Solutions jee
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
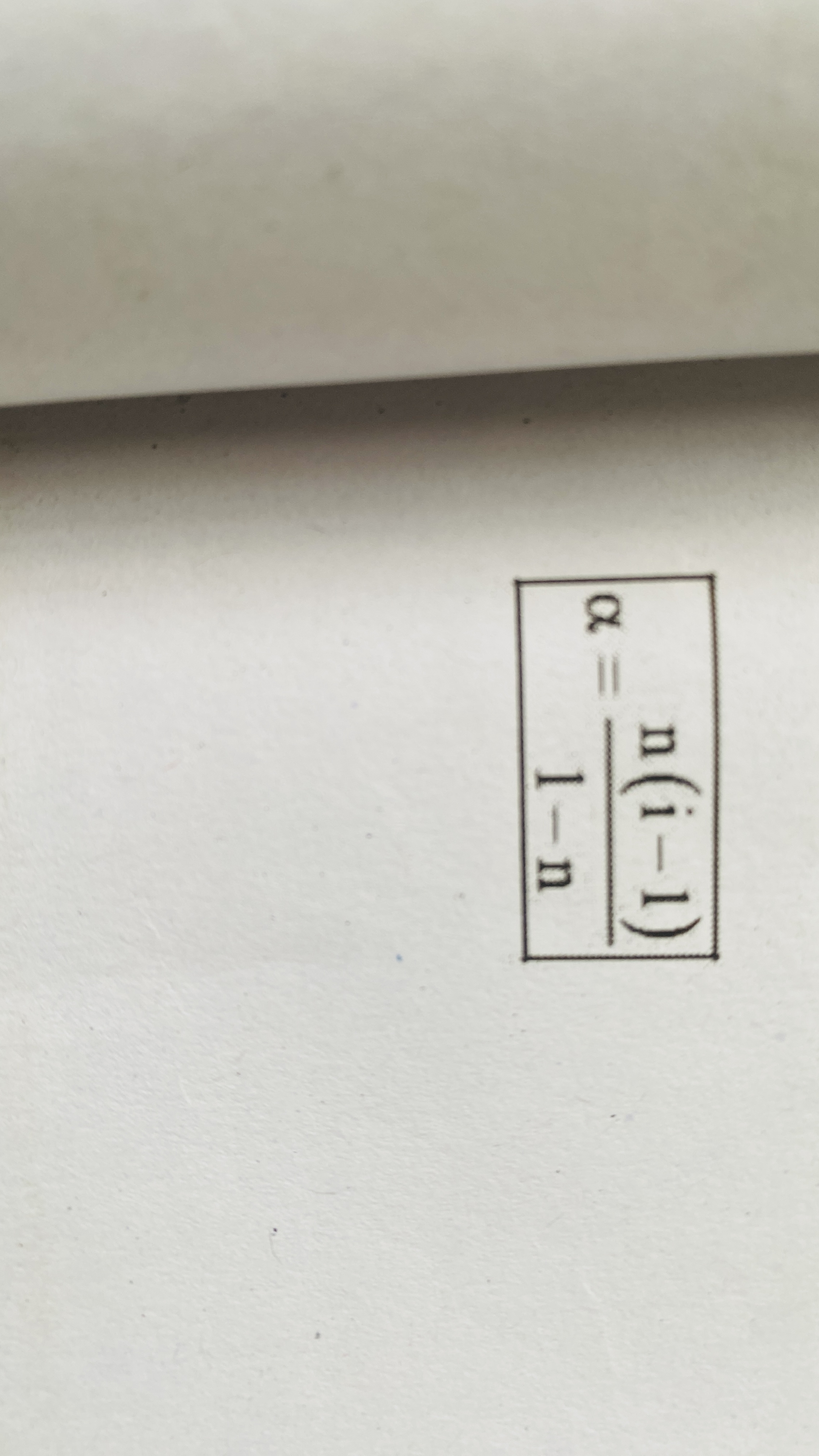
Molarity and mass %
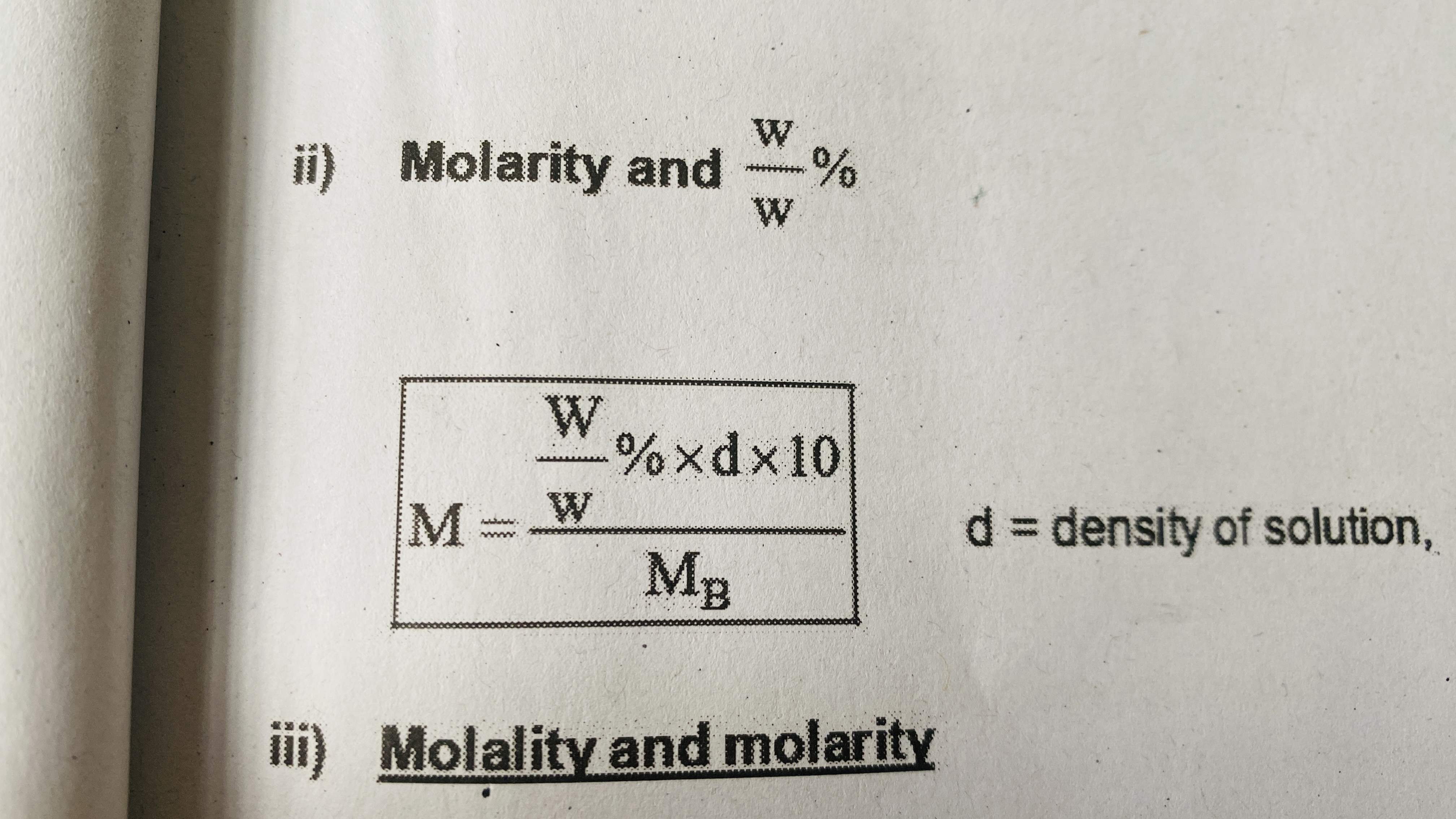
Molarity and molality
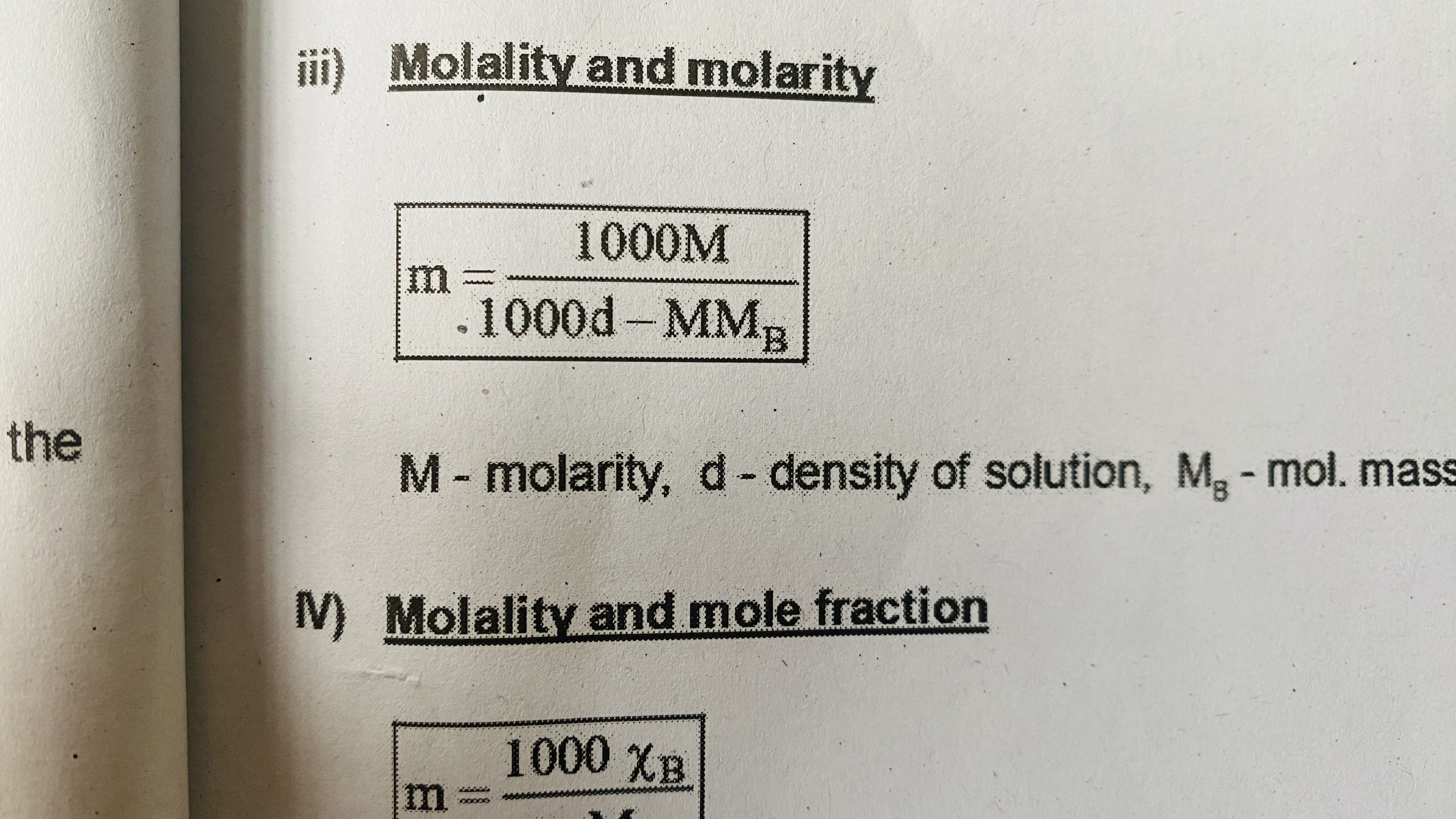
Molality and mole fraction

Molarity and mole fraction
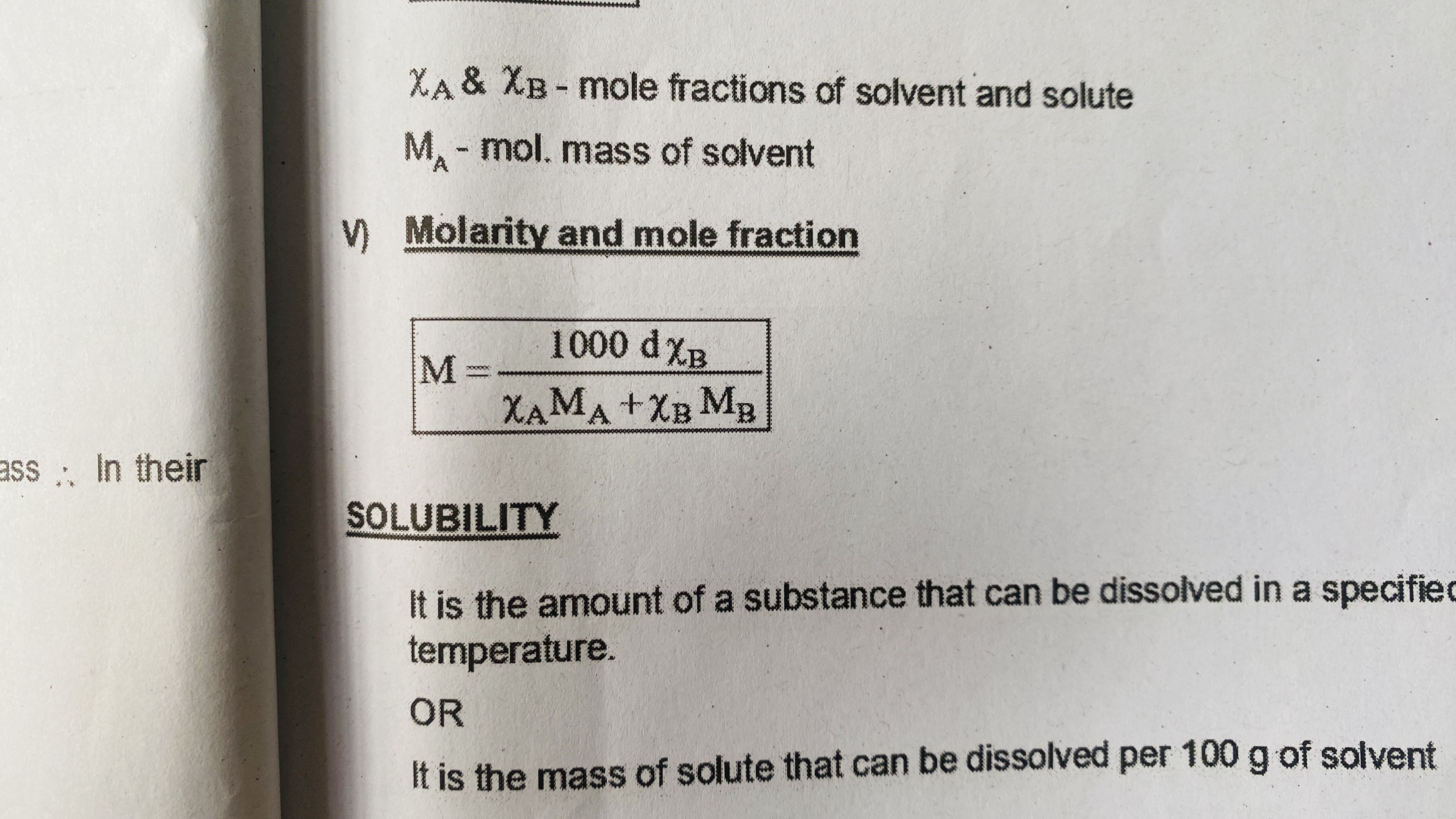
For Solubility of a solid in a liquid the endothermic dissolution favours
Solubility increases with increase in temperature
For solubility of a solid in liquid effect of pressure
Pressure has no effect
Henry’s law
Partial pressure of a gas in vapour phase is proportional to mole fraction of the gas in the solution.
Raoult’s law
For a solution of volatile liquids the partial pressure of each component in the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction
Dalton’s law of partial pressure
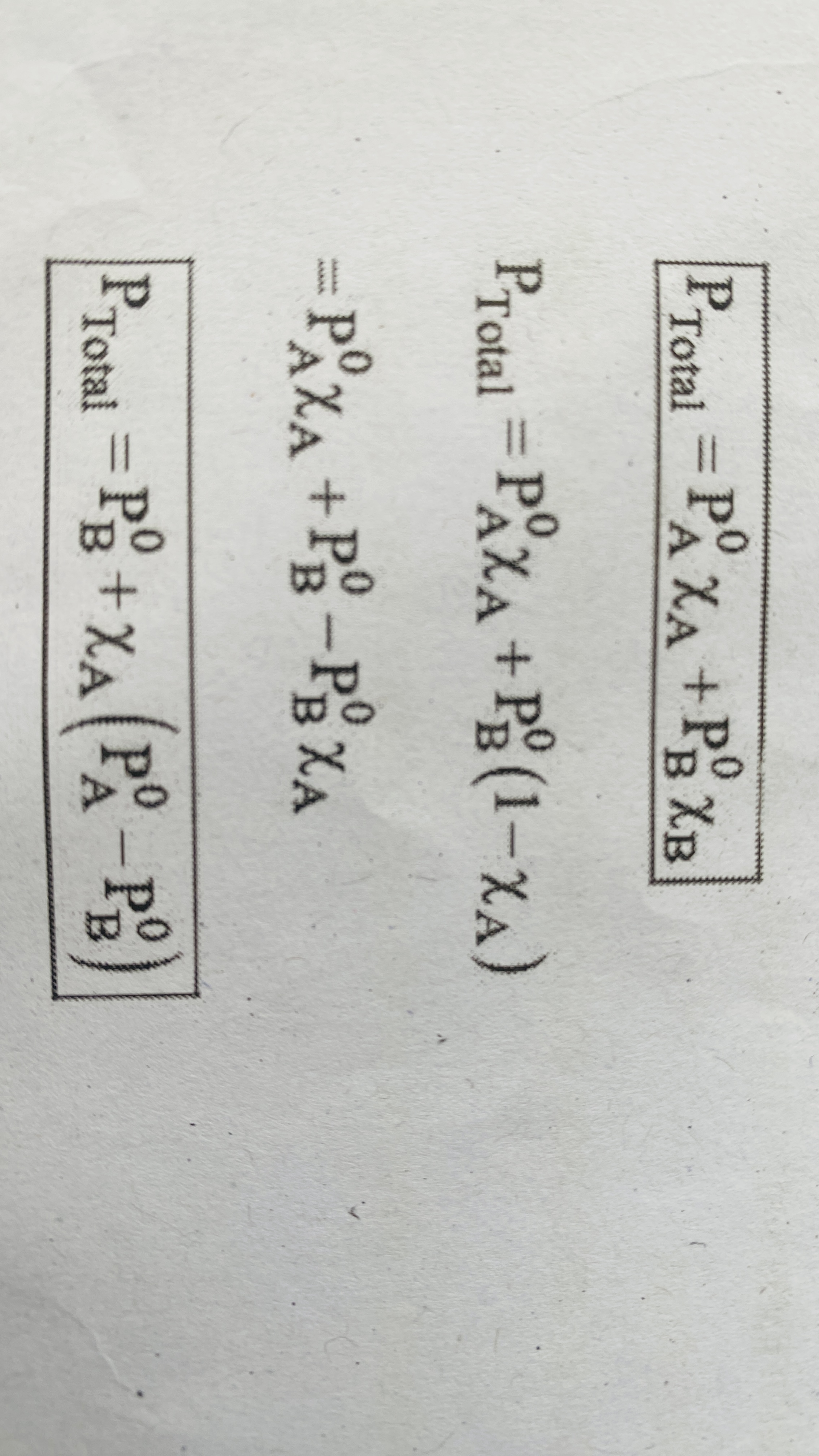
Raoults law for volatile solvent and non volatile solute

Ideal solution
Binary liquid solutions of volatile components which obey raoults law over the entire range of concentration
For an ideal solution the solvent solute interaction (A-B) is
Nearly Same as AA and BB interaction
For an ideal solution heat and volume mix change is
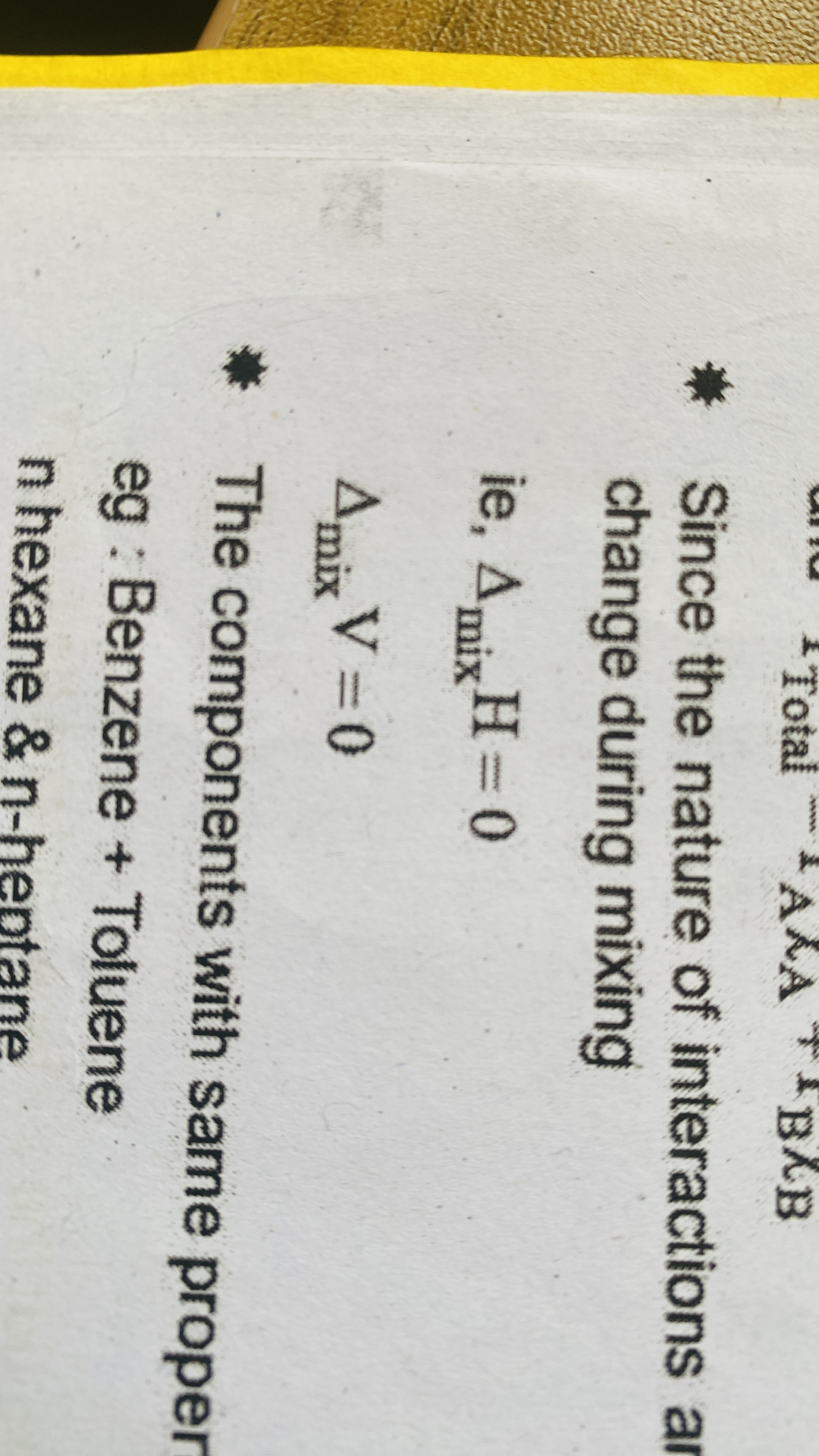
Examples of ideal solutions
Benzene + ______
N hexane +_______
Ethylbromide +________
Chloro benzene +________
Toluene
N heptane
Ethyl iodide
Bromobenzene
Mole fraction in vapour phase of an ideal solution
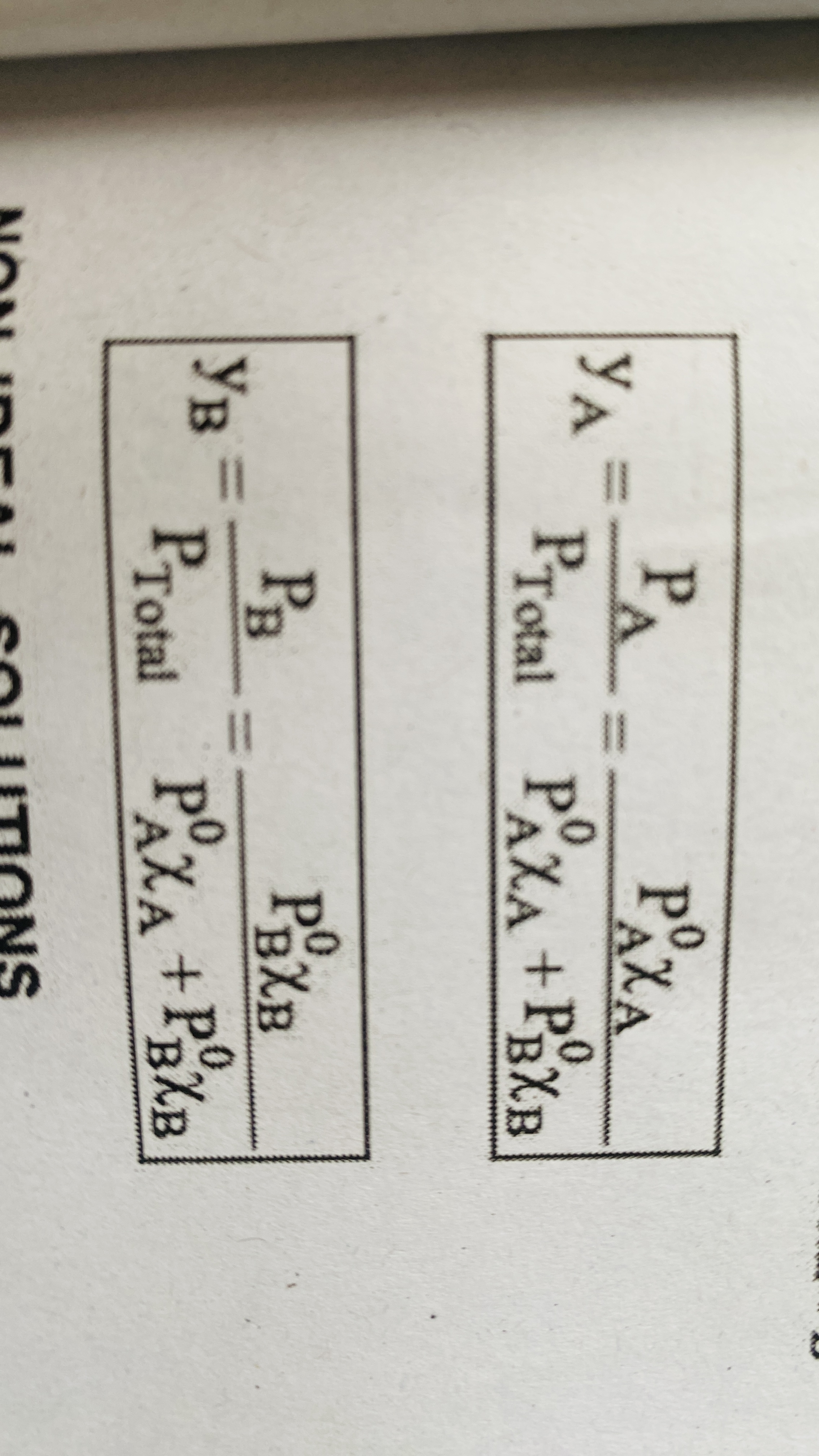
Solutions which show positive deviation of from raoults law
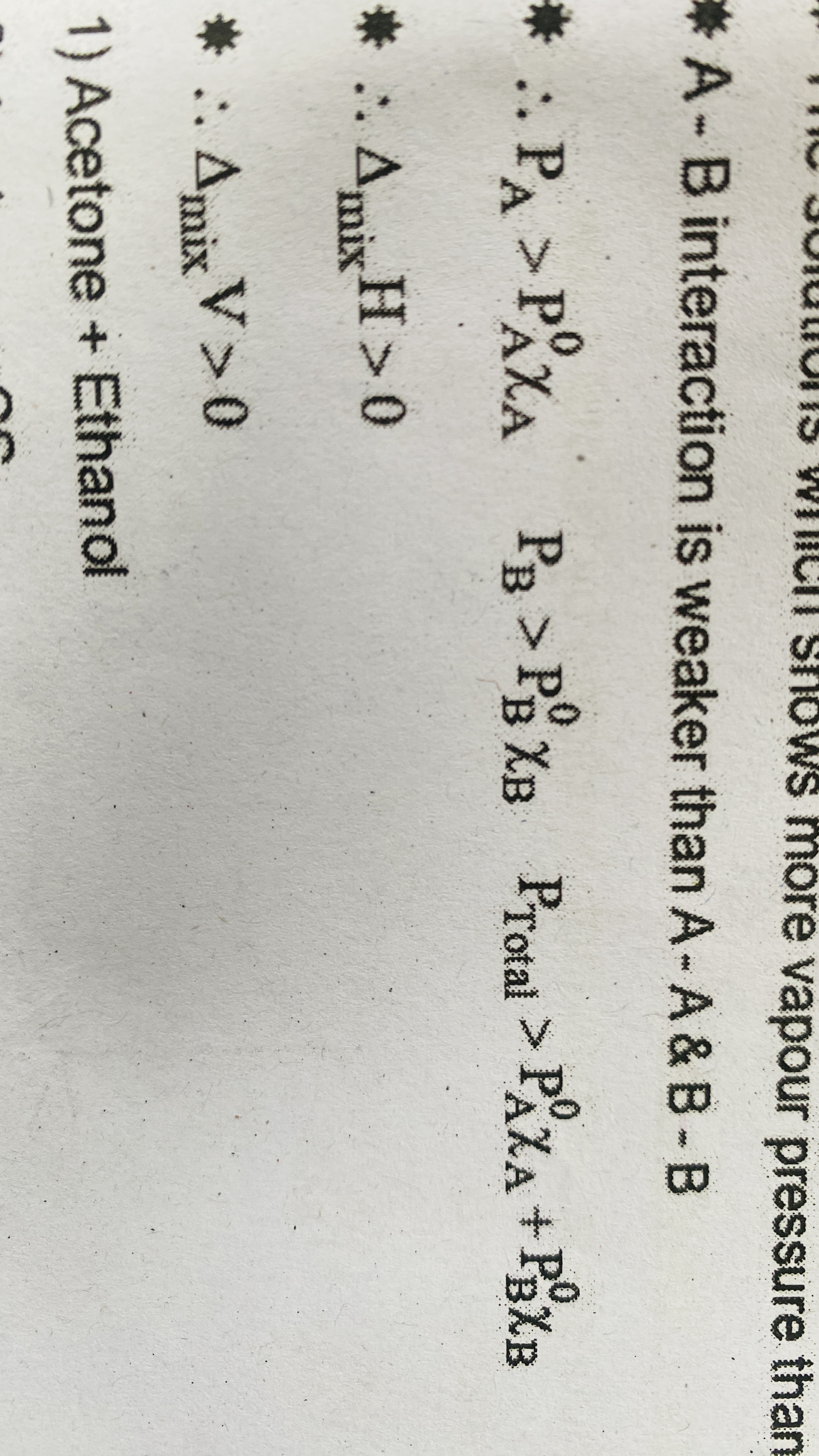
Examples of solitons with positive deviations
(12)
Acetone + ethanol
Acetone + cs2
Acetone + ccl4
Acetone + benzene
Cyclohexane + ethanol
Cyclohexane + benzene
Methanol + h2O
Ethanol + h2O
Propanol + h2O
Ccl4 + toluene
Ccl4 + chloroform
Ccl4 + Methanol
Solutions that show negative deviation form raoults law

Azeotropes
Binary mixture that have same composition. In liquid and vapour phase and boil at a constant temperature
Minimum boiling azeotrope
Show large positive deviation from raoults law. In this car booking point of azeotrope is less than that of components
Example of min boiling azeotrope

Maximum boiling azeotrope
Solutions which show large negative deviation n from raoults law. Boiling point of azeotropes in greater that that of its components
Example of max boiling azeotrope

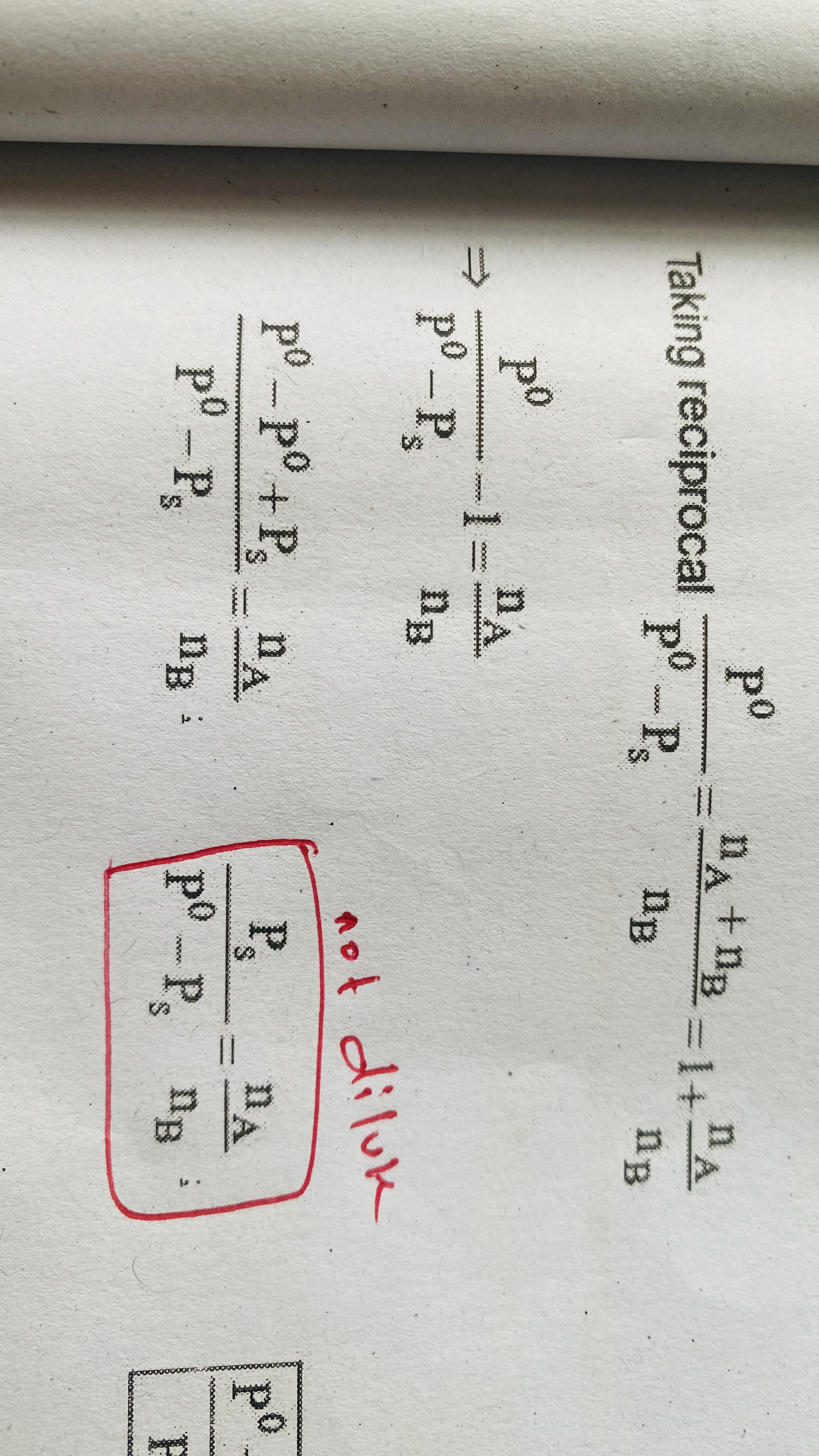
Relative lowering of vapour pressure for dilute solutions
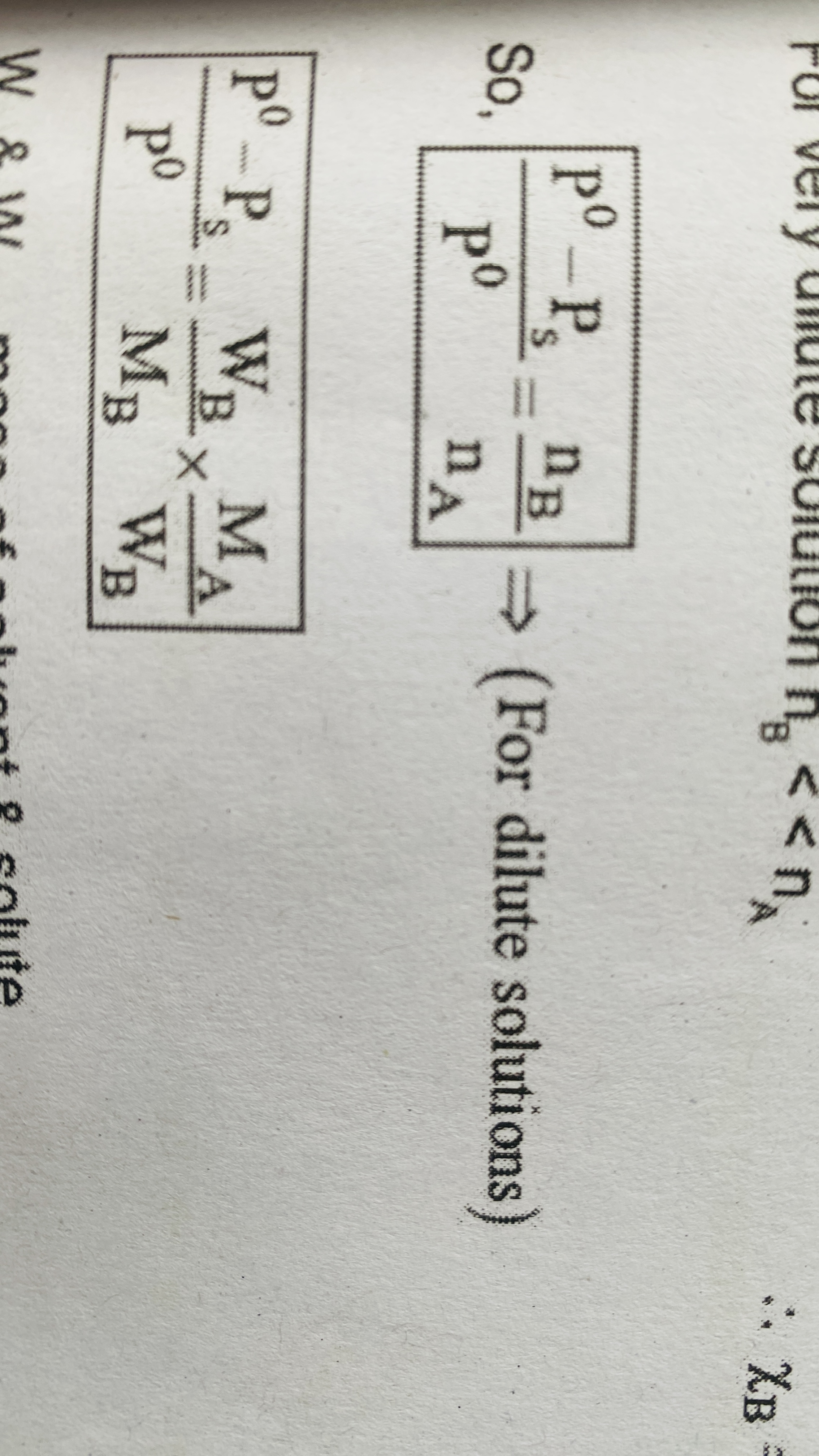
Relative lowering of vapour pressure for not dilute solution
Elevation of boiling point
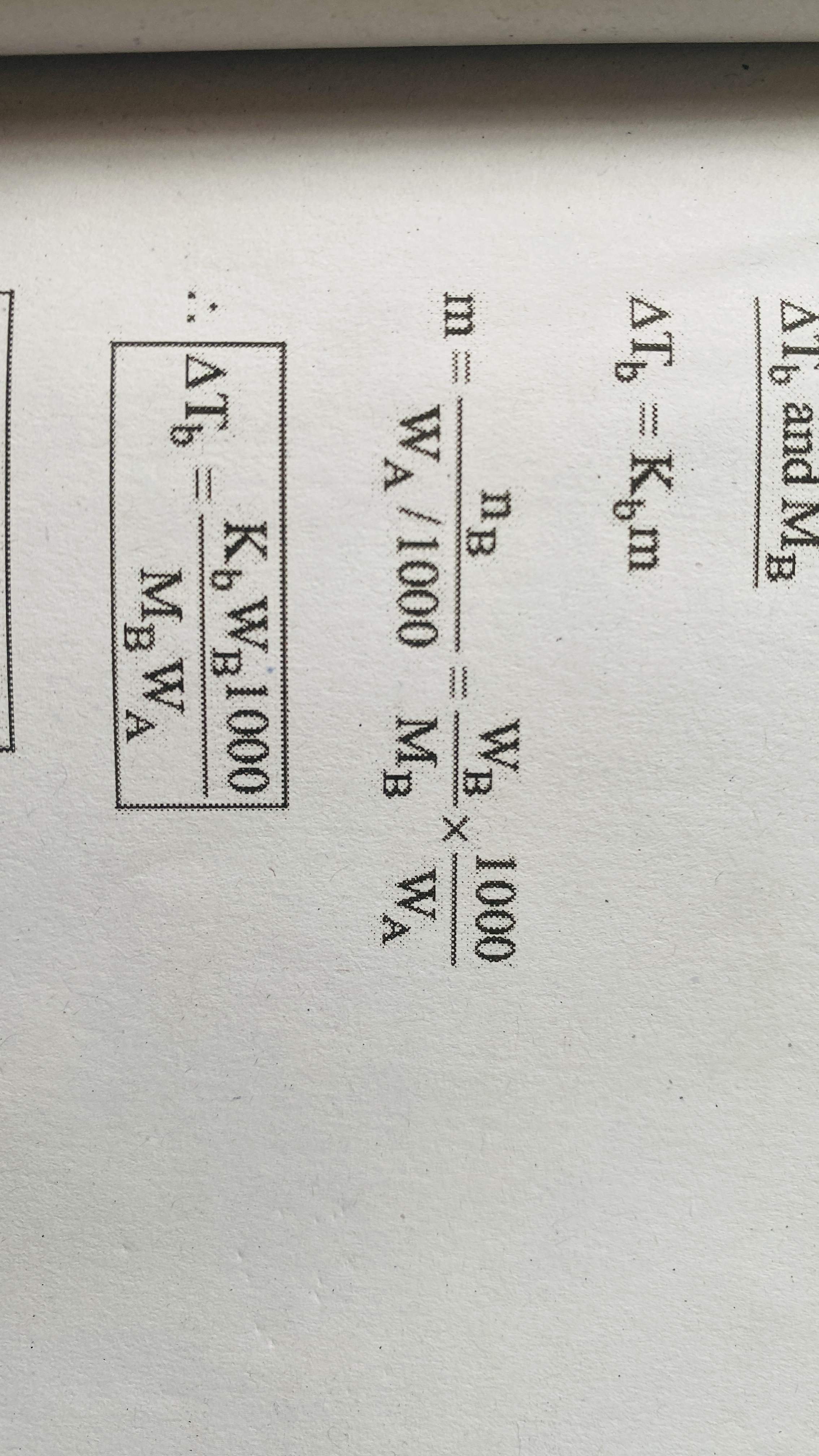
Relation between molal elevation constant and enthalpy of vapourisation

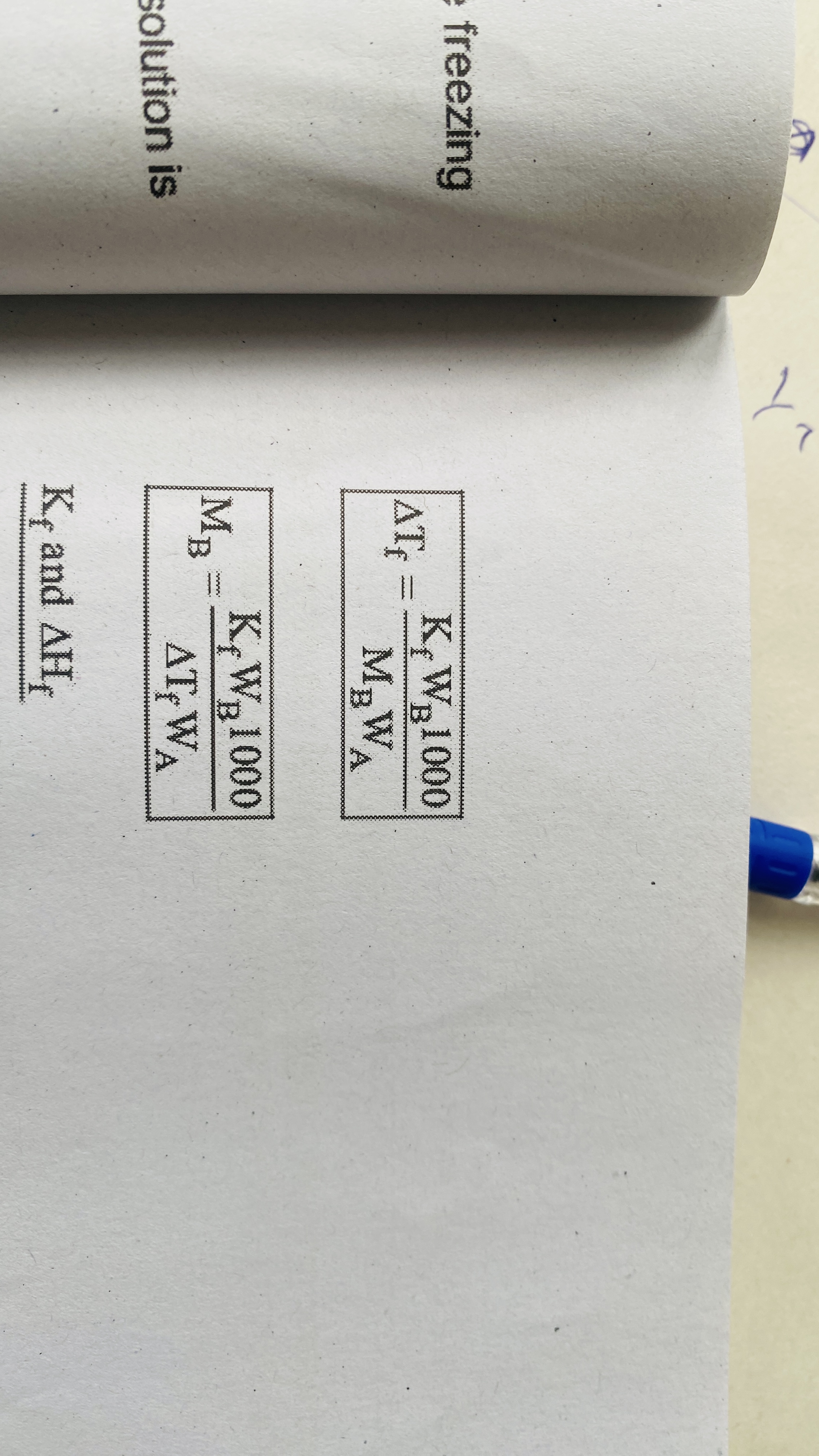
Depression of freezing point
Principle of pressure cooker
Elevation of boiling point
Applications of depression of freezing point
Back of anhydrous cacl2 use to clear snow , this is because they depress the freezing point of h2o to such an extent that it cannot freeze to form ice
35% of V/v aquous solution of ethylene glycol (antifreeze) as a coolant in automobile radiators
Osmosis
The spontaneous movement of solvent molecules form lower to higher concentrations (or viceversa) through semi preameable memberane
Osmotic pressure
The excess pressure that must be applied to solution side to stop osmosis
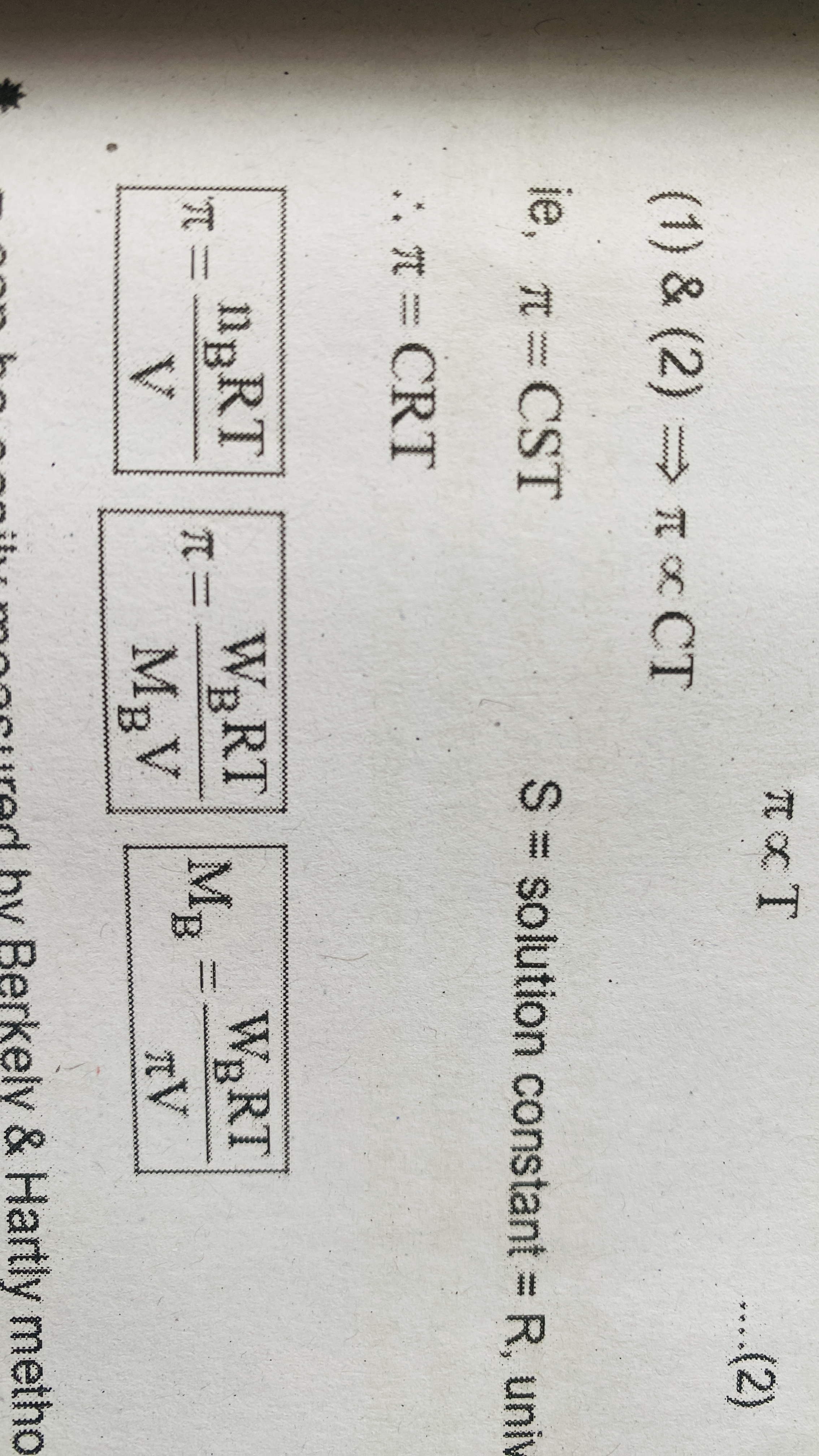
Why use osmotic pressure method
because it is easier to find out the molecular mass of macro molecules and polymers as it is more accurate and can be measure at room temp
Isotonic solutions
Solutions with same osmotic pressure at a particular temperature
Ex - 0.9 % mass / volume back solution and blood
Hypertonic solution
Higher osmotic pressure
Plasmolysis or crenation
Shrinking of plant cells due to exo osmosis when placed in a hypertonic solution
Edema
People taking a lot of slat or salty food experiences water retention in tissues and inter cellular spaces due to osmosis, the resulting puffiness or selling is called edema
Reverse osmosis
When we apply greater pressure that osmotic pressure to the solution side then the solvent molecules migrates from solution to pure solvent through the spm
Used in desalination of sea water
Abnormal molecular mass
Due to dissolution of solute the number of particles and colligative particles increases so the resultant molecular mass will be lower the original
Similarly in association it will be grater that that of actual molecular mass
vant hoff factor
i > 1 dissociation

i = 1
Urea , sugar , glucose , ethanol
Acetic and benzoin acid
Associates in benzene but dissociate in water
Collogative property and i

Degree of association or dissociation
It is the fraction of total number of mole that undergo association or dissociation
Degree of dissociation and i
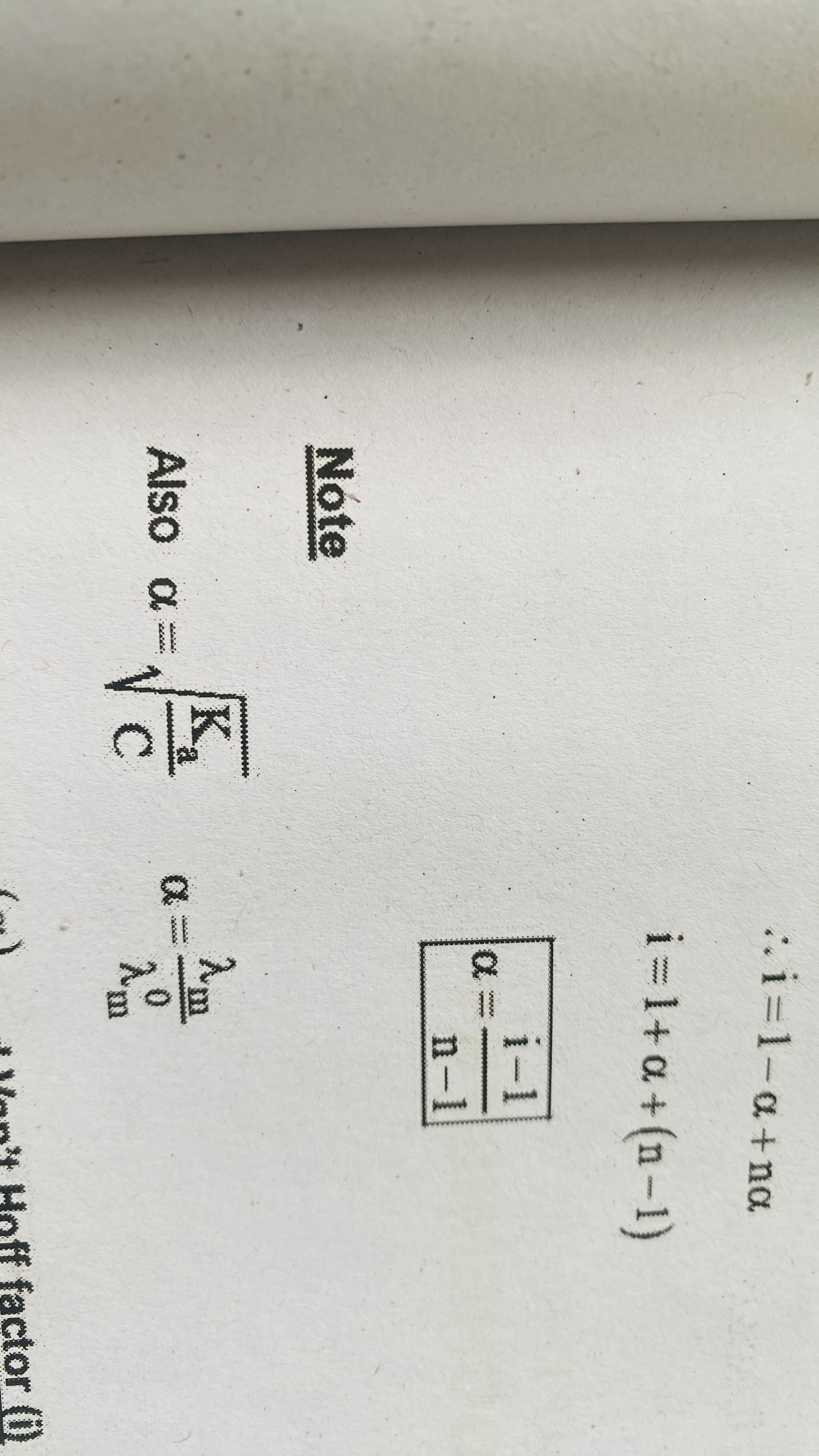
Degree of association and i