ESS SL ALL
1/171
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
SYSTEM
set of interrelated parts that function as a whole to make a complex whole
open system
A system in which matter and energy can enter from or escape to the surroundings.
closed system
A system in which no matter is allowed to enter or leave but energy can
isolated system
A system that can exchange neither energy nor matter with its surroundings.
transfers
energy or matter change locaton through flow
transformations
energy or matter change location and state through flow
EVS
A worldview that shapes the way an individual perceives and evaluates environmental issues
1st law of thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed
2nd law of thermodynamics
Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe.
negative feedback examples
Regulation of body temp
succession
cloud formation
positive feedback examples
eutrophication
albedo effect
climate change
albedo effect
the ability of a surface to reflect away solar radiation
Eutrophication
A process by which nutrients particularly phosphorus and nitrogen, become highly concentrated in a body of water, leading to increased growth of organisms such as algae.
System Resilience
ability of a system to maintain an acceptable level of service during an adverse event -sometimes refers to the ability of a system to return to a previous state after an adverse event
static equilibrium
no positive feedback inputs (eg
tipping point
the point at which a fundamental shift in the behavior of a system occurs
gaia hypothesis
earth is one organism. self regulating. homeostatic
homeostatic
a term for a stable system that isn't changing
species
A group of similar organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring.
population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
community
All the different populations that live together in an area
ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
succession
The series of predictable changes that occur in a community over time
Stage 1 of succession
pioneer community: pioneer organisms are adapted to extreme conditions. usually r-selected species start breaking down rock (ex: lichens
Stage 2 of succession
establishment: as soil layer forms & improves, species diversity increases, invertebrates move in and increase organic matter (humus), water retention improves
Stage 3 of succession
competition: larger plants increase, providing shelter and allowing K-selected species to move in, extreme conditions improved. competition for resources result in some early organisms dying out
Stage 4 of succession
stabilization
Final result of succession
Climax community: A stable, mature community that undergoes little or no change in species over time
primary succession
occurs in environment with no previous life. bedrock
secondary succession
occurs in previously inhabited environments
Herbatious Plants
need more soil to grow and can outcompete competition
r-stategists
short lived
k-stategists
long lived
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
lag phase
"flat" period of adjustment, enlargement; little growth
exponential growth phase
rapid growth; when the size of a population increases excessively
transitional phase
Phase of population growth where the population continues to grow, but increasingly slowly as competition increases as carrying capacity is being reached
stationary phase
fluctuation on carrying capacity
overshoot
population exceeds carrying capacity
dieback
Sharp reduction in the population of a species past carrying capacity due to the depletion of a limiting factor.
renewed growth
growth starts again once the depleted factor has recovered
Zonation vs. Succession
Zonation refers to changes in community along an environmental gradient due to factors such as changes in altitude, latitude, tidal level or distance from shore (coverage by water).
Succession is the process of change over time in an ecosystem involving pioneer, intermediate and climax communities.
abiotic factors
Abiotic factors are the non-living parts of an organism's habitat.
biotic factors
all the living biological parts and interactions in an ecosystem
Symbiosis
interaction between 2 dissimilar organisms living in same area. (umbrella term for parasitism/mutualism)
fundamental niche
The niche species could potentially occupy.
realised niche
the actual conditions and resources in which a species exists due to biotic interactions.
biomass
measurement of energy in organism. (kcal/m^2/year)
Productivity
the conversion of energy into biomass for a given period of time, measured as productivity
Gross Primary Productivity (GPP)
The total amount of solar energy that producers in an ecosystem capture via photosynthesis over a given amount of time.
Net Primary Productivity (NPP)
The energy captured by producers in an ecosystem minus the energy producers respire.
Gross Secondary Productivity (GSP)
The total gain by consumers in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time through absorption.
Net Secondary Productivity (NSP)
The gain by consumers in energy or biomass per unit area per unit time remaining after allowing for respiratory losses (R).
Bioaccumulation
An increased concentration of a chemical within an organism over time
Biomagnification
increase in concentration of toxins passed up in trophic levels
biome factors
insulation, precipiration, temperature, sunlight, altitude and climate
DDT
an insecticide that is also toxic to animals and humans
carbon cycle
main storages: air, animals, plants, fossil fuels, ocean
processes: photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, combustion, carbon fixation
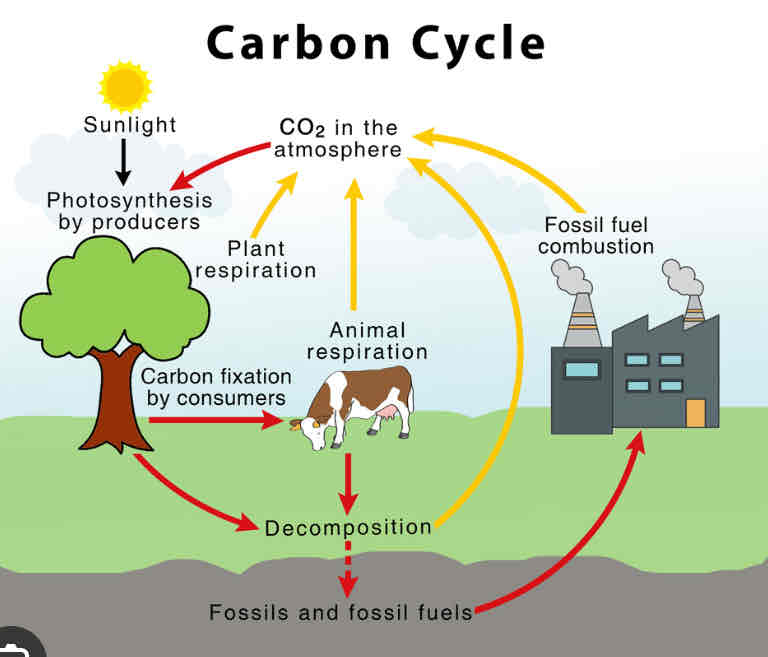
carbon fixation
The initial incorporation of carbon into organic compounds.
Nitrogen cycle
main storages: air, plants, animals, soil
transfers: absorption, consumption, decomposition
transformations: nitrogen fixation, denitrification, ammonification, nitrification, assimilation
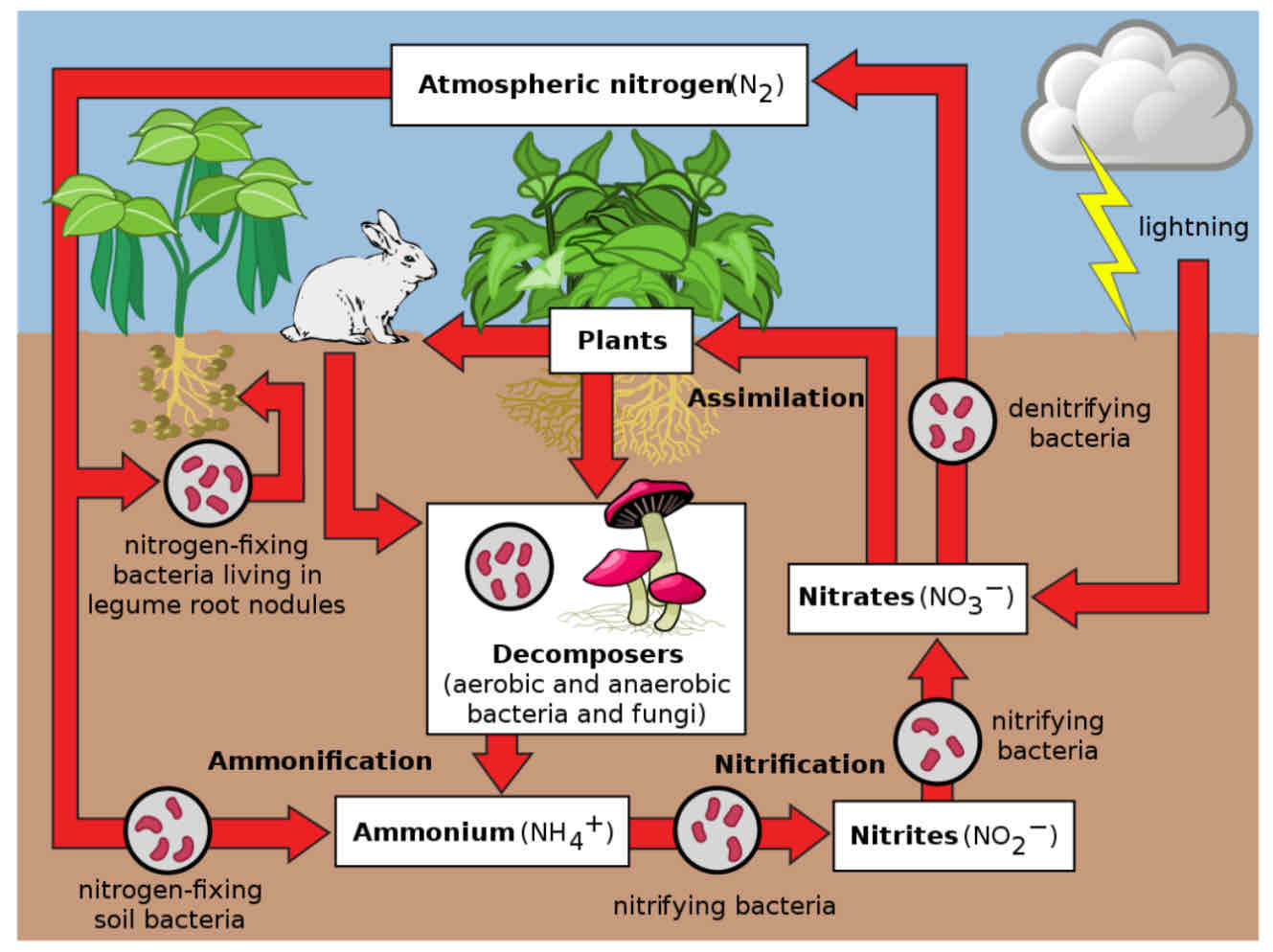
Nitrogen fixing
ammonia (NH3) --> ammonium (NH4+)
because atmospheric nitrogen cannot be used directly by plants it must first be converted into ammonia (NH3) by bacteria (rhizobium)
Denitrification
Conversion of nitrates (created by ammonium) into nitrogen gas
ammonium (NH4+) --> nitrate (NO2) --> nitrate (NO3) --> ammonia (NH3)
Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC’s)
Organic compounds that exist as gases in the atmosphere and act as pollutants, some of which are hazardous.
Photochemical smog
An atmospheric condition formed through a combination of weather conditions and pollution, especially from motor vehicle emissions/voc's
Continuous sampling
Everything is measured along a line transect
Interrupted transect sampling
Points at regular intervals are measured
Random sampling
Points are determined randomly (eg. dice)
Stratified random sampling
For a place with 2 or more distinct sampling areas, each area sampled using random method.
Systematic sampling
First sample point chosen randomly then the following points done with a set interval/distance
Species abundance
The number of organisms in a population relative to its environment
Lincoln index —> (n1xn2)/nm
Species abundance
n1= n caught in first sample
n2= n caught in second sample
n3= n marked in second sample
Species diversity
Compares relative abundance of a species in a community
Simpsons diversity index —> D= (N(N-1))/SUMn(n-1)
Species diversity
N= total n of organisms of all species found
n= number of individuals of a particular species
Ecological pyramids
= pyramid of numbers
= pyramid of biomass
= pyramid of productivity
Atmospheric movement
= Polar cell : Ferrel cell : Hadley cell | mirror
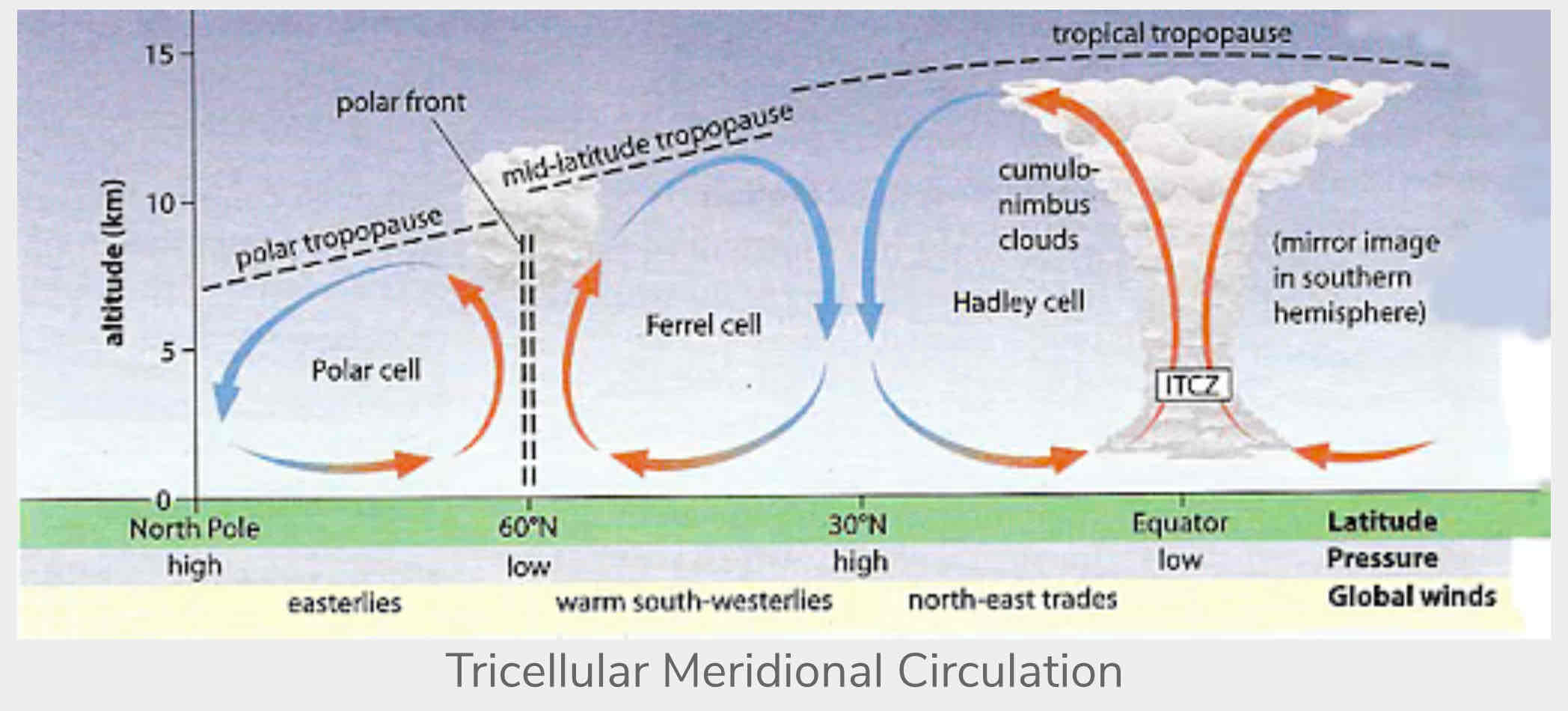
Abiotic factors of atmospheric movement
precipitation
Temperature
Insulation
All lead to a move in biomes
Crude birth rate
Number of births per 1000 people, per year
=births/populationx1000
Total fertility rate (TFR)
Average number of births per 1000 women of childbearing age
TFR =(number of births from women aged x to y / midyear population of women aged x to y) x 1000
Crude death rate
Number of deaths per 1000 people per year
CDR = deaths/ population x 1000
Natural increase
Crude birth rate - crude death rate
Doubling time
Number of years for a population to double. Assuming natural increase remains constant throughout the years
= 70/NIR (%)
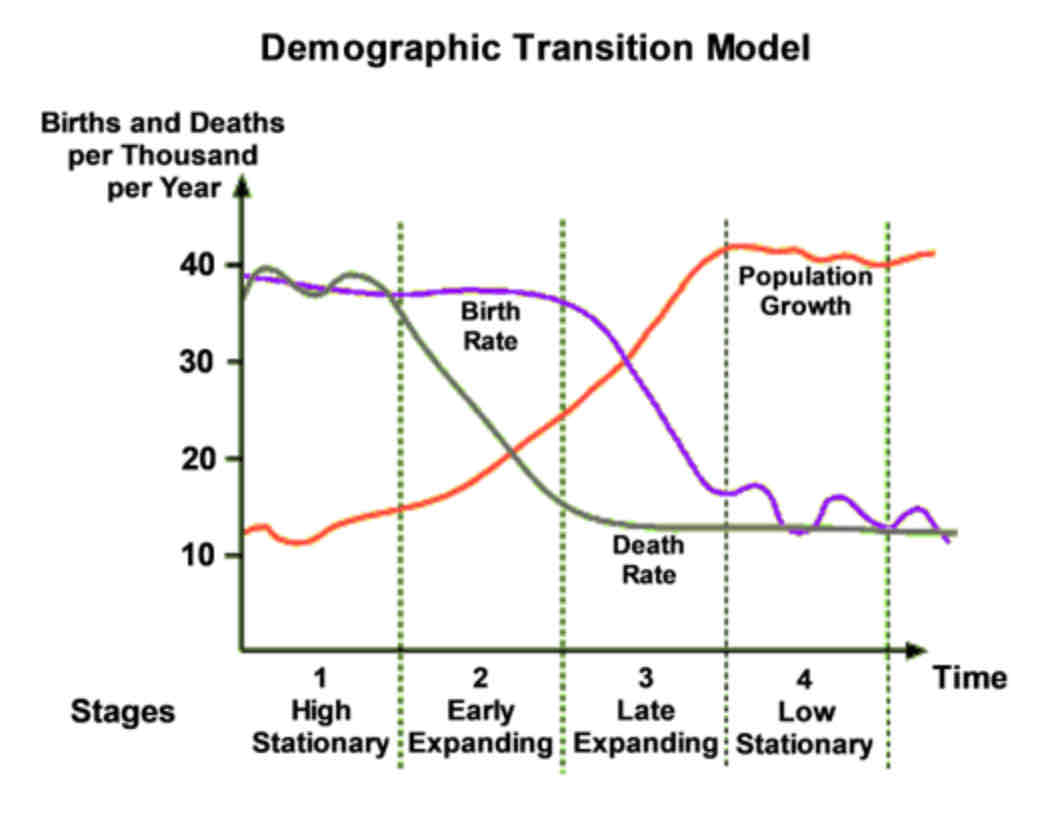
Demographic transition model
High birth rate factors
parents want children for:
labour
To care for them at old age
Continue family line
Replace dead children
Low birth rate
Decline because:
costly kids
Government pensions
Women’s careers
Family planning more widespread
Less need for kid replacement
High death rate
People die from:
lack of clean water
Lack of food
Poor hygiene
Disease
Overcrowding
Poverty
Low death rate
Decline because:
Access to clean water
Reliable food
Good hygiene
Less crowded/dense
Raised living standard (GDP)
Stage 1 of Demographic transition
= high and variable
birth and death rate high
Population growth fluctuates
Stage 2 of Demographic transition
Early and expanding
birth high death low
Rapid population growth
Stage 3 of Demographic transition
Late expanding
birth rate drops and death rate stays low
Population growth continues but slower
Stage 4 of Demographic transition
Low and variable
birth and death rates low and variable
Population growth fluctuates
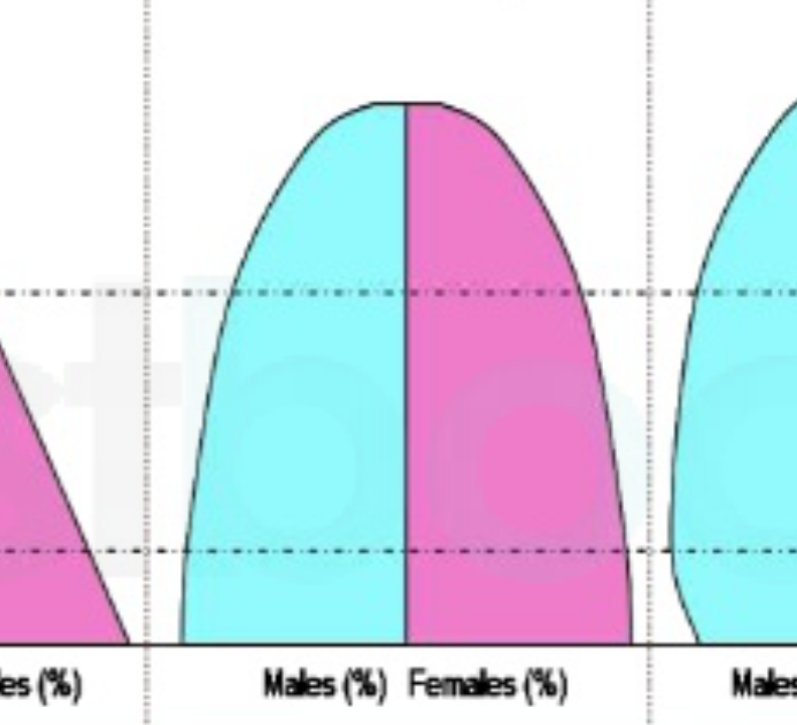
Stage 5 of Demographic transition
Slow declining
birth rate lower than death
Population decline
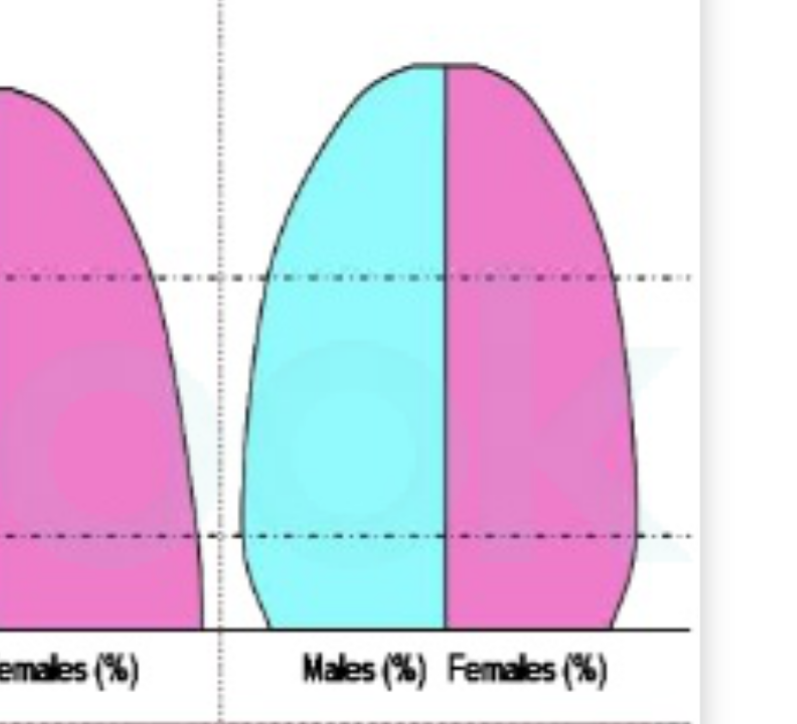
Factors that effect fertility
status of women
Education level
Wealth
Urban vs rural
Religion
Health
“One child policy” ==>
Factors that effect mortality
age structure
Social class
Disease and war
Natural capital
Natural resources that produce a sustainable income of good or services
Eg = tree, coal, oil, photosynthesis, animals and their services
Natural income
Yield obtained from natural resources (benefit)
Renewable natural capital
marketable natural resource that can produce a sustainable natural income of good or services
Replenishes itself over timescale of use (natural capital does not run out due to consumerism)
Non-renewable natural capital
irreplaceable or only replaceable over geologic timescales
Sustainability
The use and management of resources that allows full natural replacement and full recovery of ecosystems affected
Sustainable development
Meets the needs of the present without comprising the ability for future generations to meet their own needs
Pollution
Addition of a substance/agent to an environment by human activity
too much to be rendered harmless by the environment
Affects the organisms in the environment