AP Stats unit 3-Experimental design
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
population
the entire group of individuals we want information about
census
a complete count of the population; when you gather general information about the entire population
sample
a part of the population we actually examine in order to gather information
sampling design
the method used to choose the sample from the population
sampling frame
is a list or source that contains all the units (individuals, households, etc.) from which a sample will be selected.
simple random sample
is a sampling method in which every member of the population has an equal chance of being selected.
stratified random sample
is a sampling method that divides the population into distinct subgroups (strata) based on shared characteristics and then randomly selects samples from each stratum, ensuring representation across the different subgroups.
systematic random sample
randomly select a number between one and n and survey every nth person after that.
cluster random sample
The population is divided into naturally occurring groups (clusters) that are often geographically based (e.g., schools, neighborhoods, hospitals). and then randomly selects entire clusters to sample, often used for convenience or cost-effectiveness.
multistage sample
is a sampling method that combines different sampling techniques, such as stratified and cluster sampling, at various stages to obtain a more representative sample from a larger population.
describe an srs
put the names/numbers of all ___ on slips of paper and place in a hat. Mix and randomly draw ___ slips of paper without replacement. Survey the corresponding people.
describe a systematic random sample.
number all ___ and place ___ numbers in a hat. Mix and randomly select one number and survey the corresponding person. Survey every nth person on the list after that.
describe a cluster random design
number all clusters and put the numbers into a hat Mix and randomly select a number from the hat. Survey everyone in that cluster.
stratified random sample
sort everyone into strata then number ___ in all the stratum. place the numbers in a hat and draw __ numbers. survey the corresponding people in that specific stratum. repeat the process for all strata
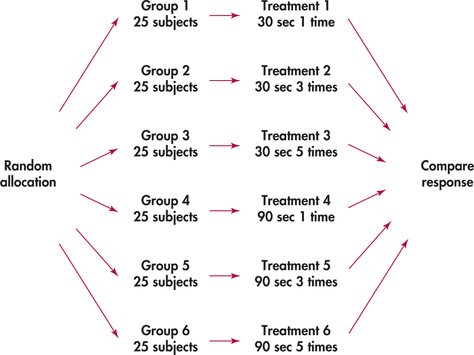
Completely randomized design
experimental units are assigned completely at random to treatments.
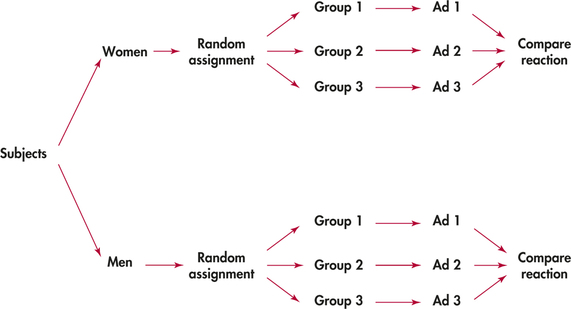
randomized block design
experimental units are blocked in homogeneous groups and then randomly assigned to treatmentswithin each block to control for variability.
matched pairs design
a special type of block design; match up experimental unit according to similar characteristics and randomly assign one to treatment A and the other get treatment B randomly.
observational study
a study where researchers observe subjects without manipulating anything; they collect data on variables of interest.
Experiment
actively impose a randomly assigned treatment in order to observe the response
experimental unit
the single individual to which the different treatments are randomly assigned
factor/ explanatory variable
what we test or what we change
Level
the specific values or settings of a factor in an experiment.
response variable
what you measure or record at the end of the experiment
treatment
a specific experimental condition applied to the units
Control group
a group that is used to compare the factor against; can be placebo
placebo
a "dummy" treatment that can have no physical effect; not required in every experiment
blinding
method used so that units or evaluators do not know which treatment units are getting
double blinding
neither the units nor the evaluators know which treatment a subject recieved.
confounding variable
a third variable that potentially affects both the factor and the response variable.
Randomized block design
completely randomized design