Anatomy Lab Quiz 2: Labelling the Cell & Hemolysis
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
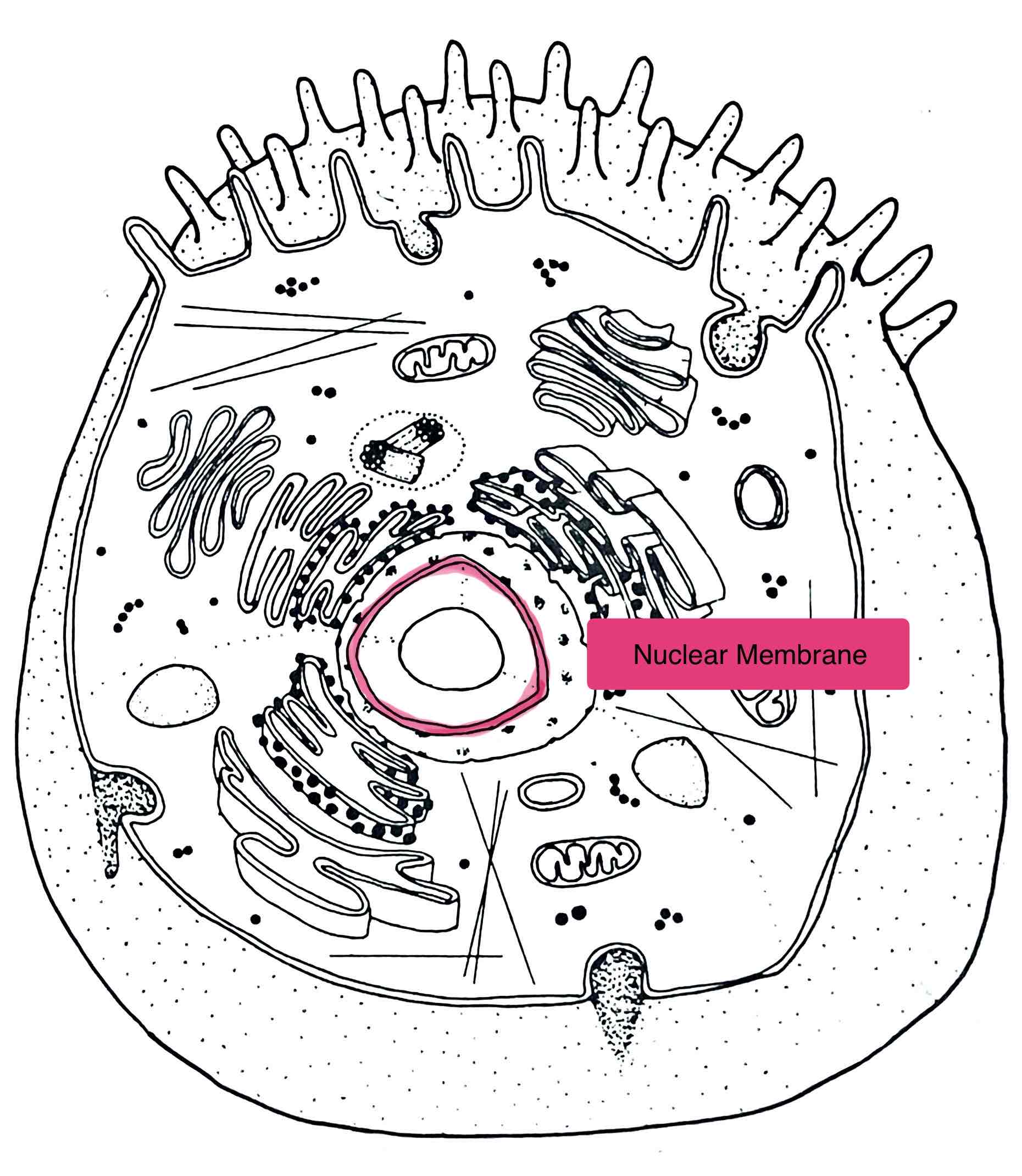
Identify the Nuclear Membrane
– selectively permeable lipid bi-layer which encloses the nucleus
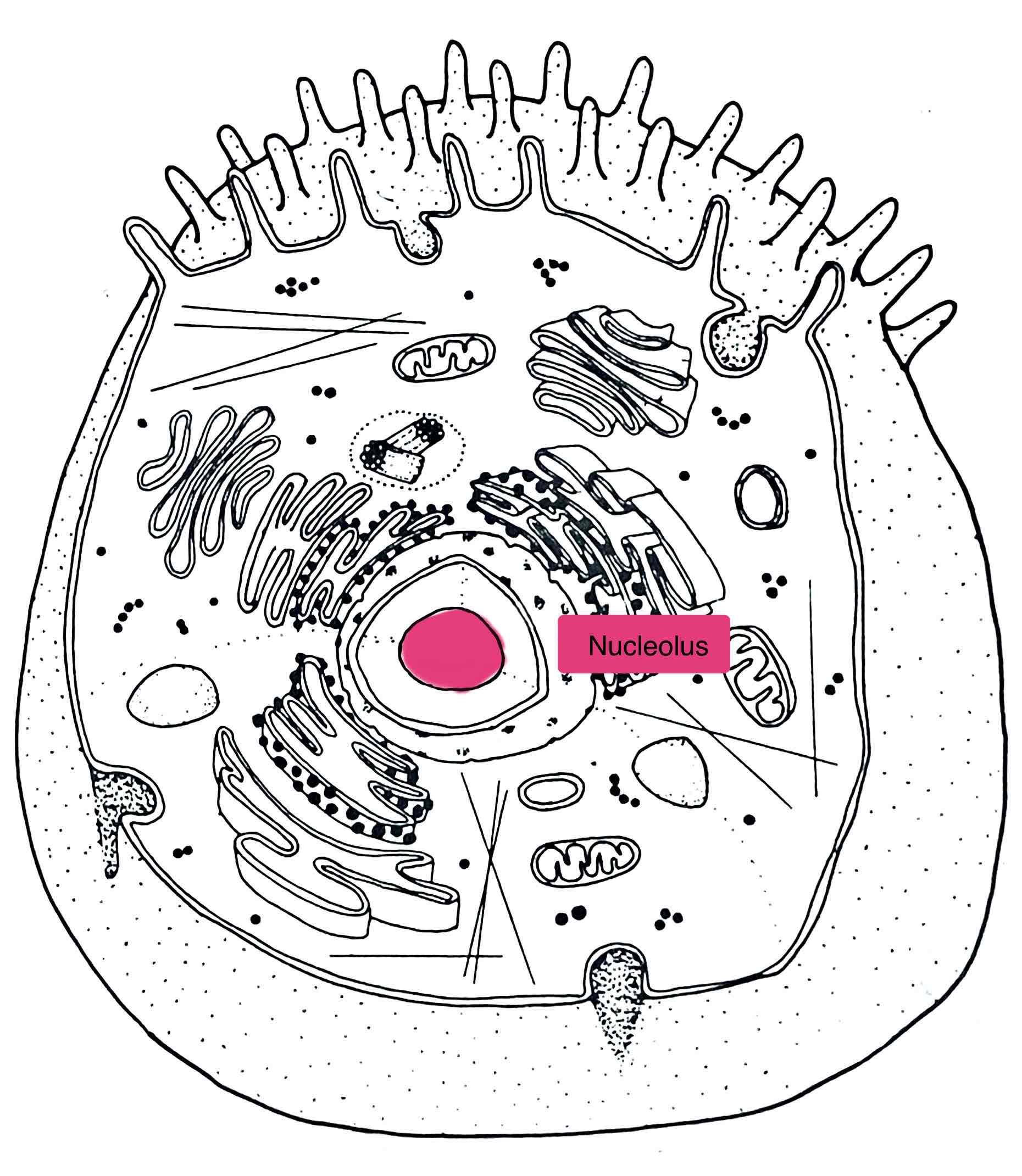
Identify the Nucleolus
– within the nucleus
- contains rRNA
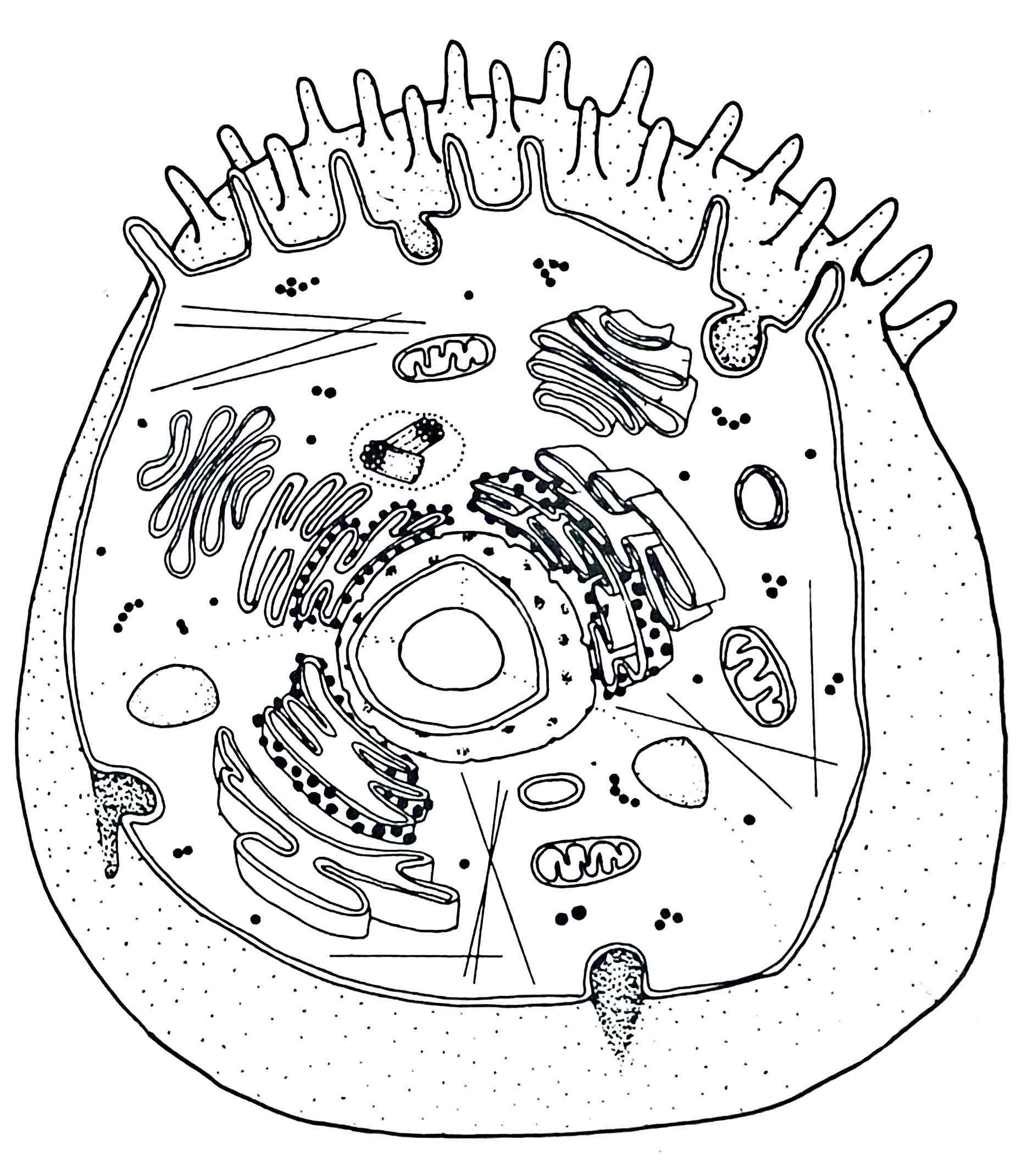
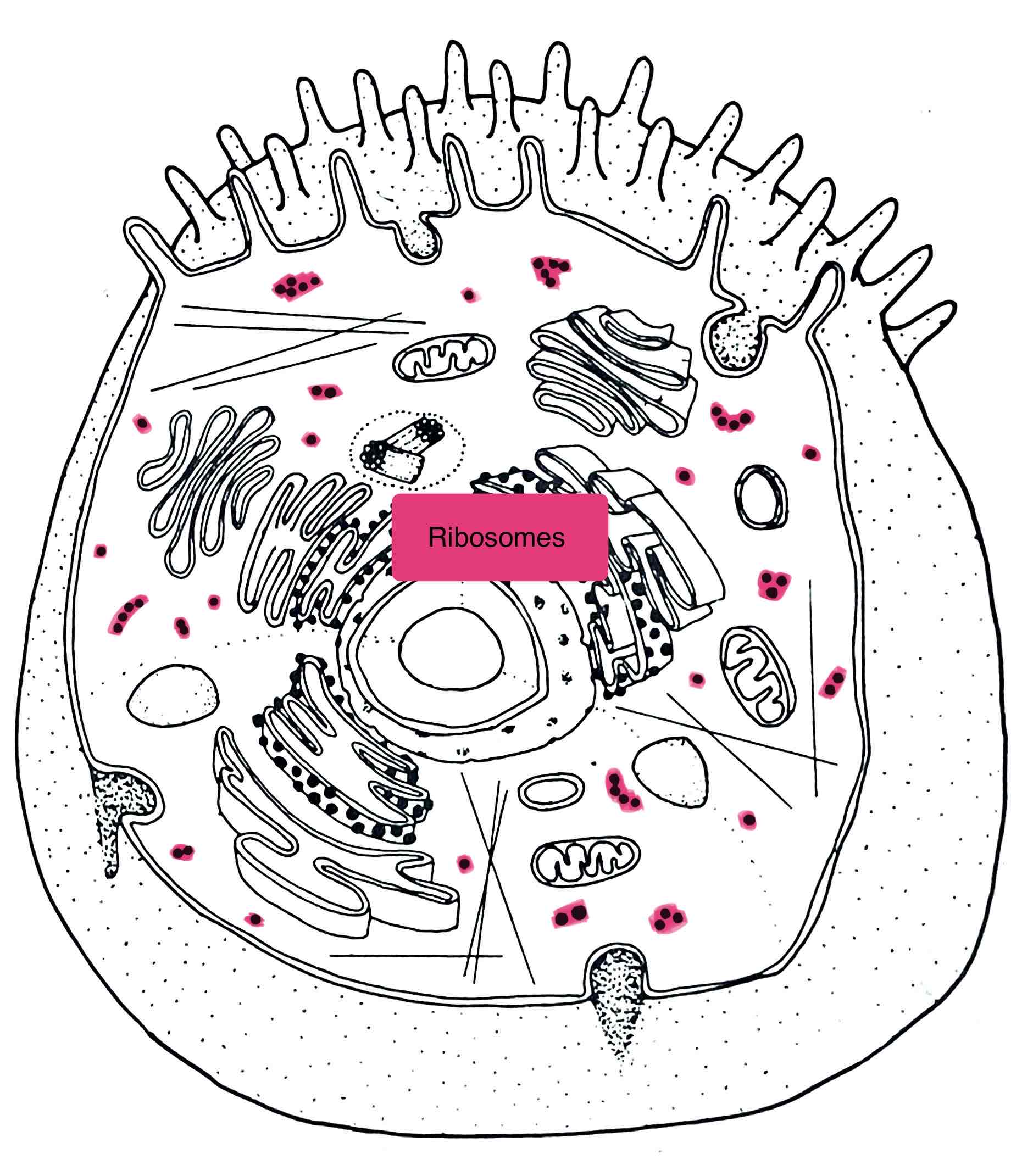
Identify the Ribosomes
– site of protein synthesis
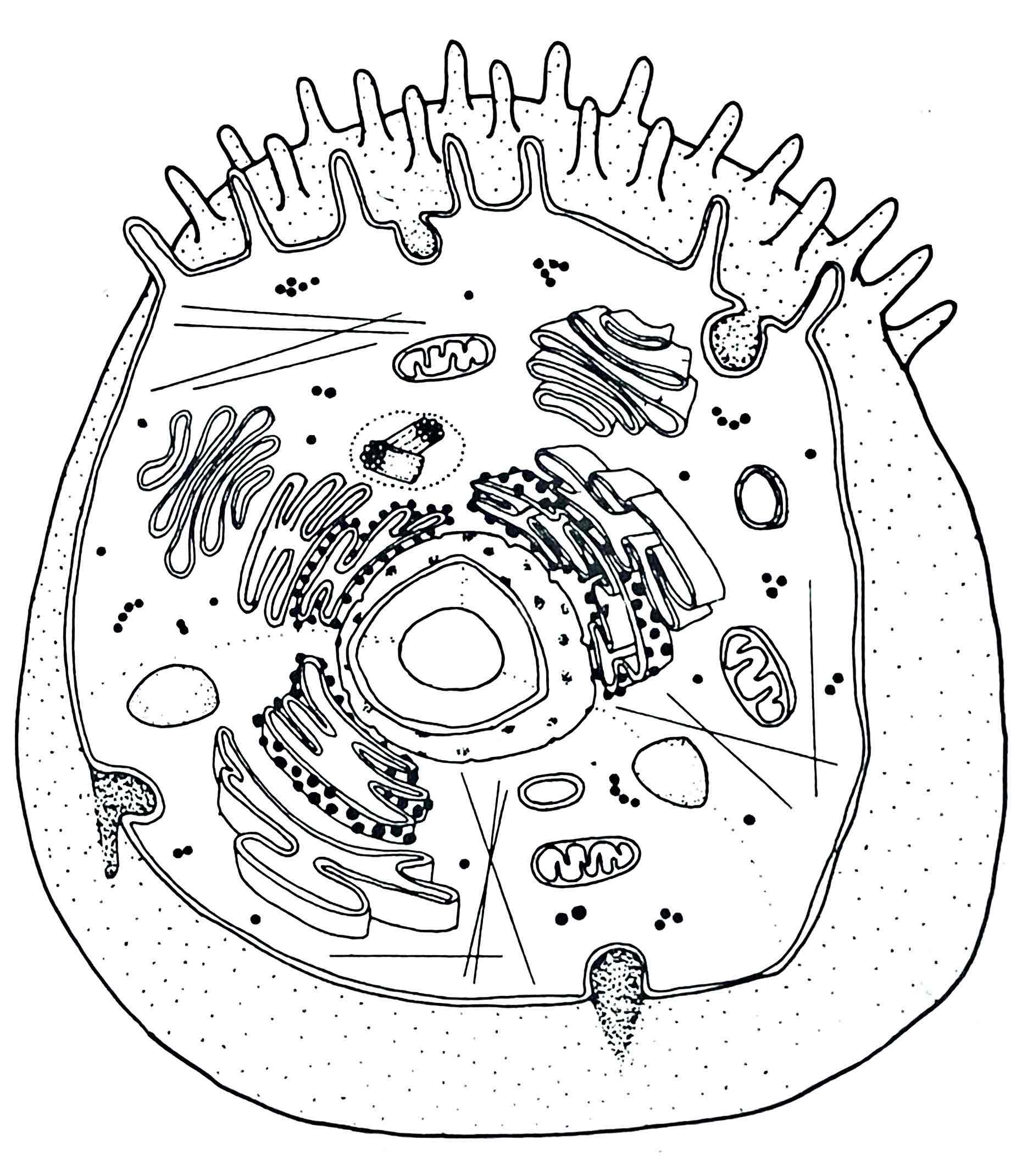
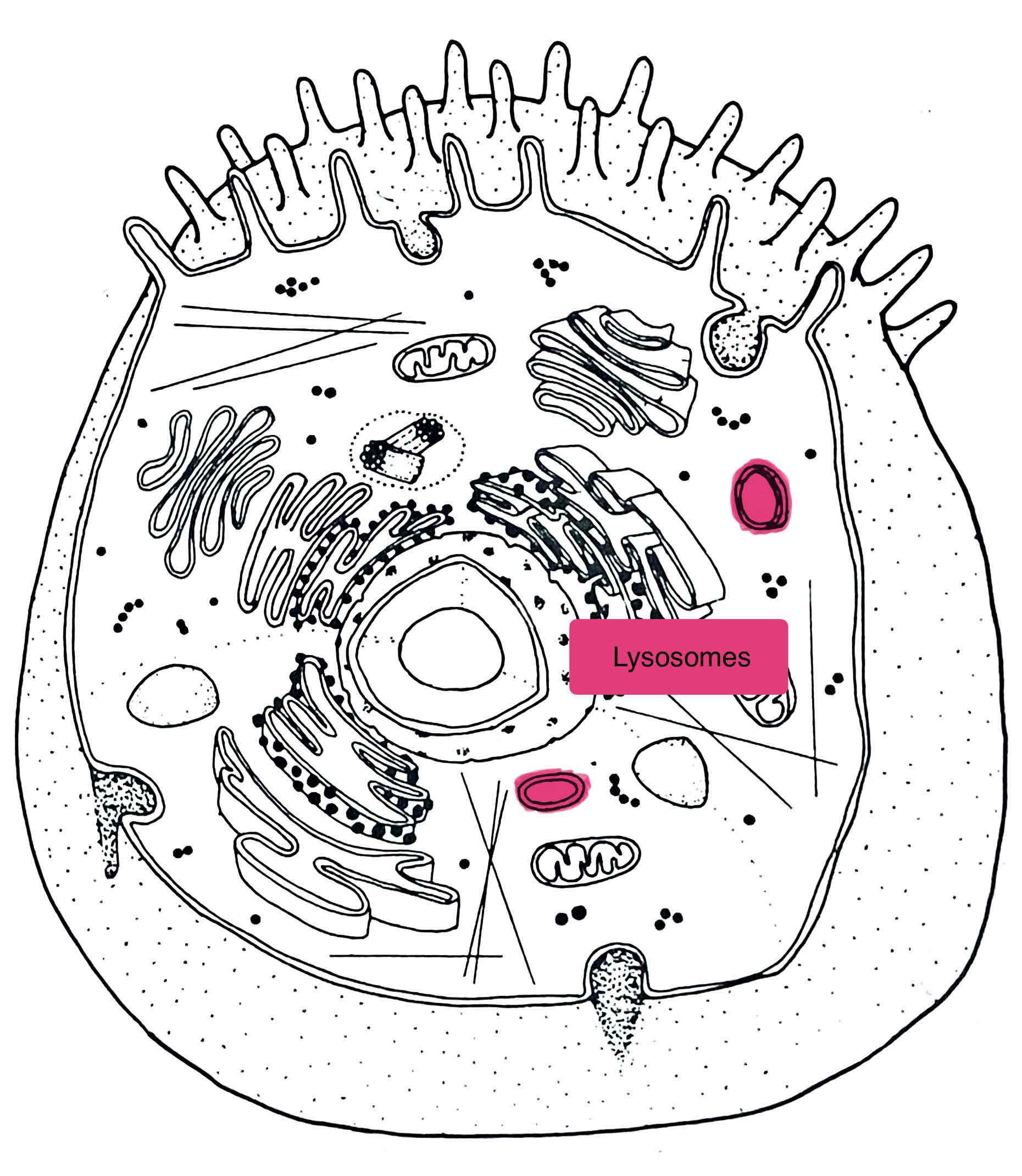
Identify the Lysosomes
– “suicide sacs”
- contain digestive enzymes
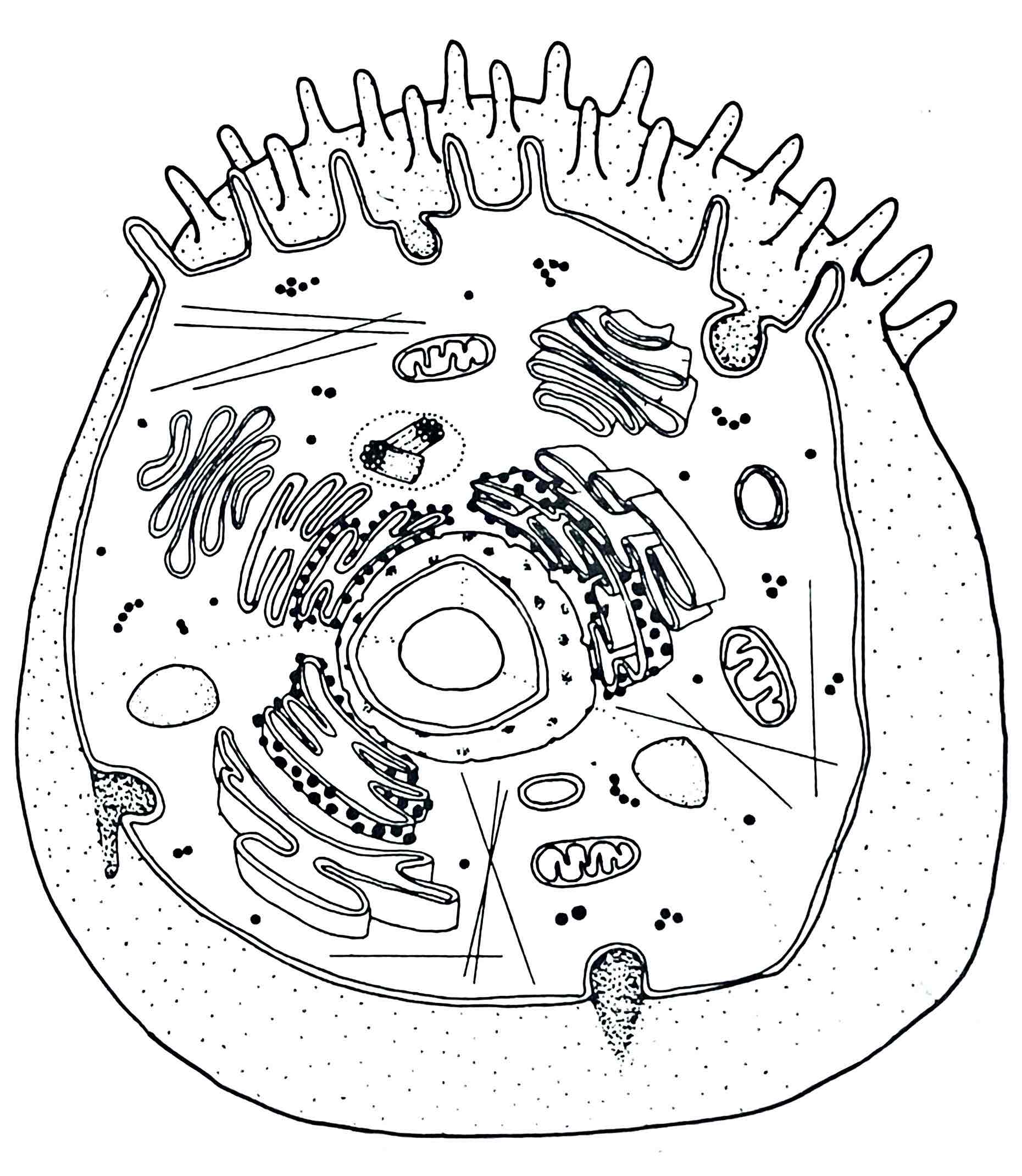
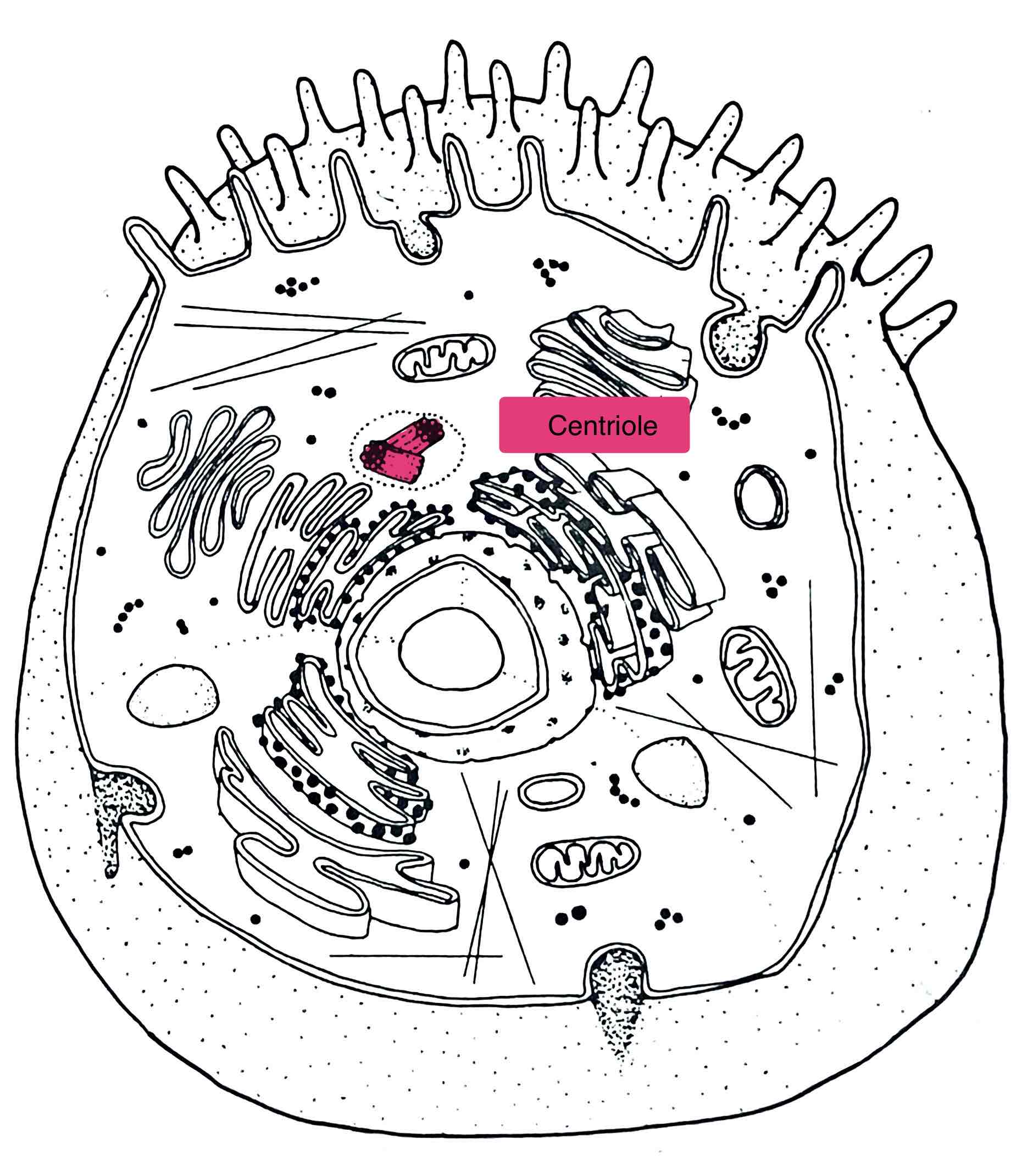
Identify the Centriole
– send out spindle fibers for cell division
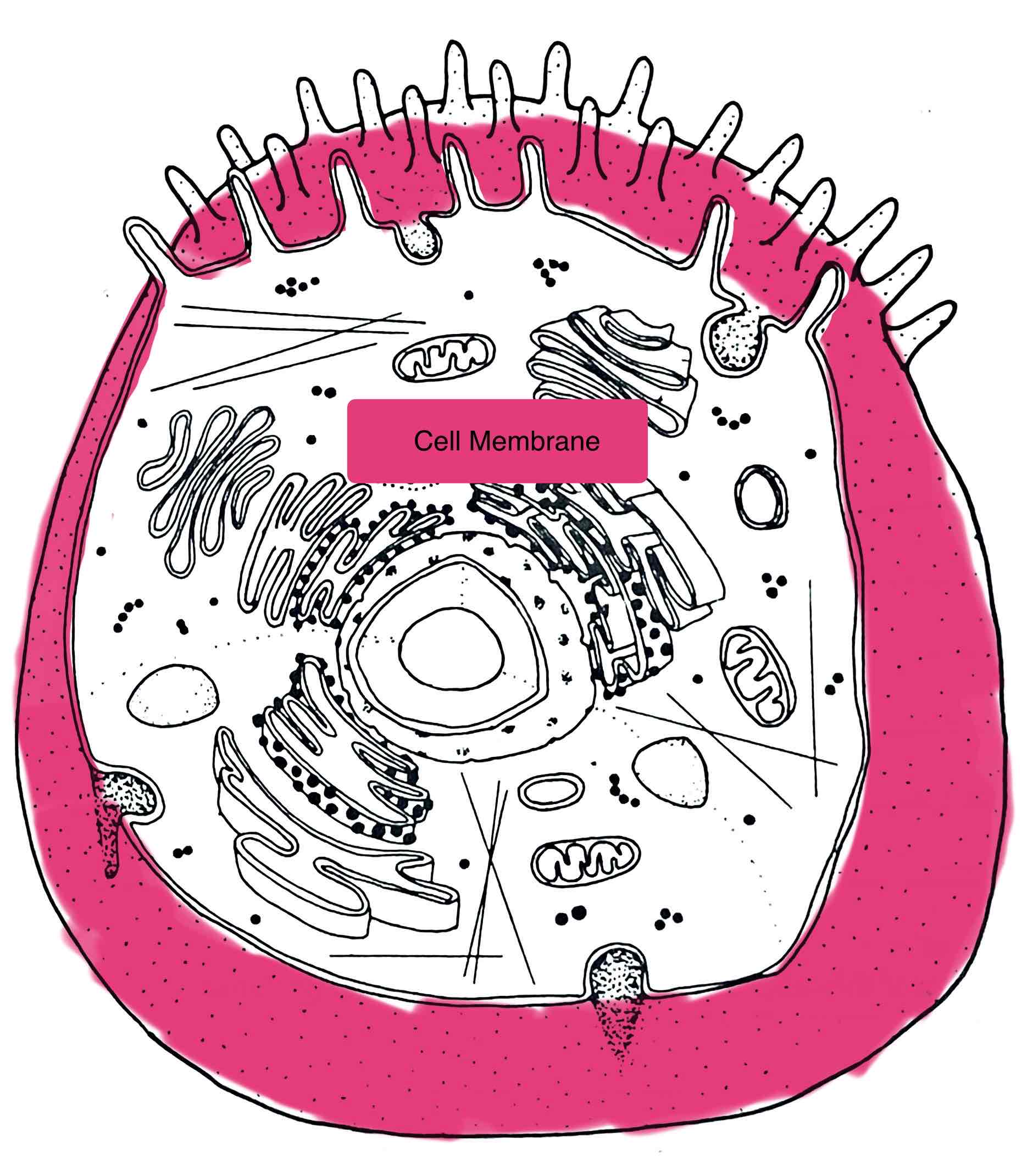
Identify the Cell Membrane
- semi-permeable phospholipids bi-layer
- separates cell from surrounding environment
- protective barrier
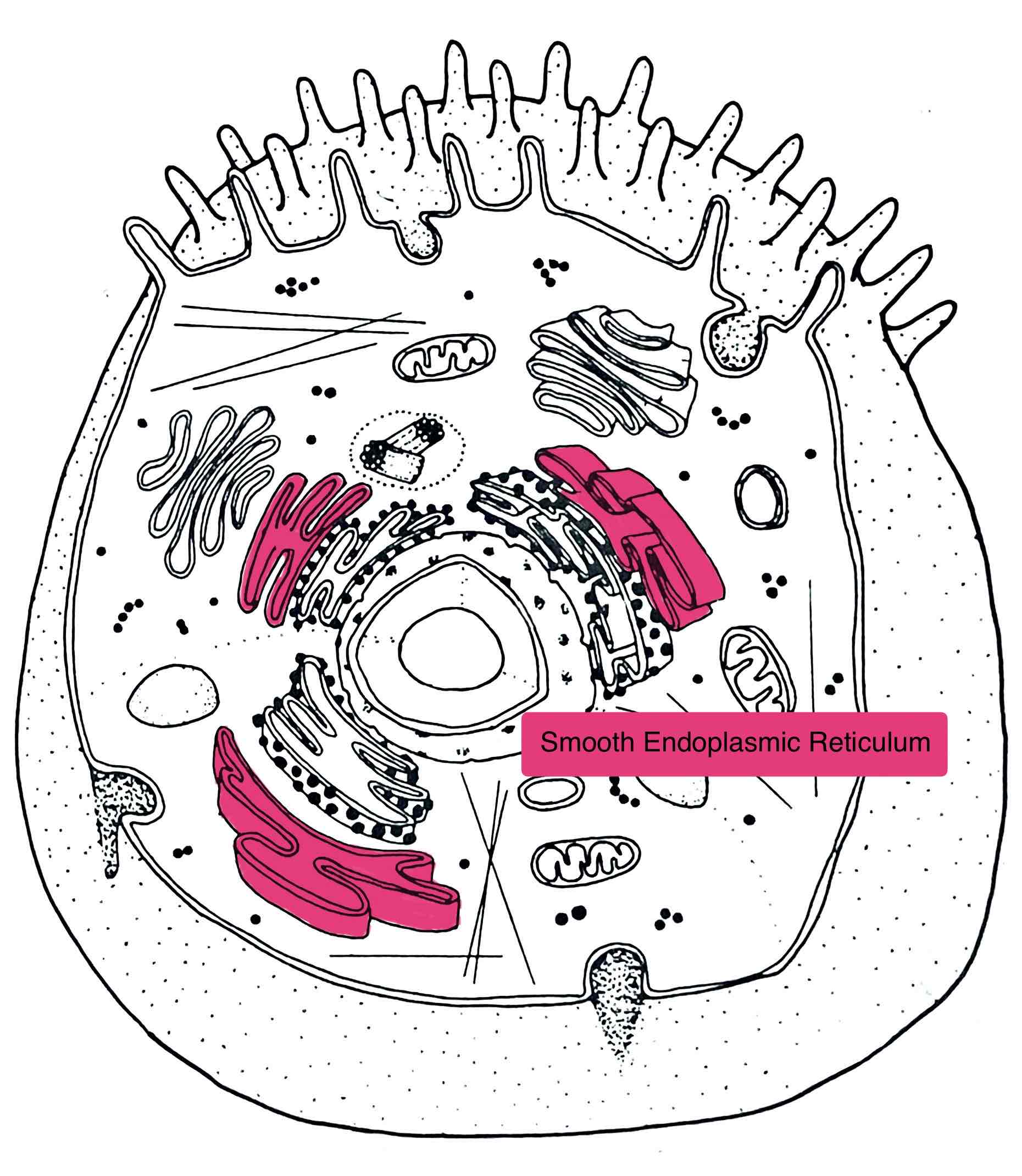
Identify the Smooth ER
- transports, synthesizes and metabolizes small molecules
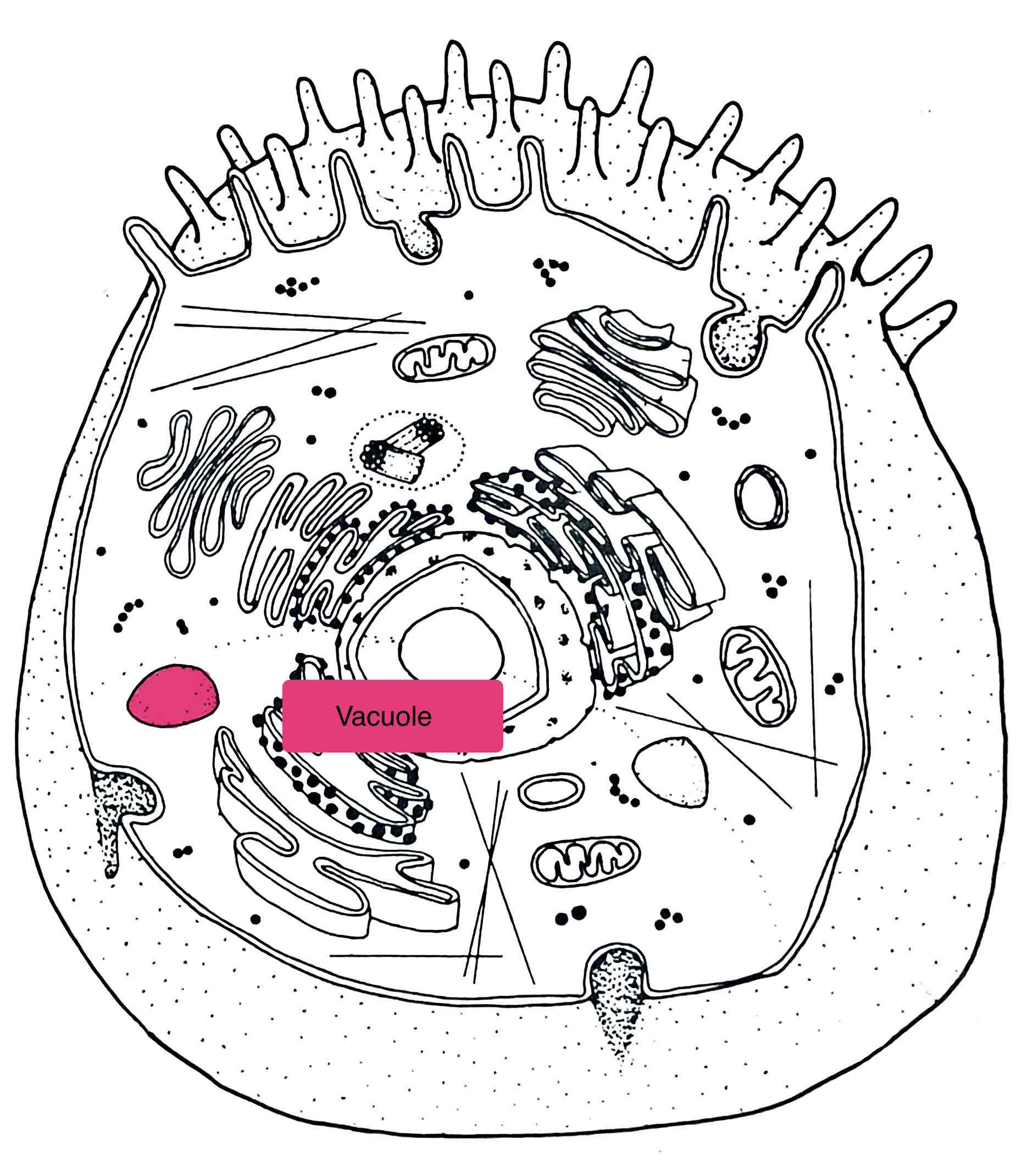
Identify the Vacuole
– holds water, waste
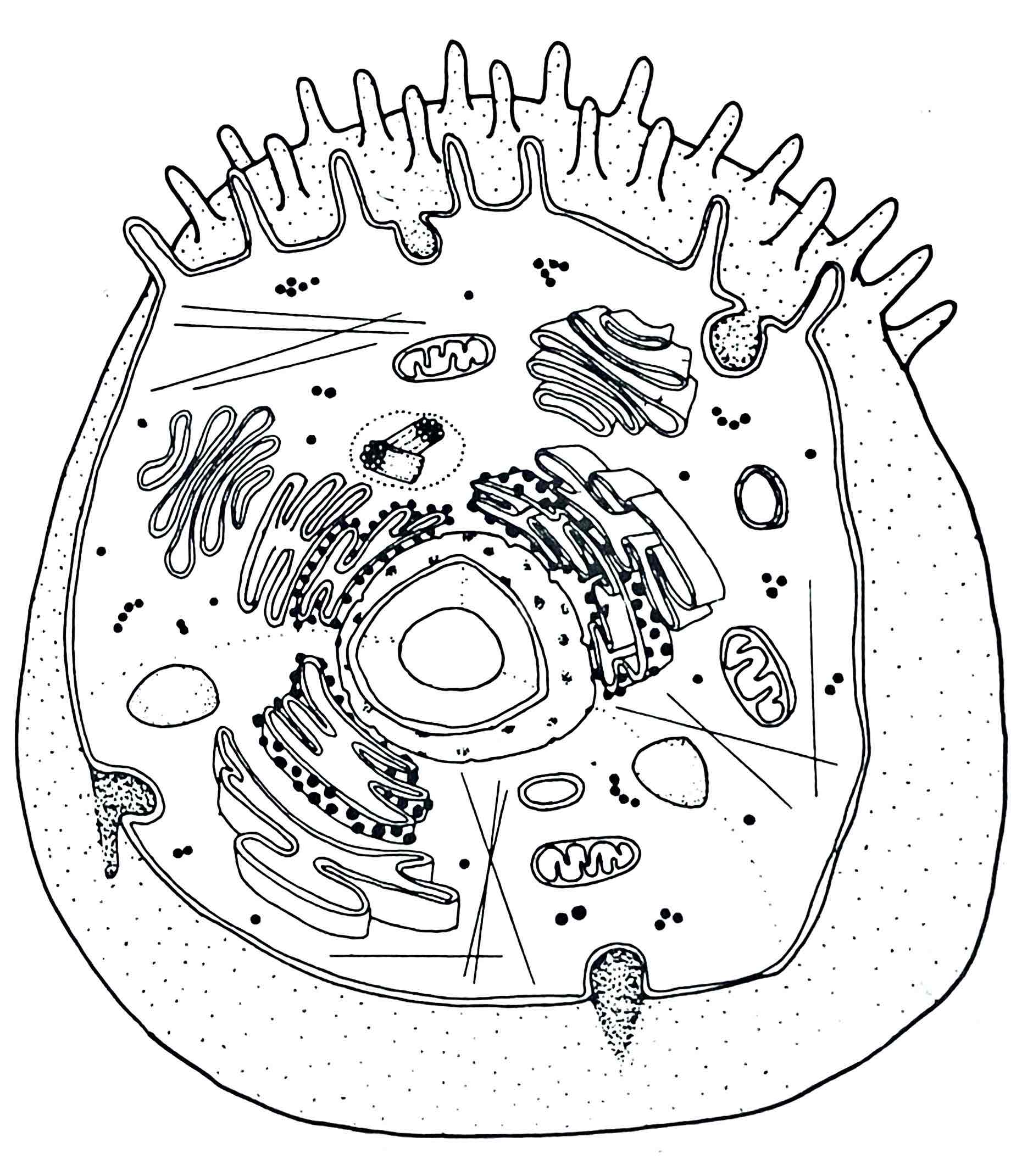
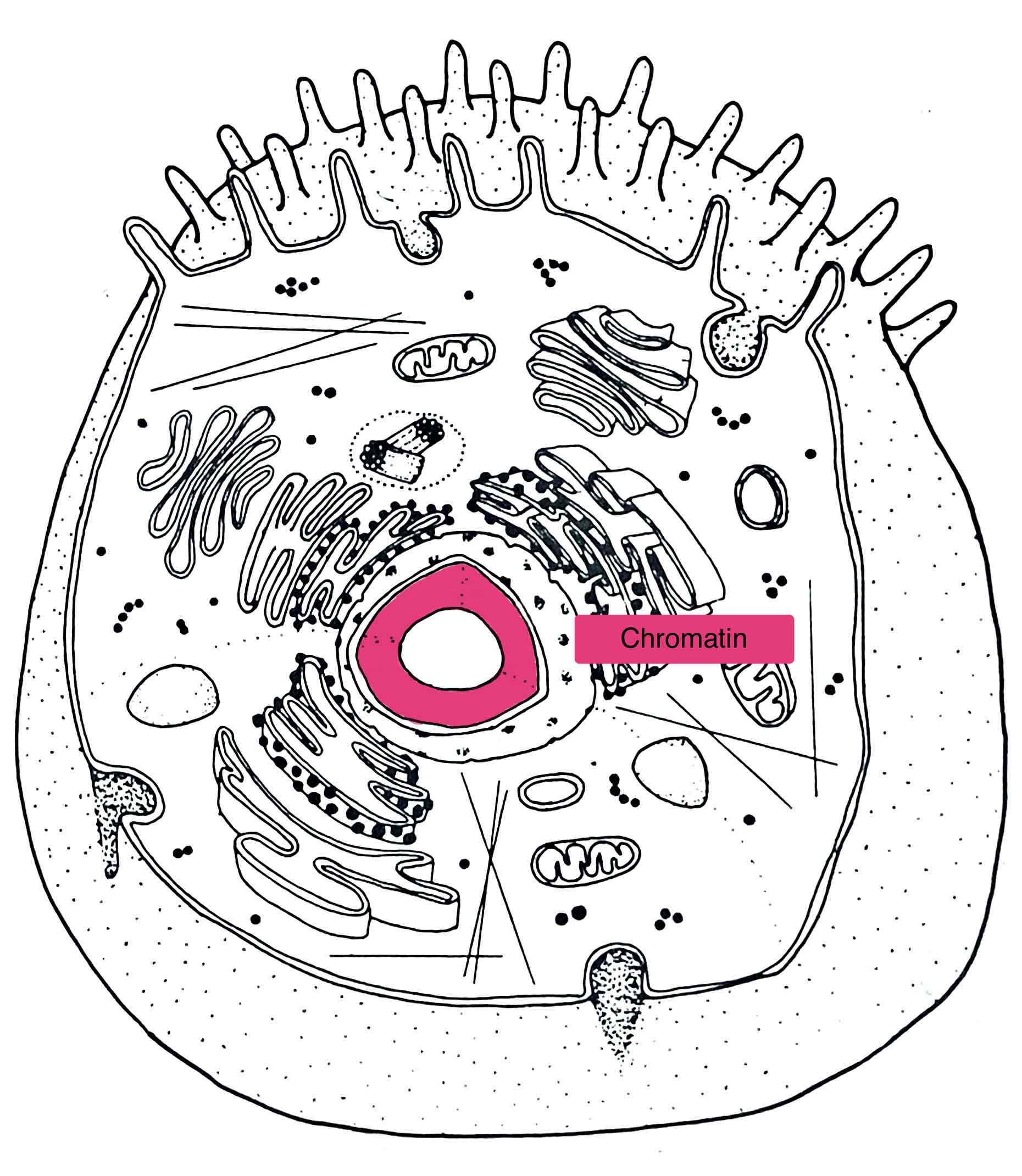
Identify the Chromatin
– the form of chromosomes in the non-dividing cell - long, thin intertwined
OR nucleoplasm – everything inside the nucleus
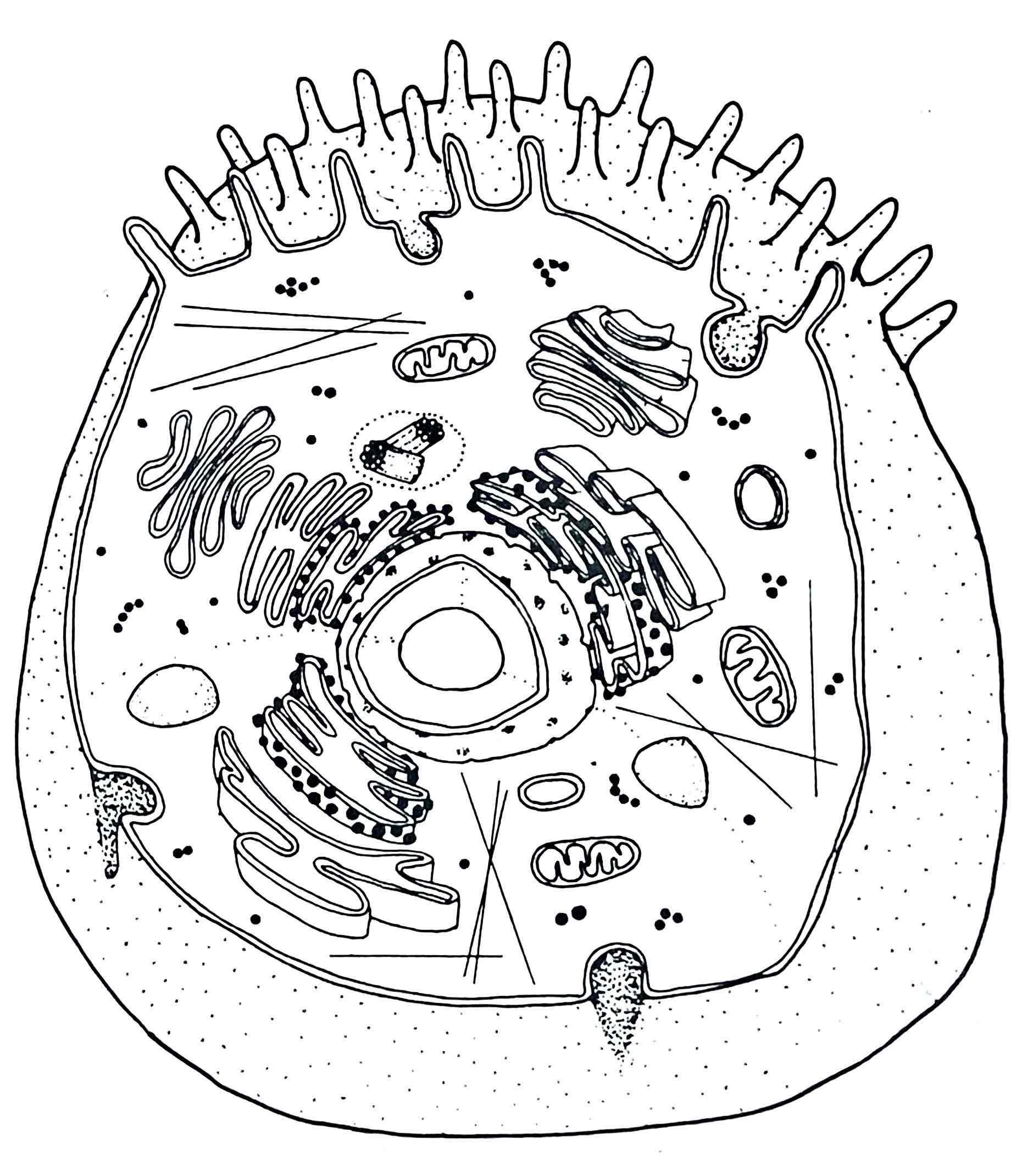
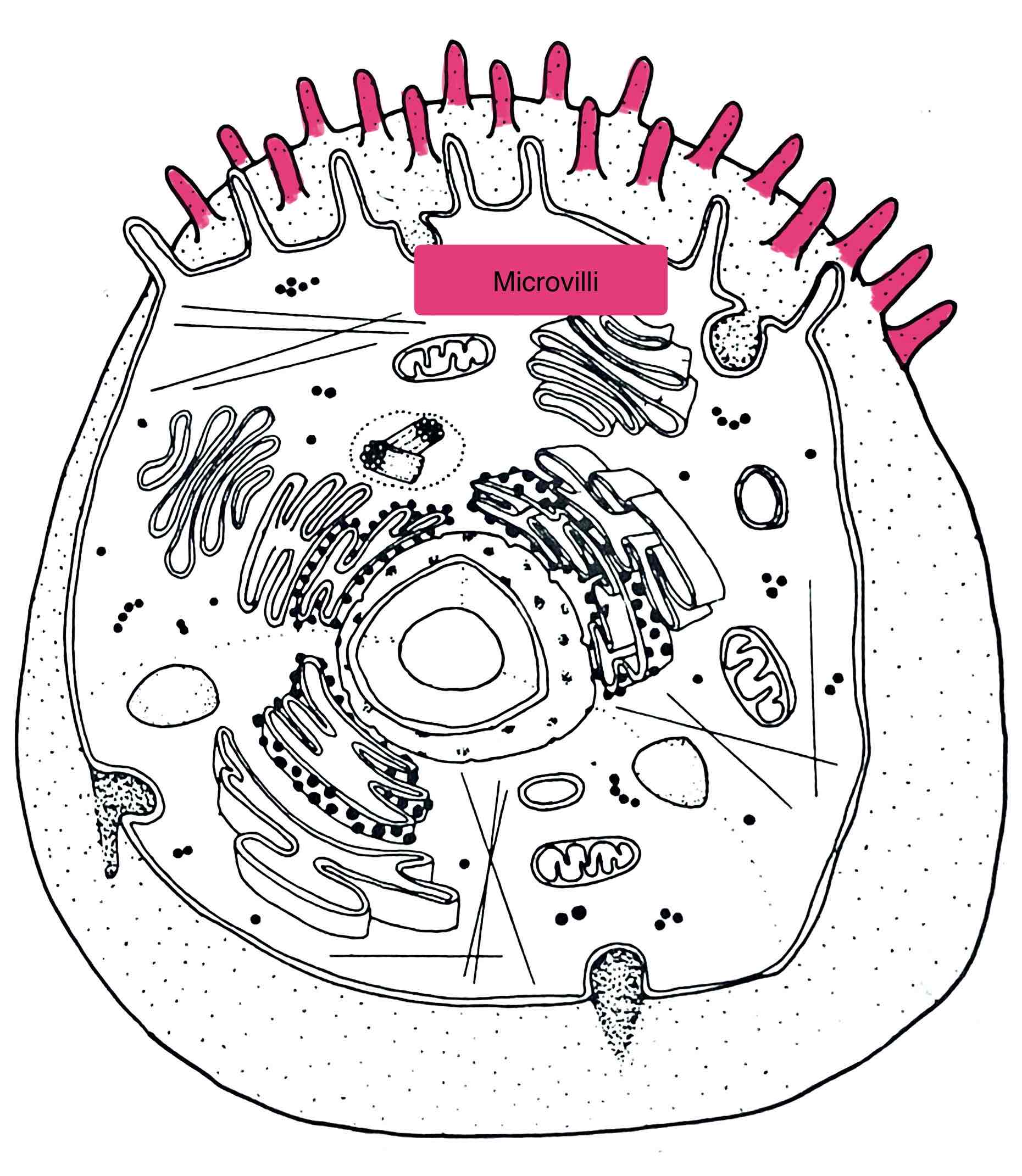
Identify the Microvilli
– surface modification which increases the surface area of the cell
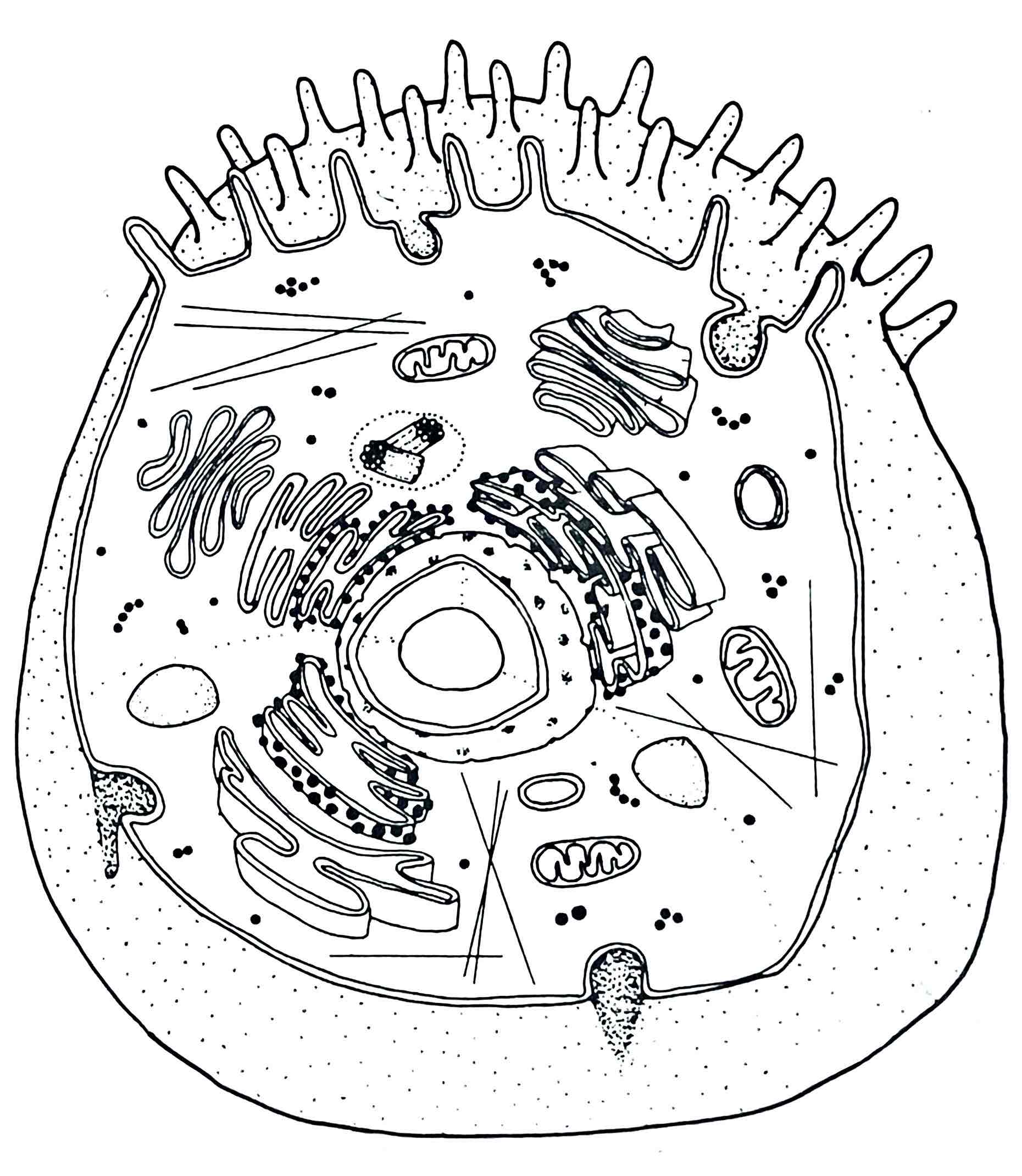
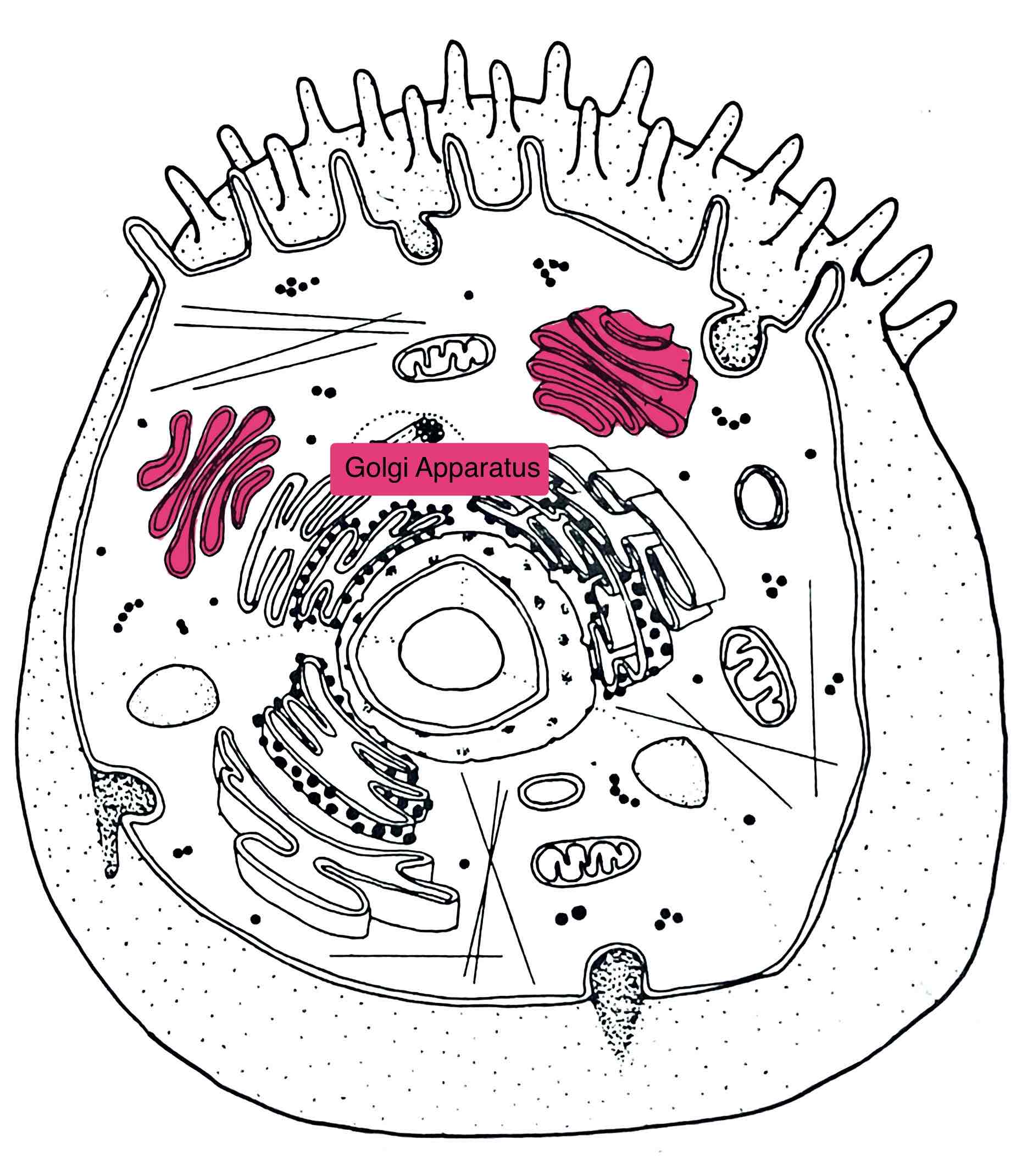
Identify the Golgi Apparatus
– modifies, packages and distributes secretory proteins
- produces lysosomes
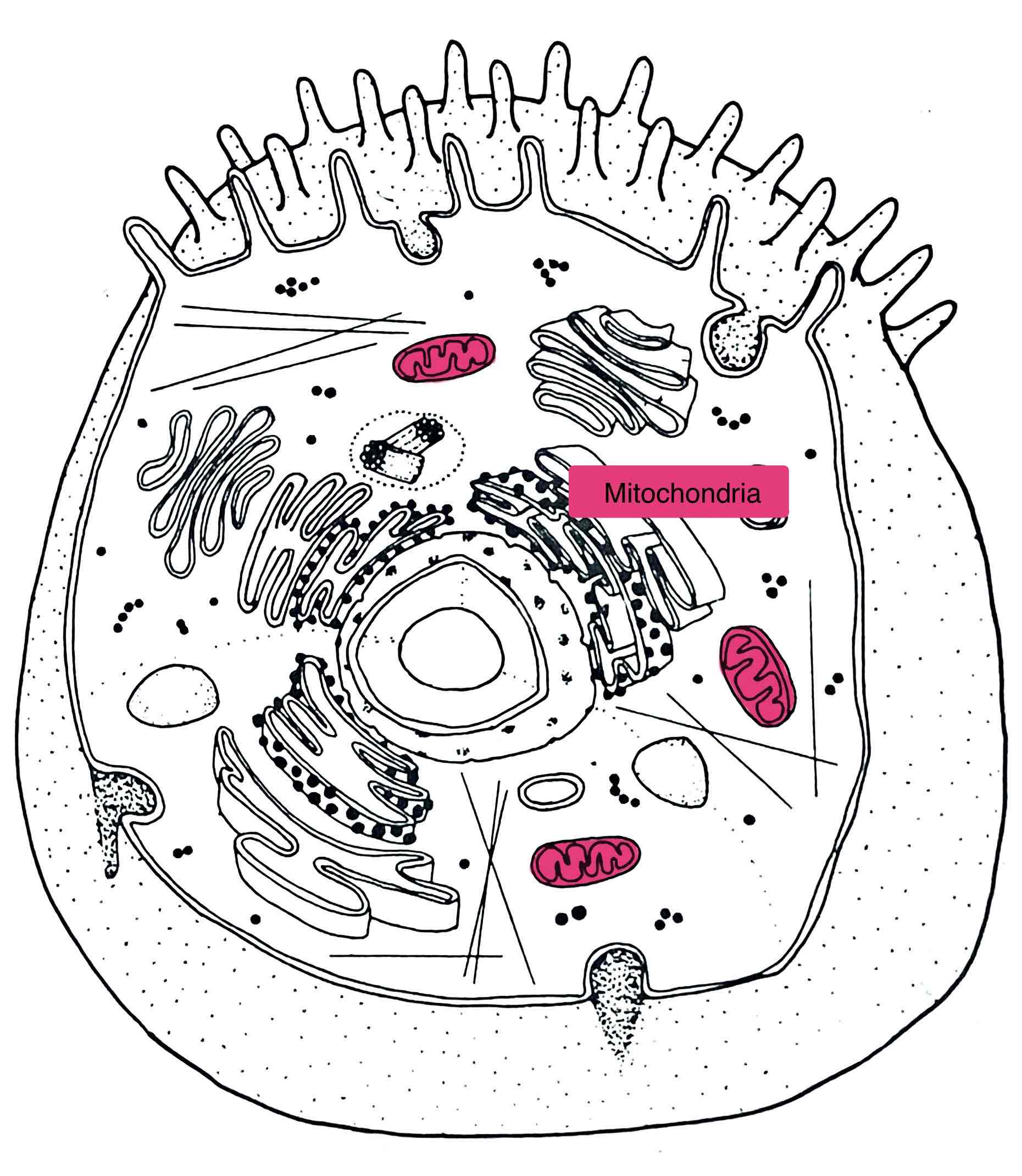
Identify the Mitochondrion
– “powerhouse”
- site of cellular respiration (oxidation, Kreb’s cycle)
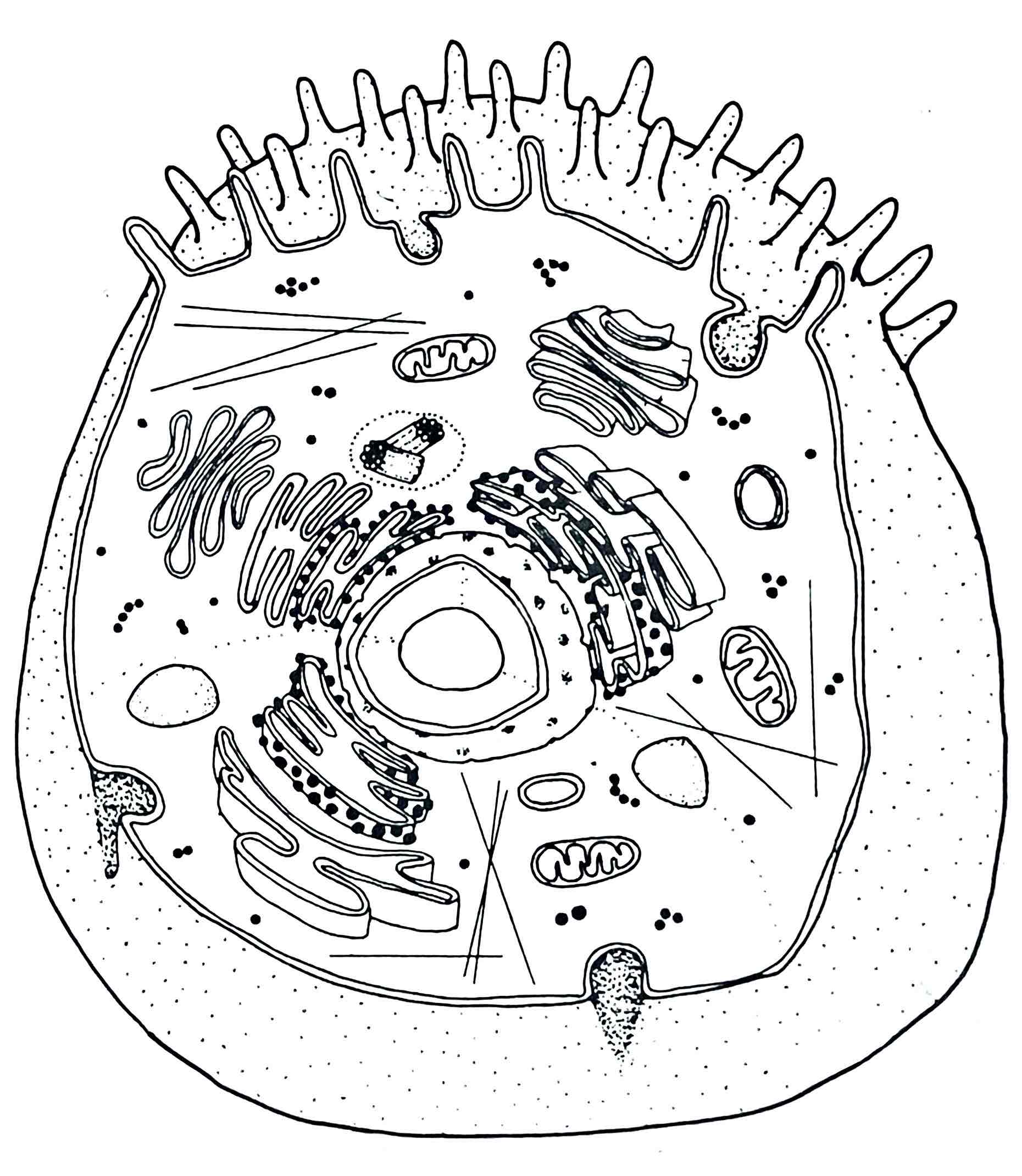
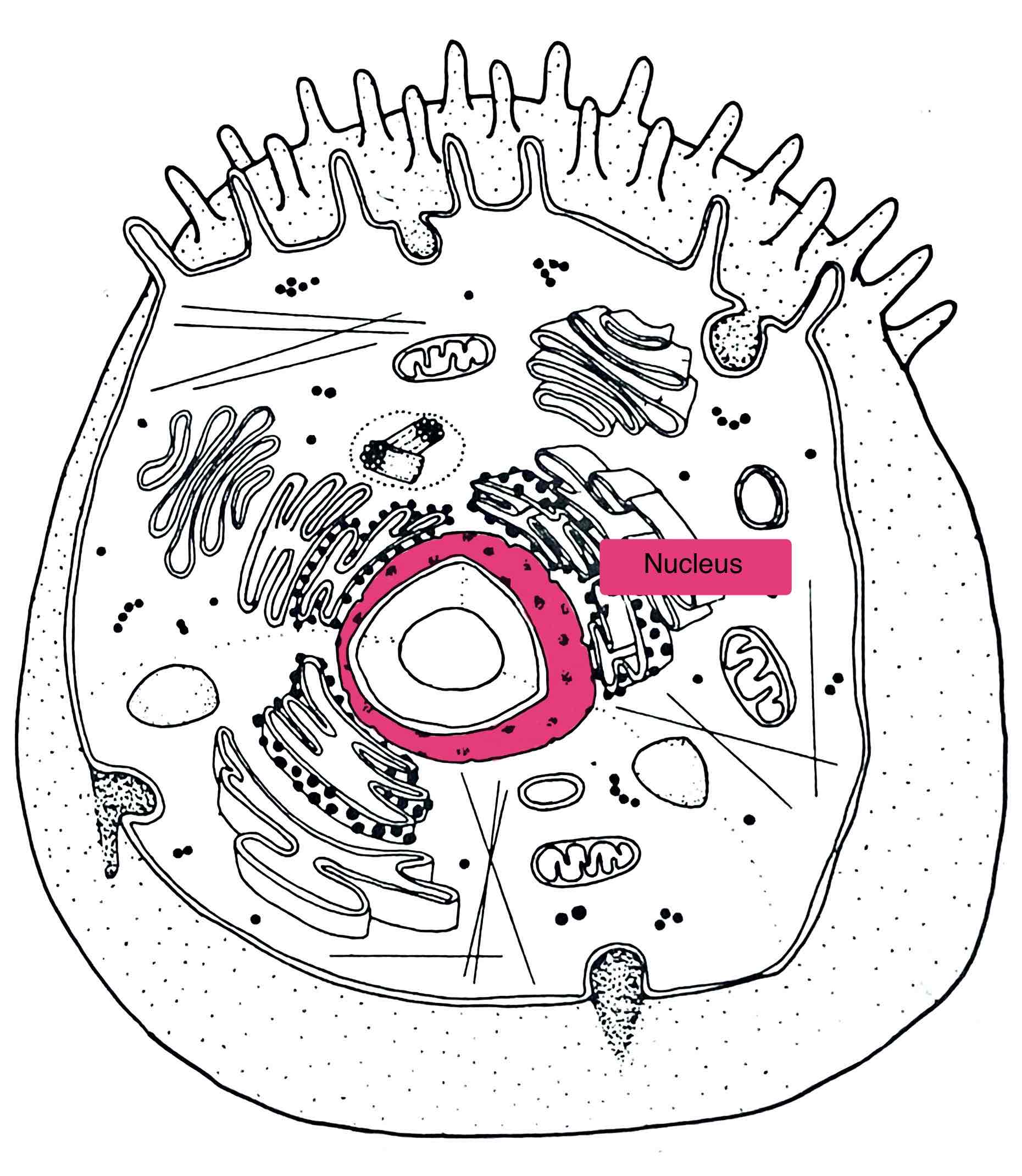
Identify the Nucelus
– control center of cell
- houses genetic information
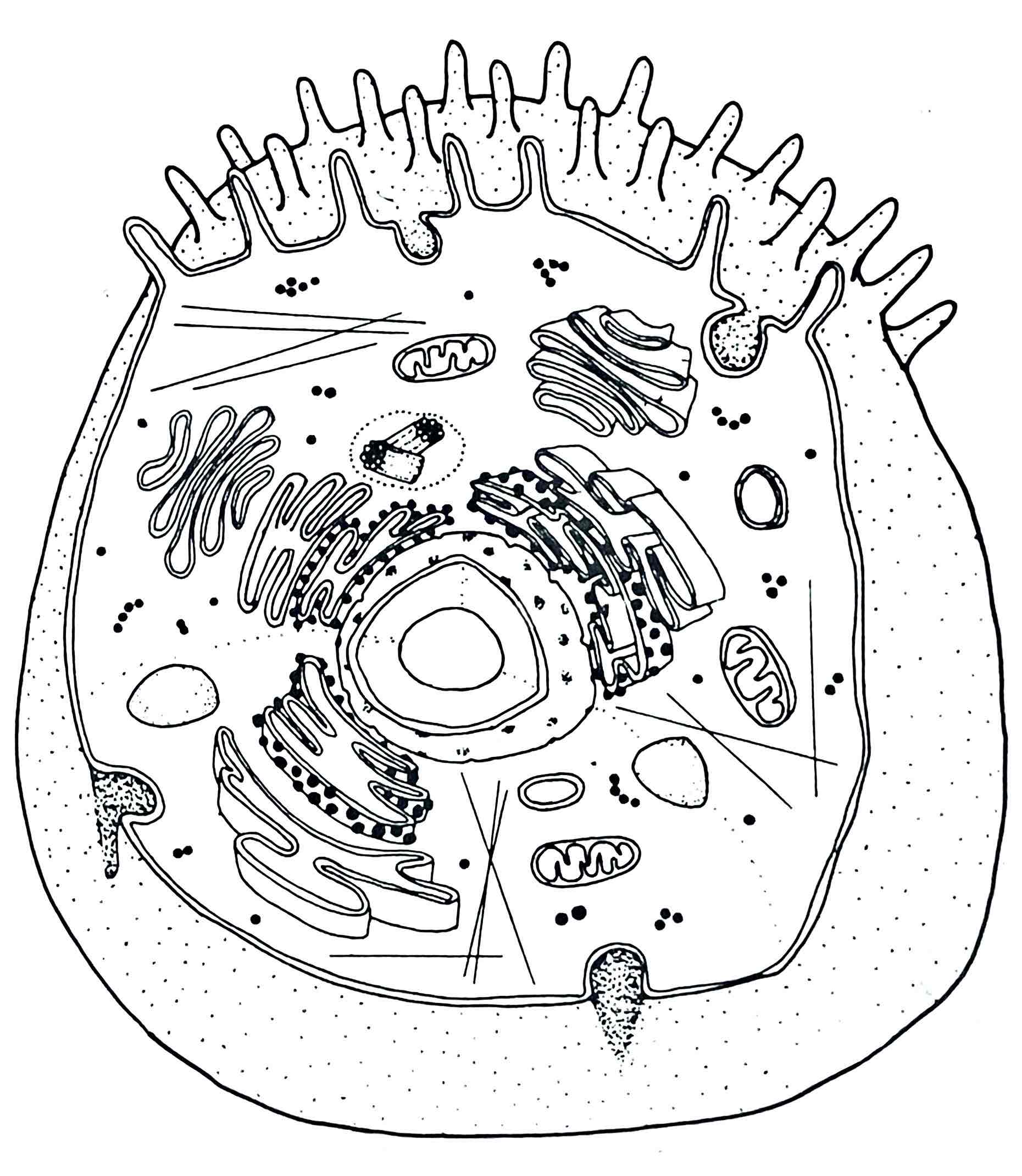
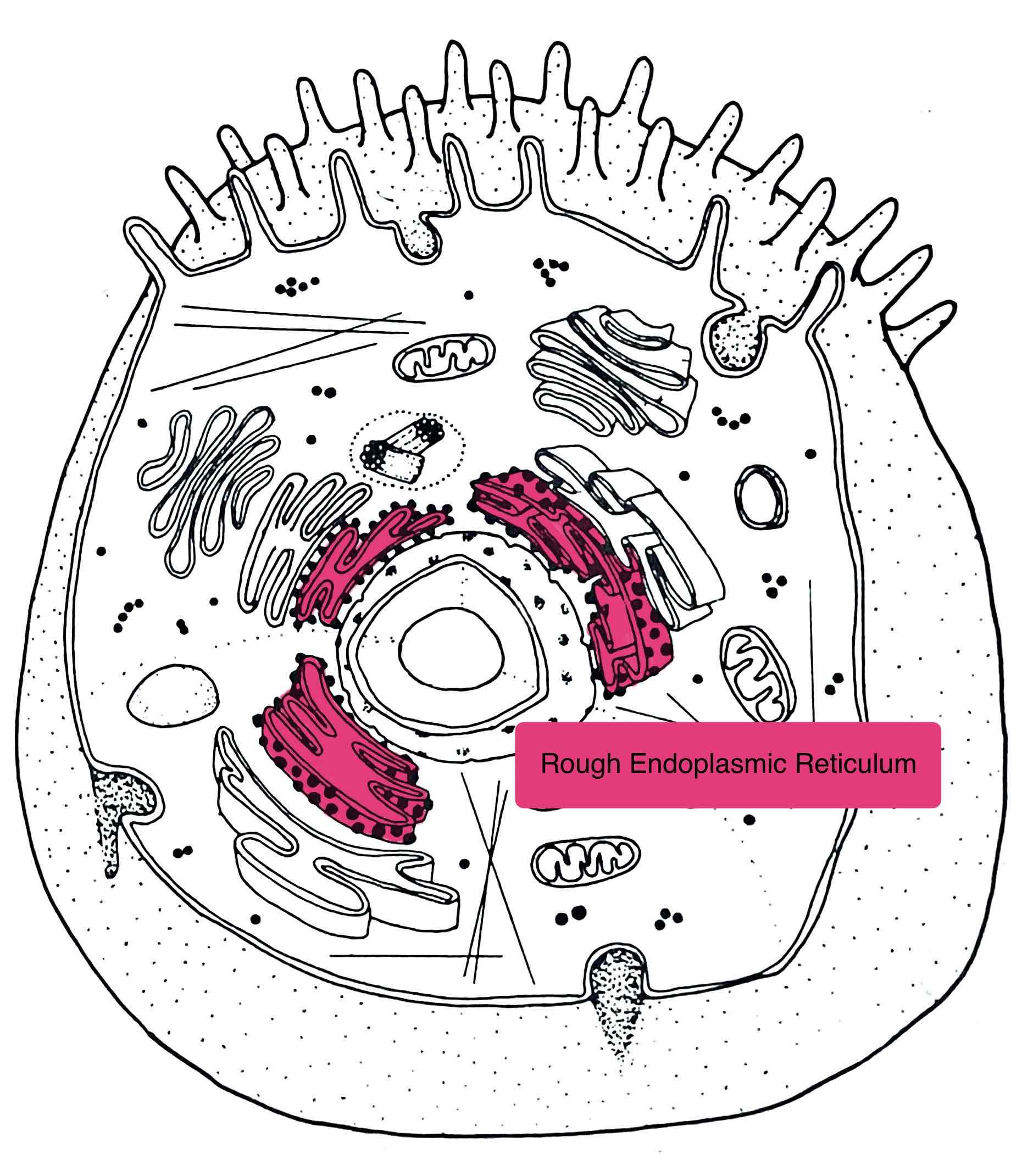
Identify the Rough ER
- transports and modifies proteins
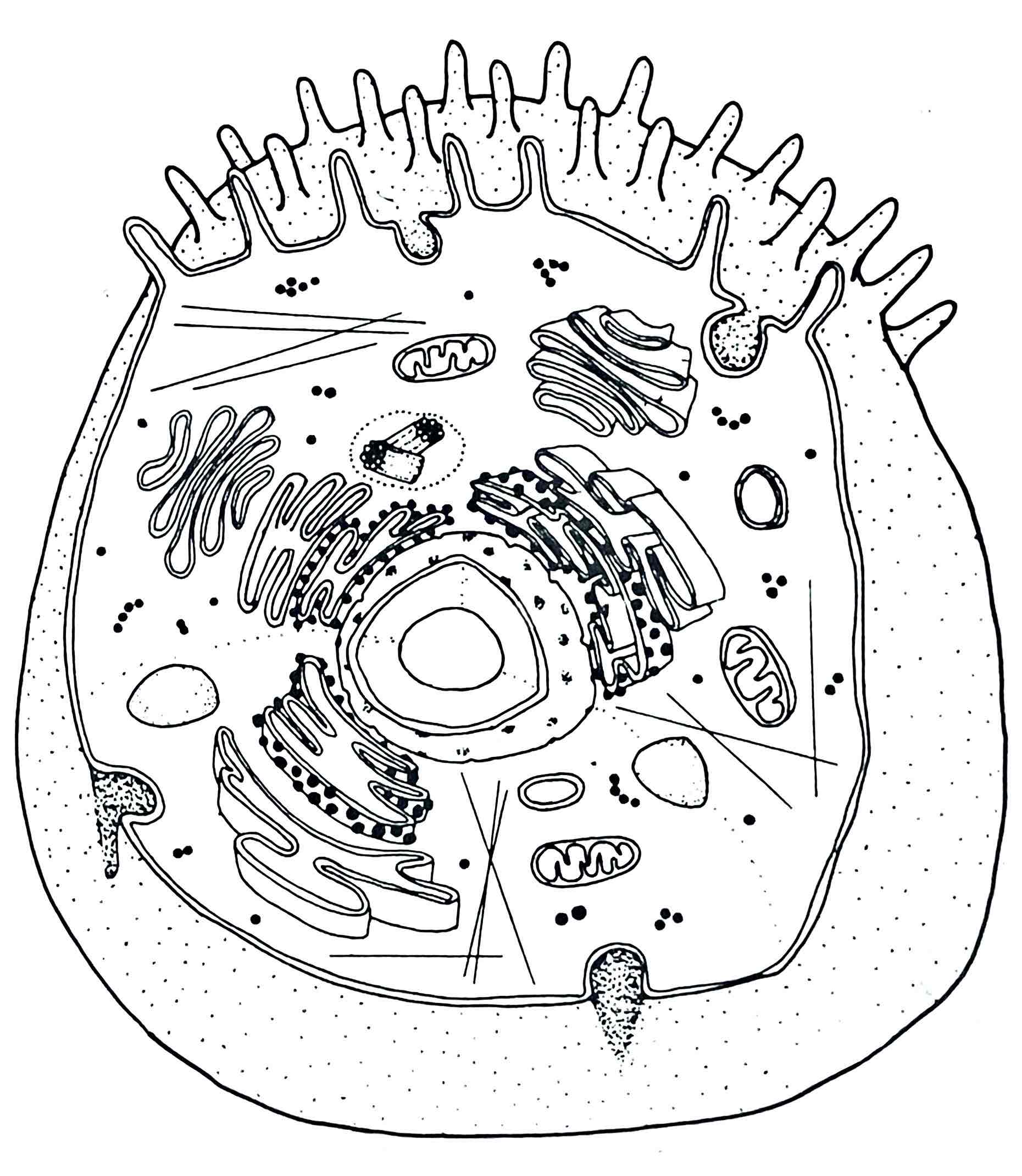
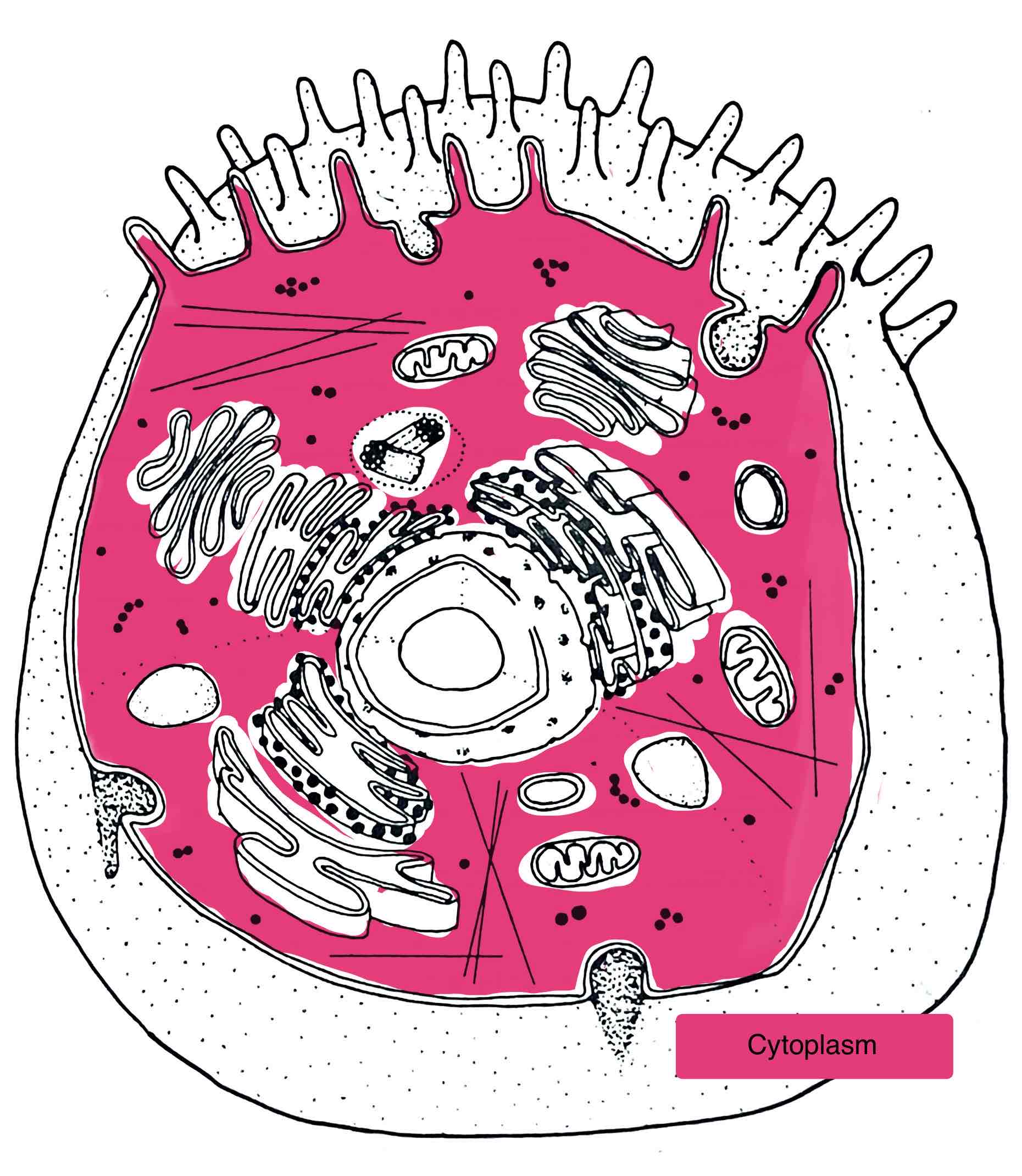
Identify the Cytoplasm
– everything within the cell except the nucleus
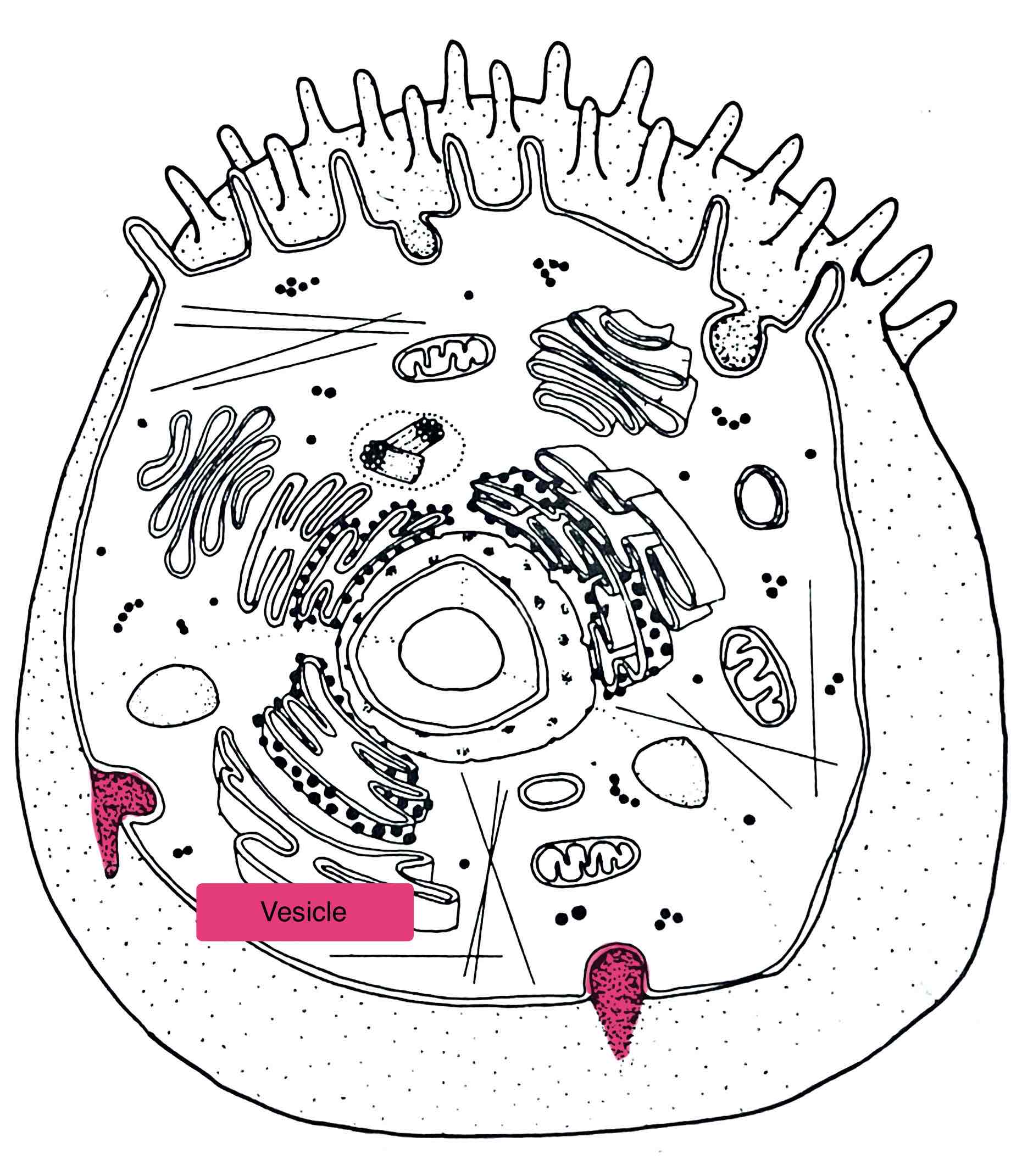
Identify the Vesicle
- membrane-bound sacs used for storage/transport
Cytoplasm vs Protoplasm
Cytoplasm: Everything within the cell except the nucleus.
Protoplasm: Everything within the cell including the nucleus.
List the 3 major regions of the cell you can see with a light microscope
Plasma membrane
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
What are the two different types of cellular organization that have been identified via electron microscope?
1. Prokaryotic (primitive nucleus)
2. Eucaryotic (true nucleus)
The prokaryotic cell is the unit of cellular organization for bacteria, is distinguished by its small size and the absence of many organelles that are found in eucaryotic type of cellular organization.
Define Solution
homogenous mixture of solute and solvent
Define Solute
substance which dissolves
Define Solvent
the fluid in which substances are dissolved
Define Soluble
capable of dissolving
Define Insoluble
cannot dissolve
Define Suspension
- molecules are too large to go into solution therefore settle on the bottom
- suspensions must be shaken to re-suspend the particles
What is the relation of # of solute particles to osmotic pressure?
The greater the number of solute particles, the higher the osmotic pressure.
When cells are placed in a solution and they remain unchanged the solution surrounding them has the same osmotic pressure as the cell - this solution is said to be …
Isotonic
When cells are placed in a solution and the cells swell and burst, the solution has a lower osmotic pressure than the cell - this solution is said to be…
Hypotonic
When cells are placed in a solution and the cells shrink, the solution has a higher osmotic pressure than the cells - this solution is said to be…
Hypertonic
What 3 solutions were used to in lab to test osmotic imbalances on cell membranes (each 5mL)?
1. 0.9% saline
2. Distilled water
3. 6% sodium chloride (NaCl)
Effects of 0.9% saline
Effect: Nothing
Solution: isotonic
Reason: Since the solute concentration (or osmolarity) is the same on both sides of the membrane no movement takes place
Effect of distilled water
Effect: Ruptured i.e hemolyzed
Solution: hypotonic
Reason: Since the red blood cells have a higher concentration of solutes than the distilled water and water moves (by osmosis) from low solute to high solute therefore water moves into the cell causing it to rupture or burst i.e hemolzye
Effect of 6% NaCl
Effect: Shrivel or shrink i.e crenate
Solution: hypertonic
Reason: Since the red blood cells have a lower concentration of solutes than the 6% NaCl and by osmosis water moves from a low solute to high solute – water moves out of the cell into the NaCl therefore causing the RBC to lose water i.e. crenate (shrink)
Define crenation. What type of solution caused crenation to happen?
Crenation: RBC’s shrinking or shriveling.
RBC’s crenate in a hypertonic solution.
Define hemolysis. What type of solution caused hemolysis to happen?
Hemolysis: RBC’s bursting, breaking or rupturing.
RBC’s hemolyze in a a hypotonic solution.