Glial Cells
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Astrocytes
Star shape
Maintain blood brain barrier and overall environment for signalling
Rugulate iron, pH, NT (clears glutamate preventing excitotoxicity via ETS)
Regulate synaptogenesis, synaptic plasticity & metabolic stuff
Stained using GFAP
Two types
Protoplasmic astrocytes
Fibrous astrocytes
Protoplasmic Astrocytes
In grey matter
Envelope cell bodies and synapses.
Most common
Have organelles
Are short thick and highly branched.
Fibrous Astrocytes
In white matter
Interact with the node of Ranvier and oligodendrocytes/myelinated axons.
Long, unbranched with few organelles.
Role of Astrocytes in the Blood Brain Barrier
BBB separates blood and CSF
Astrocytes have endfeet that surround blood vessels
This helps regulate nutrient uptake and waste clearance and mediates communication with vasculature.
Secrete paracrine factor to promote BBB and formation of synapse
Astrocytes Promote Synapse Formation
Secrete thrombospondins (TSP1/2 for excitatory synapses) that promote CNS synaptogenesis
TSP are a family of 5 extracellular matrix proteins
TSPs induce the formation of synapses by bind to a voltage gated calcium channel alpha 2 delta 1
Gabapentin (anticonvulsant drug for epilepsy) inhibits excitatory synapse formation by stopping TSP from binding to receptors blocking TSP induced synaptogenesis.
Tripartite Synapses
Presynaptic membrane, post synaptic membrane and glial cell (usually astrocyte)
Active role of astrocytes in regulating synaptic function
Bi-directional communication between astrocytes and neurons.
Astrogliosis
When astrocytes react to insults or inflammation
Astrocytes become thicker and more branched and secrete anti inflammatory molecules (cytokines)
Mild astrogliosis is associated with trauma and when initial trigger is resolved potential for resolution.
Servere astrogliosis is associated with focal lesions, infections and neurodegenerative disorders.
There is astrocyte proliferation and formation of glial scars as a barrier to protect the CNS post injury.
This can prevent recovery and produce permanent scarring preventing recovery.
Microglia
Clear debris and main life of defence when BBB is broken.
IBA1 is a microglia/macrophage specific calcium binding protein to mark microglia.
Small cell bodies with highly mobile cell processes
Derived from bone marrow from hematopoietic stem cells
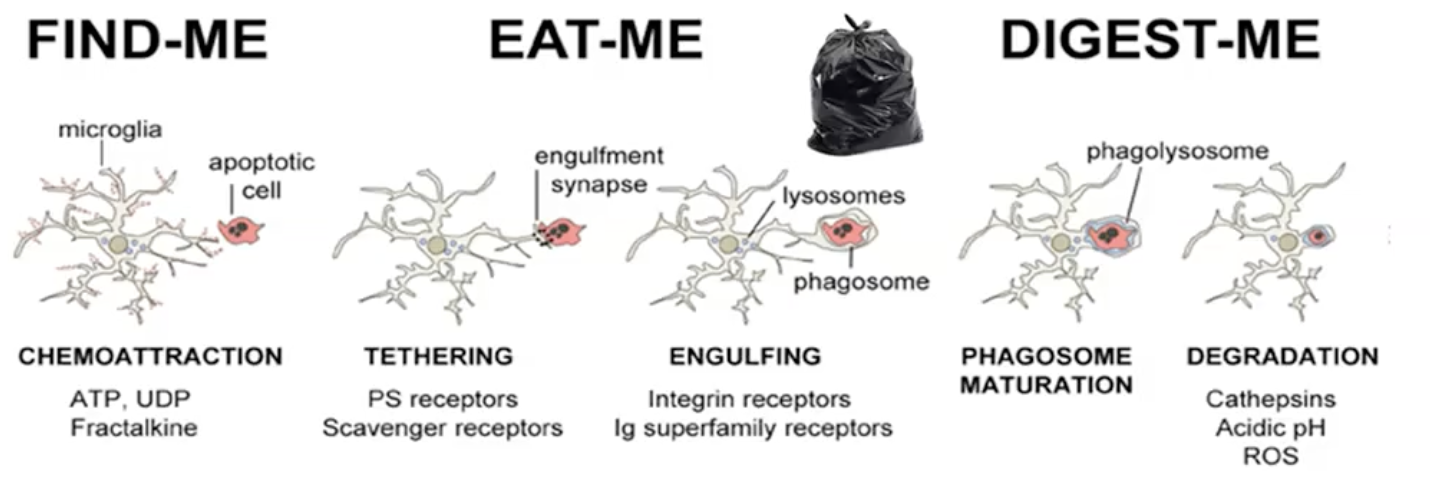
They present antigens and perform phagocytosis
They are mobile and will move towards chemoattractant cues released by dying cells
Material is tethered and engulfed in a phagosome
Phagosome matures and fuses with lysosomes and material is degraded
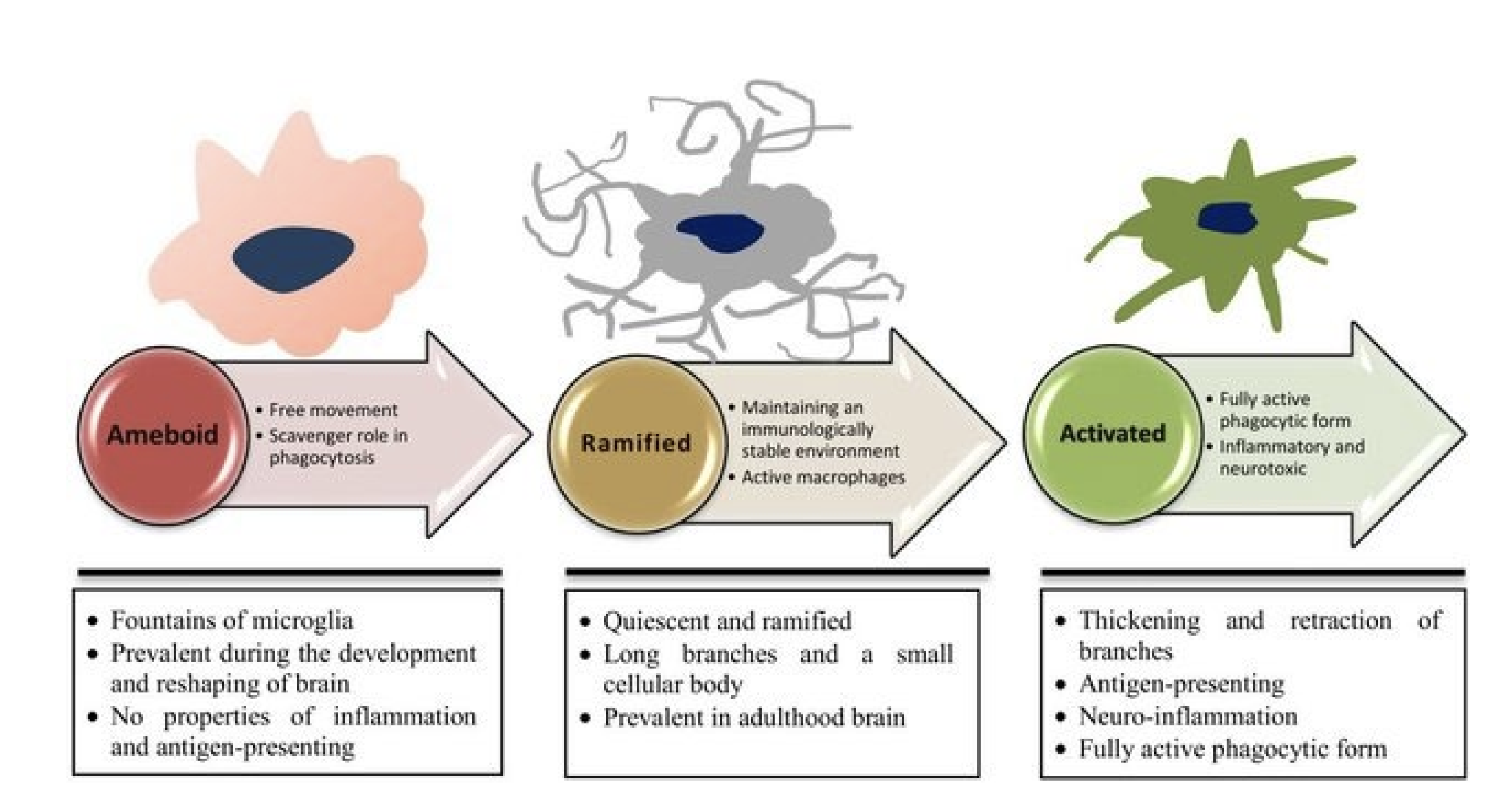
Types of Microglial
Amoeboid Microglia
Rounded
No phagocytosis or immune function
Prevalent during development and reshaping
Ramified (resting) microglia
Highly branched
Multiple processes and small body
No phagocytosis or immune function
Maintain immunologically stable environmentment
Present in adulthood
Activated microglia
Thicker shorter branches
Fully phagocytotic
Secrete pro-inflammatory mediators (Nitric oxide NO and tumour necrosis factor TNF) and neurotoxic
Antigen presenting
Oligodendrocytes
Form myelin in the CNS
Can myelinate many (30) neurons
Schwann Cells
Form myelin in the PNS
Composition of Myelin
CNS | PNS |
|
|
Demyelinating diseases
In the CNS MBP and PLP can act as autoantigens and cause multiple sclerosis
In the PNS PO and PMP22 act as autoantigens (Guillean Barrs syndrome)