ANS 123 - Neurulation
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Neurulation
formation of spinal cord precursors from epiblast
induction events and formation of neural tube
When does neurulation occur?
end of gastrulation, as primitive streak regresses
where does central nervous tissue develop from?
ectoderm origin
how does neurulation begin and end?
begins with 1st traces of neural plate cells
ends with closure of neural tube
after notochord is formed during regression, how are neural plate cells formed?
notochord sends signals to epiblast cells to become plate cells
Morphogenesis
Generation, differentiation & growth of tissues and organs during development; process through which organisms take on shape
what is the neural tube a rudiment of?
CNS
what does the neural tube eventually become?
adult brain and adult spinal column
the process of neurulation is specific to ___
chordates
notochord
temporary rod of mesoderm under midline of epiblast that triggers neural tube formation
notochord is activated by what?
induction messages from hensen's node as it moves backward
what doe notochord formation induce?
once formed it sends signals back up to epiblast ectoderm to initiate CNS formation - neural plate
is notochord a temporary structure?
yes
true or false: notochord may be involved in bone structure of spinal column
true
primordial CNS orgin
ectoderm
How does primordial CNS form
via invagination
1. notochord induces epiblast ectoderm -> form neural plate cells
2. bending of neural plate into neural groove
3.closure/pinch off neural groove (separate from ectoderm) into neural tube
neural crest cells
Cells at the tip of the neural fold; sluff off upon invagination into blastoceal
sequence of neurlation events happen in which direction?
anterior -> posterior
Describe sequence of events for neurlation.
1. during ingression epiblast cells differentiate into mesoderm within blastocel
2. hensen's node at anterior most portion of primitive streak activates mesoderm to form notochord during regression
3. notochord messages to ectoderm to determinate & differeniate into neural plate cells
4. invagination of neural plate into groove, pinching off and form neural tube
5. neural tube becomes CNS
what does the anterior most part of neural tube become?
thickening and constrictions via cell division - presumptive brain @ 3 weeks
what does the posterior most part of neural tube become?
stays tube like - spinal chord
what three vesicles from the presumptive brain?
prosencephalon (forebrain anterior)
mesencephalon (midbrain)
rhombencephalon (hind brain posterior)
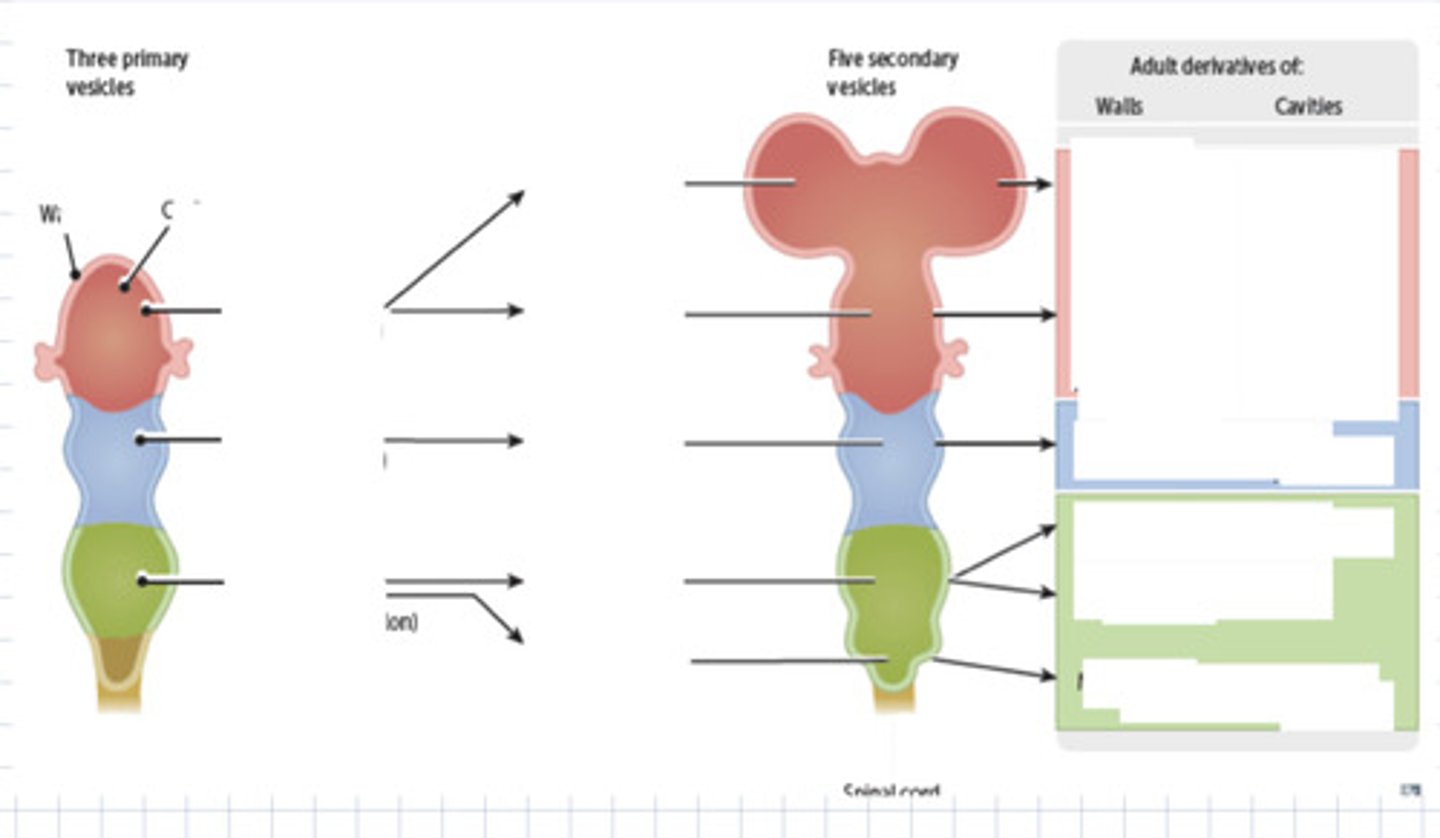
Which one of the three layers does not split>
mesencephalon
three vesciles in brain become five, what are they?
- prosencephalon (forebrain) -> telencephalon & diencephalon
- mesencephalon
- rhombencephalon -> metencephalon & myelencephalon
walls of the neural tube are made from which germ layer?
ectoderm
why does the prosencephalon have two blob shape?
important structure for eyes -> send signals to formulate brain tissue for optic nerve -> retina
the walls of the presumptive brain eventually become what?
the actually brain parts we know like cerebrum
the cavities of the presumptive brain eventually become what?
ventricles