Lab diagnosis of proteus
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Specimens
Pus, exudate, urine
Gram staining
Proteus are gram negative coccobacilli occasionally appear bacillary and in filamentous form.
Culture
Fishy odor
Swarming motility
Biochemical tests ( klebsiella to e coli )
Indole : Negative
Citrate: Variable
Urease Positive
TSI: alkaline/acid, gas present and H2S present
MR: Positive
VP: Negative
Proteus mirabilis and P. vulgaris can be differentiated by:
Indole test: Positive (P. vulgaris) , negative (P. mirabilis)
Ornithine decarboxylase test: Positive (P. mirabilis), negative (P. vulgaris)
Typing of Proteus
Bacteriocin typing:
It is antibiotic like substance produced by one bacteria that inhibits other strains of bacteria,
Bacteriophage typing:
Based on susceptibility to bacteriophage.
Ribotyping:
It is molecular technique based on ribosomal RNA.
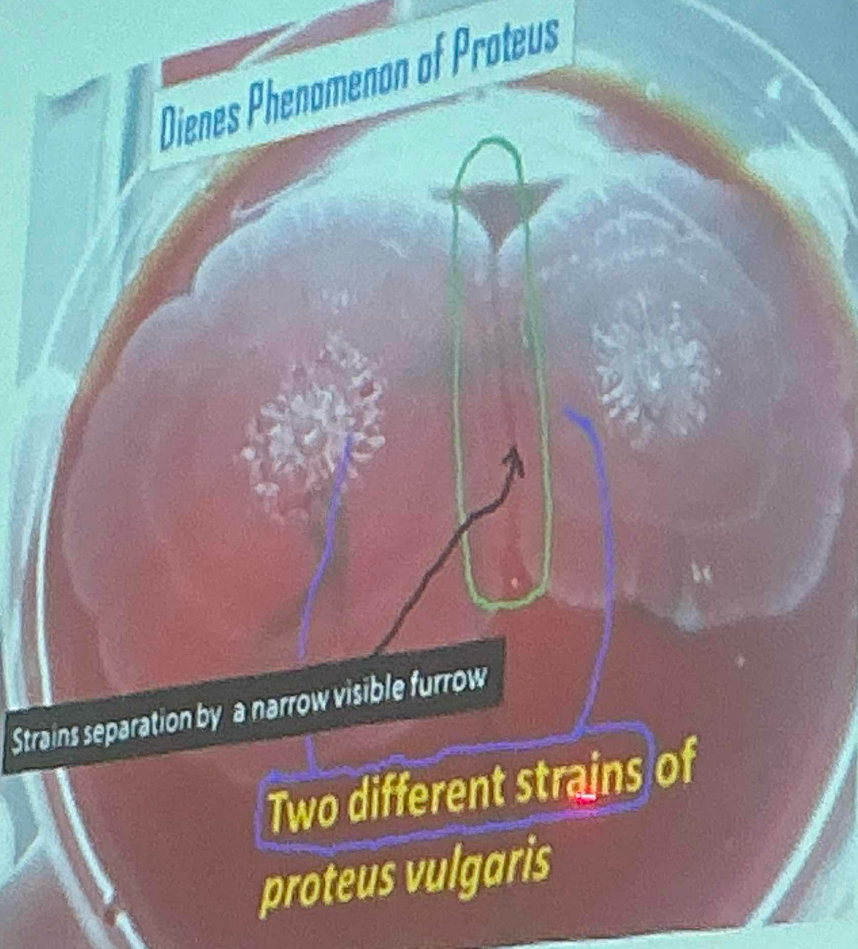
Dienes phenomena
Dienes phenomena
When two strains of Proteus are inoculated at different areas on a culture plate:
›If swarming of two strains merge incompletely, and remain separatby a narrow line of demarcation- indicates two strains are different.
›If swarming of two strains merge completely without any line ofdemarcation-indicates two strains are identical.