Ancient Greece: Notable Scientists and Mathematicians (and their Notable Works, Concepts, Contributions, and Biographical Information)
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
626 BCE - 545 BCE - Thales of Miletus (All Facts)
Greek philosopher and scientist, considered the first Greek philosopher and Western philosopher of all time
Allegedly predicted the eclipse of the sun 25 years prior to its having occurred
Taught geometry to his disciples, having drawn straight lines, points, triangles, and circles while discussing problems of measurement and relationship involving these diagrams
Does not see a practical use for geometry, but rather a theoretical base of knowledge that will help in the understanding of the universe
He rejected the mythological explanation for the creation of the world, saying it was born of a single material substance, water
610 BCE - 546 BCE - Anaximander of Miletus (All Facts)
Greek philosopher and scientist
Famous for having drawn the first map of the world, engraved on a tablet of stone
He saw the world as rounded, like a pillar, with the inhabited part on one side
An unusual feature of his world is that it is represented as being viewed from on high, as though by a bird or a god
Suggested that the earthly cylinder lies at the center of a celestial sphere in a position of perfect equilibrium
Theorized that humans were developed from animals, because animals can look after themselves very soon, while humans need to be nursed for a long period of time
Pupil of Thales
570 BCE - 495 BCE - Pythagoras of Samos (All Facts)
Greek mathematician in the Greek settlements of Southern Italy
Central to his beliefs was the idea that numbers can explain the working of the universe
Developed his namesake theorem: that the square of the hypotenuse of a right-angled triangle is equal to the sum of the squares on the other two sides
Discovered that musical harmonies can be expressed mathematically
Was vegetarian and opposed to the killing of any living creature
He and his followers carried out physical exercises like yoga
550 BCE - 476 BCE - Hectatetus of Miletus (All Facts)
Geographer
Improved the map of Anaximander, which he saw as a disc encircled by Oceanus
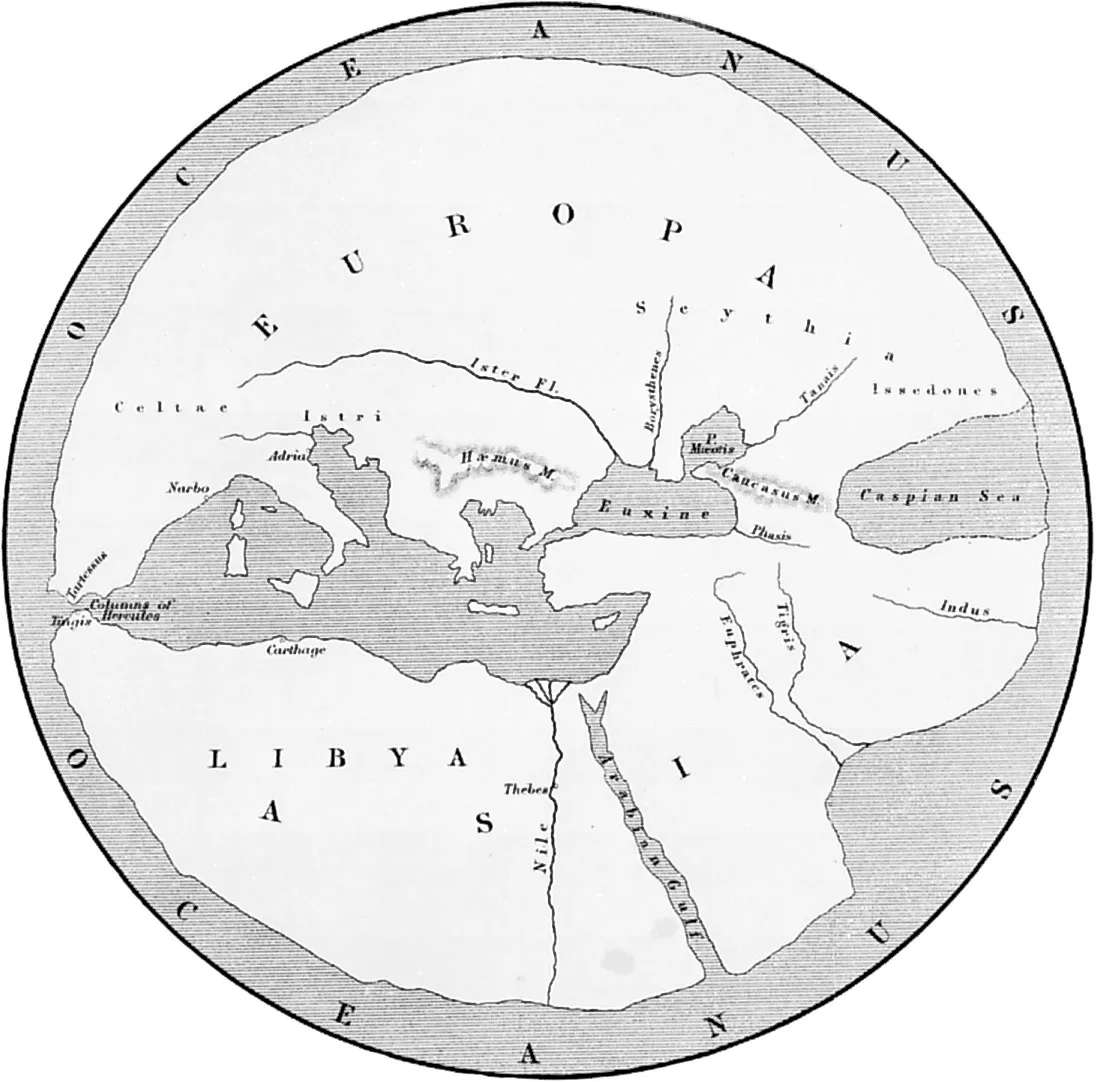
550 BCE - 476 BCE - Hecataeus: Periodos Ges / Journey Around the World (All Facts)
Work in which the author catalogues the names of people and places, mainly around Mediterranean regions and observes the local flora and fauna as well as the differences in religious traditions

460 BCE - 370 BCE - Hippocrates of Kos (All Facts)
Greek physician
Considered the “Father of Medicine”
Established medicine as a discipline in its own right set apart from philosophy and theurgy
His contributions to the field of medicine include his
use of prognosis and clinical observation
the systematic categorization of diseases
humoral theory (now false)
Developed his namesake code of medical ethics, which ended up being used by doctors throughout Greece
Insisted that disease has natural causes and is not to be explained by divine intervention
Transformed the approach to illness in the city-states of Greece
Travelled widely in mainland Greece, having taught medical students to
Study their patients carefully
Record their symptoms dispassionately
Treat their patients sympathetically
460 BCE - 370 BCE - Hippocrates of Kos: Hippocratic Oath (All Facts)
Code of medical ethics which states the following:
“I will use my power to help the sick, according to my ability and judgement, and not for their injury or any evil purpose… Whatever I see or hear in my attendance on the sick, which ought not to be divulged publicly, I will keep secret and tell nobody…”
460 BCE - 370 BCE - Hippocrates of Kos: On the Sacred Disease (All Facts)
Rejects the belief that epilepsy was caused by the gods
The author states that calling diseases sacred is a cover for ignorance
390 BCE - 340 BCE - Eudoxus of Cnidus (All Facts)
Ancient Greek astronomer, geographer, mathematician, doctor, and lawmaker
Student of Plato
Assessed the length of a year as 365 and a quarter days long
Developed a theory of concentric spheres which furthered the Greek understanding of the planetary movements
384 BCE - 322 BCE - Aristotle (All Facts)
Greek philosopher and scientist
Considered the “Father of (Western) Biology”
Taught a new approach to science for his time, in which he believed an investigation of the forms which nature takes was proper science
384 BCE - 322 BCE - Aristotle: Historia Animalium (All Facts)
Work which contains a detailed record of the behavior and habits of animals
Considered the first work of the West in the field of biology
371 BCE - 287 BCE - Theophrastus (All Facts)
Succeeded Aristotle as head of Aristotle’s school the “Lyceum”
Emphasized the scientific orientation of research
Did much work on plants and minerals
Wrote a series of caricatures of stock types called “Characters”
Hepatology / Hepatologists (All Facts)
Study of the meaning found in the livers of sacrificed animals, with fresh offal or clay models being used
Astrology / Astrologers (All Facts)
(now defunct) Study of the skies and the heavenly bodies that move there and the interpretation of such activities
The name literally means “the account of the stars”
Their vocation involved studying the appearance and disappearance of the stars and planets, and whether this happens before or after sunset
Ephemerides (All Facts)
Term used to refer to the astrological tables developed by the Greeks in Mesopotamia during the Hellenistic Period
Term that literally means “diary” or “calendar”
They plotted the way in which celestial bodies seemed to move in fixed orbits
They helped astrologers to base their opinions on the position of each star at any given moment of its course
Each planet had its own importance
For example, Jupiter regulated the life of the king
300’s BCE - 200’s BCE - Euclid (All Facts)
Considered the “Father of Geometry”
Set out his principles of geometry in his work called “Elements” around 290 BCE
287 BCE - 212 BCE - Archimedes (All Facts)
Greek Polymath of Syracuse
Mathematician who used his expertise to construct formidable war machines to resist the Roman onslaught during the Siege of Syracuse
Died in battle during the Siege of Syracuse
276 BCE - 198 BCE - Eratosthenes of Cyrene (All Facts)
Greek polymath; he was a mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theorist
Famous for having figured out the measurement for the circumference of the Earth
He recorded the angle of a shadow cast by a stick at Alexandria on the day of the summer solstice, when there was no shadow at Aswan, about 500 miles to the south
Then he divided the figure, 7.5 degrees, into 360
190 BCE - 120 BCE - Hipparchus of Nicaea (All Facts)
Greek astronomer, geographer, and mathematician
Considered the founder of trigonometry
Most famous for his incidental discovery of the precession of the equinoxes
Some consider him the greatest Greek astronomer of antiquity
64 BCE - 24 CE - Strabo (All Facts)
Greek Geographer
Born in Amaseia, in northern Anatolia
64 BCE - 24 CE - Strabo: Geography (All Facts)
Work which consisted of a general survey of Hellenistic geography and cartography, it examines the controversies between Eratosthenes (the first Greek geographer) and his successors
Work which includes regional descriptions that covered physical geography, ethnographic features, and myth
Its wide range made it an effective census of the world at the time
0’s CE - Hero of Alexandria (All Facts)
Greek Scientist, Engineer, Mathematician, and Inventor
Discovered forms of steam propulsion and systems of hydraulics
Devised an ingenious apparatus called an “aeolipile”
This was a steam source linked to a rotating sphere with two nozzles as outlets and had a boiler that generates steam that emanates from the outlets giving power to turn a wheel
Developed a device which consisted of a sophisticated system of lifting weights by the use of water pressure, a system which saved countless man-hours
Discovered his namesake formula for finding the area of triangles
His knowledge of astronomy enabled him to compute the distance from Alexandria to Rome through sightings of a lunar eclipse
0’s CE - Hero of Alexandria: Metrica (All Facts)
Work which includes a method for finding the approximate square root of any number
Work which includes the ways of computing the volume of cones, pyramids, cylinders, spheres, and prisms
0’s CE - Hero of Alexandria: Dioptra (All Facts)
Work which makes a considerable contribution to knowledge in the craft of surveying
Work which describes an instrument called a diopter which measures angle’s of elevation, essential to a surveyor’s measurements
Periplus (All Facts)
Work whose author is unknown by name but who was a Greek sea captain living in Eritrea during the Roman Empire around 106 CE
It was a guide to the Red Sea and Indian Ocean, which the author called the Eritrean sea
It provides information on
The Eritrean port of Adulis
The Ethiopian capital of Axum
Somalia (where the people are “very unruly” and “each town is ruled by a separate chief”
Zanzibar (“the last market of the continent”)
The Yemenite port Mocha (“crowded with ship owners and seafaring men)
South Arabia
The Indian Coast
100 CE - 170 CE - Ptolemy (All Facts)
Greek Astronomer and Geographer living in Alexandria in Roman Egypt
Famous for his development of the geocentric model, in which the stars and planets moved in concentric orbits around the Earth
100 CE - 170 CE - Ptolemy: Geographia / Geography (All Facts)
Work in which the author improves on the accuracy of previous maps using a grid system of latitude and longitude which would prove useful to navigators and cartographers
The world, according to the author, stretched from Iceland and the Canary Island in the west to Ceylon in the east, with unknown lands south of North Africa and beyond India
110 - 180 - Pausanias (All Facts)
Greek Geographer and Historian
He was born in Lydia
Famous for his work “Description of Greece”
290 - 350 - Pappus of Alexandria (All Facts)
Greek Mathematician
Known for his work “Mathematical Collection,” which consists of a summary of the knowledge on the titular subject up to that point