Organic Chemistry and Bonding: Key Concepts and Formulas
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Length affects strength, with longer being weaker and shorter equaling stronger bonds.
How does bond length affect strength?
Formal Charge formula
FC = #of valence electrons - [lone pair e- + 1/2bonding e-]
Sigma Bond
a bond formed when two atomic orbitals combine to form a molecular orbital that is symmetrical around the axis connecting the two atomic nuclei
Pi Bond
a bond that is formed when parallel orbitals overlap to share electrons.
Polar Bond
a covalent bond in which electrons are shared unequally
Degree of unsaturation formula
(2C+2+N-H-X)/2
structual isomers
differ in covalent arrangements of atoms and possible location of single and double bonds
Resonance hybrid
average of the resonance forms shown by the individual Lewis structures
delocalization of electrons
Refers to bonding electrons distributed among more than two atoms that are bonded together; occurs in species that exhibit resonance.
Lewis Acid
electron pair acceptor
Lewis Base
electron pair donor
Bronstead Acid
proton donor
Bronstead Base
proton acceptor
Acid strength in terms of equilibrium
If equilibrium lies far to the right, the acid is strong (dissociates almost completely).
If equilibrium lies to the left, the acid is weak (only partially dissociates).
Acid strength versus base strength
Strong acid ⇔ weak conjugate base
Weak acid ⇔ strong conjugate base
pKaH
pKa of the conjugate acid
Factors that influence acid strength
Electronegativity (Across a Period),Size of Atom (Down a Group),Resonance Stabilization,Inductive (Polar) Effect,Charge Effects,Hybridization of the Atom Bearing H
Electronegativity (Across a Period)
As electronegativity ↑ → conjugate base (A⁻) is more stable → acid strength ↑.
Size of Atom (Down a Group)
Larger atoms can spread out negative charge better → stronger acids.
Resonance Stabilization
Conjugate base stabilized by resonance → stronger acid.
Inductive (Polar) Effect
Atoms or groups that are electron-withdrawing (like -Cl, -NO₂, -CF₃, halogens in general) pull electron density through σ bonds toward themselves.
This "pull" stabilizes the negative charge on the conjugate base (A⁻).
A more stable conjugate base = a stronger acid.
Hybridization of the Atom Bearing H
More s-character = more electronegative = stronger acid.
Charge Effects
Positively charged species are more acidic (they want to lose H⁺).
Alkane
a hydrocarbon containing only single covalent bonds
General Formula For alkane
CnH2n+2
isopropyl
1-methylethyl
isobutyl
2-methylpropyl
secbutyl
1-methylpropyl
tertbutyl
1,1-dimethylethyl
Boiling point of alkanes
typically increases as the length of the carbon chain increases
melting point of alkanes
melting point increases as molecular weight increases
Newman projection
A method of visualizing a compound in which the line of sight is down a carbon-carbon bond axis.
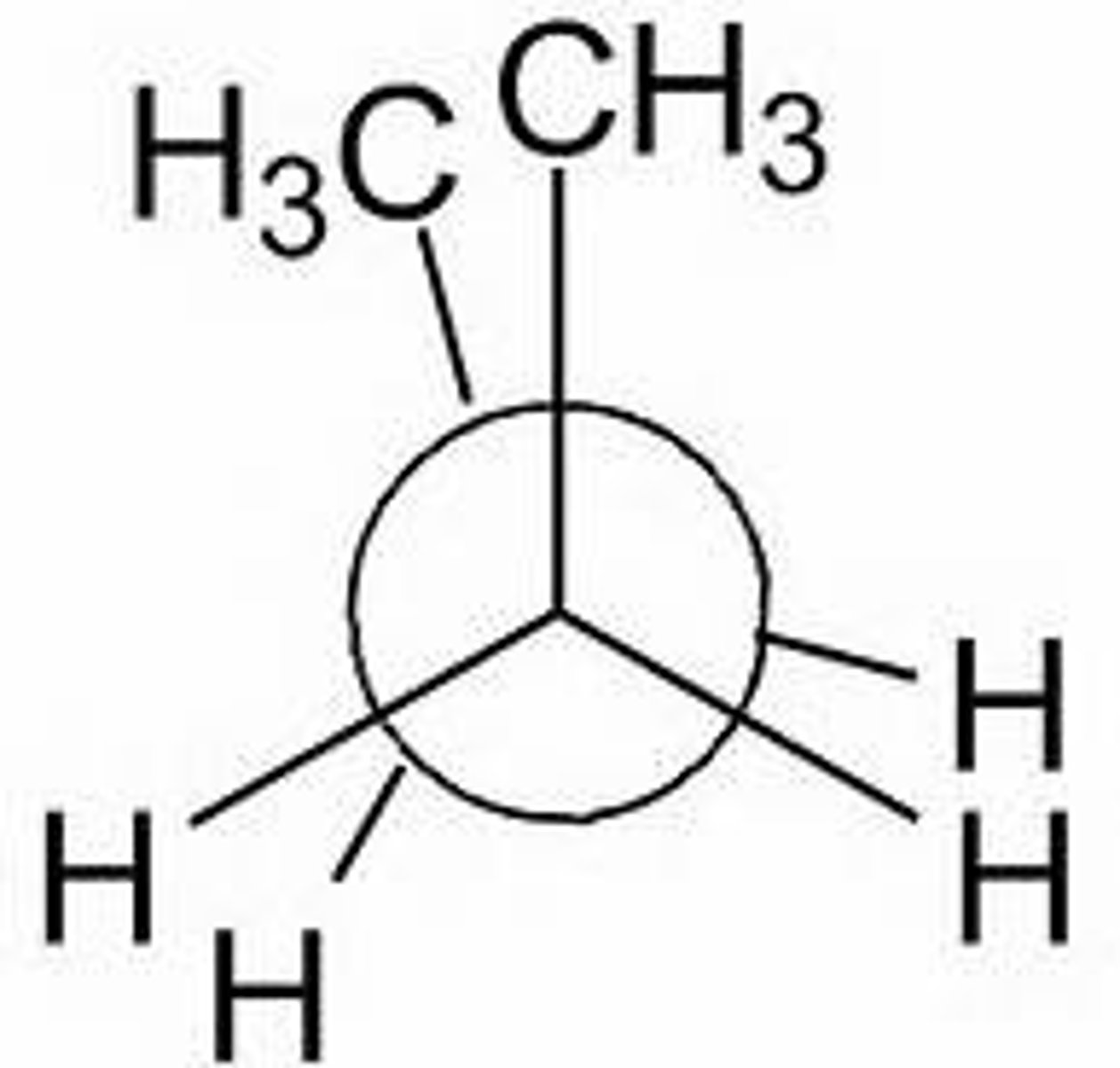
dihedral angle
the angle between two specified groups in a Newman projection
eclipsed newman projection
-unfavorable
-steric hindrance
-less stable
-higher energy
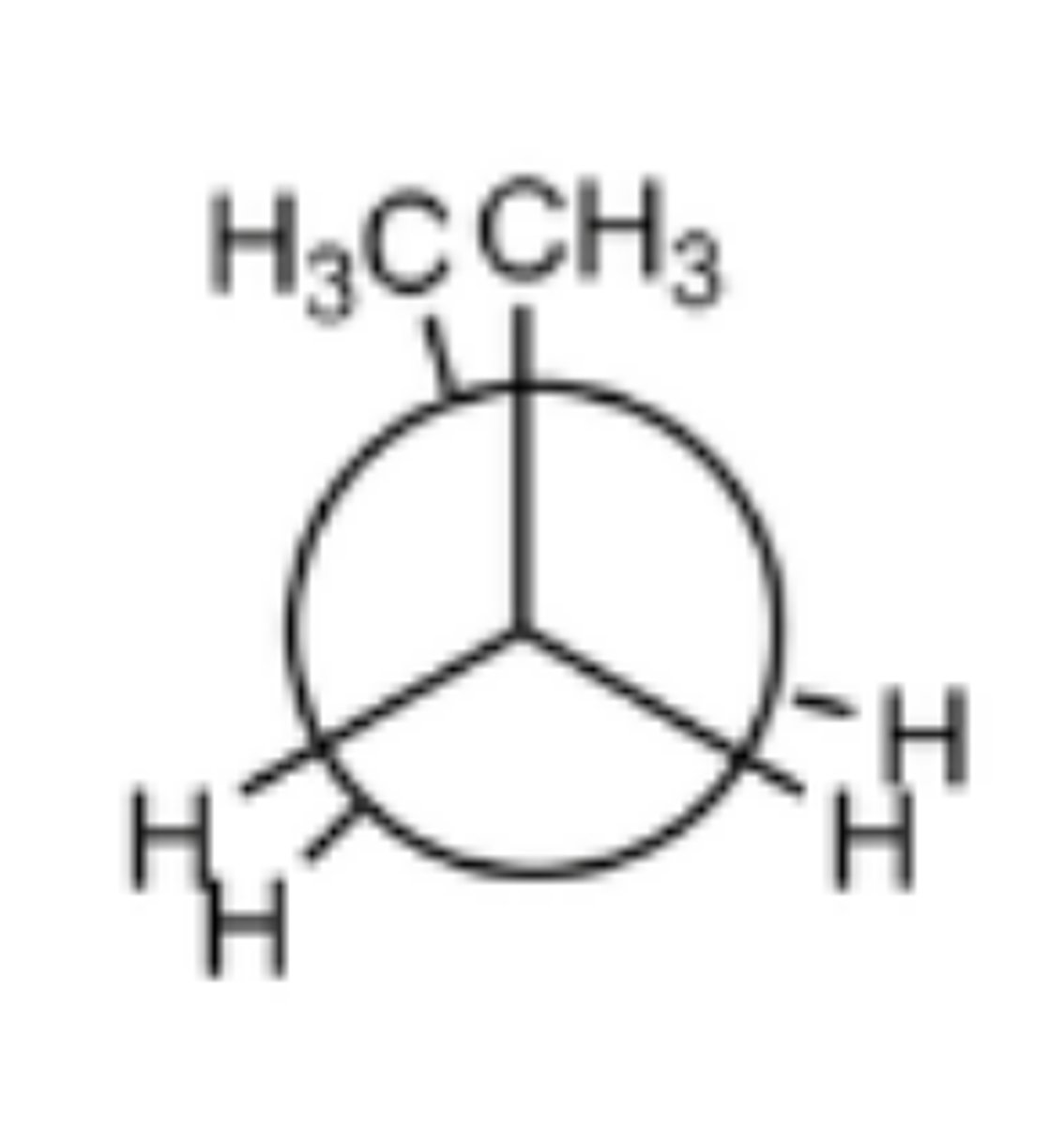
guache staggered
two largest groups are 60 degrees apart
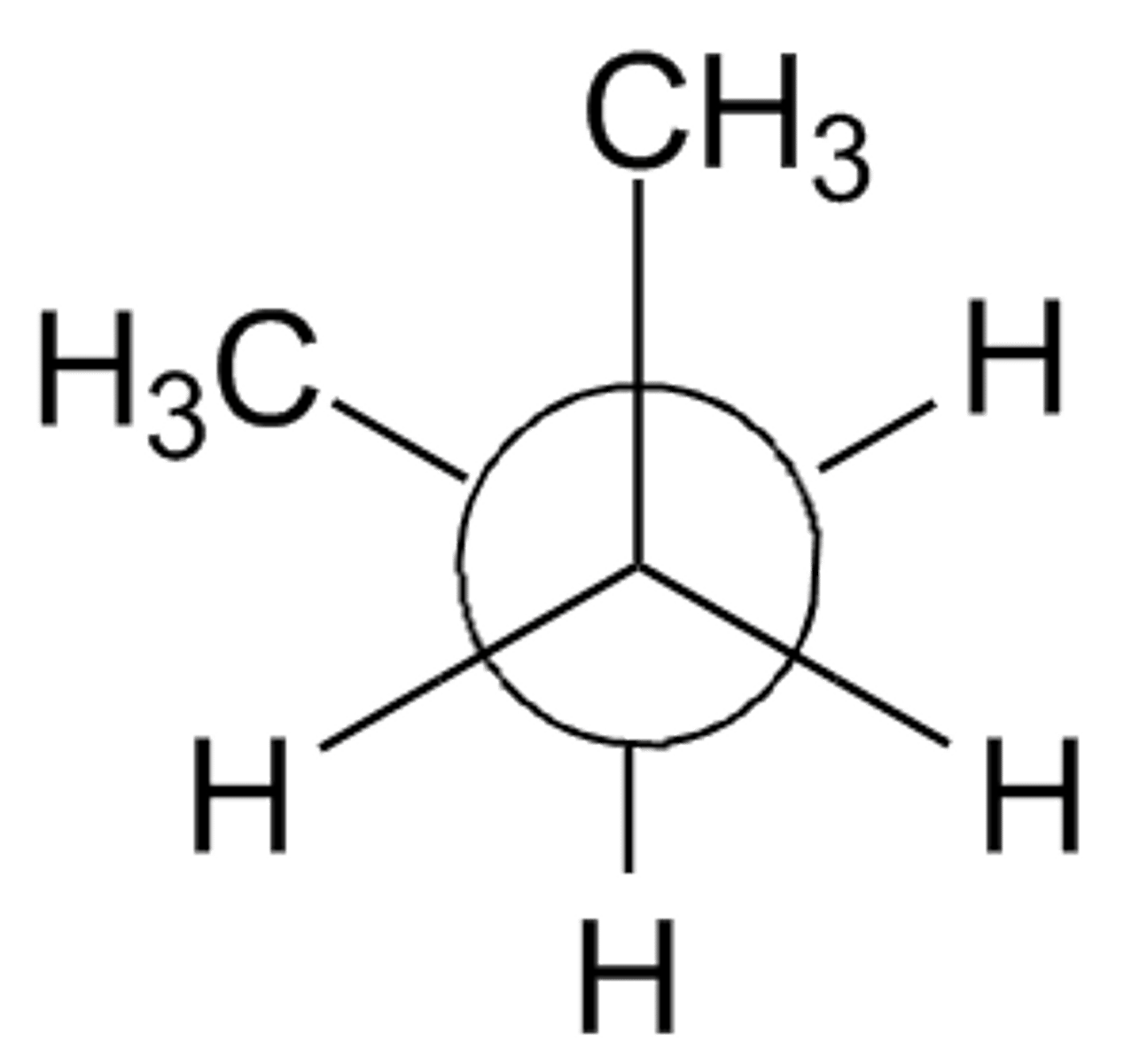
anti staggered conformation
the two largest groups are 180° apart, and strain is minimized
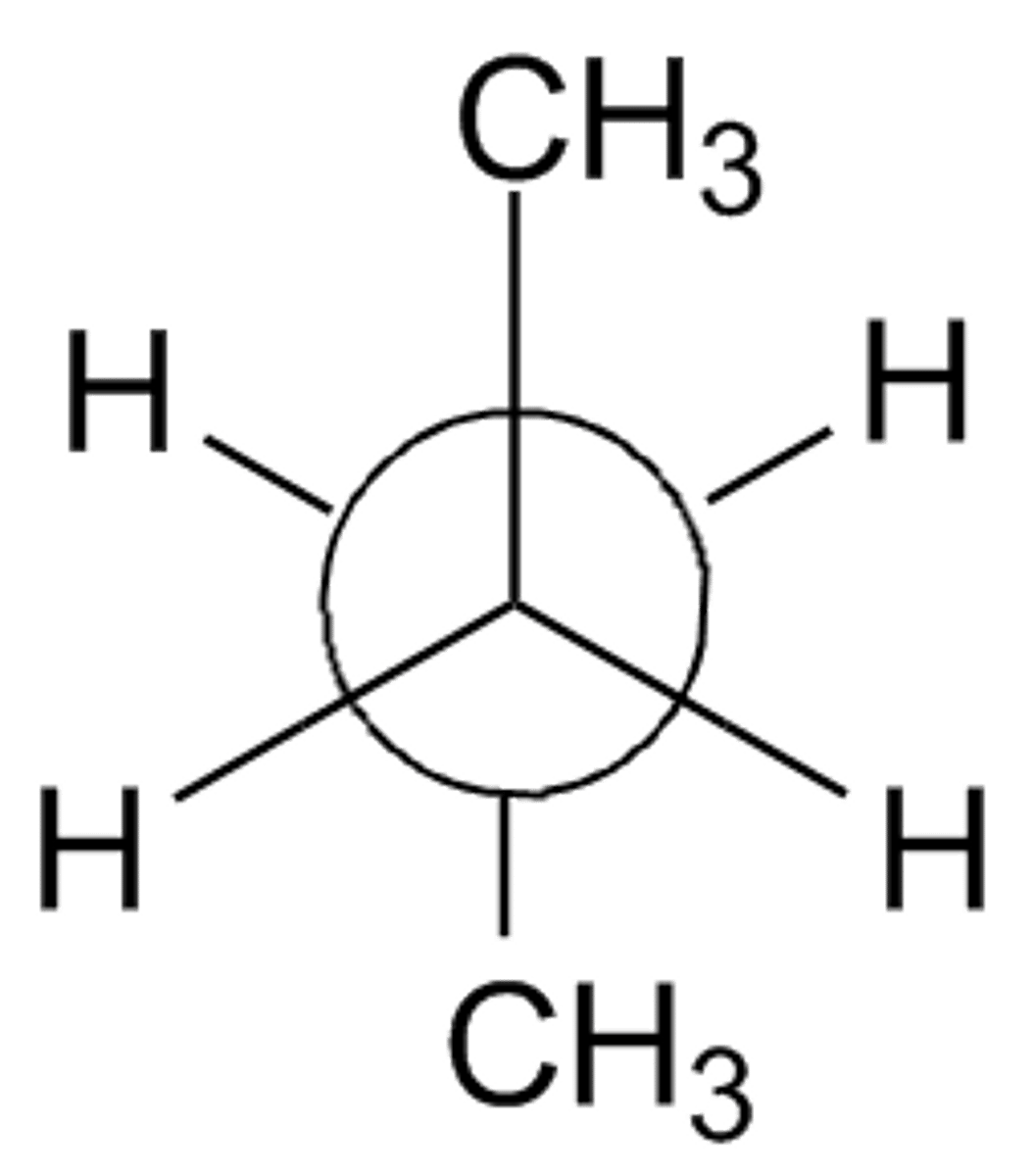
torsional strain
Caused by eclipsed bonds (bonding electron clouds repelling each other).
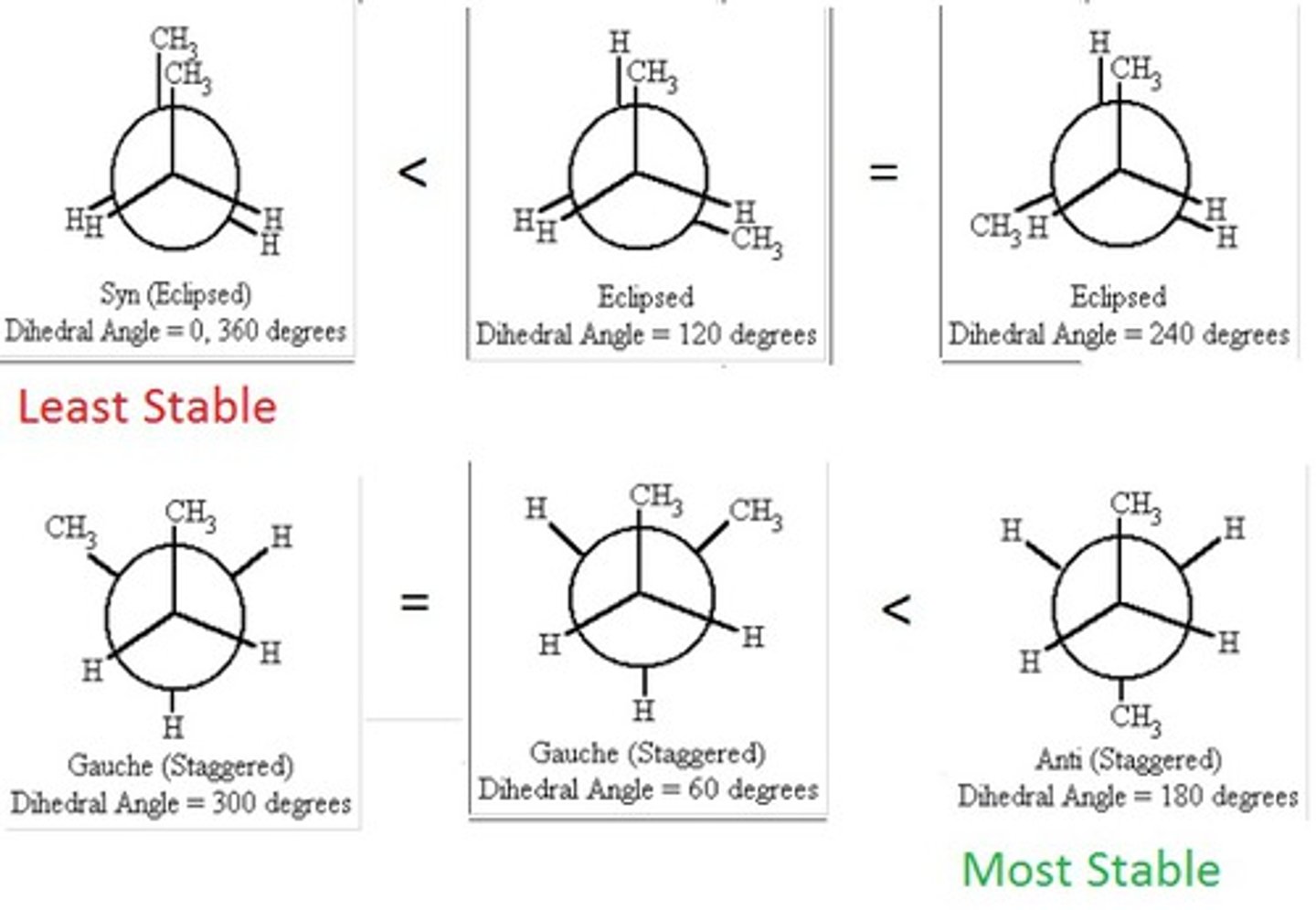
Steric Strain (a.k.a. Van der Waals repulsion)
Caused when bulky groups get too close, even if staggered.(CH₃ groups 180° apart) is lowest energy, gauche is higher, eclipsed highest.
Angle Strain
Occurs when bond angles deviate from the ideal tetrahedral 109.5°.