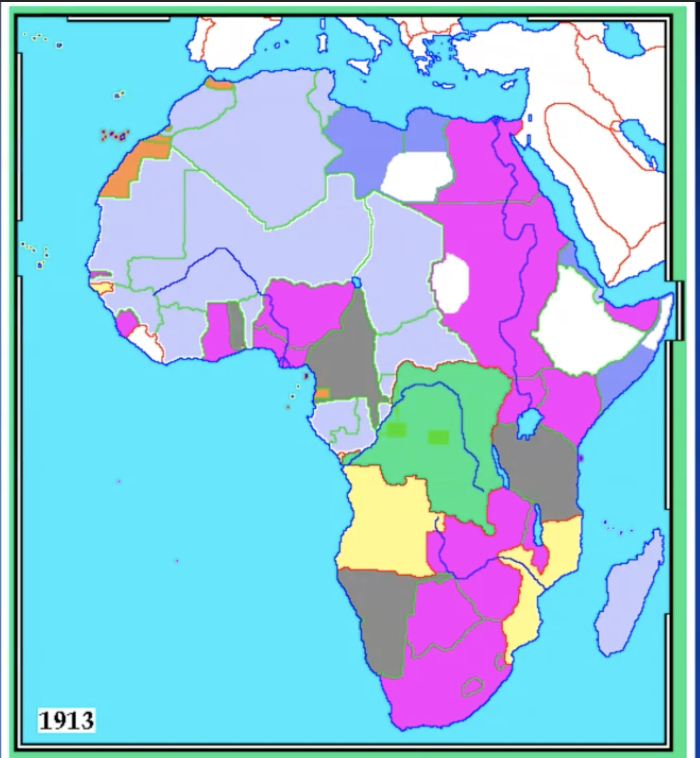
5. history of European colonization chapter 5: Africa
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
1. north africa: algeria, tunesia and egypt 2. the congo 3. southern africa 4. east africa 5. Sudan and the horn 6. west africa 7. north africa
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
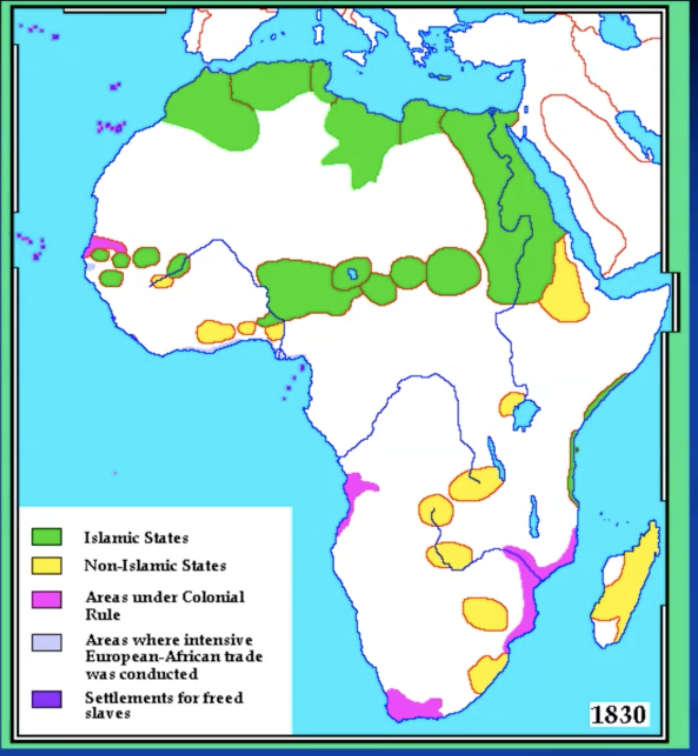
Europeans in africa before the early 19th c
portuguese colonies (first to explore)
Congo, zanzibar, mombasa,… (series of settlements along the coasts)
some lost to Omani arabs in the 17th century
cape colony
1652: Dutch
1795-1802 and 1806-: British
west Africa
related to slave trade
French in Senegal, British in Gambia: forts from 17th c
sierra leone
liberia
gold coast, slave coast, ivory coast: European forst
why such late colonization of Africa
no navigable rivers
rapids and waterfals
vs fedx Caribbean islands or mississippi
malaria
initially thought it was because of bad air, later discovered it was mosquitos
invention of quinine
from the cinchona tree in south america
isolated in 1820; large scale use from the 1850s
the conquest of algeria
precolonial
since 1517: part of the ottoman empire
largely autonomous
the french occupation of algeria
1827: the fan affair (‘affaire de l’éventail)
algiers dey insults the french consul by hitting him with a fan
use it as excuse to conquest
june-july 1830: conquest
to boost charles X’s presige
permanent occupation under Louis-Philippe
fear that British filled in vacuum
rule of in algeria
regular resistance against the French
ex freedom fighter Abd Al-Qadir (1833-37 and 1839-47)
1839: own state and administration of 2/3 of territory
1840: 1/3 of French army in Algeria (a lot of military effort necessary to crush opposition led by abd al-qadir
also after 1852 and 1870
military rule (régime de sabre)
part of france
3 departments/districts of France: Algiers, Oran and Constantine
1865: French citizenship only for non-muslims (apartheid)
colons or pieds-noirs: peasants, criminals, soldiers,…
agriculture on expropriated land
1960: 1 million pieds-noirs vs 9 million indigenous
tunisia
1574 Ottoman, since 1705 great autonomy
1878 awarded to France
after the Russo-Turkish war (russian victory)
treaty of berlin replaces treaty of san stefano
=> great bulgaria (included macedonia)
austria-hungary: Bosnia, Russia: Bessarabia and caucasus, britain: cyprus, france: tunisia, italy: nothing
french hesitancy
internal division after mexican adventure (1860s)
pro-italian environment of Gambetta
1881: french protectorate
after german & british pressure
Egypt
growing political independence from Ottomans
Muhammad Ali (albania) fills vacuum after failed French campaign
instead of official ottoman governor
successors: Pasha Said and Khedive Ismail (gave their names to two major port cities suez canal)
growing economic dependence from Europeans
economic integration and modernization
1820: introduction of cotton (muhammad ali)—> cash-crop monoculture
=> dependent on import cotton
suez canal (shortens travel from Europe to India substantially)
france pro, britain (afraid that it would bring british india closer to Europe) con
1854 concession to ferdinand de lesseps, 1869 completed
public works financed with loans (wanted to turn cairo into new paris)
hausmann’s urban planning in cairo
the ‘veiled protectorate’
growing debts
1875: Egypt sold (forced to) its share in the Suez canal to britain
1876: bankruptcy
1876: caisse de la dette publique (commission of public debt)
french-british condominium (co-rule)
european commissions and ministers
ismail dismissed and succeeded by son taufik (puppet of british and french)
1881: islamitic insurrection of ahmed arabi
britain intervenes and defeats Ahmed Arabi (1882)
france absent due to internal political problems
1882: de facto (‘veiled’) protectorate = unofficial (kept fake announcing that they would give back independence)
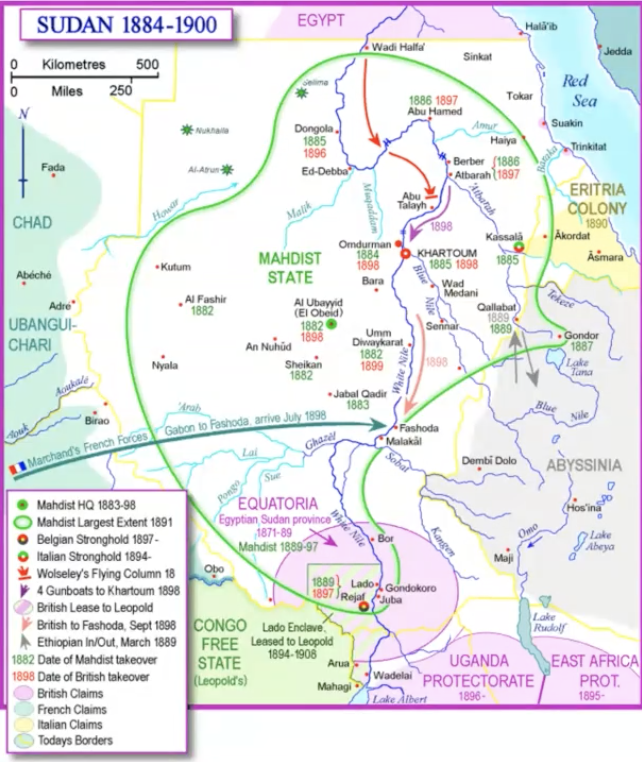
sudan
conquered by Egypt
muhammad Ali: Northern and central sudan
khedive ismail: darfur and south sudan
british: border 100 km from lake victoria
Charles gordon: 1874-77 governor Equatoria; 1877-79 governor-general of sudan
=> “chinese gordon”
the mahdi empire
1881: Muhammad Ahmad proclaimed himself mahdi
mahdi: messianic redeemer of the islamic faith
1883: conquest of territory in Sudan
1884: gordon heads for the defence of Khartoum
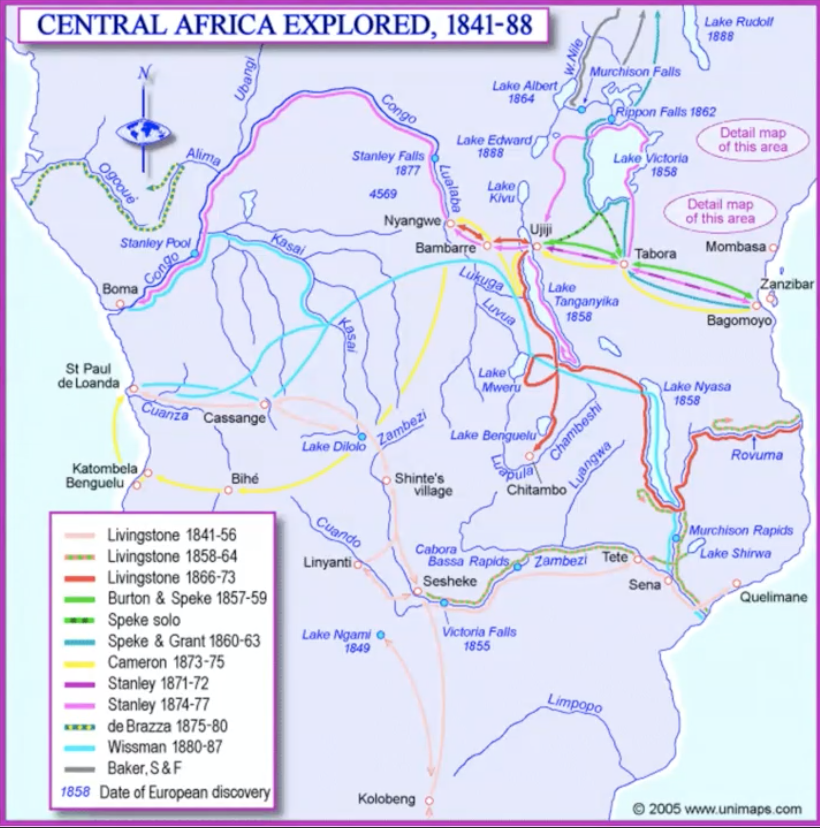
David Livinngstone
1841 as a missionary to south Africa
marriage in 1845, family returned to ENgland in 1852
1853-54 & 1858-64: zambezi (east-west)
first european to see (discover) Victoria Falls
1865: search for the sources of the nile
1868: illness forced him back to Ujiji
10/11/1871: found by Stanley
travelled together for a while
1873: death (in Africa)
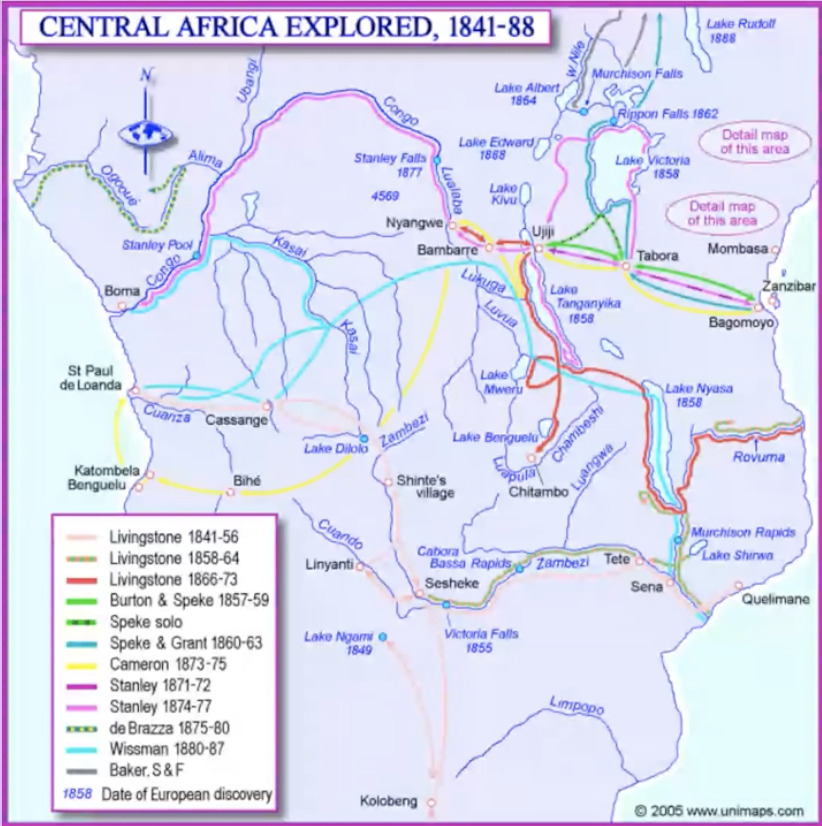
Henry Morton Stanley
in search of Livingstone (1871-72)
as a journalist for NY Herald
trans-africa exploration (1874-77: 1002 days)
tracing the course of the congo to the sea
returned to Europe
1879: return to the congo for the Belgian king
Leopold II
Belgium: disinterest in colonies
more industry than trade
no navy
neutrality
hangover after failed settlement in Guatemala (1845)
leopold II: obsession with colonies
attempts in Philippines, Borneo,…
as a private person and with his own capital
but: belgian networks, loans and benefits
initially (stanley, 1879-): science and philantropy
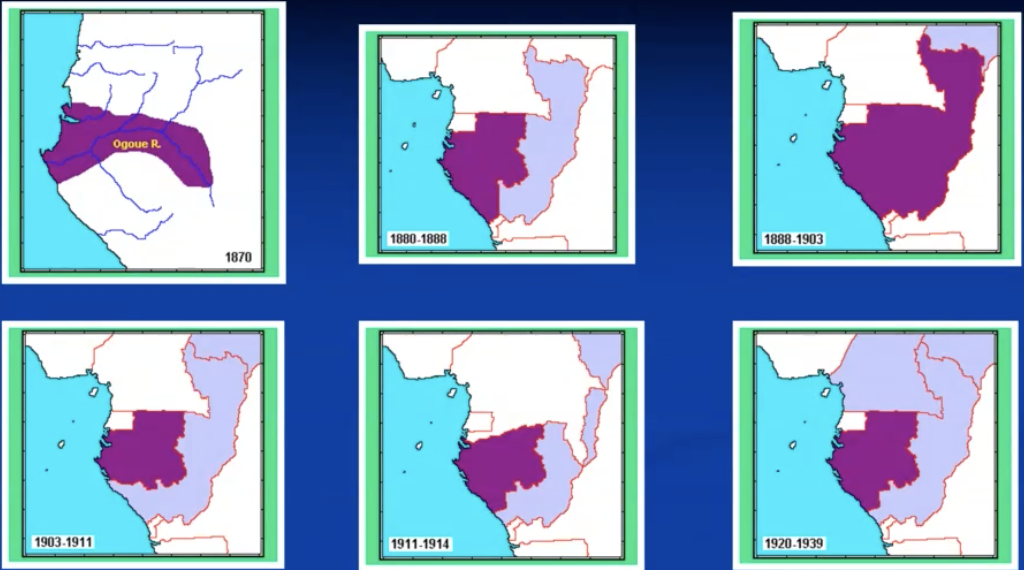
Savorgnan de Brazza
1875-78 exploration of Ogoué and Alima
Italian but worked for French
1879: upper congo
sept-oct 1880 treaties with local rulers
territories ceded to french sovereignty as protectorates
—> colony instead of scientific stations => leopold alarmed
nov 1882 paris ratifies treaties (with local rulers)
Gabon & congo-brazzaville
Leopold II: similar tactics on larger scale in congo
association internationale du Congo (AIC) = not international and not an association but a state
stanley: tribal chiefs transfer power tto the AIC
Leopold and the other European powers
Britain (>< french nationalism)
recognizes portuguese sovereignty of congo estuary (had first settled there and been active for centuries)
leopold II (stations cut off from sea)
launches concept of free state to please the British (no taxes) => thought it would collapse in the end anyway
gives paris droit de préférence
to please the french: receive the congo when AIC fails
to frighten the portuguese, who prefer AIC to France
germany (>< British ambitions, new rival of britain after russia)
bismark was against colonization but did recognize some colonial activities
does not recognize the Anglo-Portuguese treaty
created german colonies
invites diplomats to berlin => conference of Berlin
conference of Berlin
nov 1884- feb 1885
official agreements
free trade on the congo river (leopold doesnt actually put it into practise)
general principles of territorial appropriation
possession or protection after informing other countries
only coastlines, not about the inland
in the corridor
recognition of the congo free state
myth of berlin: ‘division of africa’ = not borders that were drawn but principles of colonization were agreed on
white settlement southern africa
1652 agents of the VOC
way-station on cape (almost mot southern port africa), thus also agriculture (had to supply the stations) => “boers”
also, african and indian slaves (still today a lot of people with indian background in southern africa), french huguenots,…
still lots of leftover references to this period
the rise of the cape colony
cities: cape town and stellenbosch (between cape town and franshoek, still today a lot of houses left over)
farmers gradually move to the north and east (growth of cape colony)
kafir wars/frontier wars (pejorative muslim word for non-believers)
—> only white settler colony in africa (exc algeria)
national identity: afrikaners or boers
kept own language: very close language to dutch
1795-1802 and 1806-: cape colony british (conquered during napoleonic wars)
disintegration british southern african colonies
1835-37: ‘Groot Trek’ (great trek)
unhappy boers migrated away because they were unhappy with British rule
‘voortrekkers’ want land and independence
1838: defeat Zulu (battle of Blood River)
creation of boer republics (1900)
orange free state: recognized by Brits with Bloemfontein 1854
transvaal (andries pretorius —> pretoria): 1852 recognized by britain
paul kruger?
natal: 1843 annexed by british because very strategic position on coast
cape colony
1872 responsible government (natal: 1893)
new kafir wars/frontier wars (in total 9)
Shaka
zulu leader
respected in Europe
==> european imagination —> movies celebrating european victory over strong african enemies
the first boer war
1877: annexation of Transvaal by cape colony (britain)
Disraeli (conservative prime minister britain): federal project (like in canada 1867)
tension growing: boers very keen on independence, had only 40 years ago escaped cape colony (great trek)
1880-81: first boer war
boers’ victory under paul kruger
london recognizes the independence of transvaal
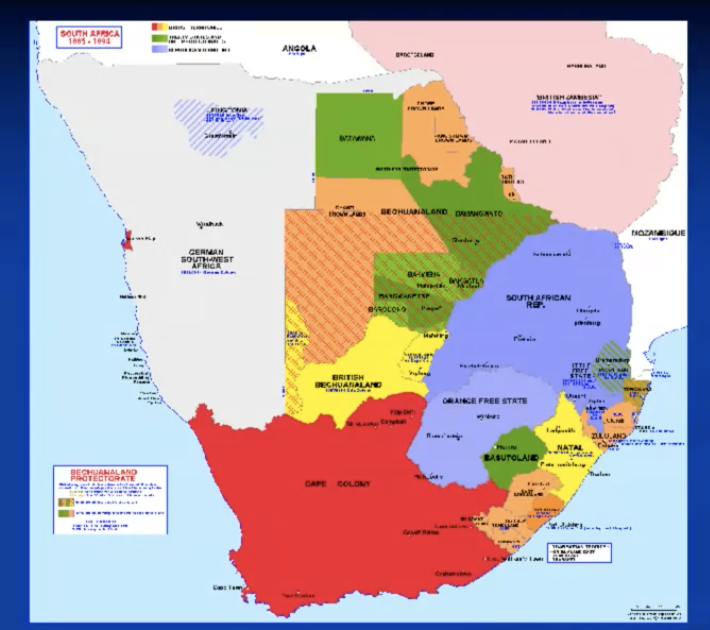
Germans in Southern Africa
germany united in 1870-71 (only then we can start talking about german colonization)
Southwest Africa
Adolf Franz Lüderitz (business)
may 1883: purchases a bay (Lüderitz) from Khoi
aug 1883: new treaty - Lüderitzland (400×150 km) = private person-local governance
Berlin (politics)
promises support and asks about british claims
britain and cape colony: only walvisbaai and some islands
1884: reichsschutz and luderitzland german protectorate
first reichskommisar: Ernst Göring
southeast africa
german exploration in 1884
Britain immediately annexes Santa Lucia Bay
discovery of gems
1867: diamond near Vaal river (Kimberley city) —> border cape colony and transvaal
disputed area, but 1871 annexed by cape colony
1884: gold near witwatersrand (now suburb johannesburg) —> in transvaal
transvaal’s transformation
from agriculture to industry
20% of global gold production
from white to multi-ethnic
immigration
threat to traditional community
‘uitlanders’ (foreign-workers): no political rights = racist society because very conservative boers
cape colony challenges 19th century
transvaal (end 19th century)
power in first boer war
transformation after discovery gold
German (and portuguese) ambitions
danger of german-boer alliance (cape-colony cut of from rest of africa)
portuguese had settlements in angola and mozambique (wanted coast-to-coast colony)
response: expansion in the north (1884-85)
South Bechuanaland (initially separate colony): crown colony
1895 absorbed by cape colony
north bechuanaland: protectorate
british bechuanaland
after independence in 1966: botswana
==> cecil rhodes
Cecil Rhodes
businessman
1871 to south africa, master in merging (de beers: diamonds)
politician
1884 deputy-commissioner bechuanaland
1890-1895 prime minister of cape colony (rival Paul Kruger)
conquistador: british south african company (founded)
1888: treaty with lobengula of matabele tribe (Zimbabwe + zambia and malawi)
1890: with pioneers through zambezia
then: (north/south) rhodesia
now: zimbabwe & zambia
the annexation of rhodesia
arrangements Britain and BSAC (british south africa company
South of zambezi: british protectorate
south rhodesia (later: rhodesia, 1979: Zimbabwe)
north of zambezi: BSAC
Rhodesia/north rhodesia (1964: zambia)
nyasaland (1964: Malawi): British protectorate
=> know present-day zimbabwe, zambia and malawi became british colonies
consequences
transvaal: cut from sea and German SW Africa
Portugal: end of ‘costa to costa’ dream (1891 treaty)
cape colony & britain: project ‘from cape to cairo’ => dominates british agenda after 1890s
1893: defeat of matabele and suicide lobengula
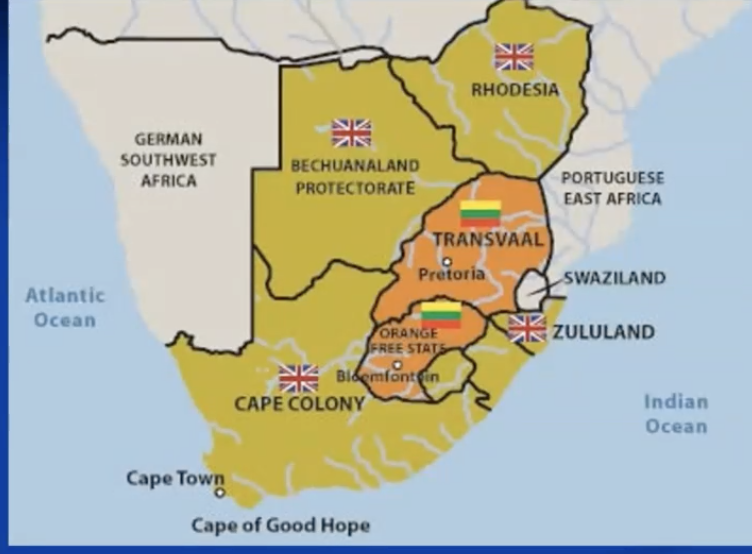
the second boer war
1899-1902
colonial war? => 2 white groups
unequal battle?
empire: initially 35.000 troops, eventually half a million
boers: 100.000 men
but horses, expertise, knowledge, local support
first successes for boers
battle of Spion Kop (many british soldiers died)
european sympathy with boers (ex language connection,…)
no intervention: far and no interest
but: firmness instead of opposition in Britain (determined to win war)
ex Baden Powell and siege of Mafeking (siege relieved by local troups led by robert baden-powell)
british victory
1900: british advance to boer republics
orange free state turned into orange river colony
transvaal turned into transvaal colony
kruger to the netherlands, died 1904
1901-02: boers’ gorilla war and british atrocities
new warfare techniques: railway gun, living hostages, barbed wire, executions,…
concentration camps (civilians are kept, before only soldiers were imprisoned) => british were first to do this on large scale
civil protest in britain
1902: peace of pretoria (british win)
south africa in 20th century
responsible government
1906: transvaal, 1907: Orange river colony
dominion
1910: union of south africa, dominated by boers
independence
1931 (statute of westminster) = independence of white settler colonies
apartheid (1948-1990)
racial legislation from 1910s onwards = former cape colony dominated by boers
voortrekker movement in 1930s = further expanding ideas of apartheid
henddrik verwoerd (in government 1950-1966) => official aparheid regime
nelson mandela (jailed 1962-1990) = first non-white president south-africa
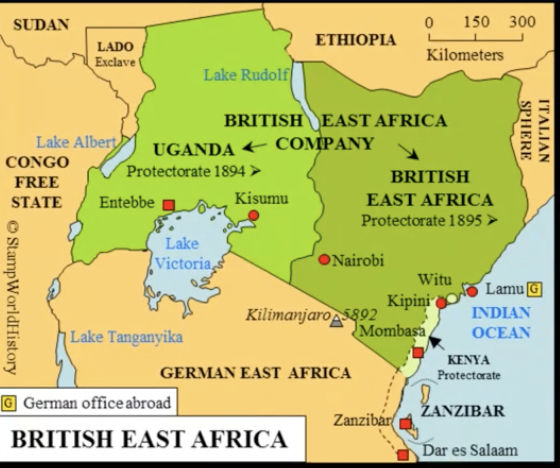
geography and history east africa
3 parts
inland: plateau around great lakes
states of changing size
coast: part of the indian ocean world (arab trade)
17th c: retaken by arbas on portuguese
ex muscat (oman, 1650), Mombasa (Kenia,1698)
formally: imam of oman, in reality autonomous shaikhs
zanzibar: emporium of Afro-Asiatic trade (trade hub indian ocean trade)
influence on east african coast and interior
1840: seat of Oman imam Said bin Sultan
succeeded by two sons (Oman/Zanzibar)
Sultan Barghash in Zanzibar (1870-1888)
interests Europeans in east africa
historical: Portugal (been there since 16th century)
economic: Britain and Germany (were developing trade with east africa)
Strategical: Britain (from cape to cairo)
expeditions europeans in east africa
Carl Peters (nov-dec 1884) = German individual explorer,
did the same as Stanley for Belgian king = twelve treaties of ‘eternal frienship’ with inland tribes
27 feb 1885, day after berlin conference: schutzbrief
the search of Emim Pasha
governor of equatoria (successor to Gordon)
stanley finds Emin near lake Albert (april 1888)
treaties east africa
<=> south africa: wars, north africa: different contexts
following berlin conference
dec 1885: Sultan Zanzibar forced to recognize (if he didnt sign, his island would be attacked)
oct-nov 1886: division of east african inland
british east africa (future Kenya)
Deutsch-Ostafrika (future Tanzania, Rwanda, Burundi)
==> straight border with distortion around Kilimanjaro which became german
dec 1886: southern border with portugal
following tension about Equatoria & Uganda (germany and britain)
1890: Zanzibar Helgoland treaty
Uganda to Britain; border with Congo to Germany
Zanzibar to Britain; Helgoland to Germany (island is north sea near germany, had been taken by britain)
(Madagascar to France)
Pacification
eufemism = not peaceful at all
Germans
1888-1902: 84 huge military operations in german east africa
1905-1906: Maji Maji war => lots of casualties among africans, named after drink Africans believed would turn the bullets into water
British
1894-1914: fifty armed incidents in West Kenya, half of them followed by a penal expedition
French (Madagascar)
Gallieni & Lyautey vs Merina Kingdom
first Franco-Hova War (1883-86)
second Franco-Hova War (1894-95)
French force decimated by fever
==> french end up taking power
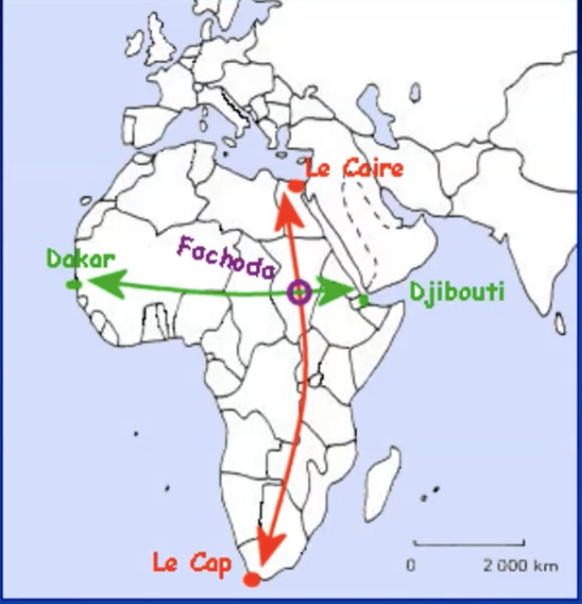
the importance of the Upper-Nile
Britain: protection of Egypt
control irrigation, flood, reclamation,…
from cape to cairo
France: emotional ties
hangovers after Napoleon and 1882
Sudan as the second Sédan
from Dakar to Djibouti
germany and Italy: regional ambitions (both newly erected states)
Leopold II: connection of Congo and Nile (last and least)
1890 & 1894 treaties with Britain not recognized => leopold II out
the horn of africa
the division of Somaliland
Britain: British Somaliland (following Aden in 1839)
France: Djibouti
Italy: Eritrea & Italian Somalia
local resistance (‘Mad Mullah’ until 1905/20 fought presence of Brits in Somalia = Mohammed Abdullah Hassan)
Ethiopia: much stronger
more or less united by ethiopian orthodox church
memory of rich history (still today many sights ex lalibela,…)
ethiopian empire: ca 1137-1917, led by ras (dukes)
claimed descent of king solomon and queen sheba
1887-1889: Menelik II to power thanks to Italian help
Menelik II
stops italian ambitions
refuses italian protectorate (feared total takeover of power)
1896 defeats Italy dear Ad(o)wa => one of the single times african army defeated Europeans => single large african state that was never colonized
40 years later Mussolini took revenge and took control of abessinia (only 10 years)
strikes up a friendship with France
jolts Britain awake
London fears a French-ethiopian alliance
1896: Britain invades Sudan from the north
Mahdiyya hit by famina and war
Egyption financial situation improved
revenge of Gordon (fell in khartoum in 1885 = motivation)
french reaction to british invasion sudan
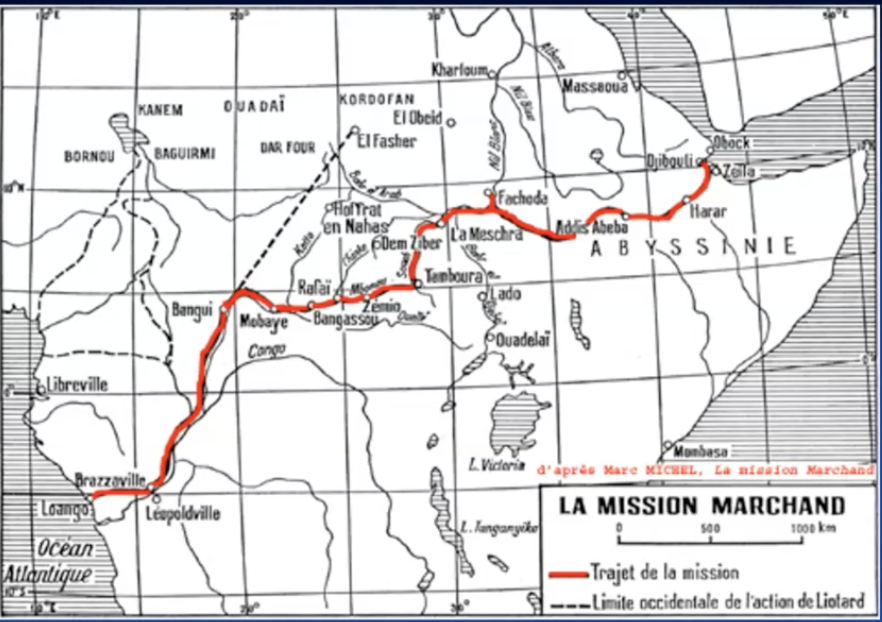
Jean-Baptiste Marchand’s raid to Fashoda (south sudan)
the plan
congo-nile midssion to enhance french presence
stronger position in expected negotiations
the expedition
biggest French expedition in Central AFrica
70.000m textile; 16.000 kg beads; 1.300 l bordeaux wine => presents to local communities
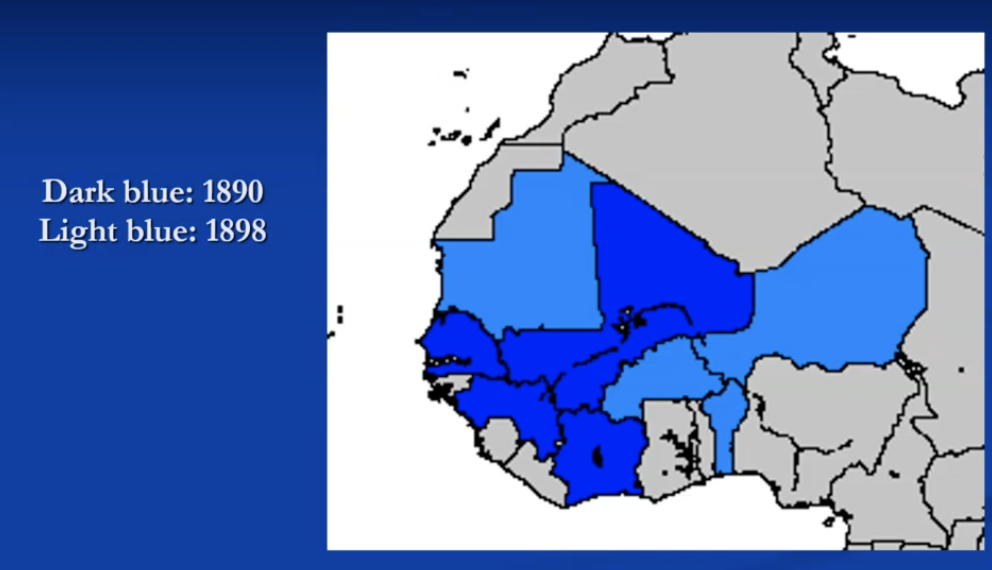
two years: departure 24/7/1996 in Loango, arrival 10/07/1898 Fashoda
=> succesful expedition = first to reach Fashoda
defeats mahdists and establishes French protectorate
the british victory
the reconquest of the sudan
dongola (sept 1896), Omdurman (sep 1898)
18/9/1898 hoists the Egyptian flag in Fashoda = Egypt was controlled by britain so actually just British but good for diplomatic reasons
consequences
Marchand returns home via Djibouti
Sudan becomes an English-Egyptian condominium = no more unclarity around sudan
Menelik unifies Ethiopia (Abessinia Ethiopia)
end to french-british rivalry
1904: entente cordiale
bakcground West Africa
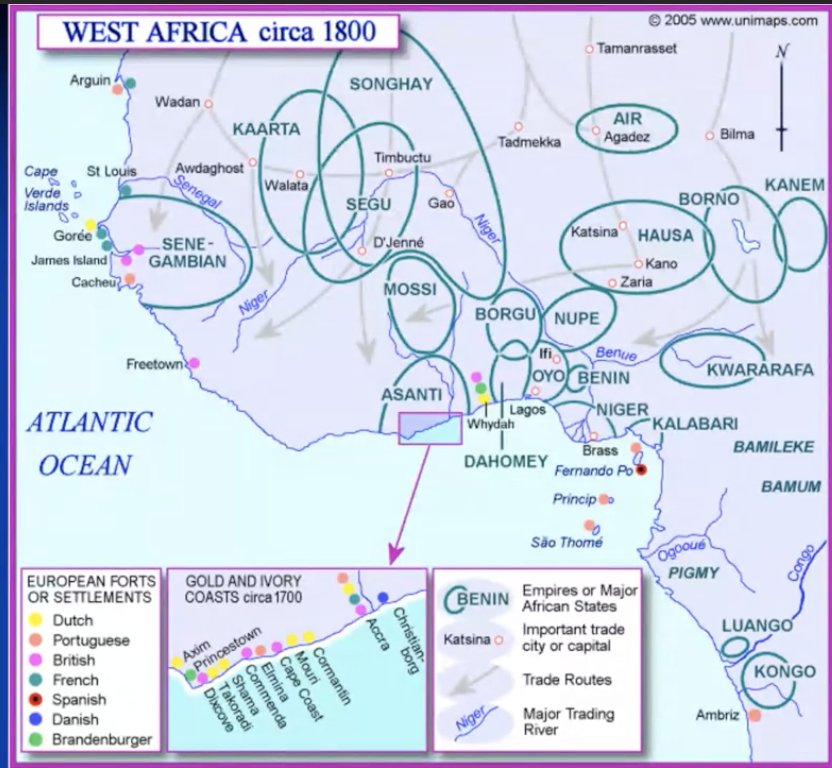
early European prescence: since 15th/16th century = slave fortresses (dutch, danish, british,…)
british and danish leave after abolishment slavery
new ambitions
palm oil after abolitionism
territorial expansion
strong resistance
historical tradition (not as prominent as Ethiopia)
Islam (like ethiopian orthodox church)
strong states ex Samori’s state, tokolor state, asanti, dahomey/Benin (amazones), sokoto caliphate,…
Multi-european presence in west africa
portugal (first for historical reasons)
portuguese guinea (1974: guinea-buissau)
spain
spanish guinea (1968: equatorial guinea)
Britain
Gambia: since 1588 (purchased from Portugal)
Sierra Leone: since 1807 (freetown 1787)
Gold coast colony (1957: Ghana): from 1850s
Lagos (consul since 1849)
the NIger delta (‘Oil Rivers’): from 1877
france
Senegal: since 1659
Ivory Coast: since 1842
Dahomey: after war of 1889-94
guinea: after defeat samori in 1898
United states
1822-47: Liberia
Germany
1884: Gustav Nachtigal in Togoland and Cameroon
unifying the French colonies
afrique occidentale française
1890 & 1898: treaties with britain
rivalry was over
no british concern: regarded sahara as a giant sandbox
new ambition: AOF with rest of french colonies
Algeria
1890 on paper, gradual conquest
djibouti
failed after fashoda
afrique-equatoriale française
Gabon & congo: pre 1885
Ubangi-shari (1894) => present day central african republic, chad (1900)
link with AOF?
European interest in Morocco
Spain
closest position
longest presence: Ceuta (since 1580)
Britain
Gibraltar (since 1704/13)
France
Algeria (regular border incidents)
germany
prestige: does not want to be neglected
Italy
frustrated after Adwa (interested in creating new roman empire)
european penetration in Morocco
similar developments as Tunisia and Egypt
growing economic dependence
1856&1863: Britain and France conclude trade treaties
growing political interference
1859: Spain conquers Tetuan and Melilla (still spanish today) after war
different outcome: conference of Madrid (1880)
Equal trade opportunities maintained for all
territorial integrity of Morocco preserved (similar as china in 20th c)
(Berlin conference 1884: western sahara to spain until 1975)
the first moroccan crisis (1905-1906)
german concerns
entente cordiale between France and Britain (1904) = used to be eternal rivals
French attempts to establish protectorate over Morocco = frustrated after fashoda
war?
1905: Wilhelm II visits Tangier
military threat to challenge entente cordiale
1906: Algeciras conference
britain supports france
french and spanish officers in morocco
(1907: triple entente with russia
the second moroccan crisis (1911-12)
1911: rebellion against sultan Abdelhafid
france intervenes
spain conquers larache
germany intimidates with gunboat panther in agadir
1912: treaty of Fez
Abdelhafid abdicates (successor: Yusef, his brother)
france establishes protectorate over morocco (becomes french colony)
pacification lasts until 1934
germany receives Neukamerun (part French Congo) => french west africa and east africa were never united
spain receives territory in south and north
italy receives Libya (war with ottomans 1911-1912)