Concept 9.5: Fermentation and anaerobic respiration enable cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen
1/7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Aerobic respiration
The most common type of cellular respiration that involves the use of oxygen to pull electrons down the electron transport chain
Anaerobic respiration
Respiration wihtout oxygen that uses an electron transport chain with an electron acceptor other than oxygen
Sulfate ions may serve the role of acceptor in some organisms, making H2S instead
Glycolysis
Process that oxidizes glucose to pyruvate without the involvement of O2 or an electron transport chain
Produces 2 net ATP by substate-level phosphorylation regardless of O2 presence
Most widespread catabolic pathway on Earth that functions in both fermentation and cellular respiration
NAD+
The oxidizing agent that accepts electrons during glycolysis
Regenerated from NADH by transferring electrons to the electron transport chain under aerobic conditions
Anaerobic conditions require fermentation to regenerate this
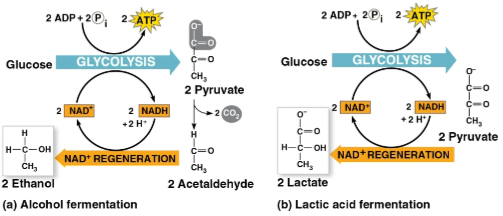
Fermentation
An extension of glycolysis that oxidizes NADH by transferring electrons to pyruvate or its derivatives, includes:
Alcohol fermentation
Lactic acid fermentation
Differs from cellular respiration as electrons are not transferred to the electron transport chain and does not produce nearly as much ATP
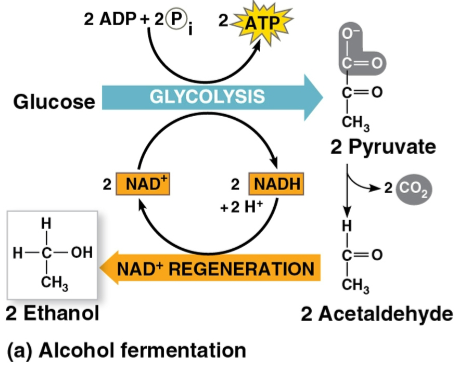
Alcohol fermentation
The conversion of pyruvate to ethanol by:
Releasing CO2 from pyruvate
Producing NAD+ and ethanol
Used in brewing, winemaking, and baking
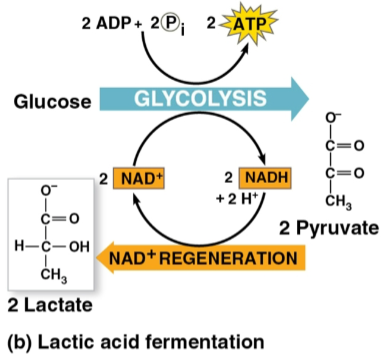
Lactic acid fermentation
The reduction of pyruvate directly by NADH to form lactate and NAD+
Does not release CO2
Used to make cheese and yogurt with fungi and bacteria
Lactate
A substance that was thought to only have been produced by human muscle cells with a lack of oxygen
Actually is produced even under aerobic conditions, thus disqualifying it from being classified as fermentation