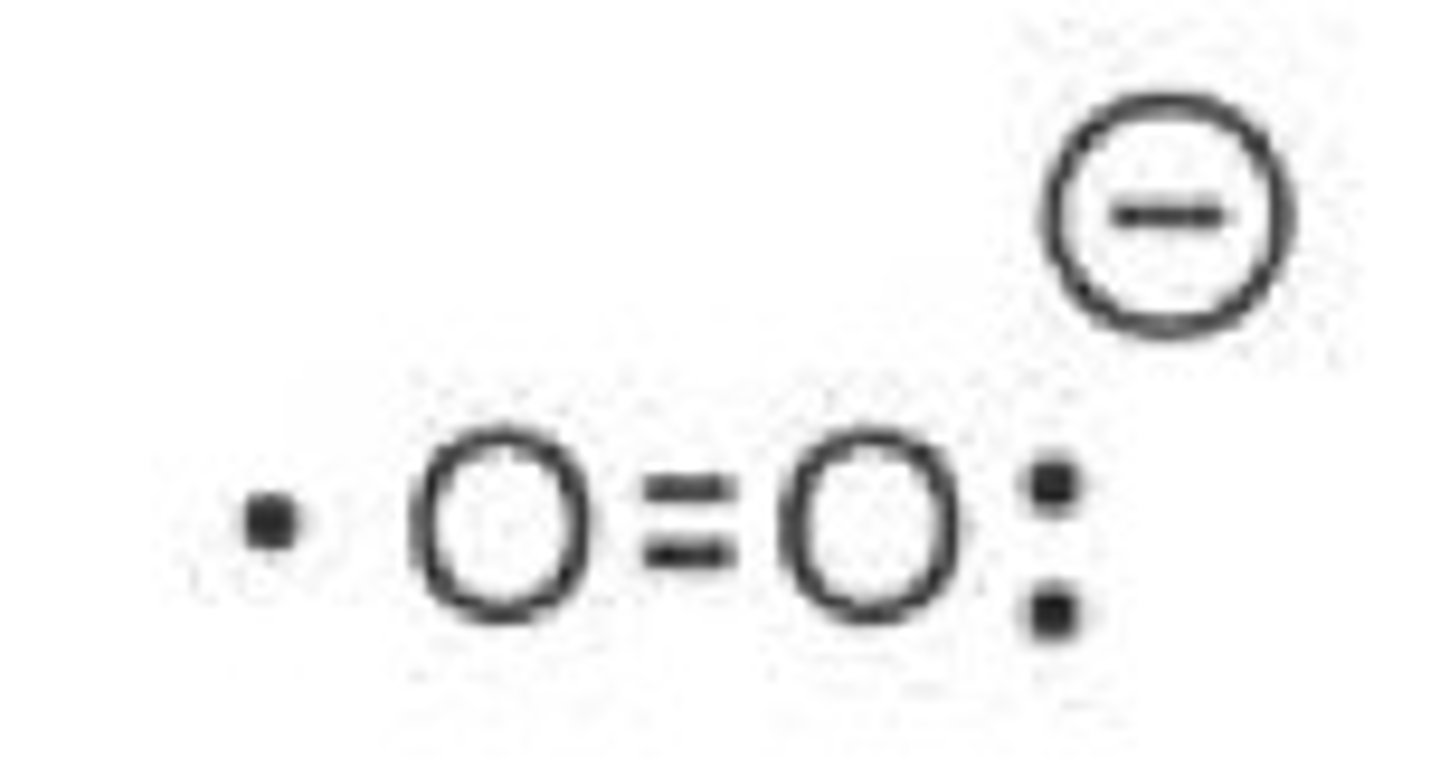Lecture 9- Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Free Radicals
Molecules with unpaired electrons that are unstable and highly reactive, often leading to undesired reactions causing pathology
Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
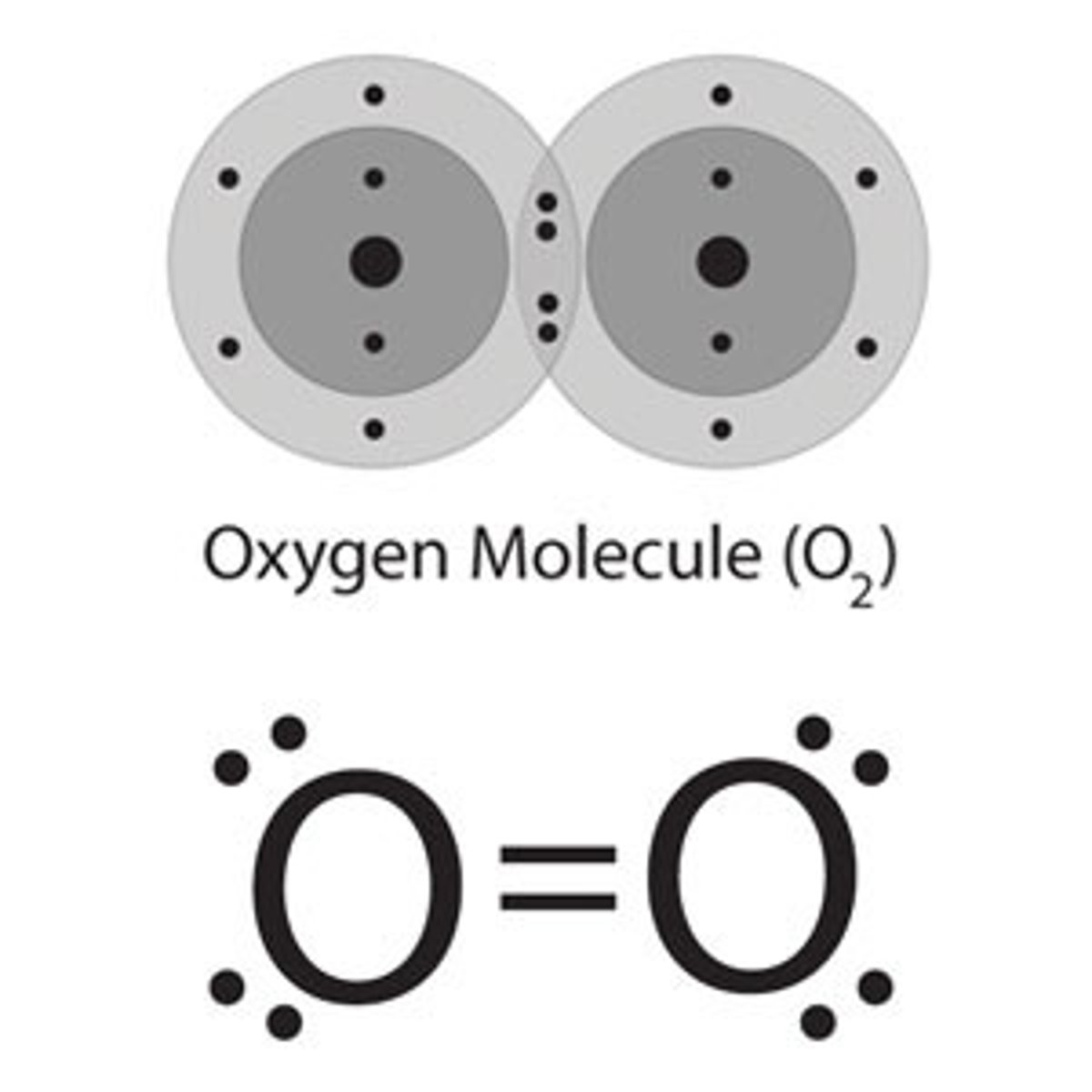
Highly reactive, unstable oxygen-containing molecules causing oxidative damage to proteins, lipids, and DNA within cells. Examples include superoxide anion (O2-) and hydroxyl radical (OH·)
Oxidative Stress
Imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and the body's ability to neutralize them, leading to cellular damage and dysfunction
Production of ROS
Generated during mitochondrial respiration for ATP production, in inflammation to combat infections, and due to exposure to environmental toxins and pollutants
Consequences of Oxidative Stress
Include cellular damage, disruption of normal cellular functions, inflammation, and contributing to neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular disease, cancer, and aging
Antioxidants
Molecules that neutralize ROS, protecting cells from oxidative damage by accepting and stabilizing free electrons and reactive molecules. Can be endogenous or exogenous, with several vitamins acting as antioxidants
Protective Strategies against Oxidative Stress
Include consuming an antioxidant-rich diet with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to provide essential antioxidants
Antioxidant Defense
Mechanisms that protect against oxidative stress, involving enzymes and non-enzymatic antioxidants
Oxygen Toxicity
Harmful effects of excessive oxygen levels leading to ROS production and tissue damage
Vitamin C
Water-soluble antioxidant in fruits and vegetables, aids in regenerating other antioxidants
Vitamin E
Fat-soluble antioxidant found in nuts and seeds, protects cell membranes
Selenium
Trace element crucial for antioxidant enzyme synthesis, found in nuts and seafood
Glutathione
Tripeptide acting as a potent intracellular antioxidant, synthesized in the body
Carotenoids
Compounds in colorful fruits and vegetables with antioxidant properties, converted to vitamin A
Superoxide Dismutase (SOD)
Enzyme converting superoxide radicals to hydrogen peroxide
Catalase
Enzyme converting hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen
Glutathione Peroxidase
Enzyme neutralizing hydrogen peroxide and lipid peroxides
Metal Binding Proteins
Proteins binding with metals to prevent free radical generation
Polyphenols
Chemical compounds in plants with antioxidant properties, e.g., flavonoids
Calcium
Mineral contributing to bone and teeth strength, blood clotting, and nerve function
Phosphorus
Mineral essential for bone structure, energy metabolism, and acid-base balance
Magnesium
Mineral crucial for nerve function, muscle contraction, and energy metabolism
Sodium
Mineral regulating fluid balance, nerve function, and blood pressure
Potassium
Mineral vital for fluid balance, nerve function, and cell growth
Chloride
Mineral important for electrolyte balance and nerve function
Iron
Mineral essential for oxygen transport in hemoglobin, preventing anemia
Zinc
Mineral supporting immune function, wound healing, and cell growth
Copper
Mineral involved in antioxidant defense, collagen synthesis, and immune support
Iodine
Mineral crucial for thyroid hormone synthesis and immune function
Fluoride
Mineral important for dental health and preventing tooth decay
Chromium
Mineral aiding in insulin function and macronutrient metabolism
Manganese
Mineral supporting enzyme function, bone health, and antioxidant defense
Molybdenum
Mineral essential for enzyme function and metabolism of certain compounds
What are the 9 water-soluble vitamins?
1) Vitamin C (ascorbic acid)
2) B1 (Thiamine)
3) B2 (Riboflavin)
4) B3 (Niacin)
5) B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
6) B6 (pyridoxine)
7) B7 (Biotin)
8) B9 ( Folate)
9) B12 (Cobalamin)
What are the 4 fat soluble vitamins?
A, D, E, K
What role(s) does Ca2+ play as a mineral?
1) strength and structure (bones)
2) Blood Clotting
What role(s) does K+ play as a mineral?
1) Electrolyte balance for nerve function
2) Blood pressure regulation
3) Blood Clotting
4) Fluid balance
What role(s) does Na+ play as a mineral?
1) Electrolyte balance for nerve function
2) Blood pressure regulation
3) Fluid balance
What role(s) does Zn play as a mineral?
1) Macronutrient Metabolism
2) Immune function
3) Critical co-factor in cell growth, division, repair and DNA synthesis
What role(s) does Fe play as a mineral?
1) Component of hemoglobin (transport of oxygen)
2) Prevention of anemia
What role(s) does Se play as a mineral?
1) assists in antioxidant defense mechanisms
2) essential for detoxification process
What role(s) does P play as a mineral?
1) Strength and Structure (bones)
2) Acid/Base balance through phosphate buffer system
What role(s) does Cu play as a mineral?
1) assists in antioxidant defense mechanisms
2) Immune functions
3)Collagen synthesis
What role(s) does Cl- play as a mineral?
1) Electrolyte balance for nerve function
What role(s) does Mg play as a mineral?
1) macronutrient metabolism
2) assists in glycolysis
3) essential for nerve transmission and muscle contractions
4) ATP activation
What role(s) does I play as a mineral?
1) Crucial for synthesis of thyroid hormone
What minerals are associated with structure and strength in bones
Ca2+ and P
which minerals assist with blood clotting?
Ca2+ and K+
Which minerals are assist in electrolyte balance for nerve function?
K+,Na+,Cl-, Ca2+*
Which mineral is critical for DNA synthesis?
Zinc
Which Mineral is crucial for thyroid hormone synthesis?
Iodine
What is Vitamin is essential for the synthesis of retinal?
Vitamin A
A deficiency in this vitamin can cause "night blindness"
Vitamin A
What are the main roles of Vitamin A?
1) retinal synthesis
2) Immune function
3) skin health
What are the main roles of Vitamin B1
1) metabolism
2) nerve function
3) heart function
What is another name for Vitamin B1
Thiamine
How does Vitamin B1 necessary for metabolism?
its a critical cofactor for the:
- pyruvate dehydrogenase reaction in glycolysis (pyruvate --> Acetyl-CoA)
- Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase reaction
- transketolase in the pentose phosphate pathway (for synthesis of nucleotides)
What is Vitamin B2 also known as?
Riboflavin
What is the role of Vitamin B2?
1) Form coenzymes
2) Corneal crosslinking
3) FAD creation
What two major coenzymes does Vitamin B2 help form?
1)FMN
2) FAD
What is Vitamin B3 also known as
Niacin
What is Vitamin B3 role?
1) Metabolism (by assisting in creation of NAD)
2) regulate Cholesterol
What are the 4 D's of Pellagra?
dermatitis, diarrhea, dementia, death
What is Vitamin B5 also called?
pantothenic acid
What is Vitamin B5 role?
Essential for synthesizing coenzyme A (CoA)
What is Vitamin B6 also called?
Pyridoxine
What is the role of Vitamin B6
cofactor in amino acid metabolism
neurotransmitter synthesis
hemoglobin synthesis
Gene expression
Glycogenolysis
Gluconeogenesis
A deficiency in vitamin B6 causes what?
Rash and inflammation around the eyes and mouth
Peripheral neuropathy
What is Vitamin B7 also called?
Biotin
What is the role of Vitamin B7 in the body?
1) metabolism
2) Healthy hair, skin, and nails
3) gene expression
Why is vitamin B7 useful in many research settings?
Binds crazy tight to streptavidin
What is Vitamin B9 also called?
folate
What is the role of Vitamin B9
Fetal development
Oocyte and sperm development
DNA and RNA synthesis
RBC formation
What is another name for Vitamin B12?
Cobalamin
What is the role of Vitamin B12?
1) nerve functions
2) DNA synthesis
3) RBC formation
What is Vitamin C also called?
ascorbic acid
What the role of Vitamin C?
Antioxidant
supports immune function
Collagen synthesis
Prevention of Scurvy
Does vitamin C prevent colds?
No
Does Vitamin C shorten colds?
Yes
What does vitamin D do?
Helps the body absorb calcium and phosphorus
Supports immune function
Mood regulation
What disease comes from a deficiency in Vitamin D?
Rickets (bowed bones)
What role does Vitamin E play?
1) antioxidant
2) Supports skin health
3) protects cell membranes from ROS
4) Helps regulate PKC (Protein Kinase C)
What role does Vitamin K play?
blood clotting
Bone health
Heart Health
What role does "Vitamin F" play?
Cell membrane structure
Supports brain function
Inflammation regulation
Which of the following is not a Vitamin?
Vitamin F
What are the real name of Vitamin F
Essential Fatty acids
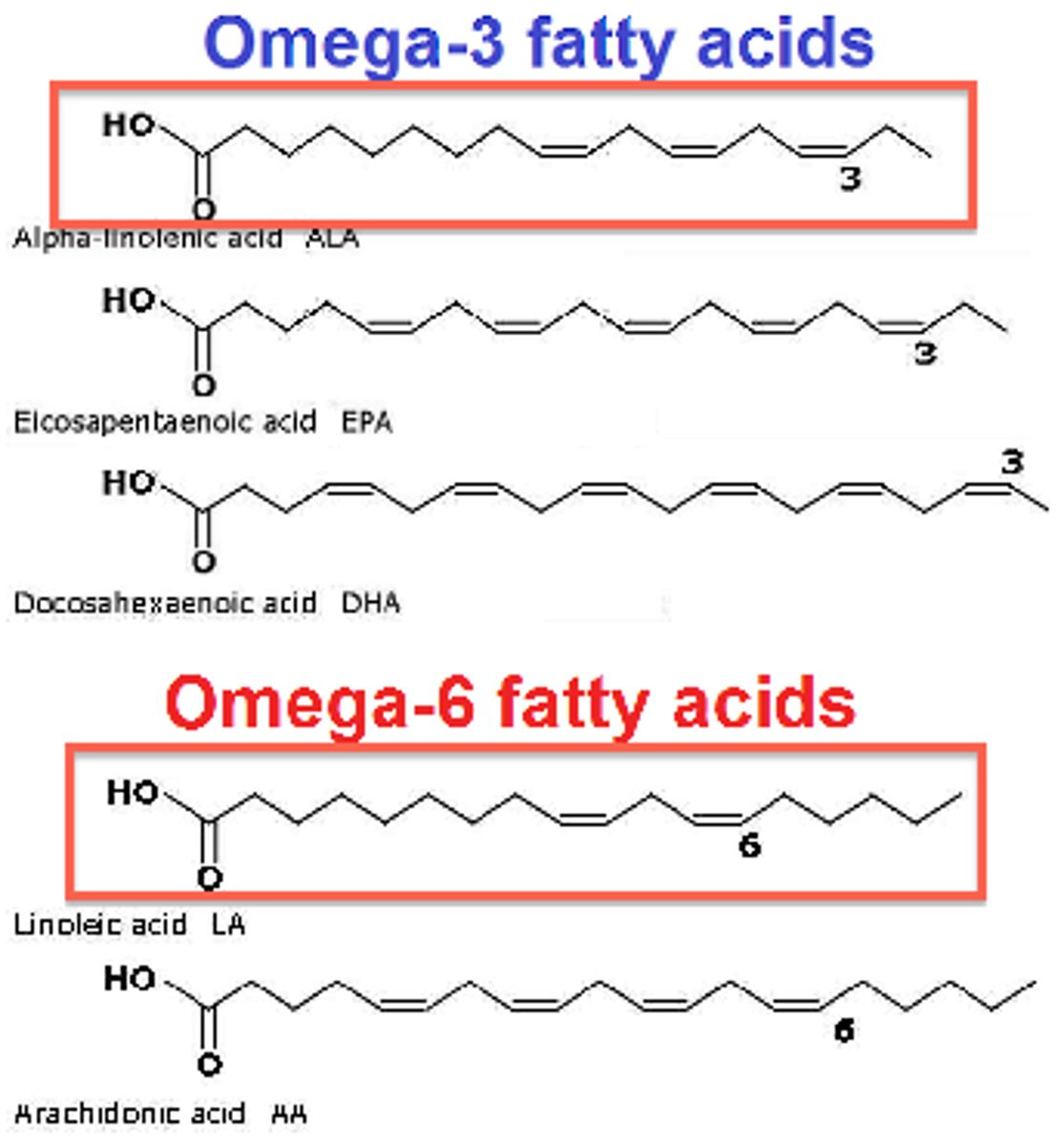
What are the two Essential fatty acids
linoleic acid and linolenic acid
omega 3 vs omega-6 structure
oxygen
What is this ROS?
superoxide anion