Acute Etiologies of Neurogenic Communication Disorders
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1
New cards
Etiology
underlying medical cause of a symptom or deficit
2
New cards
Etiologies of Neurogenic Communication Disorders
* Stroke
* TBI
* Surgical trauma
* Degenerative disorders
* Infectious diseases
* TBI
* Surgical trauma
* Degenerative disorders
* Infectious diseases
3
New cards
Idiopathic etiology
deficits or symptoms that are of an unknown cause
4
New cards
Central Nervous System
brain + spinal cord
5
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System
somatic (voluntary) and autonomic nervous (involuntary) system
6
New cards
Cerebrovascular Accident (CVA)
also known as a STROKE
7
New cards
Stroke
* 3rd leading cause of death in the US
* death is more common in women than men
* can occur within any area of the brain or brainstem
* death is more common in women than men
* can occur within any area of the brain or brainstem
8
New cards
Factors that increase risk of strokes
Tobacco use, physical inactivity, atrial fibrillation, high blood pressure
9
New cards
Cause of Strokes
Brain tissue is permanently destroyed or temporarily does not function due to the decreased or absent blood supply to affected brain tissue
10
New cards
Anoxia
**complete** lack of oxygen to a cell
11
New cards
Hypoxia
**partial** lack of oxygen to a cell
12
New cards
6 to 8 minutes
how long the brain can survive without oxygen
13
New cards
Ischemic Stroke
Occurs when a blood vessel in the brain is occluded (makes up the majority of strokes)
\
Symptoms include:
* loss of strength/sensation in one half of the body
* problems with speech and language
* changes in vison/balance
\
Symptoms include:
* loss of strength/sensation in one half of the body
* problems with speech and language
* changes in vison/balance
14
New cards
Thrombotic, embolic, and transient
three types of ischemic strokes
15
New cards
Ischemic core/infarct
Location of the focal damage of tissue within the brain following the stroke
The death of cells is called tissue necrosis and is irreversible
The death of cells is called tissue necrosis and is irreversible
16
New cards
Ischemic penumbra
Surrounds the ischemic core
Too much blood lost to function but is still receiving enough blood to stay alive
Damage to penumbra can be reversed within two to four hours of medical attention
Too much blood lost to function but is still receiving enough blood to stay alive
Damage to penumbra can be reversed within two to four hours of medical attention
17
New cards
Thrombotic Stroke
Occurs when a thrombus forms and interrupts blood flow within the brain
18
New cards
Thrombus
An occlusion of blood vessels within the brain, usually due to atherosclerosis
19
New cards
Atherosclerosis
The build-up of fatty materials that accumulate slowly on the walls of the arteries, narrowing them and restricting blood supply
20
New cards
Embolic Stroke
Occurs when an embolus lodges within a blood vessel inside the brain and cuts off blood circulation to part of the brain
21
New cards
Embolus
A mass traveling through the circulatory system that lodges in a blood vessel in the brain
22
New cards
How a thrombus becomes an embolus
If a piece of a thrombus breaks off, travels, and lodges itself within a vessel to interrupt circulation within the brain
23
New cards
Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
“Mini stroke” or small Ischemia in the brain that resolves itself in 24 hours, and does not cause permanent deficits unless TIAs are returning
May be a warning sign of a larger oncoming stroke
May be a warning sign of a larger oncoming stroke
24
New cards
Hemorrhagic Stroke
Occurs when a blood vessel within the brain ruptures, spilling blood into the brain and depriving the brain of blood flow
\
Symptoms include…
* severe headache
* nausea
* vomitting
\
Symptoms include…
* severe headache
* nausea
* vomitting
25
New cards
Causes of Hemorrhagic Strokes
Type of stroke common in individuals who…
* Have high blood pressure or hypertension
* Are engaged in high periods of physical activity
* Have a history of hemorrhagic strokes
* Experience alcohol abuse
* Have high blood pressure or hypertension
* Are engaged in high periods of physical activity
* Have a history of hemorrhagic strokes
* Experience alcohol abuse
26
New cards
Subarachnoid and Intracerebral
Two types of hemorrhagic strokes
27
New cards
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Occurs when there is a bleed between the surface of the cerebrum and the skull
28
New cards
Subarachnoid space
The area between the layers of tissue that protect the cerebrum
29
New cards
Intracerebral Hemorrage
Occurs when a blood vessel bursts within the brain itself
30
New cards
Hemorrhagic stroke damage
Three mechanisms of damage may occur:
* Blood supply to a portion of the brain has been interrupted due to a broken or burst blood vessel
* Blood spills out into the brain where it does not belong and causes damage
* Intracranial pressure increases due to the continued release of blood into the brain or between the surface of the brain and cranium
* Blood supply to a portion of the brain has been interrupted due to a broken or burst blood vessel
* Blood spills out into the brain where it does not belong and causes damage
* Intracranial pressure increases due to the continued release of blood into the brain or between the surface of the brain and cranium
31
New cards
Aneurysm
An abnormal stretching or ballooning out of the wall of a blood vessel due to disease/hereditary factors or hypertension/atherosclerosis
Usually occurs in the Circle of Willis
\
Symptoms include…
* severe headache
* nausea
* vomiting
* blurred vision
* sensitivity to light
* seizures
* loss of consciousness
Usually occurs in the Circle of Willis
\
Symptoms include…
* severe headache
* nausea
* vomiting
* blurred vision
* sensitivity to light
* seizures
* loss of consciousness
32
New cards
Circle of Willis
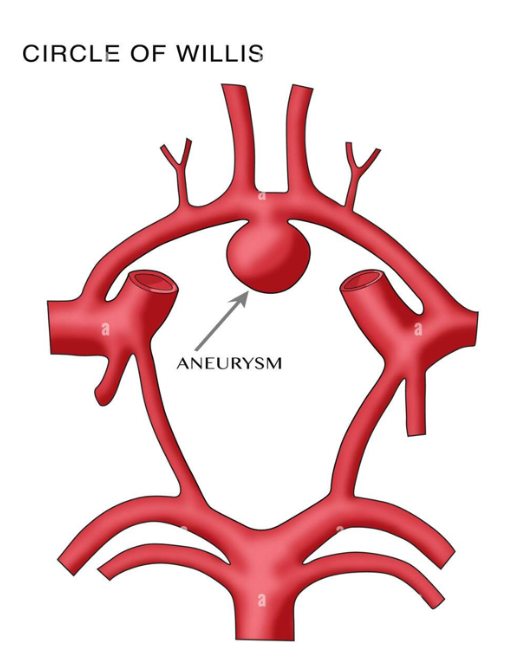
33
New cards
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
Serious and life-threatening brain damage that is the result of an external and forceful event
The immediate impact ranges from mild concussion, to coma, to death
Language and cognitive deficits are varied and complex, depending on what areas of the brain were damaged and to what extent
The immediate impact ranges from mild concussion, to coma, to death
Language and cognitive deficits are varied and complex, depending on what areas of the brain were damaged and to what extent
34
New cards
Neoplasm
Abnormal growth of cells in the brain that serve no purpose to the body
35
New cards
Oligodendroglioma
Tumors composed of myelin-producing cells (called oligodendrocytes)
36
New cards
Primary Tumor
Brain tumor that originates in the brain
37
New cards
Secondary Tumor
Cancerous tumor that spreads from another part of the body to the brain
38
New cards
Biopsy
Surgery to remove a piece of tissue for testing
39
New cards
Malignant brain tumors
Brain tumors that cause brain cancer
Grow quickly and spread to other body parts, so they must be treated with surgical removal and radiation
Grow quickly and spread to other body parts, so they must be treated with surgical removal and radiation
40
New cards
Benign brain tumors
Cannon spread to other parts of the body
Mass effect may occur
Mass effect may occur
41
New cards
Surgical Trauma
Damage to brain tissue that may occur during brain surgery
May result in acquired speech, language/cognitive/swallowing deficits, secondary seizures, additional CVAs, infections, and increased intracranial pressure
May result in acquired speech, language/cognitive/swallowing deficits, secondary seizures, additional CVAs, infections, and increased intracranial pressure
42
New cards
Infection
Cause damage to the CNS and PNS, impacting cognition, motor, and language
43
New cards
types of infection
viral, fungal, bacterial, parasitic
44
New cards
Encephalitis
An acute infection and inflammation of the brain or spinal cord that is caused by a virus or bacterial infection
\
Two types:
* Encephalitis Lethargica
* Rasmussen’s Encephalitis
\
Two types:
* Encephalitis Lethargica
* Rasmussen’s Encephalitis
45
New cards
Encephalitis Lethargica
Inflammation and damage to midbrain, basal ganglia, and substantia nigra
Display parkinsonian features
Difficulty initiating/ controlling volitional movement, inhibiting nonvolitional movement
Display parkinsonian features
Difficulty initiating/ controlling volitional movement, inhibiting nonvolitional movement
46
New cards
Rasmussen’s Encephalitis
Idiopathic
Inflammation in left or right cerebral hemisphere
Unilateral tremor in an extremity contralateral to affected hemisphere
Hemispherectomy: removal of portions of or entire cerebral hemisphere
Inflammation in left or right cerebral hemisphere
Unilateral tremor in an extremity contralateral to affected hemisphere
Hemispherectomy: removal of portions of or entire cerebral hemisphere
47
New cards
HIV/AIDS
A sexually transmitted disease that weakens the immune system (NeuroAIDS, HIV/AIDS, dementia)
48
New cards
Neurological symptoms of AIDS
Inability to learn new information, slowed processing, disfluent speech, impaired recall, reduced attention
Language is often unaffected!!
Language is often unaffected!!
49
New cards
Creutzfeldt-Jacob Disease
Degerative and fatal brain disease t caused by a prion