngeus muscle
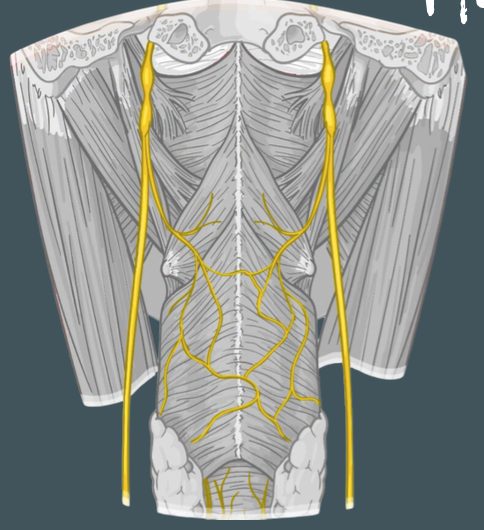
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
Innervation of stylopharyngeus muscle
Esophagus
Connects the pharynx to the stomach
Continuous with laryngopharynx
Sphincters
circular muscles that open and close passages in the body to regulate the flow of substances
Pharyngoesophageal junction
Consists of:
Superior esophageal sphincter
Narrowest part of esophagus
Superior mediastinum
Contacts with the cervical pleura at the root of the neck
Branches of inferior thyroid artery, tributaries of inferior thyroid vein
Vasculature of the esophagus
Upper half
Innervation of the esophagus
Somatic motor
Sensory fibers
Lower half
Innervation of the esophagus
Parasympathetic
Sympathetic
Visceral sensory fibers
Torus tubarius
Superior part of the opening of the pharyngotympanic tube
Ridge of levator veli palatine
Inferior part of the opening of the pharyngotympanic tube