Earth's Interior- Jeopardy
Due: Nov 14, 2025, 5:00 AM
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
What is the definition of Molten?
liquified by heat
What is an Earthquake?
Shaking and trembling that results from the movement of rock beneath Earth's surface
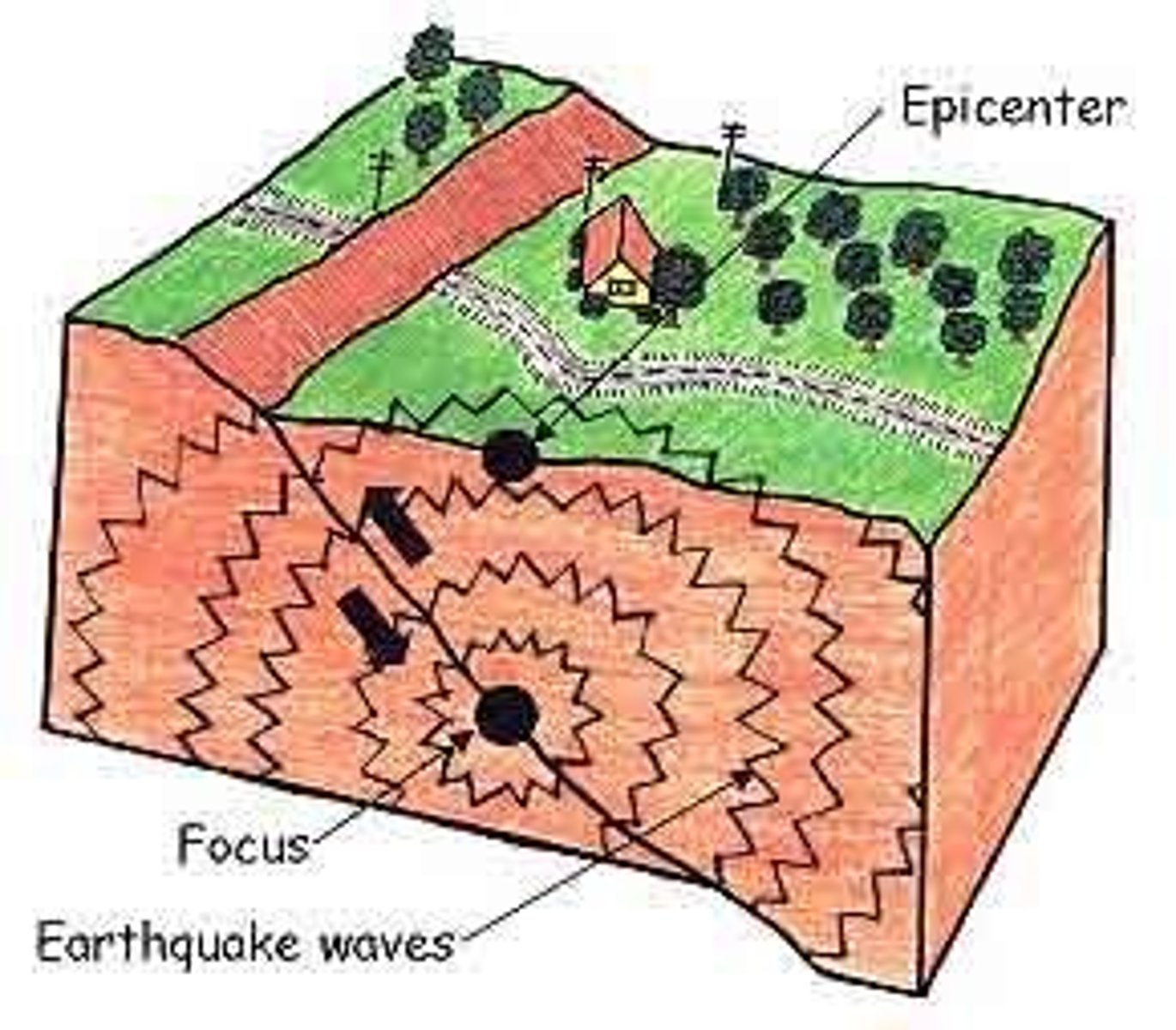
What is the definition of Seismic Waves?
Carries the energy of an earthquake away from the focus, through Earth's interior and across the surface.
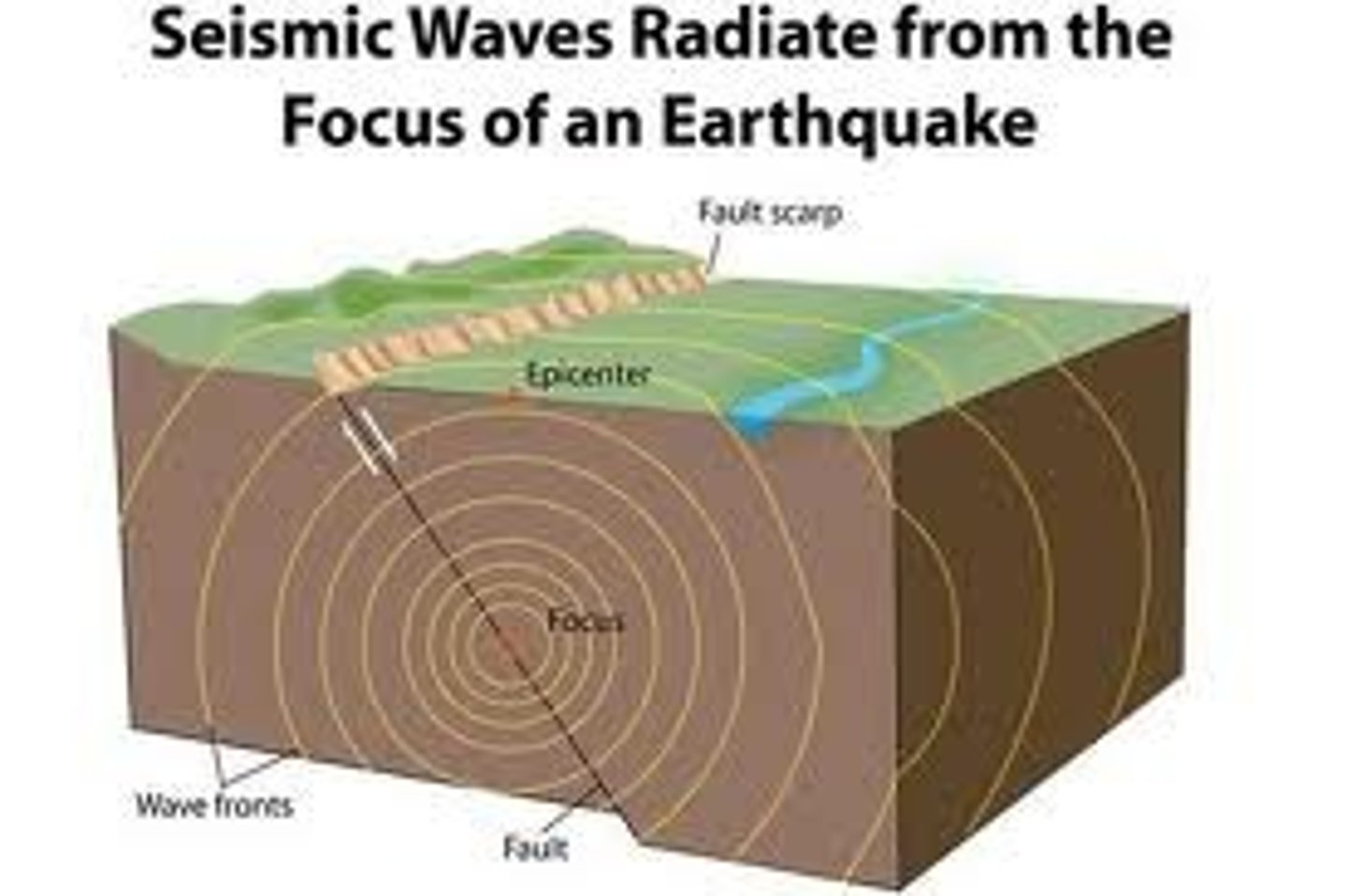
What are the three categories of Seismic Waves?
P wave
S Wave
Surface Wave
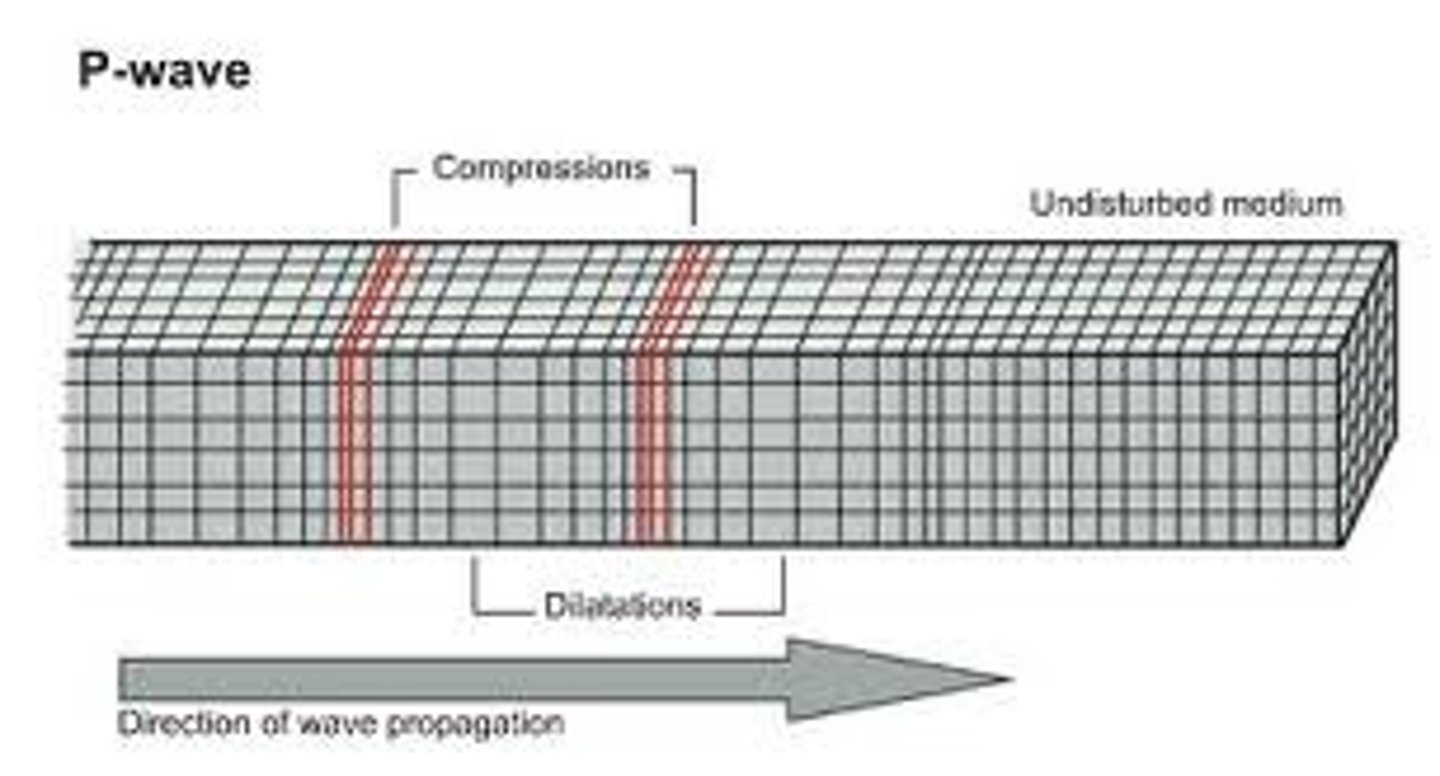
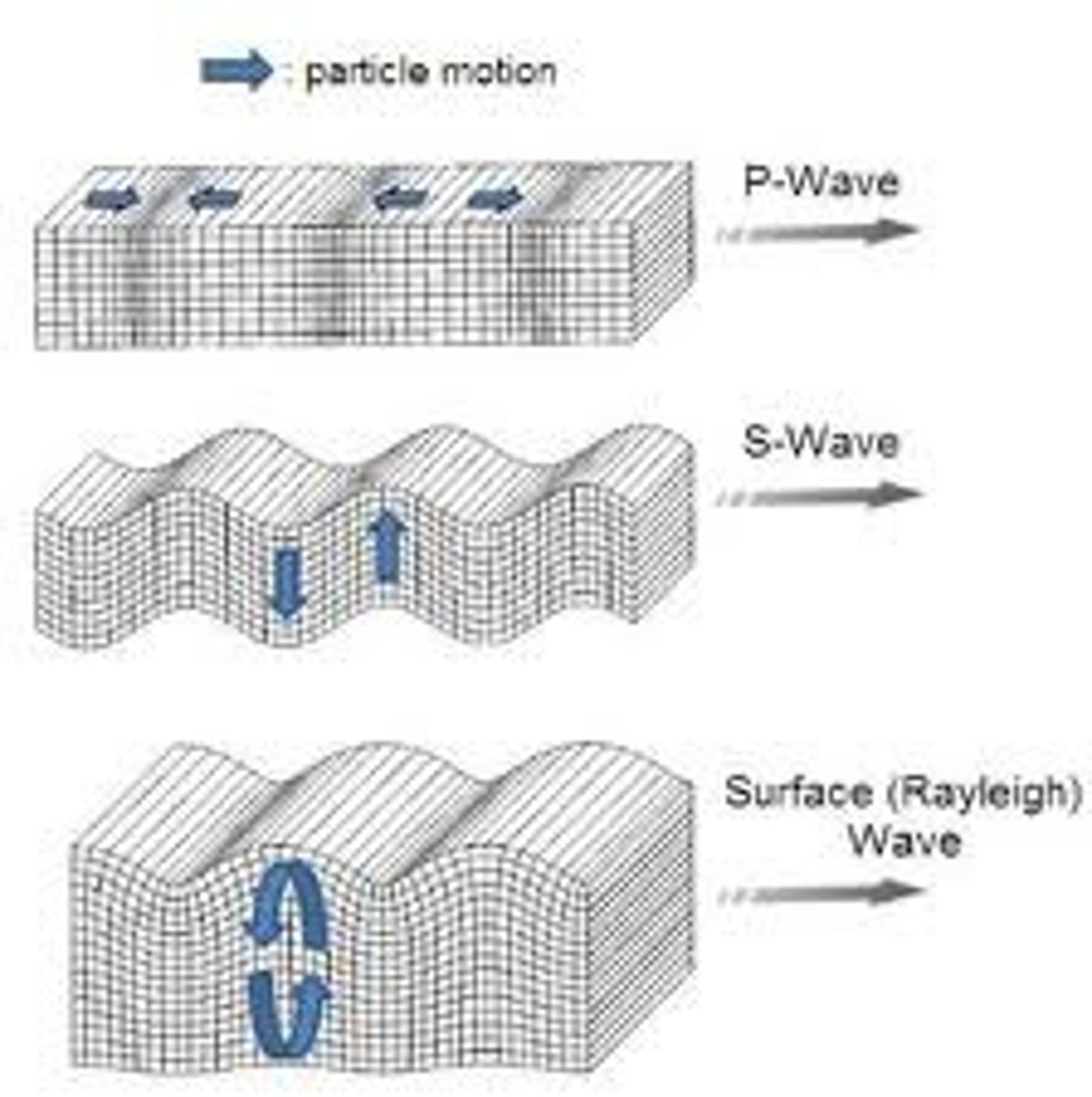
What is a P Wave?
Body Wave. Wave that compresses and expand the ground like an accordion. Damage buildings. Travel through both solids and liquids.
What is a S wave?
Body Wave. Wave that vibrates from side to side and up and down slowly. Cannot travel through liquid.
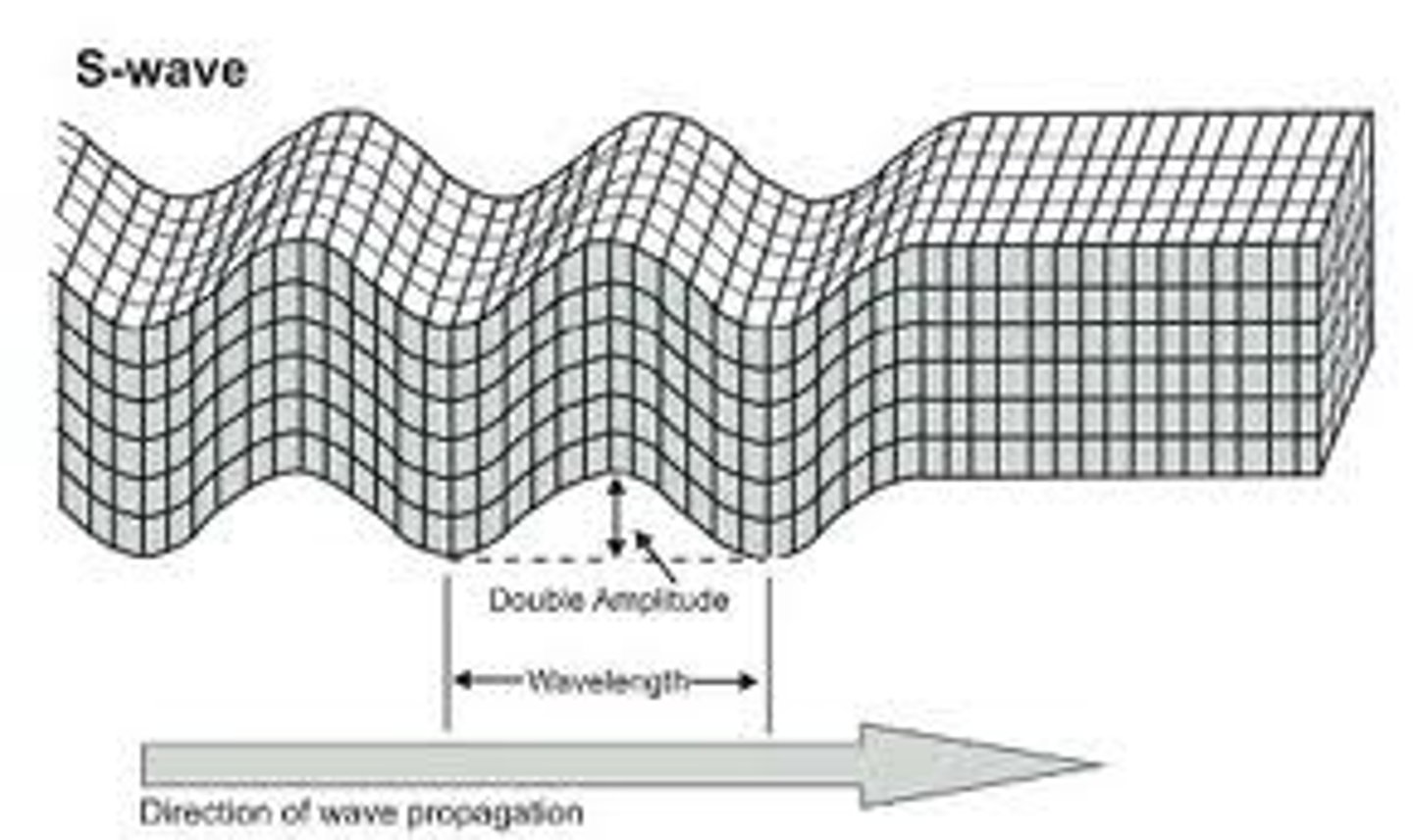
What is a surface wave Surface wave?
When P & S waves reach the surface, they also move more slowly
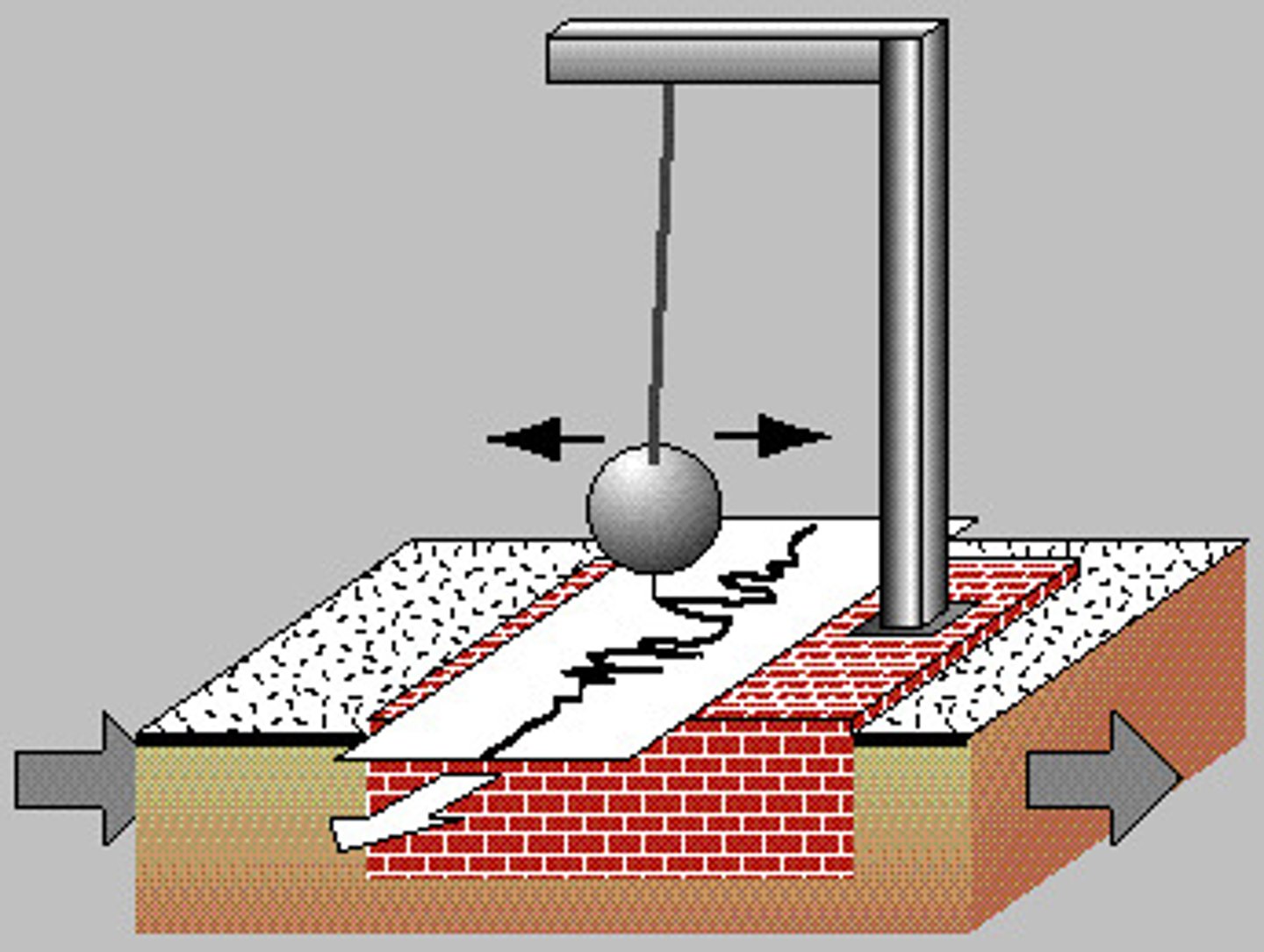
What is a Seismograph?
A machine that measures earthquakes and seismic waves
What are the two types of surface waves?
L-waves & R-waves
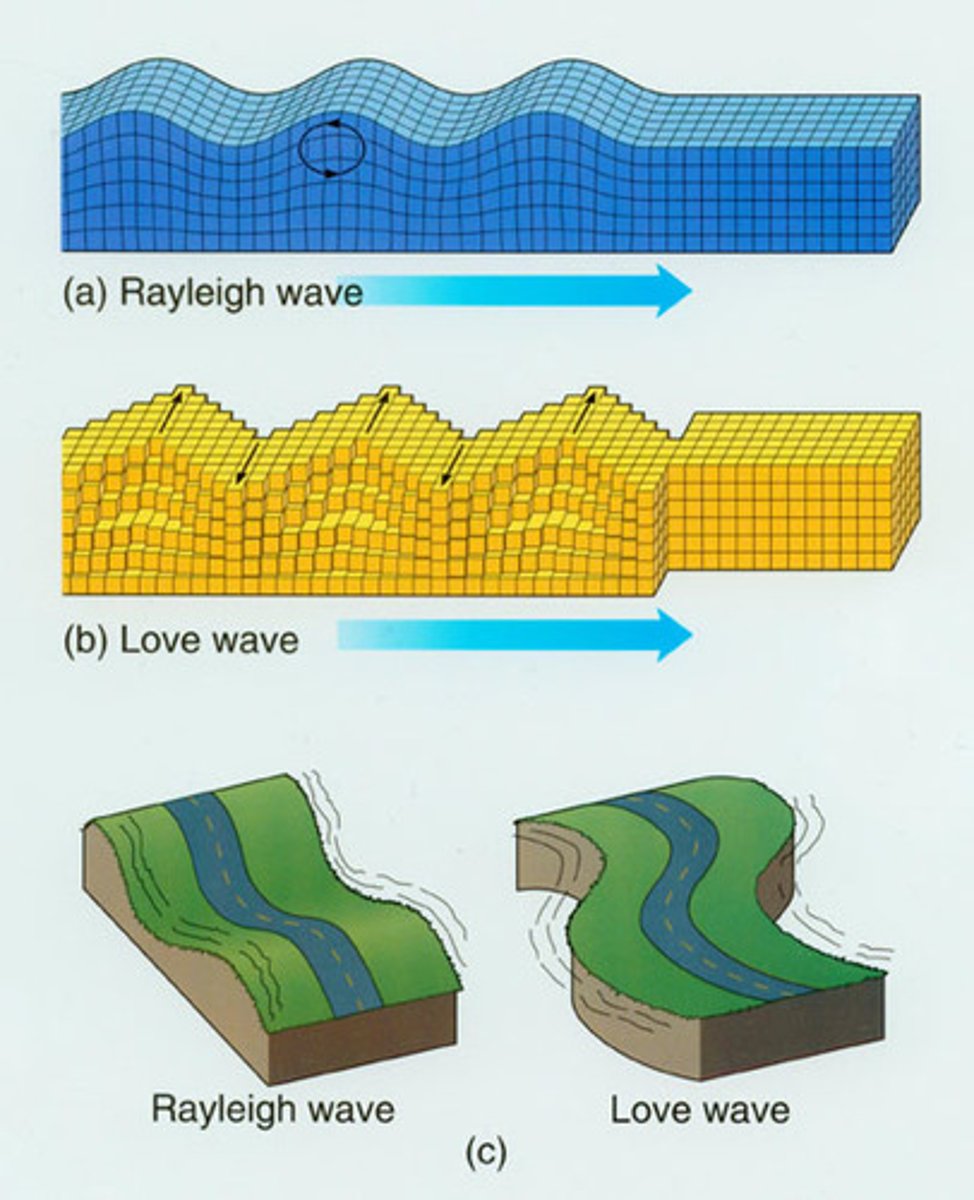
What is a L-wave (Love)?
Surface wave. Motion like an s-wave but does not go up and down, just side to side. They do not travel through water. Only travel through surface of earth. Damaging to foundations and structures.
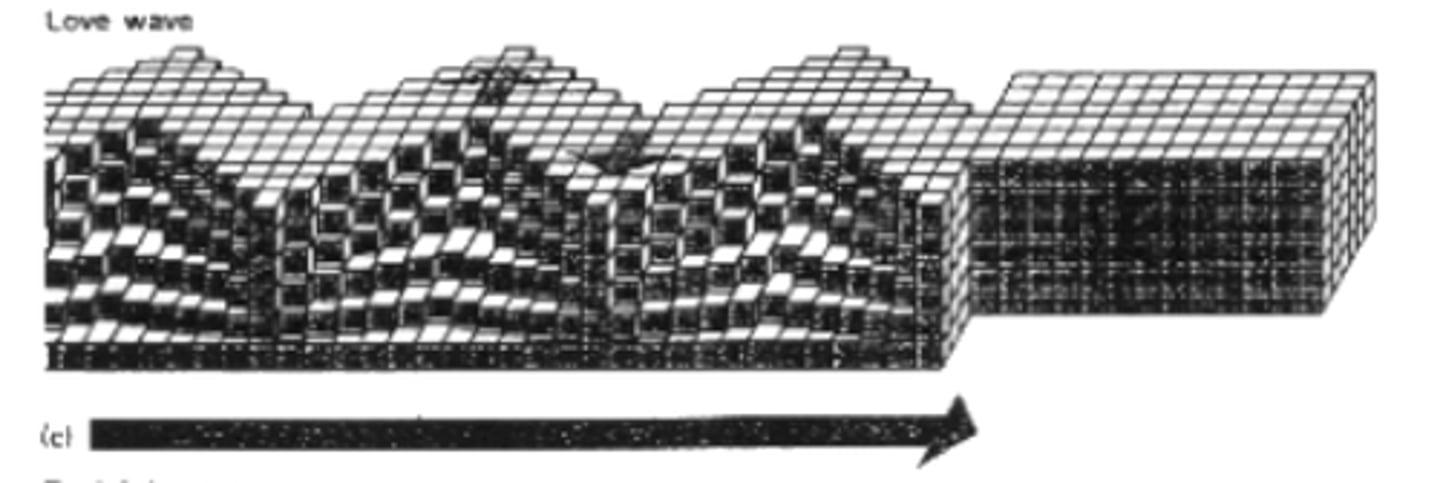
What is a R-wave (Rayleigh)?
Surface wave. Like rolling ocean waves. Move both up and down and side to side. Only travel through surface of earth.

What is portion of the outermost layer of Earth, found beneath the oceans?
Oceanic Crust
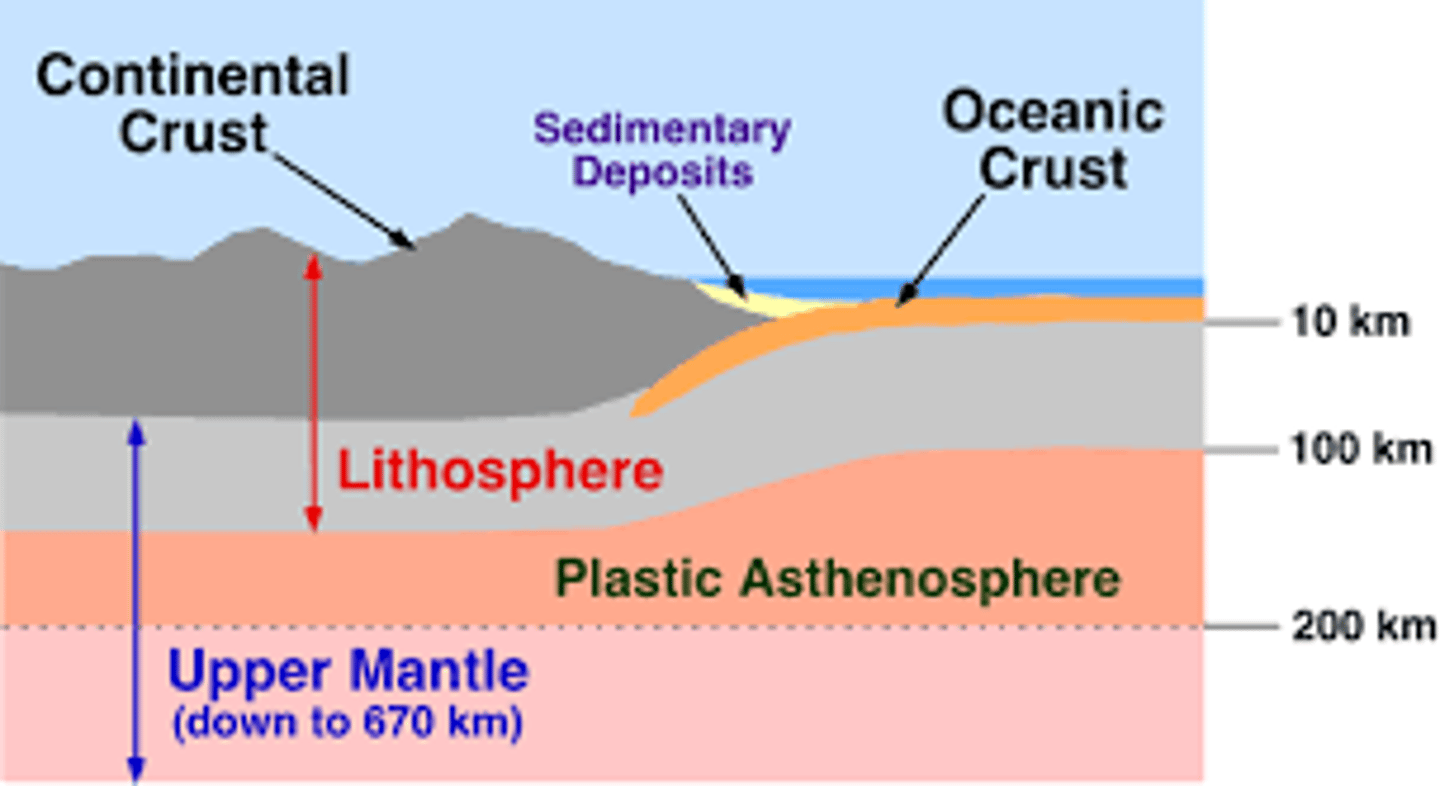
What is portion of the outermost layer of Earth, found beneath the land?
Continental Crust
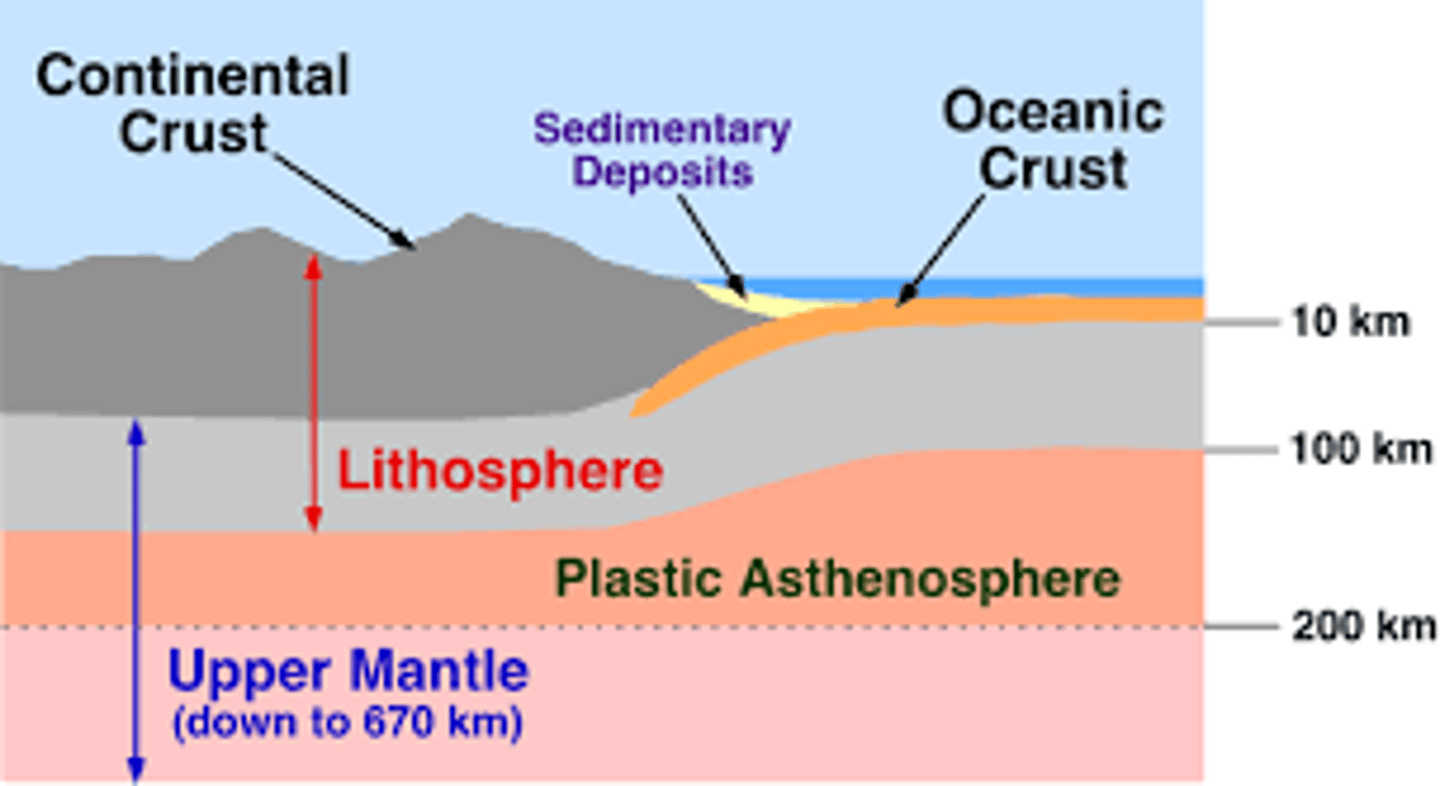
What is composed of the Earth's crust and the uppermost layer of the mantle?
Lithosphere
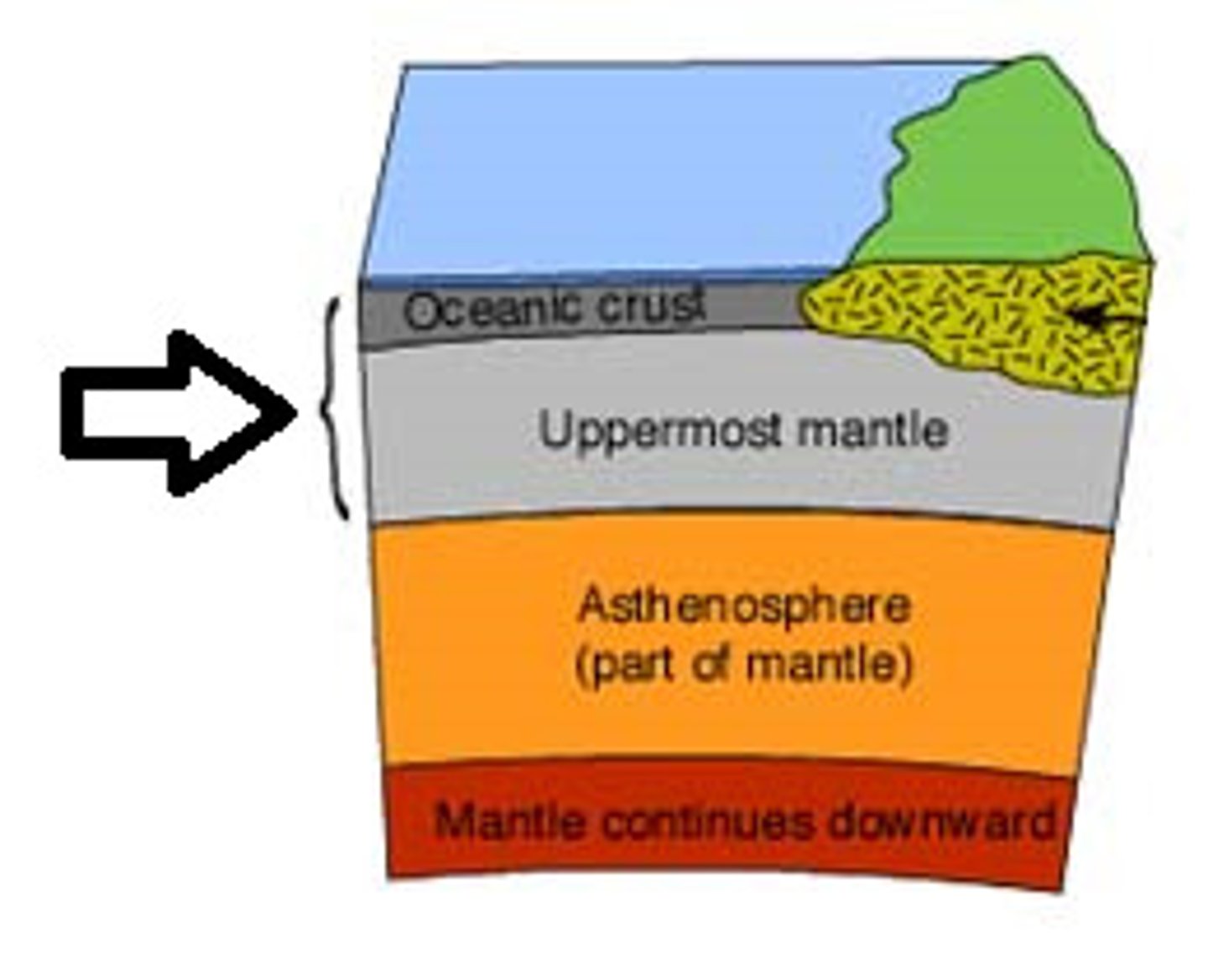
What is another term for the upper mantle, this is where convection currents are found?
Asthenosphere
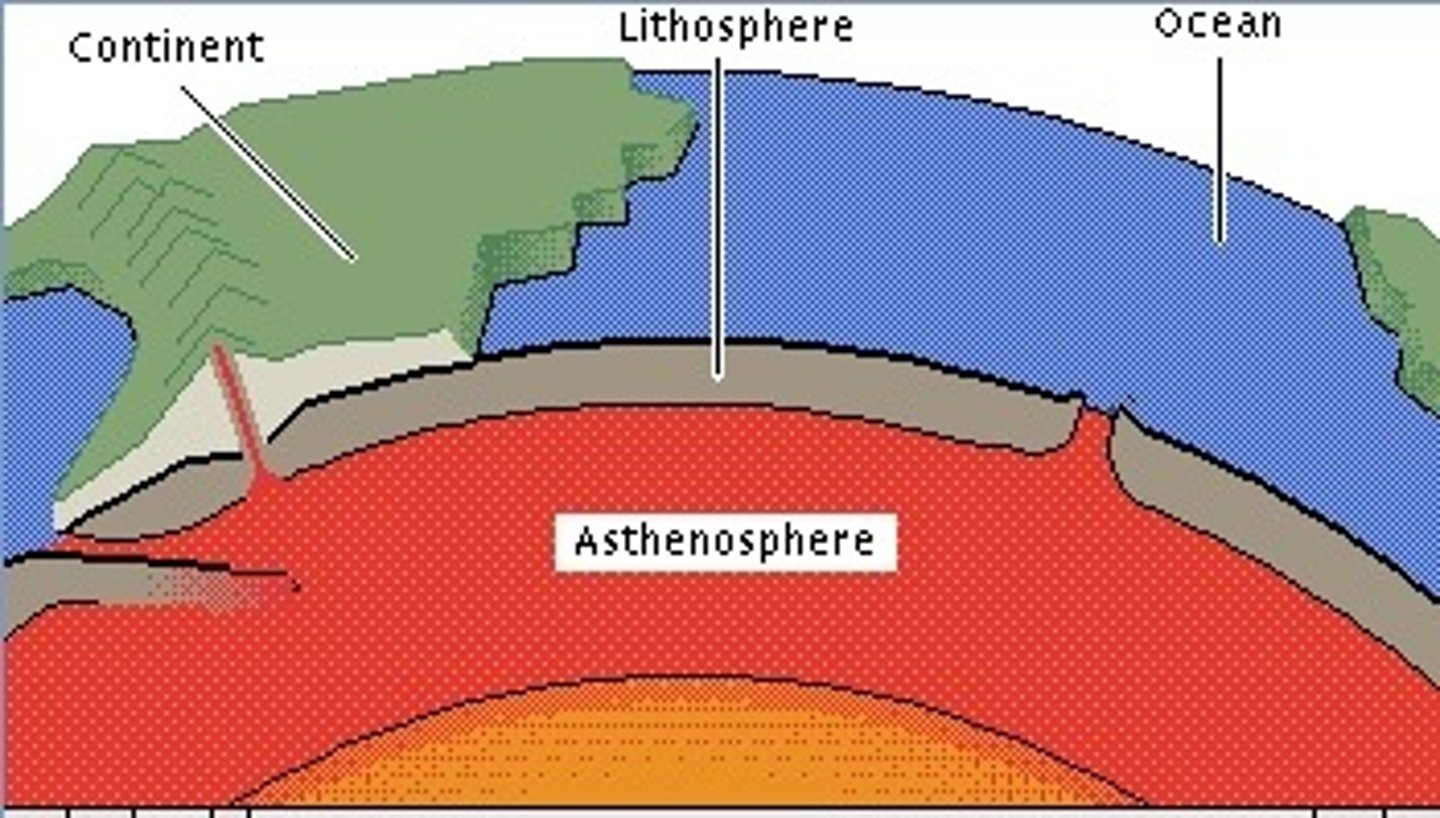
What is another term for the lower mantle?
Mesosphere
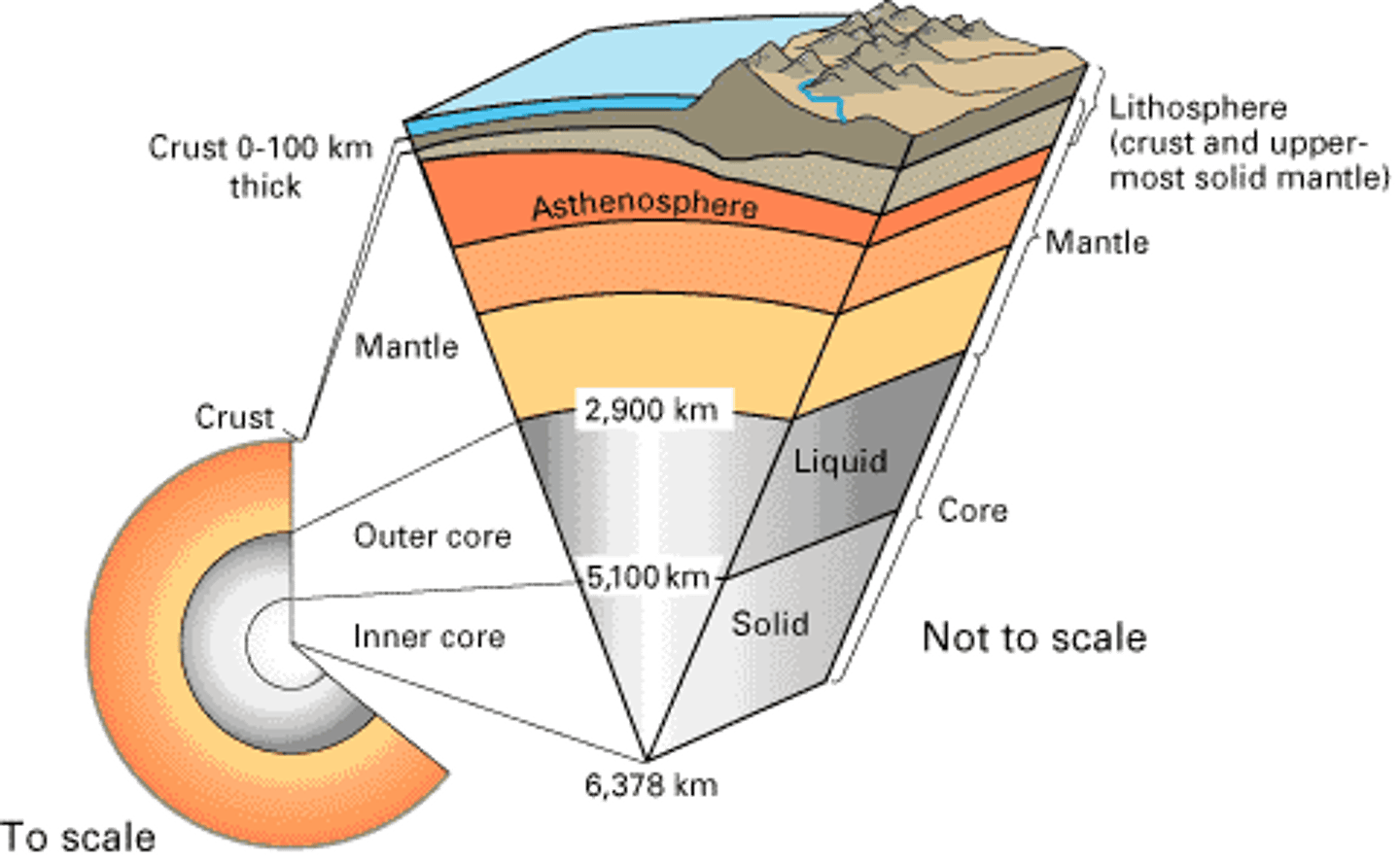
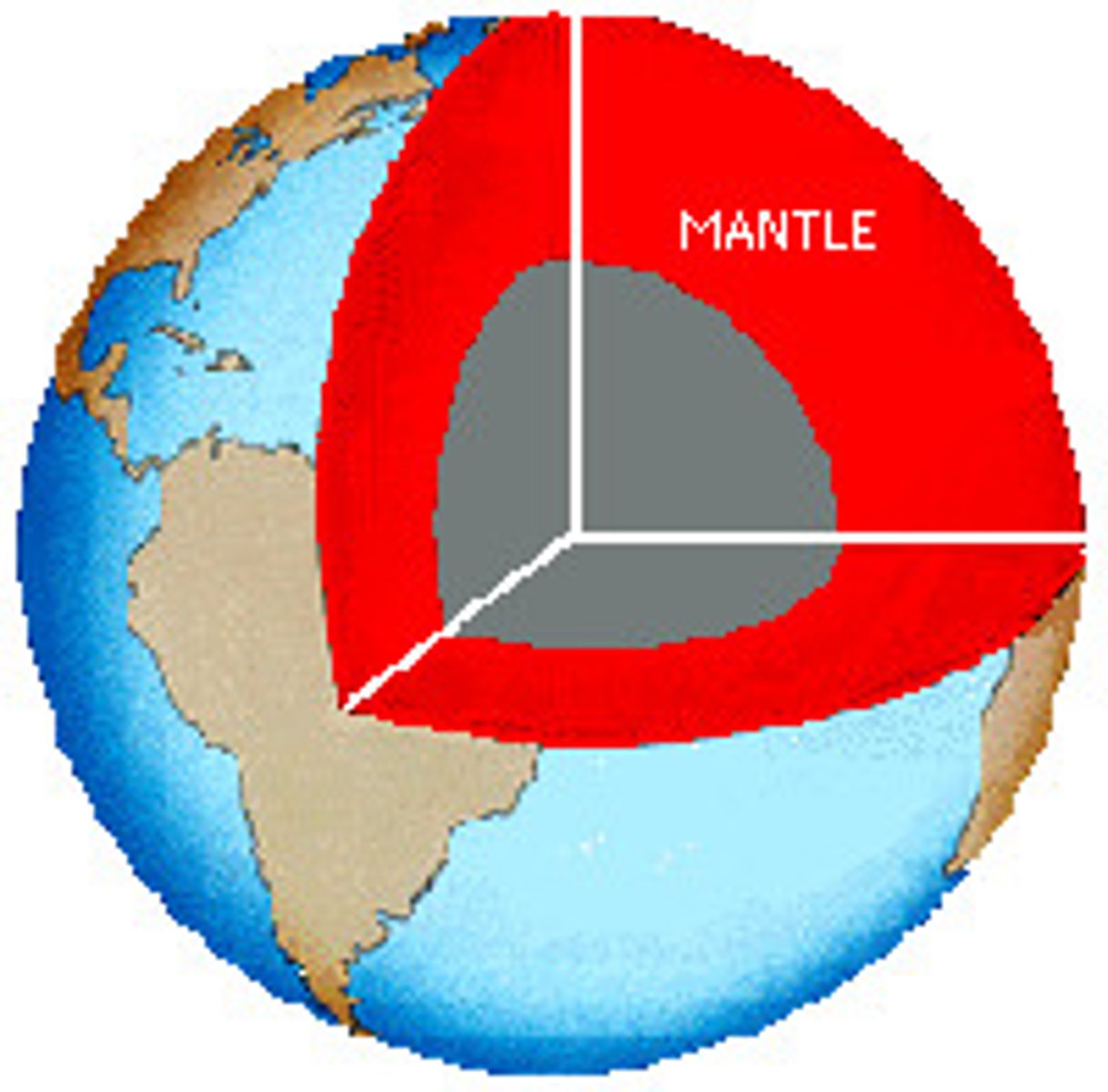
What is thickest of all Earth's layers, comprises about 85% of Earth's weight?
Mantle
What is the Earth's layer that is composed of iron and nickel, liquid state of matter?
Outer Core
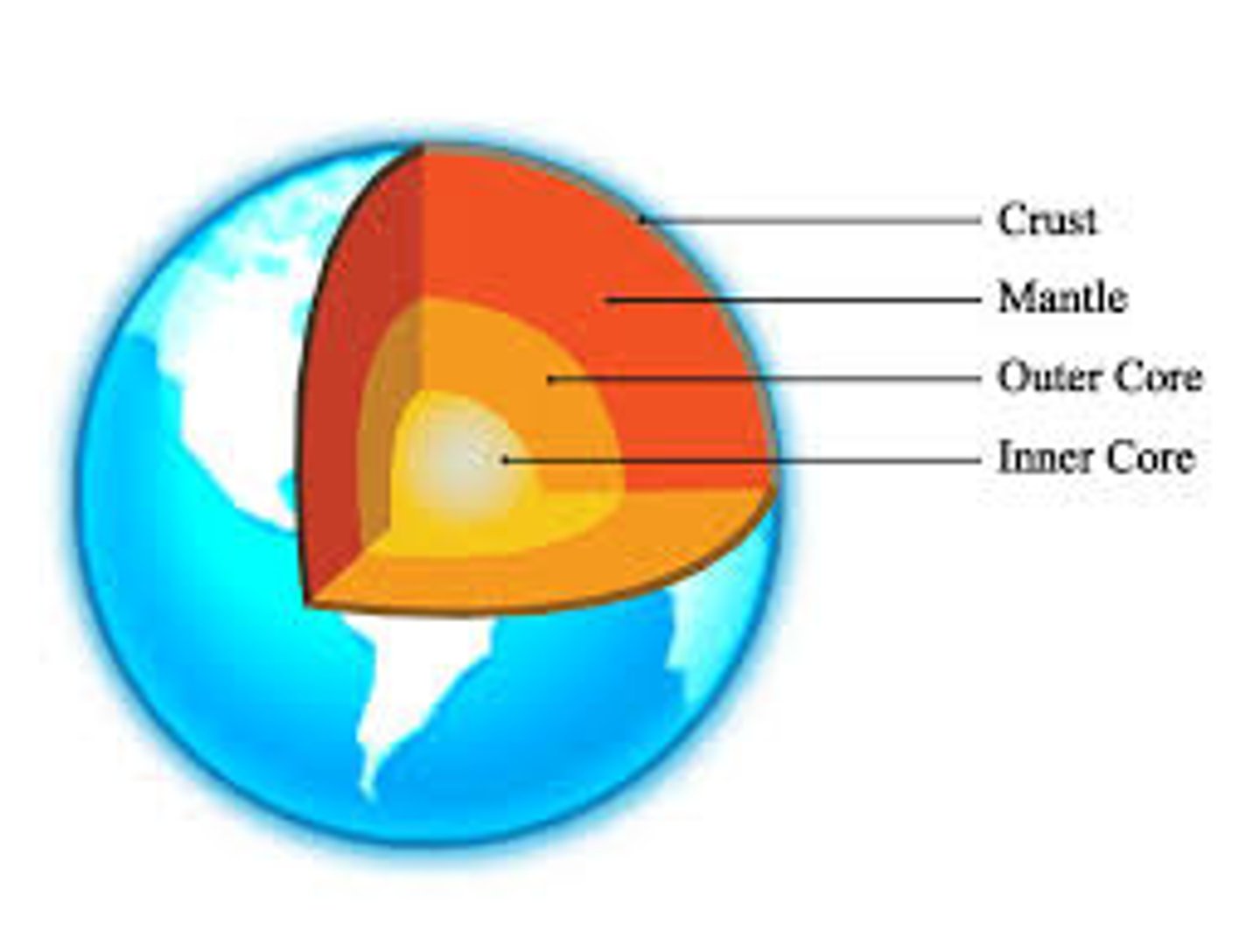
What is the most dense layer of the Earth. Composed completely of iron?
Inner core

What is the definition of Convection Currents?
Transfer of heat when there is a significant difference in temperature between two parts of a fluid. Hot fluids rise and cold fluids sink.
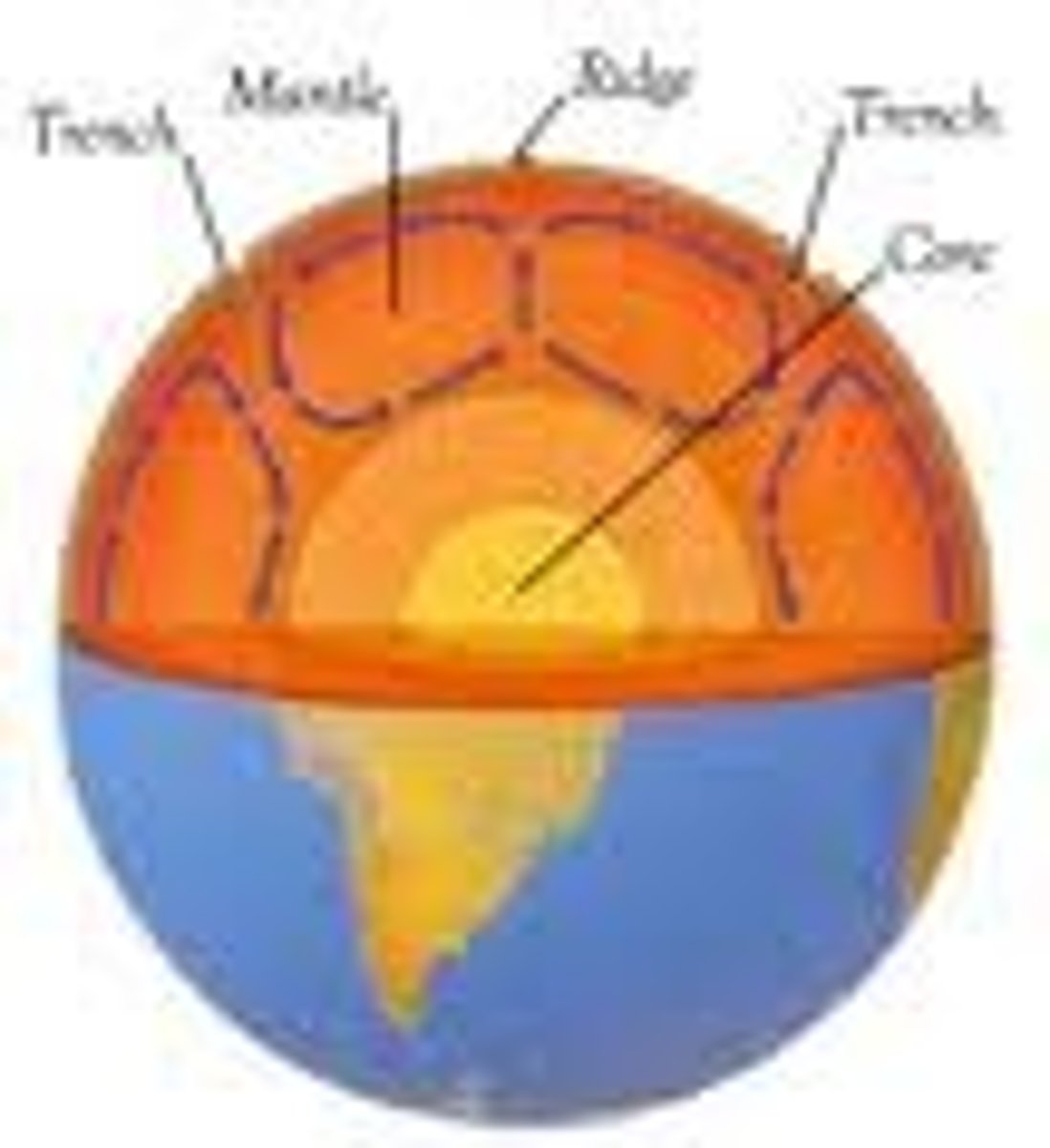
What is the definition of Planetary differentiation?
separation of layers because of their densities