OIA1011 KINETIC THEORY OF GASES
1/9
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Assumptions of Kinetic Theory
Gas has molecule of mass (m) and diameter (d) in endless random motion.
Size of gas molecules are negligible.
Molecules do not interact (neither attract nor repulse) except during collisions.
Elastic collision occurs between molecules. Energy may transfer between molecules, but total energy of all molecules remains same.
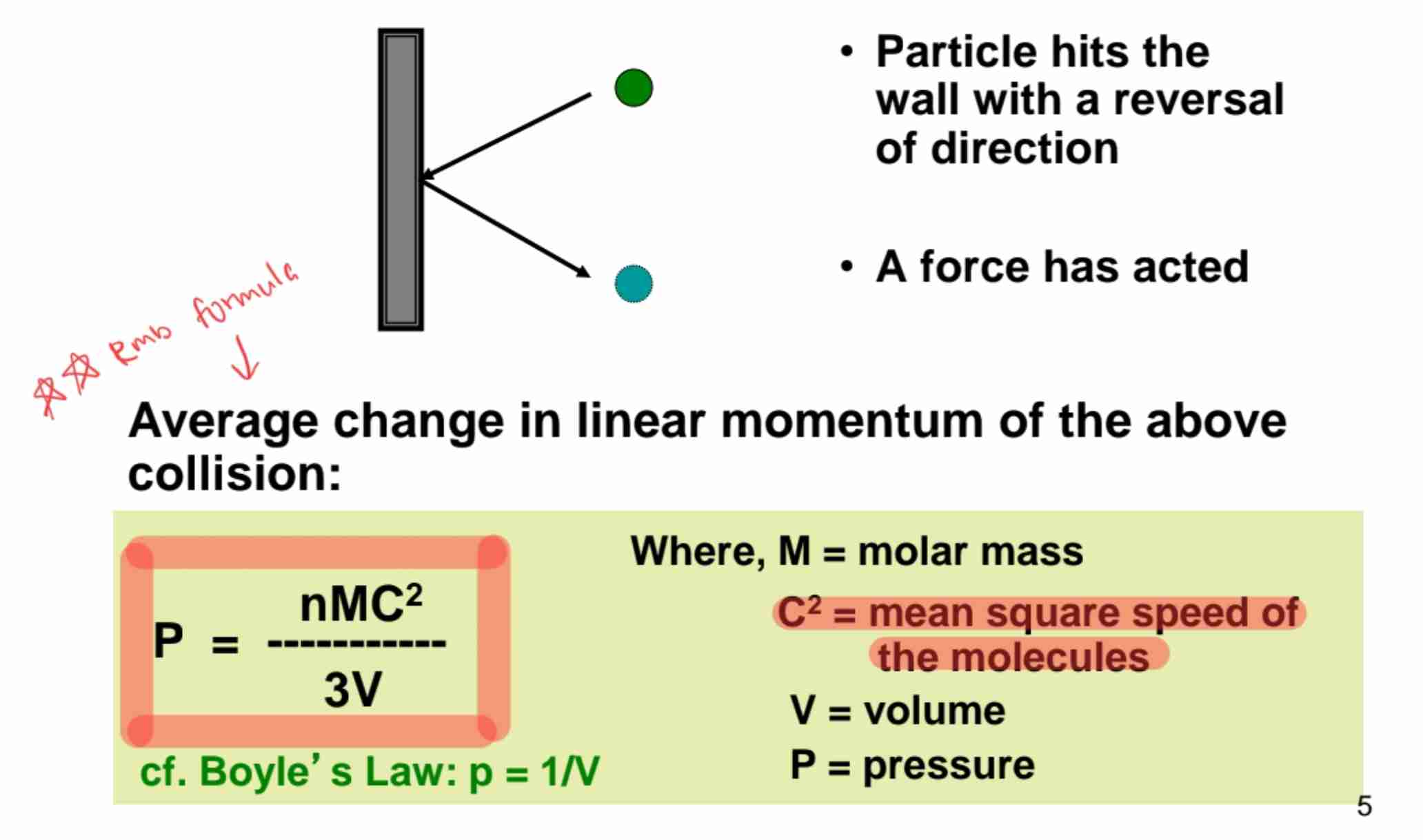
Pressure from Molecular Collisions
Gas pressure arises from collisions with container walls.
Formula for Gas Pressure
The equation links pressure with molecular speed.
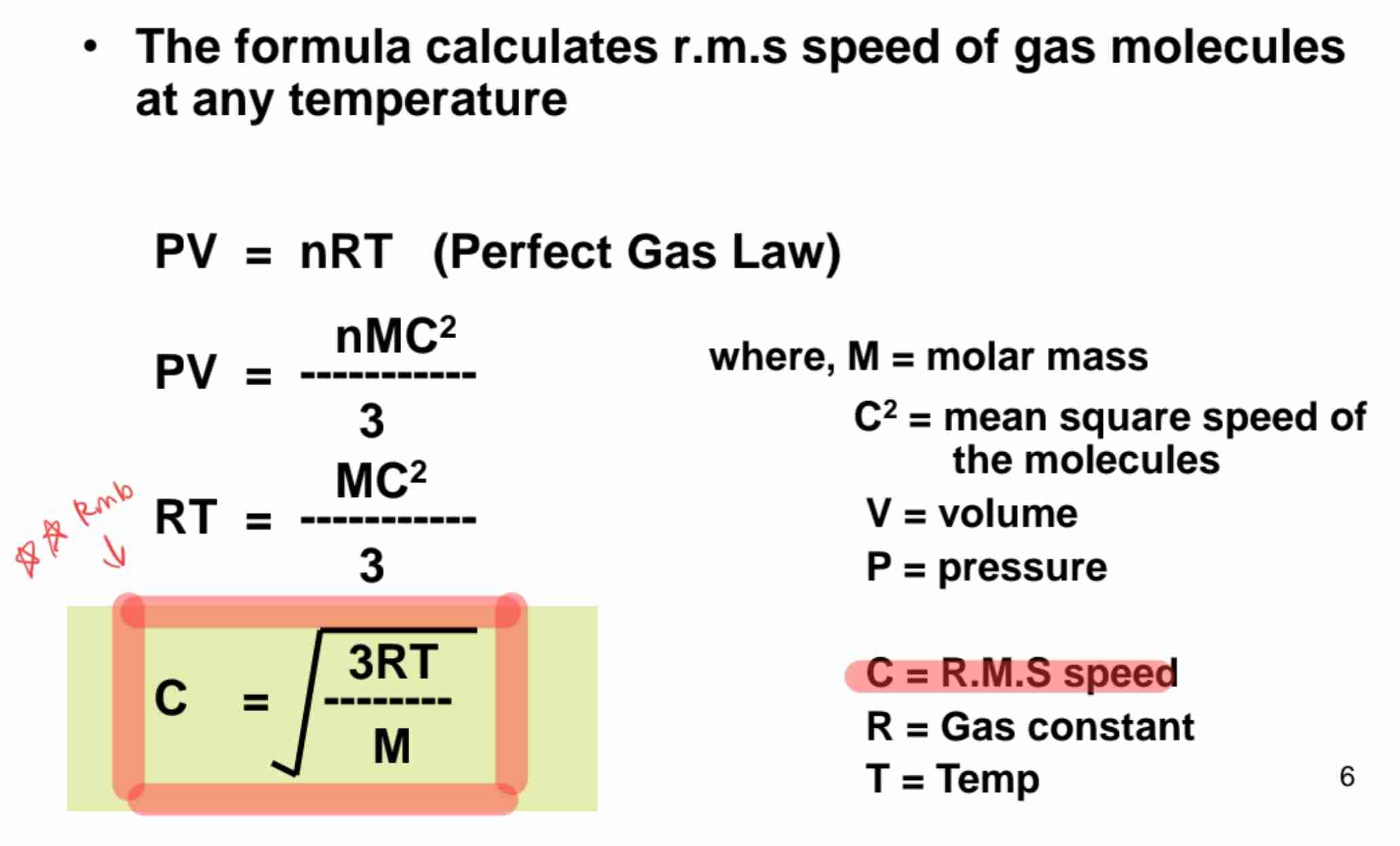
Root Mean Square (RMS) Speed
speed dependent on temperature.
Effect of Temperature on Speed
Doubling T increases RMS speed by sqrt{2}.
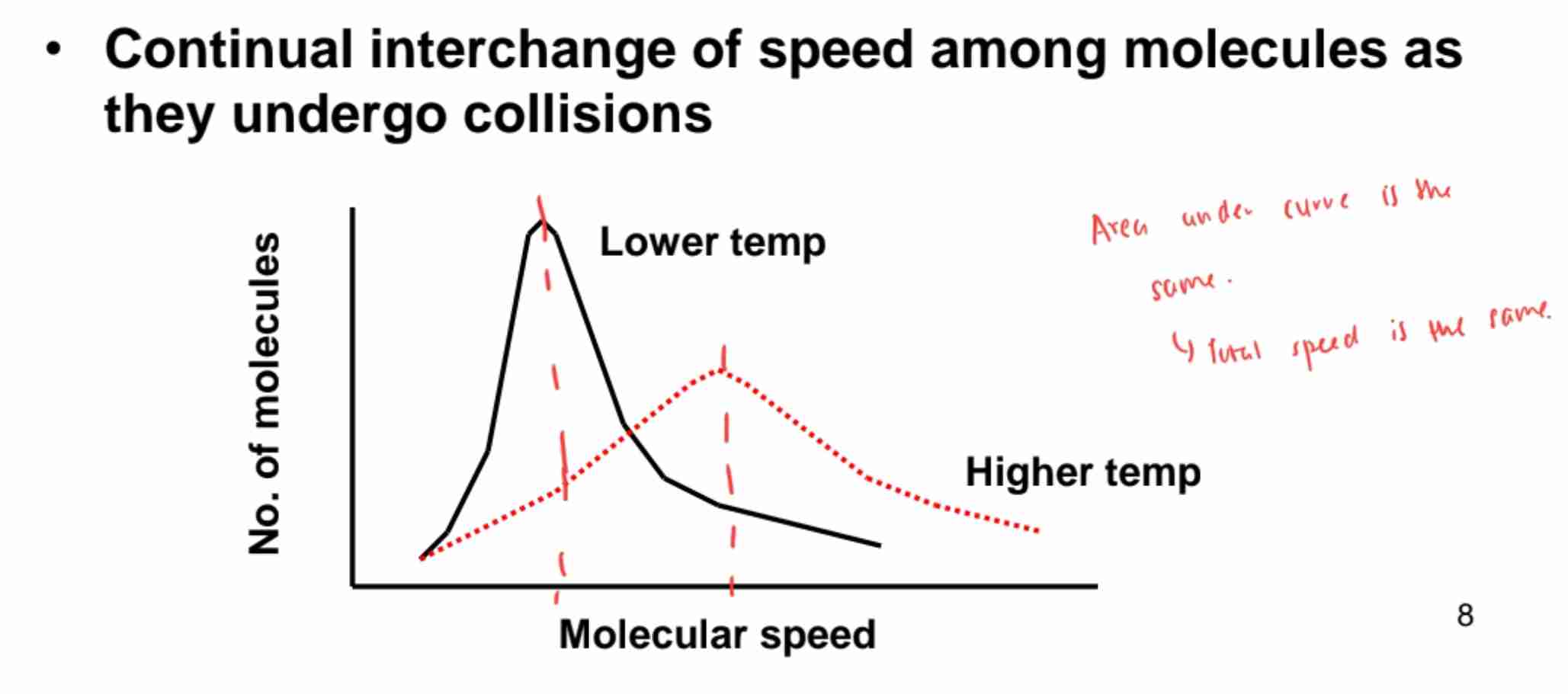
Maxwell Distribution of Speeds
Not all molecules move at the same speed; higher T broadens distribution.
Real Gas Behavior
Intermolecular forces cause deviations from ideality.
Elastic Collisions
Energy transfer occurs during collisions, total system energy conserved.
Examples of Kinetic Theory
Explains phenomena like Brownian motion.
Applications in Pharmaceuticals
Aerosol particle dispersion utilizes principles of gas motion.