exam 3
1/282
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
283 Terms
most abundant biomolecule in nature
carbohydrates
cellular functions of carbs
energy, structure, communication, precursurs for other biomolecules
what types of energy do carbohydrates link
solar energy and chemical bond energy
monosaccharides
simple sugars
polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones
aldoses
monosaccharides with an aldehyde functional group
ketoses
monosaccharides with a ketone functional group
how are carbohydrates classified
aldose/ketose
number of carbon atoms/the functional groups they contain
triose
3 carbon carbohydrate
tetrose
4 carbon carbohydrate
pentose
5 carbon carbohydrate
hexose
6 carbon carbohydrate
most abundant types of carbs in living systems
pentoses and hexoses
monosaccharide stereoisomers
increase in number of chiral carbon increases the number of possible optical isomers
2^n where n is number of chiral carbons
what are all monosaccharides derived from
D-glyceraldehyde or nonchiral dihydroxyacetone
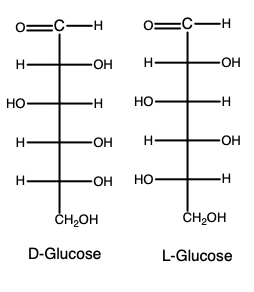
how to determine if monosaccharide is D or L
look at chiral carbon furthest from carbonyl
D : hydroxyl on right
rotates light clockwise
L : hydroxyl on left
rotates light counterclockwise
what form are almost all naturally occurring monosaccharides
D
how to determine D or L of carbohydrate
reference carbon is the asymmetric carbon furthest from the carbonyl carbon
diastereomers
stereoisomers that are not enantiomers
enantiomer
nonsuperimposable mirror image
epimers
diastereomers that differ at a single chiral carbon
sugars with more than _____ carbons primarily exist in cyclic forms
4
how does ring structure occur in monosaccharides
aldehyde and ketone groups react reversibly with hydroxyl groups in an aqueous solution to form hemiacetals and hemiketals
anomers
2 possible diastereomers that form because of cyclization
glucose structure
haworth structures
more accurately depict bond angle and length in ring structures than the original Fischer structures
drawing haworth from fischer
if OH is on the left in the fischer, it is up in the haworth
if OH is on the right in the fischer, it is down in the haworth
last carbon faces up
alpha vs beta forms
In the D-sugar form, when the anomer hydroxyl is up, it gives a b-anomeric form while down gives the a-anomeric form
furanoses
5-membered rings with an oxyen
pyranoses
6-membered rings with an oxygen
cyclic form of fructose
fructofuranose
glucose in the pyranos form
glucopyranose
anomeric carbon
carbon that was the aldehyde in the fischer projection but has OH in haworth structure
can shift back to the carbonyl and react as such
C1 in glucose, C2 in fructose
mutarotation
spontaneous process in which alpha and beta forms of monosaccharides are readily interconverted in aqueous environments
ring form opens back to chain then forms ring again in different form
produces a mixture of alpha and beta forms in both furanose and pyranose ring structures
which form can participate in redox reactions
open chain form
which form is most stable
ring form
which groups in monosaccharides can react
carbonyl and hydroxyl groups
most important reactions of monosaccharides
oxidation
reduction
isomerization
esterification
glycoside formation
glycosylation reactions
oxidation
monosaccharides may readily undergo several oxidation reactions in the presence of metal ions or certain enzymes
what are aldehydes oxidized to
carboxylic acid
what are primary alcohols oxidized to
aldehyde
isomerization
switching between open chain to ring
mutarotation
D-glucose incubated in an alkaline solution for several hours produces 2 isomers: D-mannose and D-fructose
both involve enediol intermediate
what does the enediol intermediate allow for
aldose-ketose interconversion and epimerization
epimerization
glucose converted to mannose
reducing sugars
sugars that can be oxidized by weak oxidizing agents such as Benedicts reagents
NOT a reduced sugar
have free anomeric carbon that can open up and react
what does a sugar need to be a reducing sugar
open chain
all aldoses are reducing sugars
ketoses such as fructose due to isomerization
glycoside formation
hemiacetals and hemiketals react with alcohols form the corresponding acetal and ketal
when cyclic hemiacetal or hemiketal form of the monosaccharide reacts with an alcohol, the new linkage is a glycosidic linkage and the compound is a glycoside
disaccharide formation
acetal linkage formed between hemiacetal hydroxyl of one monosaccharide and the hydroxyl of another
polysaccharide formation
large numbers of monosaccharides are linked together through acetal linkages
glucose (d-glucose)
originally called dextrose
blood sugar
found in large quantities throughout natural world
primary fuel for living cells
preferred energy source for brain cells and cells without mitochondria (erythrocytes)
fructose (d-fructose)
fruit sugar because high content in fruit
twice as sweet as sucrose per gram
often used as a sweetening agent in processed foods
sperm use fructose as an energy source
galactose
necessary to synthesize variety of important biomolecules
lactose, glycolypids, phospholipids, proteoglycan, glycoproteins
epimer of glucose
galactosemia
genetic disorder resulting from a missing enzyme in galactose metabolism
monosaccharide derivatives
amino sugars
deoxy sugars
amino sugars
hydroxyl group (usually on C2) replaced with amine group
most common are d-glucosamine and d-galactosamine and are often attached to proteins or lipids
deoxy sugars
monosaccharides that have an OH replaced by an H or CH3
reduced sugar
2-deoxy-d-ribose is pentose sugar of DNA
fucose (6-deoxygalactose) is part of ABO blood group determination
disaccharides
two monosaccharides linked by a glycosidic bond (covalent)
how are linkages named for disaccharides
α and β confirmation of anomeric carbon
which carbons are connected
hemiacetal
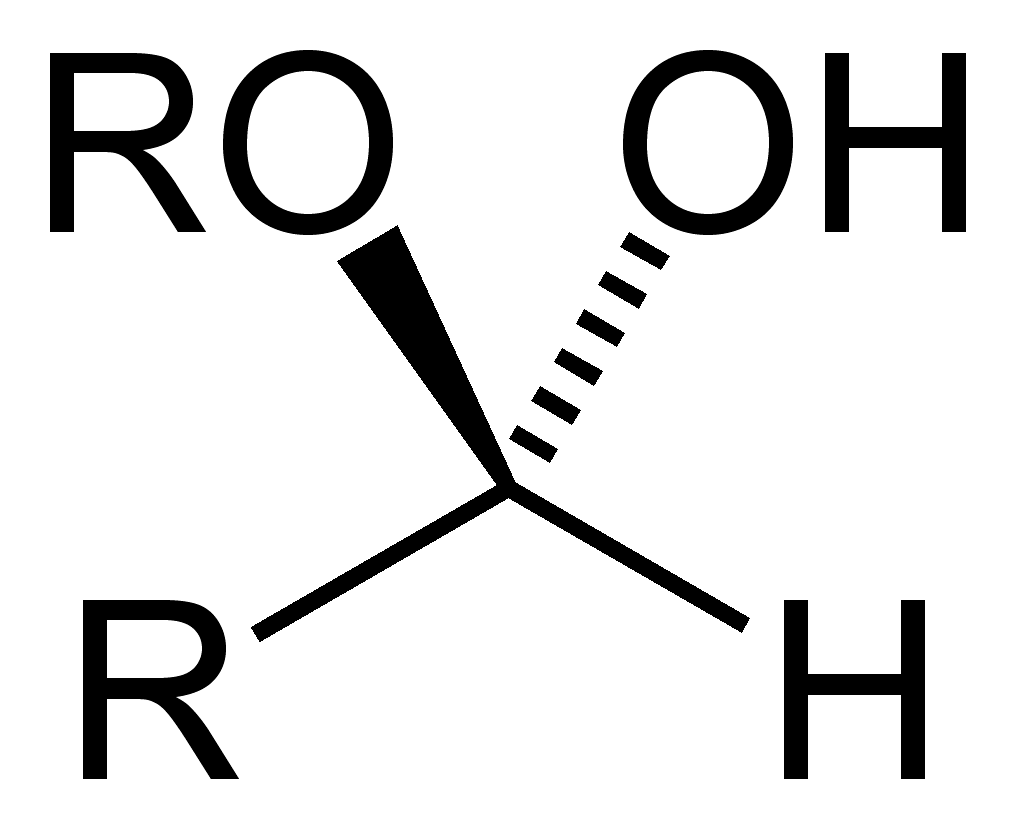
hemiketal
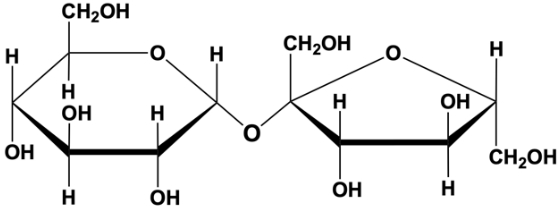
lactose
milk sugar
disaccharide found in milk
one molecule of galactose linked to one molecule of glucose
β(1,4) linkage
deficiency of lactase is common
reducing sugar
maltose
disaccharide
malt sugar
intermediate product of starch hydrolysis
α(1,4) linkage between two molecules of glucose
does not exist freely in nature
how to determine α vs β in disaccharides
difference in free anomeric carbon
what type of sugars can be absorbed in the digestive tract?
monosaccharides
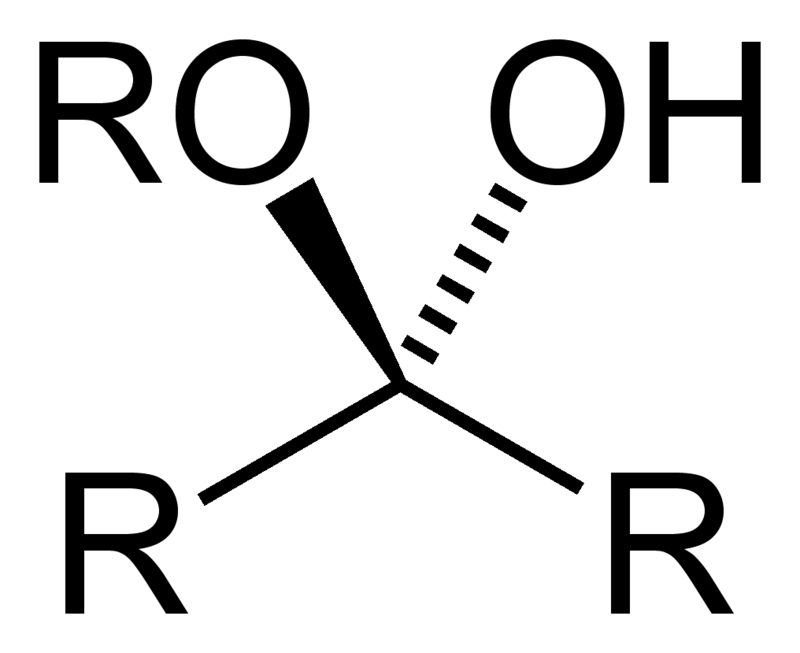
α glycosidic bond
β glycosidic bond
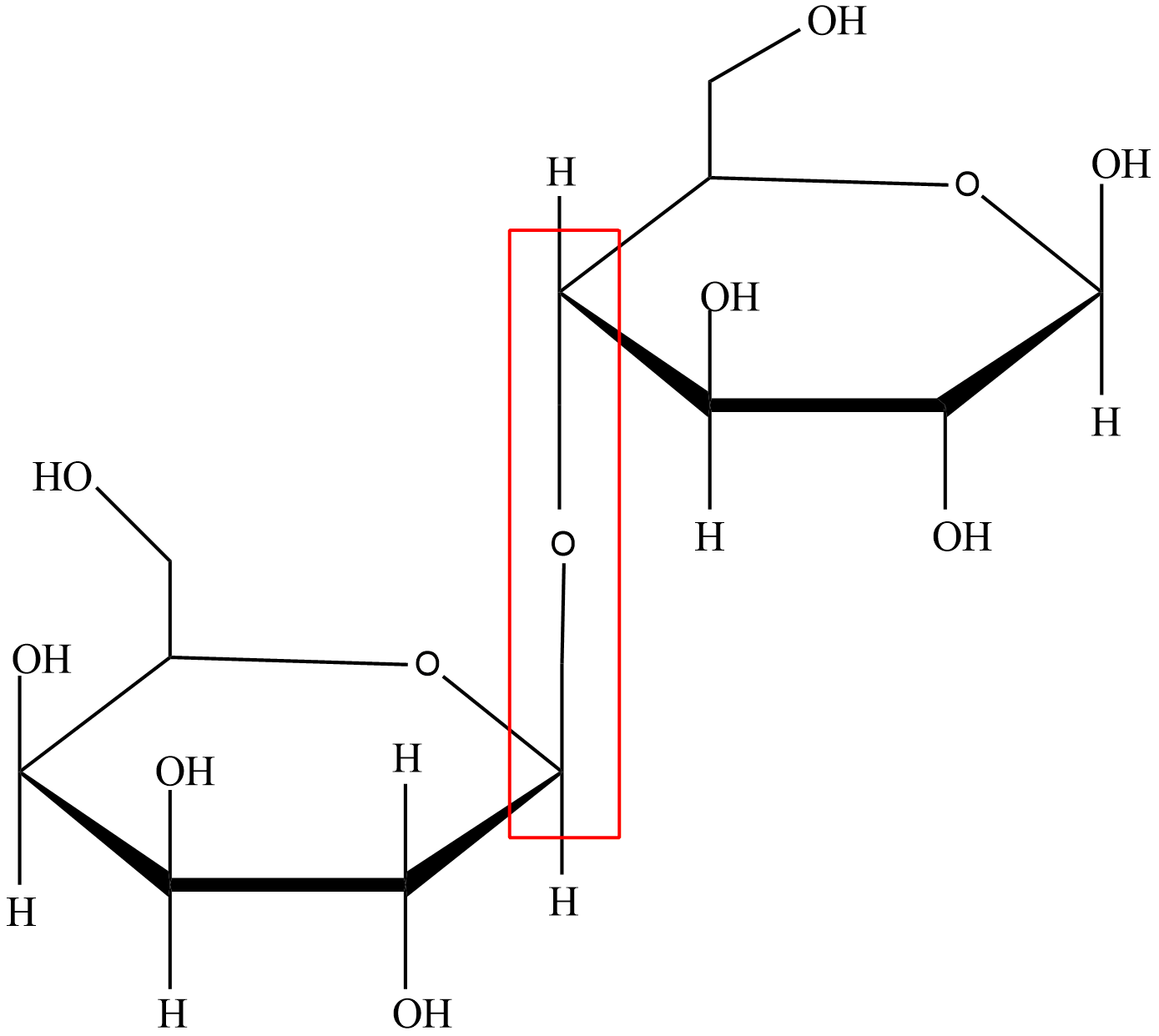
cellubiose
disaccharide
degradation product of cellulose
composed of two molecules of glucose linked with a β(1,4) bond
does not exist freely in nature
sucrose
disaccharide
table sugar (cane/beet sugar)
produced in leaves and stems of plants
one molecule of glucose linked to one molecule of fructose by an α,β(1,2) glycosidic bond
glycosidic bond between both anomeric carbons
nonreducing sugar
polysaccharides (glycans)
composed of large numbers of monosaccharides connected by glycosidic linkages
oligosaccharides
smaller glycans made of 10-15 monomers
most often attached to polypeptides as glycoproteins
2 classes of oligosaccharides
N- and O-linked
classes of polysaccharides
homoglycans and heteroglycans
polysaccharides can be ___________ or __________ in shape
linear; branched
homoglycans
have one type of monosaccharide and are found in starch, glycogen, cellulose, chitin
no fixed molecular weight because size is reflection of the metabolic state of cell producing them
starch and glycogen are ___________ molecles while chitin and cellulose are _________
energy storage; structural
chitin
polysaccharide
part of cell wall of arthropod exoskeleton
acetyl group and amine bound to glucose
cellulose
polysaccharide
primary component of plant cell walls
starch
polysaccharide
energy resevoir of plant cells and a significant source of carbohydrate in the human diet
two polysaccharides together: amylose and amylopectin
amylose
composed of long unbranched chains of D-glucose with α(1,4) bonds
thousands of glucose monomers
amylopectin
branched polymer
α(1,6) and β(1,4) linkages between glucoses
branch points every 20-25 residues (moderately)
glycogen
polysaccharide
carb storage molecule in vertebrates found in greatest abundance in liver and muscle cells
similar in structure to amylopectin, with more branch points (every 10-highly branched)
more compact and easily mobilized than other polysaccharides
glucoses linked by α(1,4) and α(1,6)
α(1,6) is branch point
cellulose
polymer of D-glucopyranosides linked by beta(1,4) glycosidic bonds
unbranched
made of 12,000 glucose units
most abundant organic substance on earth
cellulose
most important structural polysaccharide of plants
cellulose
myofibrils
pairs of unbranched cellulose molecules held together by hydrogen bonding to form sheetlike strips
tough and inflexible
high tensile strength
heteroglycans
high molecular-weight carbohydrate polymers that contain more than one type of monosaccharide
major types of heteroglycans
N and O linked glucosaminoglycans (glycans)
glycan components of glycolipids
GPI anchors
GPI
glycolsylphosphatidylinosotol
N and O glycans
many proteins have N and O linked oligosaccharides
N linked: liked via b-glycosidic bond
bond through amino group
O linked: disaccharide core of galactosyl-β-(1,3)-N-acetylgalactosamine linked via a α-glycosydic bond to the hydroxyl of serine or threonine residues
bond through O
glycoconjugates
result from carbohydrates being linked to proteins and lipids
proteoglycans
distinguished from other glycoproteins by high carbohydrate content (95%)
occur on cell surfaces or are secreted to ECM
all contain heteroglycan chain that are linked to core proteins by N and O glycosidic bonds
have roles in organizing ECM and involved in signal transduction
metabolism of proteoglycans involved in many genetic disorders, including Hurler’s syndrome
aggrecan
type of proteoglycan that is found in abundance in cartilage
core protein linked to over 100 chondroitin sulfate and 40 keratin sulfate chains
up to 100 aggrecans are attached to hyaluronic acid to form proteoglycan aggregate
glycoproteins
proteins that are covalently linked to carbohydrates through N and O linkages
several addition reactions in lumen of ER and Golgi are responsible for final N linked oligosaccharide structure
O glycan synthesis occurs later, probably in Golgi
carb could be 1%-85% of total weight
functions of glycoproteins
enzymes
blood clotting
hormone
receptor proteins
transport proteins
cell adhesion
the sugar code
sugars placed on molecules that change function, has ability to encode information in cell
living organisms require large coding capacities for information transfer because of profound complexity of functioning systems
to succeed as a coding mechanism, a class of molecules must have a large capacity for variation
more possibilities with hexasaccharides than hexapeptides
most important posttranslational modification in terms of coding capacity
glycosylation
glycome
total set of sugars and glycans in cell or organism
constantly in flux depending on cell’s response to environment (different than genome)
no template for glycan biosynthesis; done in a stepwise process
glycoforms
can result based on slight variations in glycan composition of each glycoprotein
catabolism
the degradation of fuel molecules which provides energy for cellular energy-requiring functions
cells use an energy conversion strategy that oxidizes glucose
small amounts of energy are released at several points in this pathway
energy is harvested and stored in bonds of ATP
universal energy currency
ATP (adenoside triphosphate)